Understanding the Concept: Sex and Socioeconomic Status
The correlation between sex and wealth is a multifaceted phenomenon that intertwines socioeconomic aspects with gender. This correlation is often characterized by disparities in income, assets, and opportunities between individuals of different genders. It is crucial to examine the underlying factors contributing to these disparities and their implications on individuals and society as a whole.
Gender plays a significant role in determining financial status, with women often facing unique challenges in their quest for economic empowerment. Factors such as the gender pay gap, occupational segregation, and societal expectations contribute to the persistent disparities in wealth accumulation between men and women. Understanding these dynamics is essential for developing targeted strategies to address the correlation between sex and wealth.
Moreover, the correlation between sex and wealth extends beyond individual experiences and has broader societal implications. Economic inequality between genders can perpetuate cycles of poverty, limit access to essential resources, and hinder overall societal progress. By shedding light on this complex relationship, we can foster a more informed and inclusive conversation about the importance of gender and economic equality.

Historical Perspective: The Evolution of Gender and Wealth
To fully understand the correlation between sex and wealth, it is essential to examine the historical context of gender roles and wealth distribution. Throughout history, gender norms have significantly influenced financial opportunities and outcomes.
In the past, societal expectations often relegated women to domestic roles, limiting their access to education, employment, and financial resources. Men, on the other hand, were more likely to hold positions of power and authority, enabling them to accumulate wealth and pass it down through generations. This historical imbalance has contributed to the persistent gender wealth gap that exists today.
However, it is crucial to recognize that the correlation between sex and wealth has not remained static over time. As societies have evolved, so too have gender roles and wealth distribution patterns. For instance, the women’s rights movement of the 20th century led to significant advancements in women’s access to education, employment, and financial resources. Despite these gains, disparities persist, highlighting the ongoing need for progress and advocacy.
By understanding the historical context of the correlation between sex and wealth, we can better appreciate the complex interplay of factors that have shaped contemporary gender and economic dynamics. This knowledge can inform our efforts to address ongoing disparities and promote a more equitable future.
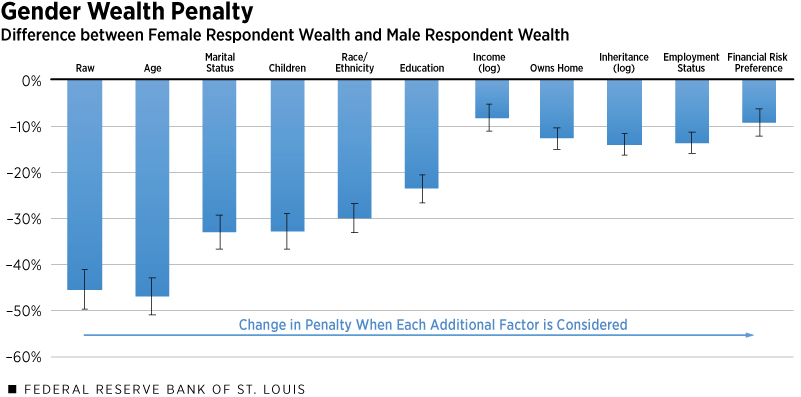
Global Overview: Sex and Wealth Across Different Cultures
To gain a more comprehensive understanding of the correlation between sex and wealth, it is valuable to explore how this relationship manifests in various cultural contexts. By examining similarities and differences across different societies, we can deepen our knowledge of the complex factors that shape gender and economic dynamics.
For instance, in some cultures, gender norms may be more rigidly defined, leading to more pronounced disparities in wealth accumulation between men and women. In these societies, women may face significant barriers to education, employment, and financial independence, resulting in a widened wealth gap. Conversely, in cultures with more egalitarian gender norms, the correlation between sex and wealth may be less pronounced, with women enjoying greater access to financial resources and opportunities.
However, it is essential to avoid oversimplifying the relationship between sex and wealth in different cultural contexts. Factors such as race, ethnicity, class, and geography can intersect with gender to shape financial outcomes in complex and nuanced ways. For example, a woman of color in a developed country may face different financial challenges than a man of the same racial or ethnic background in a developing country.
By taking a global perspective on the correlation between sex and wealth, we can develop a more sophisticated understanding of the ways in which gender and economic dynamics intersect with cultural norms and values. This knowledge can inform our efforts to promote gender and economic equality, both within our own communities and around the world.

How to Assess: Evaluating the Correlation in Your Surroundings
To gain a deeper understanding of the correlation between sex and wealth in your local community or personal life, it is essential to develop practical skills and tools for assessment. By evaluating the ways in which gender and financial resources intersect in your own context, you can gain valuable insights into the complex factors that shape economic outcomes for men and women.
