Why Image Compression Matters for Your Website
When it comes to website performance, image compression plays a crucial role in ensuring a seamless user experience. Large image files can significantly slow down page load times, leading to higher bounce rates and a negative impact on search engine rankings. In fact, according to Google, a one-second delay in page load time can result in a 7% reduction in conversions. By reducing image size without losing quality, you can improve your website’s overall performance and provide a better experience for your visitors.
Moreover, image compression is essential for mobile users, who often have limited bandwidth and slower internet connections. By optimizing your images, you can ensure that your website loads quickly and efficiently on all devices, regardless of screen size or connection speed. This is particularly important, as mobile devices now account for the majority of internet traffic.
In addition to improving website performance, image compression can also help reduce the file size of your images, making them easier to upload and share. This can be especially useful for websites with large image galleries or e-commerce sites with numerous product images. By reducing the file size of your images, you can also reduce the amount of storage space needed, resulting in cost savings and improved website maintenance.
Furthermore, image compression can also help improve your website’s search engine optimization (SEO). By reducing the file size of your images, you can improve your website’s page load times, which is a key ranking factor. Additionally, optimized images can also improve your website’s user experience, which is another important ranking factor. By providing a fast and seamless user experience, you can improve your website’s visibility and drive more traffic to your site.
Overall, image compression is a critical aspect of website performance and optimization. By reducing image size without losing quality, you can improve your website’s page load times, user experience, and search engine rankings. In the next section, we’ll explore the different image file formats and how to choose the right one for your website.
Understanding Image File Formats: Choosing the Right One
When it comes to image file formats, there are several options to choose from, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The most common image file formats are JPEG, PNG, and GIF. Understanding the differences between these formats is crucial in selecting the right one for your images and reducing their size without losing quality.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is a popular format for photographic images. It uses a lossy compression algorithm, which means that some of the image data is discarded during compression, resulting in a smaller file size. JPEG is ideal for images with many colors and complex scenes, such as photographs. However, it’s not suitable for images with text or graphics, as the compression algorithm can cause artifacts and distortions.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics) is a format that uses a lossless compression algorithm, which means that the image data is preserved during compression. PNG is ideal for images with text, graphics, and transparent backgrounds. It’s also suitable for images with a limited color palette, such as logos and icons. However, PNG files can be larger than JPEG files, especially for complex images.
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) is a format that uses a lossless compression algorithm and is ideal for images with a limited color palette and simple animations. GIF is suitable for images with text, graphics, and transparent backgrounds. However, it’s not suitable for photographic images, as the compression algorithm can cause artifacts and distortions.
When choosing an image file format, consider the type of image, its intended use, and the desired level of compression. For example, if you’re working with a photographic image, JPEG may be the best choice. However, if you’re working with an image that contains text or graphics, PNG or GIF may be more suitable.
In addition to choosing the right image file format, it’s also important to consider the image’s resolution and dimensions. Reducing the image’s resolution and dimensions can significantly reduce its file size without compromising its quality. In the next section, we’ll explore various techniques for reducing image size without losing quality, including resizing, cropping, and compressing.
How to Reduce Image Size without Losing Quality: Techniques and Tools
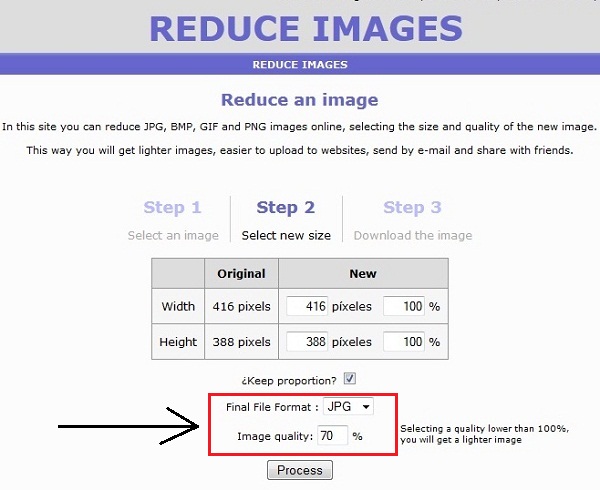
Reducing image size without losing quality is a delicate balance between compression and image fidelity. Fortunately, there are several techniques and tools available to help achieve this balance. In this section, we’ll explore various methods for reducing image size, including resizing, cropping, and compressing.
