Understanding the Basics of Tax Rates
Tax rates are a crucial component of the tax system, and understanding how they work is essential for individuals and businesses alike. A tax rate is the percentage of an individual’s or business’s income that is paid in taxes. There are two primary types of tax rates: marginal and effective. The marginal tax rate is the rate applied to the last dollar of income earned, while the effective tax rate is the average rate paid on all income earned.
To calculate tax liability, tax rates are applied to taxable income. Taxable income is the amount of income that is subject to taxation, after deductions and exemptions have been taken into account. The tax rate is then applied to this amount to determine the total tax liability. For example, if an individual has a taxable income of $50,000 and a marginal tax rate of 24%, their tax liability would be $12,000.
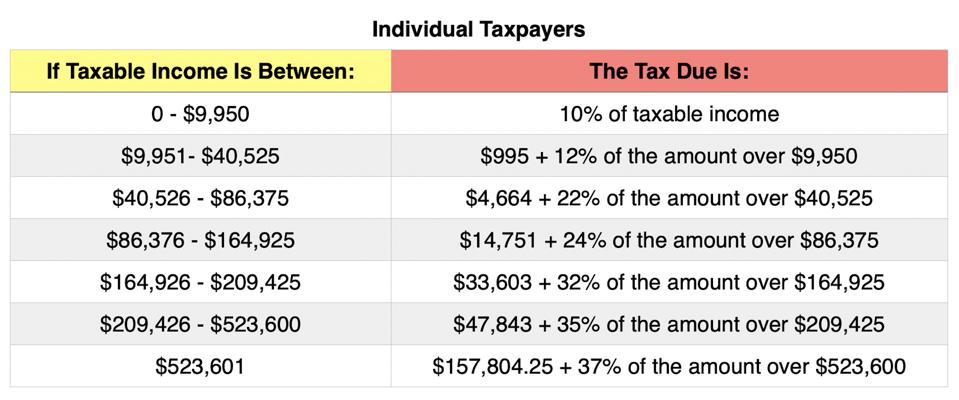
It’s essential to note that tax rates can vary significantly depending on the jurisdiction, income level, and filing status. In the United States, for instance, there are seven tax brackets, ranging from 10% to 37%. The tax rate applied to an individual’s income depends on their filing status and the amount of income earned.
When searching for information on how to find tax rate, it’s crucial to understand the different types of tax rates and how they are applied. This knowledge will help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their tax obligations and plan accordingly. By understanding the basics of tax rates, individuals can better navigate the tax system and ensure they are in compliance with all tax laws and regulations.
Identifying Your Tax Filing Status
Determining your tax filing status is a crucial step in understanding how to find tax rate. Your tax filing status affects the tax rates and brackets that apply to your income, as well as the deductions and credits you are eligible for. There are five main tax filing statuses: single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, and qualifying widow(er).
Single filers are individuals who are unmarried or considered unmarried for tax purposes. Married filing jointly filers are couples who are married and file their taxes together. Married filing separately filers are couples who are married but file their taxes separately. Head of household filers are individuals who are unmarried and have dependents, such as children or elderly parents. Qualifying widow(er) filers are individuals who have lost their spouse and have dependents.
It’s essential to choose the correct tax filing status, as it can significantly impact your tax liability. For example, married filing jointly filers may be eligible for a lower tax rate than single filers, while head of household filers may be eligible for a higher standard deduction. To determine your tax filing status, you can use the IRS’s Interactive Tax Assistant tool or consult with a tax professional.
Once you have determined your tax filing status, you can use tax rate schedules and tables to find your tax rate. The IRS provides tax rate schedules and tables for each tax filing status, which can be found on their website or through tax software. By understanding your tax filing status and using the correct tax rate schedules and tables, you can accurately determine your tax rate and ensure you are in compliance with all tax laws and regulations.
