Understanding the Basics of Sailboat Sails
Sails are a crucial component of a sailboat, harnessing the wind to propel the vessel through the water. A sailboat’s performance and maneuverability rely heavily on the type, size, and shape of its sails. There are several types of sails on a sailboat, each with its unique characteristics and functions. The mainsail, jib, and spinnaker are the most common sails found on a sailboat.
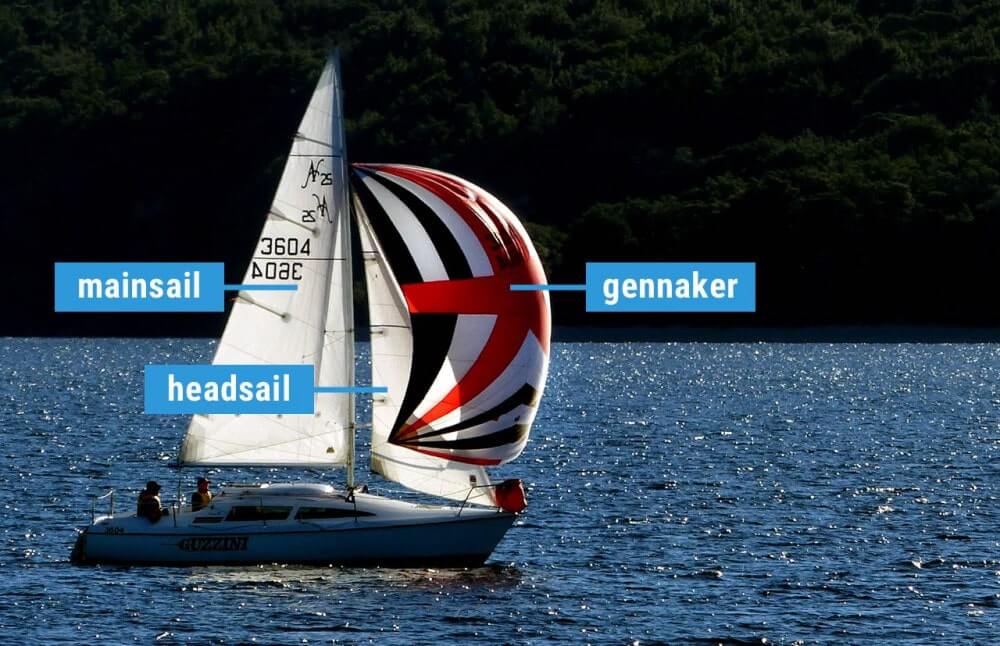
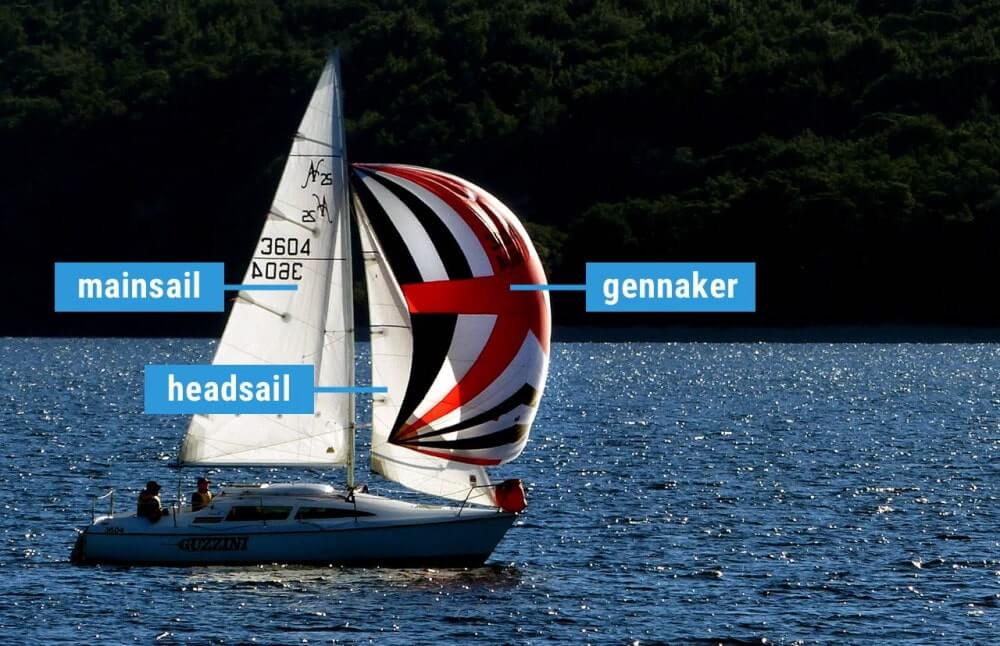
The mainsail is the largest and most powerful sail on a sailboat, providing the majority of the boat’s propulsion. The jib, also known as the headsail, is a triangular sail set on the forestay, which helps to stabilize the boat and optimize its performance. The spinnaker is a large, billowing sail used when sailing downwind, providing maximum speed and control.