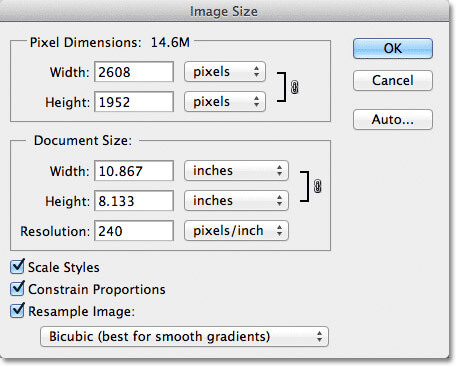
Resizing is one of the simplest ways to reduce image size. By reducing the dimensions of an image, you can significantly decrease its file size. However, be careful not to over-resize, as this can lead to a loss of image quality. A good rule of thumb is to resize images to the exact dimensions required for your website or application.
Cropping is another technique for reducing image size. By removing unnecessary parts of an image, you can reduce its file size and improve its overall composition. Cropping can also help to focus attention on the main subject of the image.
Compressing is a more advanced technique for reducing image size. Compression algorithms work by removing redundant data from an image, resulting in a smaller file size. There are two types of compression: lossless and lossy. Lossless compression preserves the original image data, while lossy compression discards some of the data to achieve a smaller file size.
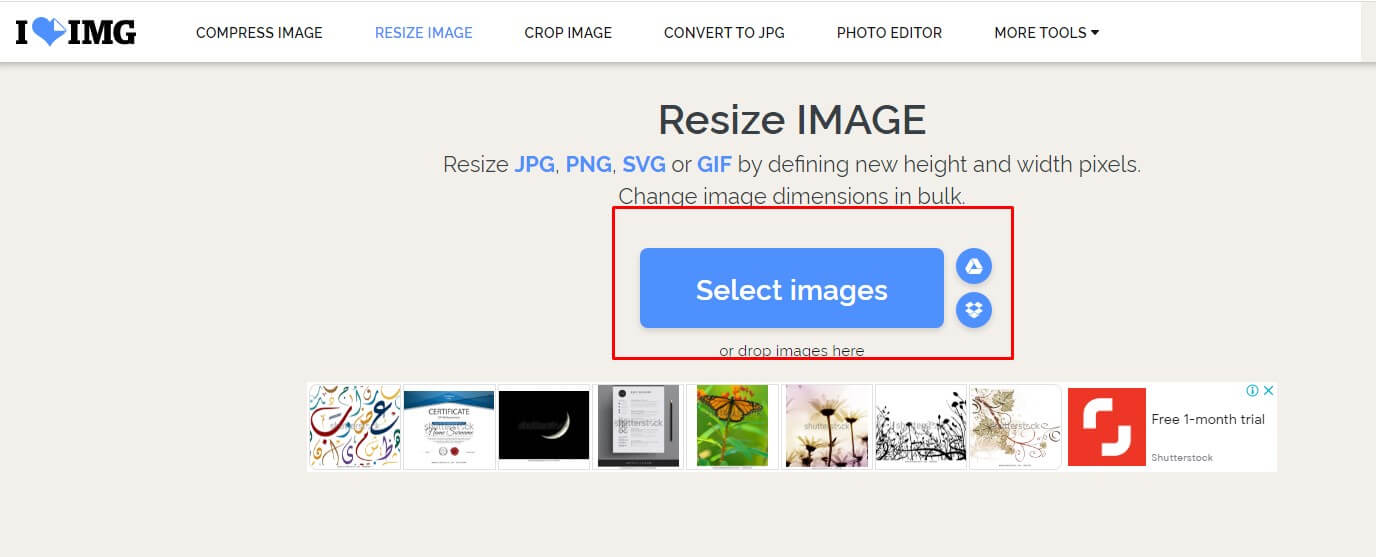
Fortunately, there are many tools available to help with image compression. TinyPNG, ImageOptim, and ShortPixel are popular options that offer advanced compression algorithms and easy-to-use interfaces. These tools can help to reduce image size without losing quality, making them essential for web developers and designers.