Locating Tax Rate Schedules and Tables
When it comes to understanding tax rates, having access to the right resources is crucial. Knowing how to find tax rate schedules and tables can help individuals accurately calculate their tax liability. In this section, we will explore the various ways to locate tax rate schedules and tables, making it easier to navigate the tax filing process.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides tax rate schedules and tables on its official website. The IRS website offers a comprehensive collection of tax rate schedules and tables for different tax years, making it a valuable resource for taxpayers. To access these resources, simply visit the IRS website and navigate to the “Tax Tables” or “Tax Rate Schedules” section.
In addition to the IRS website, tax software and online tools can also provide access to tax rate schedules and tables. Popular tax software like TurboTax and H&R Block often include tax rate schedules and tables within their programs. These tools can help individuals quickly and accurately calculate their tax liability, taking into account their specific tax situation.
For those who prefer a more traditional approach, printed tax tables are also available. The IRS publishes an annual tax table booklet that includes tax rate schedules and tables for the current tax year. This booklet can be downloaded from the IRS website or obtained by contacting the IRS directly.
When using tax rate schedules and tables, it’s essential to ensure that you are using the correct tax year and filing status. Tax rates and tables can change from year to year, so it’s crucial to use the most up-to-date resources. By knowing how to find tax rate schedules and tables, individuals can accurately calculate their tax liability and make informed decisions about their tax strategy.
To find tax rate schedules and tables, follow these steps:
- Visit the IRS website and navigate to the “Tax Tables” or “Tax Rate Schedules” section.
- Use tax software or online tools that include tax rate schedules and tables.
- Download or obtain the IRS annual tax table booklet.
- Ensure you are using the correct tax year and filing status.
By following these steps and using the right resources, individuals can easily locate tax rate schedules and tables, making it easier to navigate the tax filing process and accurately calculate their tax liability.
Calculating Your Taxable Income
Calculating taxable income is a crucial step in determining tax liability. Taxable income is the amount of income that is subject to taxation, and it is calculated by subtracting deductions and exemptions from gross income. In this section, we will explore the process of calculating taxable income, including gross income, deductions, and exemptions.
Gross income is the total amount of income earned from all sources, including wages, salaries, tips, and self-employment income. It also includes income from investments, such as interest, dividends, and capital gains. To calculate gross income, individuals should gather all relevant financial documents, including W-2 forms, 1099 forms, and investment statements.
Once gross income is calculated, deductions and exemptions can be subtracted to arrive at taxable income. Deductions are expenses that can be subtracted from gross income to reduce taxable income. Common deductions include mortgage interest, charitable donations, and medical expenses. Exemptions, on the other hand, are amounts that are excluded from taxable income, such as the standard deduction or personal exemptions.
For example, let’s say John has a gross income of $100,000 and claims a standard deduction of $12,000. He also has mortgage interest deductions of $10,000 and charitable donations of $5,000. To calculate his taxable income, John would subtract his deductions and exemptions from his gross income:
Gross income: $100,000 Standard deduction: -$12,000 Mortgage interest deductions: -$10,000 Charitable donations: -$5,000 Taxable income: $73,000
In this example, John’s taxable income is $73,000, which is the amount of income that is subject to taxation.
Calculating taxable income can be complex, especially for individuals with multiple sources of income or complex financial situations. However, by following these steps and using the right resources, individuals can accurately calculate their taxable income and determine their tax liability.
To calculate taxable income, follow these steps:
- Gather all relevant financial documents, including W-2 forms, 1099 forms, and investment statements.
- Calculate gross income by adding up all sources of income.
- Identify deductions and exemptions, such as mortgage interest, charitable donations, and personal exemptions.
- Subtract deductions and exemptions from gross income to arrive at taxable income.
By following these steps and using the right resources, individuals can accurately calculate their taxable income and take the first step towards determining their tax liability.
Applying Tax Credits and Deductions
Tax credits and deductions can significantly reduce tax liability, and understanding how to apply them is crucial for minimizing tax payments. In this section, we will discuss the impact of tax credits and deductions on tax rates, including the earned income tax credit, child tax credit, and mortgage interest deduction.