Understanding the different types of sails on a sailboat is essential for any sailor, from beginner to experienced. Knowing the names and functions of each sail enables sailors to optimize their boat’s performance, maneuverability, and overall sailing experience. Whether you’re sailing on a small day-sailer or a large offshore cruiser, understanding the basics of sailboat sails is crucial for safe and enjoyable sailing.
In addition to the mainsail, jib, and spinnaker, there are several other types of sails that can be found on a sailboat, including genoas, staysails, and mizzens. Each of these sails has its unique characteristics and functions, and understanding their roles is essential for optimizing sailboat performance.
When it comes to sailboat sailing, the right sails can make all the difference. Knowing the names and functions of each sail, as well as how to trim and optimize them, is essential for getting the most out of your sailing experience. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or just starting out, understanding the basics of sailboat sails is the key to unlocking your full sailing potential.
How to Identify and Name the Different Sails on a Sailboat
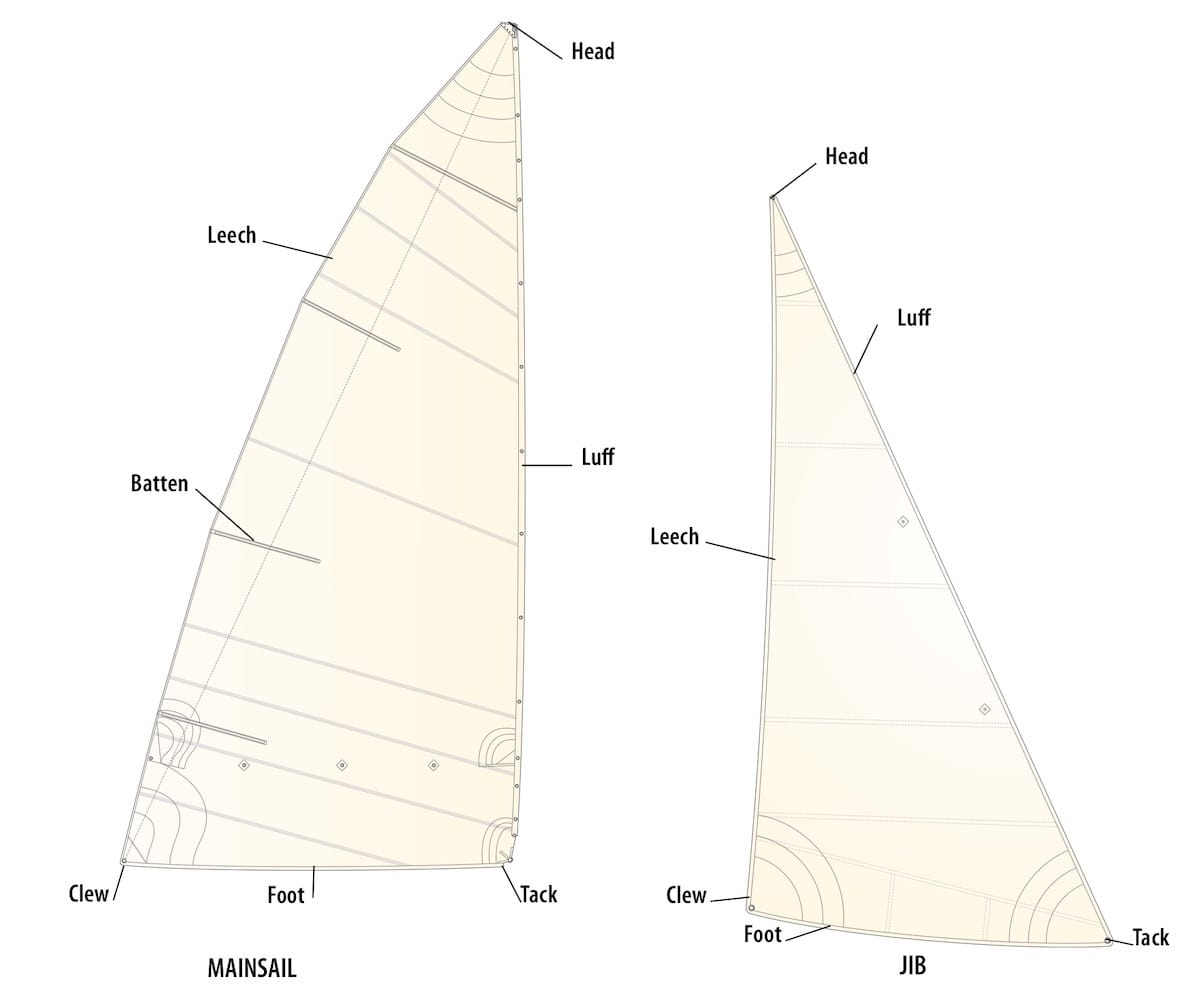
Identifying and naming the different sails on a sailboat can be a daunting task, especially for beginners. However, understanding the various sail types and their positions on the boat is essential for optimizing sailboat performance and ensuring safe sailing. In this section, we will provide a comprehensive guide on how to identify and name the different sails on a sailboat, including diagrams and illustrations to help readers visualize the various sail types.
Let’s start with the mainsail, which is the largest and most powerful sail on a sailboat. The mainsail is typically triangular in shape and is set on the mast, which is the vertical pole that supports the sail. The mainsail is used to harness the wind and provide stability to the sailboat.
The jib, also known as the headsail, is a triangular sail set on the forestay, which is the wire that runs from the bow of the boat to the mast. The jib is used to optimize sailboat performance and maneuverability, and is typically smaller than the mainsail.
The spinnaker is a large, billowing sail used when sailing downwind. It is typically set on the spinnaker pole, which is a horizontal pole that extends from the mast to the bow of the boat. The spinnaker is used to maximize speed and control when sailing downwind.
In addition to the mainsail, jib, and spinnaker, there are several other types of sails that can be found on a sailboat, including genoas, staysails, and mizzens. Each of these sails has its unique characteristics and functions, and understanding their roles is essential for optimizing sailboat performance.
