Understanding Why You Might Want to Exclude Content from Google
Excluding content from Google search results can be a crucial step in maintaining a positive online presence. There are several reasons why someone might want to exclude content from Google, including removing outdated or irrelevant information, protecting personal data, or avoiding negative publicity. For instance, a business may want to exclude a webpage that contains outdated pricing information or a personal blog post that contains sensitive information. By excluding this content, individuals and businesses can ensure that their online presence is accurate, up-to-date, and free from unnecessary or damaging information.
In today’s digital age, it’s easier than ever for content to be shared and accessed online. However, this also means that it’s easier for outdated or irrelevant content to be found and shared. By learning how to exclude something from Google search, individuals and businesses can take control of their online presence and ensure that their content is accurate and relevant. This can be especially important for businesses, as a single outdated or negative webpage can have a significant impact on their reputation and bottom line.
Furthermore, excluding content from Google can also be an important step in protecting personal data. With the rise of online harassment and identity theft, it’s more important than ever to be mindful of the information that is available online. By excluding personal data from Google search results, individuals can reduce their risk of being targeted by online predators and protect their personal information.
Overall, excluding content from Google search results is an important step in maintaining a positive online presence and protecting personal data. By understanding why you might want to exclude content from Google, you can take the first step towards taking control of your online presence and ensuring that your content is accurate, up-to-date, and free from unnecessary or damaging information.
How Google Crawls and Indexes Content: A Brief Overview
Google’s algorithms play a crucial role in crawling and indexing content from across the web. To understand how to exclude something from Google search, it’s essential to grasp how Google’s crawlers work. Google uses software programs called “spiders” or “crawlers” to continuously scan and index the web for new and updated content. These spiders follow hyperlinks from one webpage to another, indexing the content they find along the way.
When a spider crawls a webpage, it looks for specific signals that indicate what content should be indexed and what should be ignored. One of the key signals is the presence of a sitemap, which is a file that lists all the URLs on a website. By submitting a sitemap to Google, website owners can help ensure that their content is crawled and indexed correctly.
Meta tags also play a crucial role in how Google crawls and indexes content. Meta tags are small pieces of code that are embedded in the HTML of a webpage, providing information about the content to search engines. For example, the “title” meta tag specifies the title of the webpage, while the “description” meta tag provides a brief summary of the content.
Google’s algorithms use a combination of these signals to determine what content to crawl, index, and display in search results. By understanding how Google’s crawlers work, website owners can optimize their content to improve its visibility in search results. However, this also means that website owners need to be mindful of what content is being crawled and indexed, and take steps to exclude content that is not intended for public consumption.
For example, website owners may want to exclude certain pages or directories from being crawled and indexed, such as internal search results or administrative pages. By using the robots.txt file or meta tags, website owners can instruct Google’s crawlers to ignore these pages and prevent them from being indexed.
By understanding how Google’s algorithms work, website owners can take control of their online presence and ensure that their content is accurately represented in search results. This is especially important for businesses, as a single mistake can have a significant impact on their reputation and bottom line.
Using Robots.txt to Block Google Crawlers
The robots.txt file is a simple yet effective way to block Google crawlers from accessing specific pages or directories on a website. By adding specific syntax to the robots.txt file, website owners can instruct Google’s crawlers to ignore certain content and prevent it from being indexed.
The robots.txt file is a text file that is placed in the root directory of a website. It contains a series of directives that tell Google’s crawlers what content to crawl and what content to ignore. The most common directive is the “Disallow” directive, which specifies the URLs or directories that should be blocked from crawling.
For example, to block Google’s crawlers from accessing a specific page, the following syntax can be added to the robots.txt file:
User-agent: * Disallow: /path/to/page
This syntax tells Google’s crawlers to ignore the page located at “/path/to/page” and prevent it from being indexed. The “*” symbol is a wildcard character that specifies all user-agents, including Google’s crawlers.
Website owners can also use the “Allow” directive to specify URLs or directories that should be crawled, even if they are located within a disallowed directory. For example:
User-agent: * Disallow: /path/to/directory Allow: /path/to/directory/subdirectory
This syntax tells Google’s crawlers to ignore the “/path/to/directory” directory, but allow crawling of the “/path/to/directory/subdirectory” subdirectory.
It’s also important to note that the robots.txt file is not a foolproof method for blocking Google’s crawlers. Google’s crawlers can still access content that is linked to from other websites, even if it is blocked in the robots.txt file. Additionally, the robots.txt file only applies to Google’s crawlers, and does not affect other search engines or web crawlers.
By using the robots.txt file to block Google’s crawlers, website owners can take control of their online presence and prevent unwanted content from being indexed. However, it’s also important to use this method judiciously and only block content that is truly unnecessary or sensitive.
Meta Tags: A Simple Way to Exclude Pages from Google Search
Meta tags are a simple and effective way to exclude pages from Google search results. By adding specific meta tags to a webpage, website owners can instruct Google’s crawlers to ignore the page and prevent it from being indexed.