In addition to these tools, there are also several online services that offer image compression. These services often use advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to optimize images for web use. Some popular options include Kraken.io, Imagecompressor, and Compressor.io.
When using these tools and services, it’s essential to test the compressed images to ensure that they meet your quality standards. A good rule of thumb is to compare the original image with the compressed image to ensure that there is no noticeable loss of quality.
By using these techniques and tools, you can reduce image size without losing quality, resulting in faster page loads, improved user experience, and better search engine rankings. In the next section, we’ll delve into the world of image compression algorithms, exploring their strengths and weaknesses, and discussing the trade-offs between compression ratio and image quality.
The Role of Image Compression Algorithms: A Deep Dive
Image compression algorithms play a crucial role in reducing image size without losing quality. These algorithms work by analyzing the image data and removing redundant information, resulting in a smaller file size. In this section, we’ll delve into the world of image compression algorithms, exploring their strengths and weaknesses, and discussing the trade-offs between compression ratio and image quality.
There are two main types of image compression algorithms: lossless and lossy. Lossless compression algorithms preserve the original image data, while lossy compression algorithms discard some of the data to achieve a smaller file size. Lossless compression algorithms are typically used for images that require high quality, such as medical images or images used in graphic design. Lossy compression algorithms, on the other hand, are commonly used for web images, as they can achieve a smaller file size without significantly affecting image quality.
One of the most popular image compression algorithms is the Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT). The DCT is a lossy compression algorithm that works by dividing the image into small blocks and applying a mathematical transform to each block. The resulting data is then quantized and encoded, resulting in a smaller file size. The DCT is widely used in image compression formats such as JPEG and WebP.
Another popular image compression algorithm is the Predictive Coding (PC) algorithm. The PC algorithm is a lossless compression algorithm that works by predicting the value of each pixel based on the values of neighboring pixels. The predicted values are then encoded and stored, resulting in a smaller file size. The PC algorithm is commonly used in image compression formats such as PNG and GIF.
When choosing an image compression algorithm, it’s essential to consider the trade-offs between compression ratio and image quality. A higher compression ratio can result in a smaller file size, but may also affect image quality. On the other hand, a lower compression ratio may result in a larger file size, but may also preserve image quality. The key is to find a balance between compression ratio and image quality that meets your specific needs.
In addition to the compression algorithm, other factors can also affect image quality, such as the quality of the original image, the compression settings, and the image format. By understanding these factors and how they interact, you can optimize your
Best Practices for Image Optimization: Tips and Tricks
Optimizing images for web use requires a combination of technical skills and attention to detail. In this section, we’ll provide actionable advice on image optimization, including how to use image editing software, leverage browser caching, and implement lazy loading.