One way to assess the correlation between sex and wealth is to gather data on key indicators such as income, employment, and education. By comparing these indicators across different genders, you can identify any disparities or inequities that may exist. For example, you might examine the gender pay gap in your community or the representation of women in high-paying industries.
Another approach is to engage in critical reflection and self-assessment. By examining your own assumptions and biases around gender and wealth, you can develop a more nuanced understanding of the ways in which these factors intersect. For example, you might reflect on your own experiences of financial decision-making, considering how gender norms and expectations may have influenced your choices and opportunities.
Additionally, it can be helpful to engage in dialogue and conversation with others around the correlation between sex and wealth. By sharing perspectives and experiences, you can build a more comprehensive understanding of the ways in which gender and financial resources intersect in your community. You might consider joining local advocacy groups or community organizations focused on gender and economic equality, or engaging in online forums and discussions around these issues.
By developing practical skills and tools for assessing the correlation between sex and wealth, you can contribute to a more equitable and just society. By identifying and addressing disparities and inequities in your own context, you can help to promote gender and economic equality for all.
Debunking Myths: Common Misconceptions Surrounding Sex and Wealth
The correlation between sex and wealth is often shrouded in myths and stereotypes, which can perpetuate harmful gender norms and economic disparities. By addressing and debunking these misconceptions, we can promote a more nuanced and accurate understanding of the ways in which gender and financial resources intersect.
One common myth is that women are inherently less capable of managing wealth than men. This stereotype is often perpetuated by media representations of women as emotional or irrational investors, or by cultural norms that discourage women from pursuing financial education and literacy. However, research has shown that women are just as capable as men when it comes to managing wealth, and may even be more risk-averse and financially conservative in their decision-making.
Another myth is that the correlation between sex and wealth is solely a matter of individual choice and responsibility. This perspective ignores the systemic and structural factors that shape economic outcomes for men and women, such as gender discrimination, unequal pay, and limited access to education and employment opportunities. By focusing solely on individual choices and behaviors, we risk overlooking the larger social and economic forces that contribute to gender and financial disparities.
A related myth is that the correlation between sex and wealth is a zero-sum game, in which men’s financial gains come at the expense of women’s economic opportunities. However, research has shown that gender and economic equality can benefit everyone, by promoting economic growth, innovation, and social stability. By challenging the myth of the zero-sum game, we can build a more inclusive and equitable economy that benefits all members of society.
Finally, it is important to debunk the myth that the correlation between sex and wealth is a fixed or unchangeable aspect of society. By recognizing the historical and cultural contingency of gender roles and wealth distribution, we can imagine and work towards alternative futures in which gender and financial resources are more equitably distributed. This may involve challenging and transforming the social and economic structures that perpetuate gender and financial disparities, as well as promoting individual empowerment and agency.

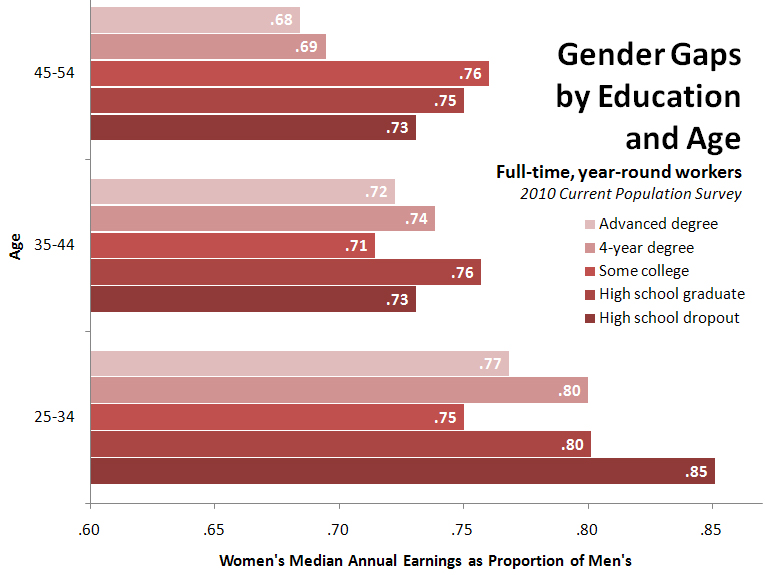
The Role of Education and Employment
The correlation between sex and wealth is significantly influenced by education and employment opportunities. Gender disparities in these areas can perpetuate financial inequalities and limit social mobility. By examining the relationship between education, employment, and wealth, we can better understand the systemic factors that contribute to the correlation between sex and wealth, and identify potential solutions for promoting gender and economic equality.