When it comes to identifying and naming the different sails on a sailboat, it’s essential to understand the sail plan, which is the arrangement of sails on the boat. The sail plan will typically include the mainsail, jib, and spinnaker, as well as other sails such as genoas and staysails.
By understanding the different sail types and their positions on the boat, sailors can optimize their sailboat’s performance and ensure safe sailing. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced sailor, knowing the names and functions of the different sails on a sailboat is essential for getting the most out of your sailing experience.
The Role of the Mainsail: The Largest and Most Powerful Sail
The mainsail is the largest and most powerful sail on a sailboat, playing a crucial role in harnessing the wind to propel the vessel. The mainsail is typically triangular in shape and is set on the mast, which is the vertical pole that supports the sail. The mainsail’s size and shape are designed to maximize its surface area, allowing it to capture the wind and generate the most power.
The mainsail’s function is to provide stability and propulsion to the sailboat. When the wind fills the mainsail, it creates a force that pushes the sailboat forward, allowing it to move through the water. The mainsail’s shape and angle are critical in determining the sailboat’s performance, as they affect the amount of wind that is captured and the direction of the force generated.
The mainsail’s size and shape can vary depending on the type of sailboat and its intended use. For example, a racing sailboat may have a larger mainsail with a more complex shape, designed to maximize its speed and performance. On the other hand, a cruising sailboat may have a smaller mainsail with a simpler shape, designed to provide stability and ease of handling.
When it comes to sails on a sailboat names, the mainsail is often referred to as the “main” or “mains’l”. It is the most critical sail on the boat, and its proper trimming and adjustment are essential for optimal performance. By understanding the role of the mainsail and how to optimize its performance, sailors can improve their sailboat’s speed, stability, and overall sailing experience.
In addition to its size and shape, the mainsail’s material and construction are also critical factors in its performance. Modern sailboat sails are made from a variety of materials, including Dacron, Kevlar, and Mylar. Each of these materials has its own unique characteristics, and the choice of material will depend on the sailboat’s intended use and the sailor’s preferences.