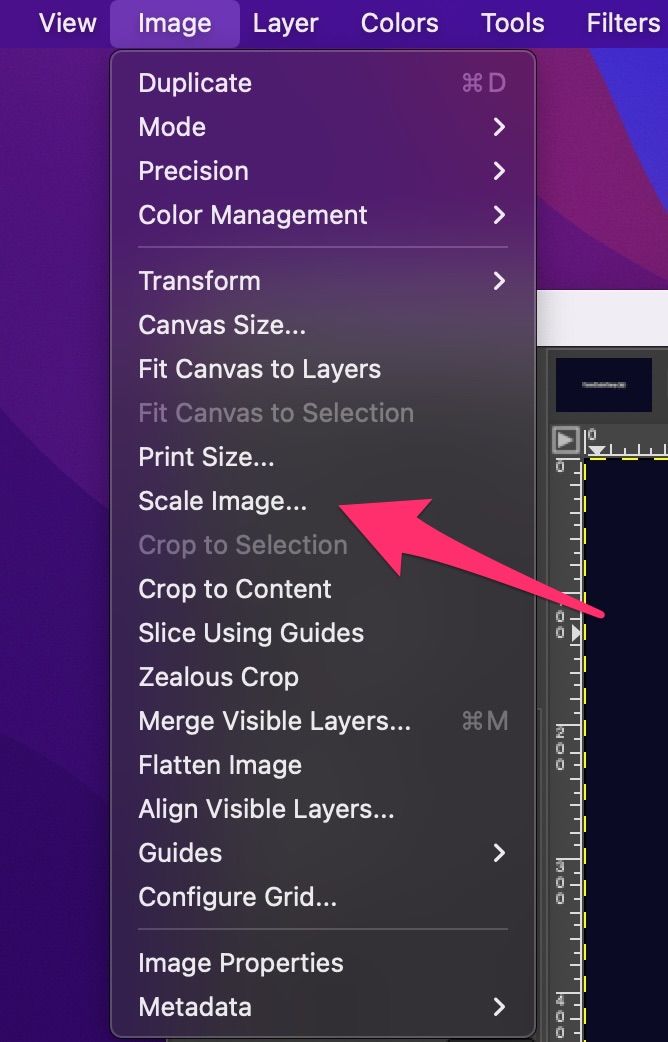
One of the most important steps in image optimization is to use image editing software to compress and resize images. Adobe Photoshop and GIMP are popular options that offer advanced features for image compression and resizing. When using these tools, it’s essential to balance compression ratio and image quality to ensure that the image is optimized for web use.
Another key strategy for image optimization is to leverage browser caching. Browser caching allows web browsers to store frequently-used images in memory, reducing the need for repeat downloads and improving page load times. To implement browser caching, use the Cache-Control header to specify the caching behavior for your images.
Lazy loading is another technique for improving image optimization. Lazy loading involves loading images only when they are needed, rather than loading all images at once. This approach can significantly improve page load times and reduce the amount of data transferred over the network. To implement lazy loading, use JavaScript libraries such as Lazy Load or IntersectionObserver.
In addition to these techniques, it’s also essential to consider the image format and compression algorithm used. As discussed earlier, different image formats and compression algorithms have different strengths and weaknesses. By choosing the right format and algorithm for your images, you can optimize them for web use without sacrificing quality.
Finally, it’s essential to test and validate your image optimization efforts. Use tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights or ImageOptim to analyze your images and identify areas for improvement. By testing and validating your image optimization efforts, you can ensure that your images are optimized for web use and provide the best possible user experience.
By following these best practices for image optimization, you can improve the performance and user experience of your website, while also reducing the amount of data transferred over the network. In the next section, we’ll explore real-world examples of successful image optimization, highlighting the benefits and results achieved by websites and businesses.
Real-World Examples: Successful Image Optimization Case Studies
Image optimization is a crucial aspect of website performance and user experience. In this section, we’ll showcase real-world examples of successful image optimization, highlighting the benefits and results achieved by websites and businesses.
One notable example is the website of the popular online retailer, Amazon. Amazon’s website is known for its fast page load times and high-quality images. To achieve this, Amazon uses a combination of image compression algorithms and caching techniques to optimize its images for web use. As a result, Amazon’s website loads quickly and efficiently, even on slower internet connections.
Another example is the website of the popular news organization, The New York Times. The New York Times uses a combination of image compression algorithms and lazy loading to optimize its images for web use. This approach allows the website to load quickly and efficiently, even on slower internet connections. Additionally, the website’s images are optimized for mobile devices, ensuring that readers can access the content on-the-go.
Google’s website is another example of successful image optimization. Google uses a combination of image compression algorithms and caching techniques to optimize its images for web use. As a result, Google’s website loads quickly and efficiently, even on slower internet connections. Additionally, Google’s images are optimized for mobile devices, ensuring that users can access the content on-the-go.