The two most common meta tags used for excluding pages from Google search results are the “noindex” and “nofollow” tags. The “noindex” tag tells Google’s crawlers not to index the page, while the “nofollow” tag tells Google’s crawlers not to follow any links on the page.
To use the “noindex” tag, website owners can add the following syntax to the HTML header of the webpage:
This syntax tells Google’s crawlers not to index the page and prevent it from being displayed in search results.
The “nofollow” tag is used to prevent Google’s crawlers from following any links on the page. This can be useful for preventing the spread of spam or malware. To use the “nofollow” tag, website owners can add the following syntax to the HTML header of the webpage:
It’s also possible to combine the “noindex” and “nofollow” tags to prevent both indexing and link following. To do this, website owners can add the following syntax to the HTML header of the webpage:
Meta tags are a simple and effective way to exclude pages from Google search results. By using the “noindex” and “nofollow” tags, website owners can take control of their online presence and prevent unwanted content from being indexed.
However, it’s also important to note that meta tags are not a foolproof method for excluding pages from Google search results. Google’s crawlers can still access content that is linked to from other websites, even if it is blocked by meta tags. Additionally, meta tags only apply to Google’s crawlers, and do not affect other search engines or web crawlers.
By using meta tags to exclude pages from Google search results, website owners can improve their online presence and prevent unwanted content from being indexed. However, it’s also important to use this method judiciously and only block content that is truly unnecessary or sensitive.
Removing Outdated or Duplicate Content from Google Search
Removing outdated or duplicate content from Google search results is an important step in maintaining a clean and accurate online presence. Outdated or duplicate content can negatively impact a website’s search engine rankings and user experience, making it essential to remove it from Google’s index.
One way to remove outdated or duplicate content from Google search results is to use the Google Search Console. The Google Search Console is a free tool that allows website owners to monitor and manage their website’s presence in Google search results. By using the Google Search Console, website owners can identify and remove outdated or duplicate content from Google’s index.
Another way to remove outdated or duplicate content from Google search results is to update the website’s sitemap. A sitemap is a file that lists all the URLs on a website, making it easier for Google’s crawlers to find and index new content. By updating the sitemap, website owners can ensure that Google’s crawlers are aware of the latest changes to the website and can remove outdated or duplicate content from the index.
Canonical URLs are another important tool for removing outdated or duplicate content from Google search results. A canonical URL is a URL that is designated as the preferred version of a webpage. By specifying a canonical URL, website owners can tell Google’s crawlers which version of a webpage is the most up-to-date and relevant, and remove outdated or duplicate content from the index.
For example, if a website has multiple versions of the same webpage, such as a mobile and desktop version, the website owner can specify a canonical URL to indicate which version is the most up-to-date and relevant. This can help to remove outdated or duplicate content from Google’s index and improve the website’s search engine rankings.
Removing outdated or duplicate content from Google search results is an important step in maintaining a clean and accurate online presence. By using the Google Search Console, updating the website’s sitemap, and specifying canonical URLs, website owners can ensure that their website is accurately represented in Google search results and improve their search engine rankings.
It’s also important to note that removing outdated or duplicate content from Google search results can take time, and may require multiple attempts. Website owners should be patient and persistent in their efforts to remove outdated or duplicate content, and should regularly monitor their website’s presence in Google search results to ensure that the content has been successfully removed.
Excluding Personal Data from Google Search Results
Excluding personal data from Google search results is an important step in protecting one’s online privacy. Personal data, such as phone numbers, addresses, and financial information, can be sensitive and potentially damaging if it falls into the wrong hands.
One way to exclude personal data from Google search results is to use opt-out services. Opt-out services, such as the Google Opt-out Service, allow individuals to request that their personal data be removed from Google’s search results. This can be a useful tool for individuals who want to protect their online privacy and prevent their personal data from being accessed by others.
Another way to exclude personal data from Google search results is to use the “remove outdated content” tool. This tool allows individuals to request that outdated or irrelevant content be removed from Google’s search results. This can be useful for individuals who want to remove old or outdated personal data from Google’s search results.
In addition to using opt-out services and the “remove outdated content” tool, individuals can also take steps to protect their personal data from being indexed by Google in the first place. This can include using secure websites and online services, being cautious when sharing personal data online, and using strong passwords and two-factor authentication.
It’s also important to note that excluding personal data from Google search results can be a complex and time-consuming process. It may require multiple attempts and may not always be successful. However, by taking steps to protect one’s online privacy and using the tools and services available, individuals can reduce the risk of their personal data being accessed by others.
Furthermore, individuals can also use the Google Search Console to monitor and manage their online presence. The Google Search Console provides a range of tools and features that allow individuals to monitor their website’s traffic, optimize their website’s content, and manage their online presence.
By using the Google Search Console and other tools and services, individuals can take control of their online presence and protect their personal data from being accessed by others. This can help to ensure that their online presence is accurate, up-to-date, and secure.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Trying to Exclude Content from Google
When attempting to exclude content from Google search results, it’s essential to be aware of common mistakes that can hinder the process or even lead to unintended consequences. By understanding these pitfalls, individuals can take steps to avoid them and ensure a successful exclusion process.