Overall, the mainsail is a critical component of a sailboat’s sail plan, and its proper trimming and adjustment are essential for optimal performance. By understanding the role of the mainsail and how to optimize its performance, sailors can improve their sailboat’s speed, stability, and overall sailing experience.
Understanding Jibs and Genoas: The Headsails of a Sailboat
Jibs and genoas are two types of headsails used on sailboats, each with its own unique characteristics and functions. The jib is a triangular sail set on the forestay, which is the wire that runs from the bow of the boat to the mast. The genoa, on the other hand, is a larger sail that overlaps the mainsail and is set on the same forestay as the jib.
The main difference between a jib and a genoa is their size and shape. A jib is typically smaller and more triangular in shape, while a genoa is larger and more rectangular. The jib is used for sailing upwind, while the genoa is used for sailing downwind or on a reach.
Both jibs and genoas are used to optimize sailboat performance and maneuverability. They help to stabilize the boat and provide additional power to the mainsail. The jib and genoa work together to create a smooth and efficient sail plan, allowing the sailboat to move quickly and easily through the water.
When it comes to sails on a sailboat names, the jib and genoa are often referred to as the “headsails”. They are critical components of the sail plan, and their proper trimming and adjustment are essential for optimal performance. By understanding the difference between jibs and genoas, sailors can optimize their sailboat’s performance and maneuverability, and improve their overall sailing experience.
In addition to their size and shape, the jib and genoa also differ in their material and construction. Modern sailboat sails are made from a variety of materials, including Dacron, Kevlar, and Mylar. Each of these materials has its own unique characteristics, and the choice of material will depend on the sailboat’s intended use and the sailor’s preferences.
Overall, the jib and genoa are critical components of a sailboat’s sail plan, and their proper trimming and adjustment are essential for optimal performance. By understanding the difference between these two types of headsails, sailors can optimize their sailboat’s performance and maneuverability, and improve their overall sailing experience.
Spinnakers and Downwind Sails: Maximizing Speed and Control
Spinnakers and downwind sails are specialized sails designed to maximize speed and control when sailing downwind. These sails are typically larger and more symmetrical than upwind sails, with a more rounded shape and a longer luff. The spinnaker is a large, billowing sail that is set on the spinnaker pole, which is a horizontal pole that extends from the mast to the bow of the boat.
The spinnaker is used to maximize speed and control when sailing downwind, particularly in light to moderate wind conditions. It is typically set on a reach or a run, and is used to stabilize the boat and provide additional power to the mainsail. The spinnaker is also used to help the boat maintain its course and direction, particularly in windy or choppy conditions.
Downwind sails, on the other hand, are designed to provide maximum speed and control when sailing directly downwind. These sails are typically smaller and more triangular in shape than spinnakers, with a shorter luff and a more pointed tip. Downwind sails are used to provide additional power to the mainsail, and to help the boat maintain its speed and direction.
When it comes to sails on a sailboat names, spinnakers and downwind sails are often referred to as “off-wind sails”. They are critical components of the sail plan, and their proper trimming and adjustment are essential for optimal performance. By understanding the role of spinnakers and downwind sails, sailors can optimize their sailboat’s performance and maneuverability, and improve their overall sailing experience.
In addition to their size and shape, spinnakers and downwind sails also differ in their material and construction. Modern sailboat sails are made from a variety of materials, including Dacron, Kevlar, and Mylar. Each of these materials has its own unique characteristics, and the choice of material will depend on the sailboat’s intended use and the sailor’s preferences.
Overall, spinnakers and downwind sails are critical components of a sailboat’s sail plan, and their proper trimming and adjustment are essential for optimal performance. By understanding the role of these sails, sailors can optimize their sailboat’s performance and maneuverability, and improve their overall sailing experience.
Sail Materials and Construction: What to Look for in a High-Quality Sail
When it comes to sails on a sailboat names, the materials and construction methods used can make a significant difference in performance and durability. Modern sailboat sails are made from a variety of materials, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. In this section, we will examine the most common materials and construction methods used in sailboat sails, and discuss what to look for in a high-quality sail.
One of the most common materials used in sailboat sails is Dacron, a type of polyester fabric that is known for its durability and resistance to stretch. Dacron sails are often used on cruising sailboats, as they are easy to handle and maintain. However, they can be heavy and may not provide the best performance in light wind conditions.
Another popular material used in sailboat sails is Kevlar, a type of aramid fiber that is known for its high strength-to-weight ratio. Kevlar sails are often used on racing sailboats, as they are lightweight and provide excellent performance in a variety of wind conditions. However, they can be expensive and may require specialized care and maintenance.