Tax credits are direct reductions to tax liability, and they can be more valuable than deductions. The earned income tax credit (EITC) is a refundable tax credit designed to help low-to-moderate-income working individuals and families. The child tax credit is another popular tax credit that provides up to $2,000 per child under the age of 17. To qualify for these credits, individuals must meet specific income and eligibility requirements.
Tax deductions, on the other hand, reduce taxable income, which in turn reduces tax liability. The mortgage interest deduction is a popular tax deduction that allows homeowners to deduct the interest paid on their mortgage. This deduction can be especially valuable for homeowners with large mortgages. Other common tax deductions include charitable donations, medical expenses, and business expenses.
To apply tax credits and deductions, individuals should follow these steps:
- Determine eligibility for tax credits, such as the EITC and child tax credit.
- Gather documentation for tax deductions, such as mortgage interest statements and charitable donation receipts.
- Claim tax credits and deductions on the tax return, using the correct forms and schedules.
- Calculate the impact of tax credits and deductions on tax liability.
For example, let’s say Sarah is a single mother with two children under the age of 17. She earns $40,000 per year and pays $10,000 in mortgage interest. She is eligible for the child tax credit and claims the mortgage interest deduction. Her tax liability would be reduced by the amount of the tax credit and deduction.
Tax credits and deductions can be complex, and individuals should consult with a tax professional or use tax software to ensure accurate calculations. By applying tax credits and deductions, individuals can minimize their tax liability and keep more of their hard-earned money.
Some popular tax credits and deductions include:
- Earned income tax credit (EITC)
- Child tax credit
- Mortgage interest deduction
- Charitable donation deduction
- Medical expense deduction
- Business expense deduction
By understanding how to apply tax credits and deductions, individuals can take control of their tax situation and reduce their tax liability.
Using Tax Software and Online Tools
Tax software and online tools have revolutionized the way individuals prepare and file their taxes. These tools can help individuals find their tax rate, calculate their tax liability, and even file their taxes electronically. In this section, we will introduce popular tax software and online tools, such as TurboTax and H&R Block, and explain their benefits and limitations.
TurboTax is one of the most popular tax software programs available. It offers a range of features, including tax rate calculations, deductions and credits, and electronic filing. TurboTax also offers a free version for simple tax returns, as well as more advanced versions for complex tax situations.
H&R Block is another well-known tax software program. It offers a range of features, including tax rate calculations, deductions and credits, and electronic filing. H&R Block also offers a free version for simple tax returns, as well as more advanced versions for complex tax situations.
Other popular tax software and online tools include TaxAct, Credit Karma Tax, and FreeTaxUSA. These tools offer a range of features, including tax rate calculations, deductions and credits, and electronic filing.
The benefits of using tax software and online tools include:
- Accuracy: Tax software and online tools can help individuals accurately calculate their tax rate and liability.
- Convenience: Tax software and online tools can be used from the comfort of one’s own home, and can be accessed at any time.
- Speed: Tax software and online tools can help individuals quickly and easily prepare and file their taxes.
- Cost-effective: Many tax software and online tools offer free or low-cost versions, making them a cost-effective option for individuals.
However, there are also some limitations to using tax software and online tools. These include:
- Complexity: Tax software and online tools may not be able to handle complex tax situations, such as self-employment income or rental income.
- Technical issues: Tax software and online tools can be prone to technical issues, such as glitches or errors.
- Limited support: Some tax software and online tools may not offer adequate support or customer service.
Despite these limitations, tax software and online tools can be a valuable resource for individuals looking to find their tax rate and prepare their taxes. By using these tools, individuals can save time and money, and ensure that their taxes are accurate and complete.
To get the most out of tax software and online tools, individuals should:
- Choose a reputable and well-established tax software or online tool.
- Read reviews and do research before selecting a tax software or online tool.
- Follow the instructions carefully and accurately enter all information.
- Take advantage of customer support and resources offered by the tax software or online tool.
By following these tips, individuals can use tax software and online tools to find their tax rate and prepare their taxes with confidence.