One of the most common mistakes is using incorrect syntax in the robots.txt file. A single error in the syntax can render the entire file ineffective, allowing Google crawlers to access the content that was intended to be excluded. To avoid this, it’s crucial to carefully review the robots.txt file and ensure that the syntax is correct.
Another mistake is blocking entire websites or subdomains instead of specific pages or directories. This can lead to a significant loss of visibility and traffic, as well as potential penalties from Google. To avoid this, it’s essential to use the robots.txt file and meta tags strategically, targeting only the specific content that needs to be excluded.
Not updating sitemaps and canonical URLs is another common mistake. When content is updated or removed, it’s essential to update the sitemap and canonical URLs to reflect the changes. Failure to do so can lead to outdated content being indexed by Google, which can negatively impact search engine rankings.
Not monitoring and verifying the exclusion process is also a common mistake. It’s essential to regularly check Google Search Console and other tools to ensure that the content has been successfully excluded from search results. This helps to identify any issues or errors that may have occurred during the exclusion process.
Finally, not considering the impact of excluding content on search engine rankings is a mistake that can have unintended consequences. Excluding content can lead to a loss of visibility and traffic, as well as potential penalties from Google. It’s essential to carefully consider the potential impact of excluding content and to develop a strategy that minimizes any negative effects.
By being aware of these common mistakes, individuals can take steps to avoid them and ensure a successful exclusion process. By following best practices and using the right tools and techniques, it’s possible to effectively exclude content from Google search results and maintain a strong online presence.
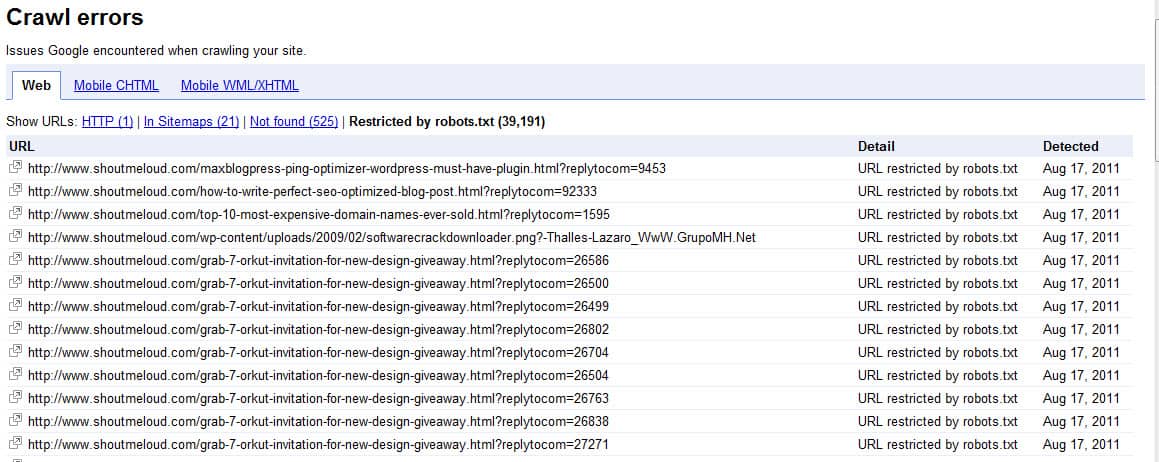
Monitoring and Verifying Google Search Exclusions
After taking steps to exclude content from Google search results, it’s essential to monitor and verify that the exclusion has been successful. This involves using various tools and techniques to ensure that the content is no longer visible in search results.
One of the most effective ways to monitor and verify Google search exclusions is by using the Google Search Console. This tool provides insights into how Google crawls and indexes content, including any errors or issues that may have occurred during the exclusion process. By regularly checking the Search Console, individuals can identify any problems and take corrective action to ensure that the exclusion is successful.
Another way to monitor and verify Google search exclusions is by using the “site:” operator in Google search. This operator allows individuals to search for specific content within a website, making it easy to verify whether the content has been excluded from search results. For example, if an individual wants to verify that a specific page has been excluded, they can use the “site:” operator followed by the URL of the page.
In addition to using the Google Search Console and the “site:” operator, individuals can also use other tools such as Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to monitor and verify Google search exclusions. These tools provide detailed insights into website crawlability and indexability, making it easy to identify any issues that may have occurred during the exclusion process.
It’s also important to regularly check for any errors or warnings in the Google Search Console, as these can indicate issues with the exclusion process. For example, if Google encounters an error while crawling a website, it may not be able to exclude the content as intended. By regularly checking for errors and warnings, individuals can take corrective action to ensure that the exclusion is successful.
Finally, it’s essential to be patient when monitoring and verifying Google search exclusions. The exclusion process can take time, and it may take several days or even weeks for the content to be fully removed from search results. By regularly monitoring and verifying the exclusion process, individuals can ensure that the content is successfully excluded from Google search results.
By following these steps and using the right tools and techniques, individuals can effectively monitor and verify Google search exclusions, ensuring that their content is successfully excluded from search results. This helps to maintain a strong online presence and avoid any potential negative consequences of having unwanted content in search results.