Research has consistently shown that education is a key determinant of financial success. Higher levels of education are associated with higher income, greater wealth, and better job opportunities. However, gender disparities in education persist in many parts of the world, with girls and women facing barriers to access and achievement. These disparities can limit women’s economic opportunities and perpetuate gender and financial inequalities.
Employment is another critical factor in the correlation between sex and wealth. Women are more likely to work in low-paying, precarious, or informal jobs, and are underrepresented in leadership and decision-making positions. Gender discrimination, unequal pay, and limited access to education and training can all contribute to these employment disparities. By addressing these systemic barriers, we can promote gender and economic equality and reduce the correlation between sex and wealth.
One potential solution is to promote gender and economic equality in education and employment. This may involve implementing policies and programs that address gender disparities in access, achievement, and opportunity. For example, governments and institutions can invest in gender-responsive education and training programs, provide affordable childcare and family-friendly policies, and enforce equal pay and non-discrimination laws. Employers can also take steps to promote gender and economic equality in the workplace, such as implementing diversity and inclusion initiatives, providing flexible work arrangements, and offering equal pay and promotion opportunities.
Another potential solution is to challenge and transform the social and economic structures that perpetuate gender and financial disparities. This may involve advocating for systemic change, such as reforming tax and transfer policies, promoting social protection and redistribution, and challenging gender norms and stereotypes. By working towards a more equitable and just society, we can reduce the correlation between sex and wealth and promote gender and economic equality for all members of society.
Strategies for Change: Empowering Individuals and Challenging Structures
Addressing the correlation between sex and wealth requires a multi-faceted approach that focuses on both individual empowerment and systemic change. By empowering individuals and challenging the social, economic, and political structures that perpetuate gender and financial disparities, we can promote gender and economic equality and reduce the correlation between sex and wealth.
One strategy for addressing the correlation between sex and wealth is to empower individuals through education, skills training, and financial literacy programs. These programs can help individuals develop the knowledge and skills needed to access education and training opportunities, secure better-paying jobs, and manage their finances effectively. By investing in the empowerment of individuals, we can promote gender and economic equality and reduce the correlation between sex and wealth.
Another strategy is to challenge and transform the social, economic, and political structures that perpetuate gender and financial disparities. This may involve advocating for policies and practices that promote gender and economic equality, such as equal pay and non-discrimination laws, affordable childcare and family-friendly policies, and social protection and redistribution measures. It may also involve challenging gender norms and stereotypes, promoting diversity and inclusion, and advocating for systemic change in areas such as taxation, trade, and investment.
In addition to these strategies, it is important to promote intersectional approaches that recognize and address the intersecting forms of discrimination and disadvantage that can affect individuals and communities. This may involve addressing the unique challenges faced by women of color, LGBTQ+ individuals, individuals with disabilities, and other marginalized groups, and promoting inclusive and equitable policies and practices that reflect the diversity of society.
Ultimately, addressing the correlation between sex and wealth requires a sustained and collective effort from individuals, communities, and institutions. By working together to promote gender and economic equality, we can create a more just and equitable society where all members have the opportunity to thrive and succeed.

Future Outlook: Predicting Trends and Advocating for Equality
As we look to the future, it is important to consider the potential trends and developments in the correlation between sex and wealth. While progress has been made in recent decades, there is still much work to be done to promote gender and economic equality and reduce the correlation between sex and wealth.
One potential trend is the increasing importance of education and skills training in the labor market. As technology advances and automation becomes more prevalent, individuals with higher levels of education and skills are likely to have a competitive advantage in the labor market. This trend may disproportionately benefit men, who have historically had greater access to education and training opportunities. However, it may also create new opportunities for women to access education and training programs and secure better-paying jobs.
Another potential trend is the increasing importance of flexible and remote work arrangements. As technology enables more people to work from home or other remote locations, this may create new opportunities for women to balance work and family responsibilities and reduce the gender pay gap. However, it may also create new challenges, such as the potential for increased surveillance and monitoring of remote workers.
Regardless of the specific trends and developments that emerge, it is clear that continued advocacy and action are needed to promote gender and economic equality and reduce the correlation between sex and wealth. This may involve advocating for policies and practices that promote gender and economic equality, such as equal pay and non-discrimination laws, affordable childcare and family-friendly policies, and social protection and redistribution measures. It may also involve challenging gender norms and stereotypes, promoting diversity and inclusion, and advocating for systemic change in areas such as taxation, trade, and investment.
Ultimately, addressing the correlation between sex and wealth requires a sustained and collective effort from individuals, communities, and institutions. By working together to promote gender and economic equality, we can create a more just and equitable society where all members have the opportunity to thrive and succeed.