Mylar is another material that is commonly used in sailboat sails, particularly in high-performance applications. Mylar sails are known for their excellent durability and resistance to stretch, and are often used on sailboats that require high-speed performance.
In addition to the materials used, the construction methods employed in sailboat sail construction can also make a significant difference in performance and durability. Modern sailboat sails are often constructed using advanced techniques such as computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-controlled cutting (CNC). These techniques allow for precise control over the sail’s shape and size, and can result in a more efficient and effective sail.
When it comes to choosing a high-quality sail, there are several factors to consider. First and foremost, the sail should be made from a durable and high-quality material that is suitable for the sailboat’s intended use. The sail should also be constructed using advanced techniques and materials, and should be designed to provide optimal performance and efficiency.
In addition to the materials and construction methods used, the sail’s design and shape can also make a significant difference in performance and durability. A well-designed sail should be able to harness the wind effectively, while also providing stability and control to the sailboat.
Overall, the materials and construction methods used in sailboat sails can make a significant difference in performance and durability. By understanding the different materials and construction methods available, sailors can choose a high-quality sail that meets their needs and provides optimal performance.
Tips for Sail Trim and Optimization: Getting the Most Out of Your Sails
Sail trim and optimization are critical components of sailboat sailing, as they can significantly impact the performance and efficiency of the sailboat. In this section, we will provide expert advice on how to adjust sail angle, tension, and shape to maximize performance and efficiency.
One of the most important factors in sail trim and optimization is sail angle. The sail angle refers to the angle at which the sail is set in relation to the wind. A sail that is set too far back will not be able to harness the wind effectively, while a sail that is set too far forward will be prone to stalling. The ideal sail angle will depend on the wind conditions and the type of sail being used.
Another important factor in sail trim and optimization is sail tension. Sail tension refers to the amount of tension that is applied to the sail, and it can have a significant impact on the sail’s performance. A sail that is too loose will not be able to harness the wind effectively, while a sail that is too tight will be prone to stalling. The ideal sail tension will depend on the wind conditions and the type of sail being used.
In addition to sail angle and tension, sail shape is also an important factor in sail trim and optimization. Sail shape refers to the shape of the sail, and it can have a significant impact on the sail’s performance. A sail that is too flat will not be able to harness the wind effectively, while a sail that is too full will be prone to stalling. The ideal sail shape will depend on the wind conditions and the type of sail being used.
When it comes to sails on a sailboat names, understanding the different types of sails and how to trim and optimize them is critical for maximizing performance and efficiency. By adjusting sail angle, tension, and shape, sailors can optimize their sailboat’s performance and get the most out of their sails.
In order to optimize sail trim and performance, sailors should use a combination of visual and instrumental cues. Visual cues include the shape of the sail, the angle of the sail, and the movement of the sailboat. Instrumental cues include the use of sail trim instruments, such as sail trim gauges and anemometers.
By using a combination of visual and instrumental cues, sailors can optimize their sail trim and performance, and get the most out of their sails. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced sailor, understanding sail trim and optimization is critical for maximizing performance and efficiency.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Sailboat Sailing with the Right Sails
In conclusion, understanding sail types, names, and functions is essential for mastering the art of sailboat sailing. By knowing the different types of sails, including mainsails, jibs, and spinnakers, sailors can optimize their sailboat’s performance and maneuverability. Additionally, understanding sail materials and construction, as well as sail trim and optimization, can help sailors get the most out of their sails.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced sailor, it’s essential to practice and refine your sailing skills with the right sails. By following the tips and advice outlined in this article, you can improve your sailboat’s performance and enjoy a more successful and enjoyable sailing experience.
Remember, sails on a sailboat names are not just a matter of aesthetics; they play a critical role in the performance and safety of the vessel. By understanding the different types of sails and how to use them effectively, sailors can ensure a safe and enjoyable sailing experience.
In summary, mastering the art of sailboat sailing requires a deep understanding of sail types, names, and functions. By following the tips and advice outlined in this article, sailors can optimize their sailboat’s performance and enjoy a more successful and enjoyable sailing experience.
So, the next time you’re out on the water, take a moment to appreciate the importance of sails on a sailboat names. With the right knowledge and skills, you can harness the power of the wind and enjoy a truly unforgettable sailing experience.