These examples demonstrate the importance of image optimization for website performance and user experience. By using a combination of image compression algorithms and caching techniques, websites can optimize their images for web use, resulting in faster page load times and improved user experience.
In addition to these examples, there are many other websites and businesses that have successfully optimized their images for web use. By following best practices for image optimization, such as using image compression algorithms and caching techniques, websites can improve their performance and user experience, resulting in increased engagement and conversion rates.
By learning from these examples and implementing image optimization techniques on your own website, you can improve your website’s performance and user experience, resulting in increased engagement and conversion rates. In the next section, we’ll explore common mistakes to avoid when reducing image size, including over-compression, incorrect formatting, and neglecting to test image quality.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Reducing Image Size
When reducing image size, it’s essential to avoid common pitfalls that can compromise image quality or lead to inefficient compression. In this section, we’ll warn readers about common mistakes to avoid when reducing image size, including over-compression, incorrect formatting, and neglecting to test image quality.
One of the most common mistakes when reducing image size is over-compression. Over-compression can lead to a loss of image quality, making the image appear pixelated or distorted. To avoid over-compression, it’s essential to find the right balance between compression ratio and image quality. This can be achieved by using image compression algorithms that preserve image quality, such as lossless compression algorithms.
Another common mistake is incorrect formatting. Incorrect formatting can lead to images that are not optimized for web use, resulting in slower page load times and poor user experience. To avoid incorrect formatting, it’s essential to choose the right image file format for the type of image being used. For example, JPEG is suitable for photographic images, while PNG is suitable for images with transparent backgrounds.
Neglecting to test image quality is another common mistake when reducing image size. Neglecting to test image quality can lead to images that are not optimized for web use, resulting in poor user experience. To avoid neglecting to test image quality, it’s essential to use image editing software to test and validate image quality before uploading the image to a website.
Other common mistakes to avoid when reducing image size include using the wrong image compression algorithm, neglecting to use browser caching, and not implementing lazy loading. By avoiding these common mistakes, website owners can ensure that their images are optimized for web use, resulting in faster page load times and improved user experience.
By being aware of these common mistakes, website owners can take steps to avoid them and ensure that their images are optimized for web use. In the next section, we’ll explore emerging trends and technologies in image optimization, including the role of AI, machine learning, and new image file formats like WebP and AVIF.
Future-Proofing Your Images: Emerging Trends and Technologies
As technology continues to evolve, new trends and technologies are emerging in the field of image optimization. In this section, we’ll explore emerging trends and technologies in image optimization, including the role of AI, machine learning, and new image file formats like WebP and AVIF.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are playing an increasingly important role in image optimization. AI-powered image compression algorithms can analyze images and optimize them for web use, resulting in faster page load times and improved user experience. ML-powered image optimization tools can also learn from user behavior and adapt to changing image optimization needs.
New image file formats like WebP and AVIF are also emerging as popular alternatives to traditional image file formats like JPEG and PNG. WebP, developed by Google, offers improved compression ratios and faster page load times compared to JPEG. AVIF, developed by the Alliance for Open Media, offers improved compression ratios and faster page load times compared to PNG.
Other emerging trends and technologies in image optimization include the use of cloud-based image optimization services, which can optimize images in real-time and reduce the need for manual image optimization. Additionally, the use of image optimization plugins for popular content management systems like WordPress and Drupal can simplify the image optimization process and improve website performance.
By staying up-to-date with emerging trends and technologies in image optimization, website owners can ensure that their images are optimized for web use and provide the best possible user experience. Whether it’s using AI-powered image compression algorithms or new image file formats like WebP and AVIF, there are many ways to future-proof your images and improve website performance.
In conclusion, image optimization is a critical aspect of website performance and user experience. By understanding the importance of image compression, choosing the right image file format, and using emerging trends and technologies, website owners can ensure that their images are optimized for web use and provide the best possible user experience.