Consulting a Tax Professional
When it comes to navigating complex tax situations, consulting a tax professional can be a valuable resource. Tax professionals, such as certified public accountants (CPAs) and enrolled agents (EAs), have the expertise and knowledge to help individuals find their tax rate and ensure they are in compliance with tax laws and regulations.
A tax professional can help individuals with a variety of tax-related tasks, including:
- Preparing and filing tax returns
- Calculating tax liability and finding tax rates
- Identifying and claiming tax credits and deductions
- Representing individuals in front of the IRS
- Providing tax planning and consulting services
One of the main benefits of consulting a tax professional is their ability to navigate complex tax situations. Tax professionals have the expertise and knowledge to handle complex tax issues, such as self-employment income, rental income, and investment income. They can also help individuals identify and claim tax credits and deductions they may be eligible for.
In addition to their technical expertise, tax professionals can also provide valuable guidance and advice on tax planning and strategy. They can help individuals develop a tax plan that meets their specific needs and goals, and provide guidance on how to minimize tax liability and maximize tax savings.
When selecting a tax professional, it’s essential to choose someone who is qualified and experienced. Look for a tax professional who is certified by a reputable organization, such as the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) or the National Association of Enrolled Agents (NAEA). You should also ask about their experience and expertise in handling tax situations similar to yours.
Some popular types of tax professionals include:
- Certified Public Accountants (CPAs)
- Enrolled Agents (EAs)
- Tax Attorneys
- Tax Consultants
By consulting a tax professional, individuals can ensure they are in compliance with tax laws and regulations, and that they are taking advantage of all the tax credits and deductions they are eligible for. A tax professional can provide valuable guidance and advice, and help individuals navigate complex tax situations with confidence.
To get the most out of consulting a tax professional, individuals should:
- Be prepared to provide all necessary tax documents and information
- Ask questions and seek clarification on any tax-related issues
- Be open and honest about their tax situation and goals
- Follow the tax professional’s advice and guidance
By following these tips, individuals can ensure they are getting the most out of consulting a tax professional, and that they are on the path to finding their tax rate and minimizing their tax liability.
Staying Up-to-Date with Tax Law Changes
Tax laws and regulations are constantly changing, and it’s essential to stay informed about these changes to ensure you’re in compliance and taking advantage of all the tax credits and deductions you’re eligible for. In this section, we’ll discuss the importance of staying up-to-date with tax law changes and provide resources for staying current.
Tax law changes can have a significant impact on your tax liability, and it’s crucial to understand how these changes affect you. For example, changes to tax rates, deductions, and credits can all impact your tax liability. Additionally, new tax laws and regulations can be introduced, and existing ones can be modified or repealed.
So, how can you stay up-to-date with tax law changes? Here are a few resources to help you stay informed:
- IRS Website: The IRS website is a valuable resource for staying up-to-date with tax law changes. You can find information on new tax laws, regulations, and guidance on the IRS website.
- Tax Professional Associations: Many tax professional associations, such as the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) and the National Association of Enrolled Agents (NAEA), provide updates on tax law changes and offer guidance on how to navigate these changes.
- Tax Software and Online Tools: Many tax software and online tools, such as TurboTax and H&R Block, provide updates on tax law changes and offer guidance on how to navigate these changes.
- Tax News and Publications: There are many tax news and publications available that provide updates on tax law changes and offer guidance on how to navigate these changes.
By staying up-to-date with tax law changes, you can ensure you’re in compliance with tax laws and regulations and taking advantage of all the tax credits and deductions you’re eligible for. Remember, tax laws and regulations are constantly changing, so it’s essential to stay informed to avoid any potential penalties or fines.
Some popular resources for staying up-to-date with tax law changes include:
- IRS Website: irs.gov
- AICPA Website: aicpa.org
- NAEA Website: naea.org
- TurboTax Website: turbotax.com
- H&R Block Website: hrblock.com
By using these resources, you can stay informed about tax law changes and ensure you’re in compliance with tax laws and regulations. Remember, staying up-to-date with tax law changes is essential for minimizing your tax liability and avoiding any potential penalties or fines.