Understanding the Google Ads Ecosystem
The Google Ads platform is a complex ecosystem that enables businesses and individuals to monetize their online presence through targeted advertising. At its core, Google Ads is a pay-per-click (PPC) advertising model that allows advertisers to create and display ads on Google’s search engine and other websites across the internet. But have you ever wondered how much does Google Ads pay its advertisers? The answer lies in understanding the various components of the Google Ads ecosystem.
Google Ads is comprised of several key components, including AdWords, AdSense, and Google Ad Manager. AdWords is the platform that allows advertisers to create and manage their ad campaigns, while AdSense is the program that enables publishers to monetize their website traffic with targeted ads. Google Ad Manager, on the other hand, is a comprehensive ad management platform that allows publishers to manage their ad inventory and optimize their ad revenue.
So, how do businesses and individuals make money through Google Ads? The answer is simple: by creating and displaying relevant, high-quality ads that resonate with their target audience. Advertisers can use Google Ads to promote their products or services, drive website traffic, and generate leads. Publishers, on the other hand, can use Google Ads to monetize their website traffic and earn revenue from targeted ads.
But to maximize their revenue potential, advertisers and publishers need to understand how Google Ads calculates revenue. This is where the concept of cost-per-click (CPC) and cost-per-thousand impressions (CPM) comes in. CPC refers to the amount that advertisers pay each time a user clicks on their ad, while CPM refers to the amount that advertisers pay for every 1,000 times their ad is displayed. By understanding these metrics, advertisers and publishers can optimize their ad campaigns and maximize their revenue potential.
In the next section, we’ll delve into the mechanics of Google Ads’ revenue calculation and explore the factors that impact advertiser revenue. But for now, it’s essential to understand the basics of the Google Ads ecosystem and how it enables businesses and individuals to monetize their online presence.
How Google Ads Calculates Advertiser Revenue
Understanding how Google Ads calculates advertiser revenue is crucial for maximizing return on investment (ROI). The platform uses a complex algorithm that takes into account various factors, including cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-thousand impressions (CPM), and conversion rates. But how much does Google Ads pay its advertisers? The answer lies in understanding these metrics and how they impact ad revenue.
CPC is the amount that advertisers pay each time a user clicks on their ad. This metric is influenced by the ad’s relevance, landing page quality, and bidding strategy. Advertisers can optimize their CPC by improving ad relevance, increasing ad quality, and using smart bidding strategies. For example, using a cost-per-conversion bidding strategy can help advertisers pay only for conversions, rather than clicks.
CPM, on the other hand, is the amount that advertisers pay for every 1,000 times their ad is displayed. This metric is influenced by ad visibility, ad placement, and user engagement. Advertisers can optimize their CPM by improving ad visibility, using high-performing ad formats, and increasing user engagement.
Conversion rates also play a crucial role in determining advertiser revenue. A conversion is a desired action taken by a user, such as filling out a form or making a purchase. Advertisers can optimize their conversion rates by improving ad relevance, increasing ad quality, and using smart bidding strategies.
So, how can advertisers optimize their campaigns for maximum ROI? The answer lies in understanding the interplay between CPC, CPM, and conversion rates. By improving ad relevance, increasing ad quality, and using smart bidding strategies, advertisers can maximize their ROI and increase their revenue potential.
For example, an advertiser can use a cost-per-conversion bidding strategy to pay only for conversions, rather than clicks. This can help increase ROI and reduce waste. Additionally, advertisers can use ad extensions to increase ad visibility and improve user engagement.
By understanding how Google Ads calculates advertiser revenue, advertisers can make informed decisions about their campaigns and maximize their ROI. In the next section, we’ll explore the role of Ad Rank and Quality Score in determining advertiser revenue.
The Role of Ad Rank and Quality Score in Advertiser Revenue
Ad Rank and Quality Score are two crucial metrics that play a significant role in determining advertiser revenue on Google Ads. Ad Rank is a metric that determines the position of an ad on the search engine results page (SERP), while Quality Score is a metric that measures the relevance and quality of an ad. But how do these metrics impact advertiser revenue?
Ad Rank is calculated based on the maximum cost-per-click (CPC) bid, ad relevance, and landing page quality. A higher Ad Rank means that an ad will be displayed in a more prominent position on the SERP, increasing its visibility and click-through rate (CTR). This, in turn, can lead to higher revenue for advertisers. However, a lower Ad Rank can result in lower ad visibility, CTR, and revenue.
Quality Score, on the other hand, is a metric that measures the relevance and quality of an ad. A higher Quality Score means that an ad is more relevant to the user’s search query, increasing its CTR and conversion rate. This can lead to higher revenue for advertisers. However, a lower Quality Score can result in lower ad relevance, CTR, and revenue.
So, how can advertisers improve their Ad Rank and Quality Score to increase their revenue? The answer lies in optimizing their ad campaigns for relevance, quality, and user experience. Advertisers can improve their Ad Rank by increasing their CPC bid, improving ad relevance, and optimizing their landing page quality. They can also improve their Quality Score by creating high-quality ad copy, using relevant keywords, and optimizing their ad extensions.
By understanding the role of Ad Rank and Quality Score in determining advertiser revenue, advertisers can make informed decisions about their ad campaigns and optimize them for maximum ROI. In the next section, we’ll explore the payment terms and conditions for Google Ads, including payment schedules, thresholds, and methods.
It’s worth noting that Ad Rank and Quality Score are not the only factors that impact advertiser revenue. Other factors, such as ad placement, ad format, and user engagement, also play a significant role. However, by optimizing their ad campaigns for Ad Rank and Quality Score, advertisers can increase their revenue potential and achieve their marketing goals.
Google Ads Payment Terms and Conditions
Understanding the payment terms and conditions for Google Ads is crucial for advertisers and publishers to manage their payments and resolve any issues that may arise. Google Ads offers various payment options, including credit cards, bank transfers, and PayPal. Advertisers can choose the payment method that best suits their needs and budget.
Google Ads also has a payment threshold, which is the minimum amount that must be accrued in an advertiser’s account before a payment is made. The payment threshold varies depending on the payment method and the advertiser’s location. Advertisers can check their payment threshold in their Google Ads account settings.
In addition to payment thresholds, Google Ads also has a payment schedule. Advertisers are typically billed on a monthly basis, with payments due on the 15th of each month. However, advertisers can also choose to be billed on a daily or weekly basis, depending on their payment preferences.
Advertisers can also manage their payments and resolve any issues that may arise through the Google Ads platform. The platform provides a range of tools and resources, including payment history, payment schedules, and payment thresholds. Advertisers can also contact Google Ads support for assistance with payment-related issues.
But how much does Google Ads pay its advertisers? The answer depends on various factors, including the advertiser’s bid strategy, ad relevance, and landing page quality. Advertisers can optimize their ad campaigns to increase their revenue potential and achieve their marketing goals.
For example, advertisers can use cost-per-conversion bidding to pay only for conversions, rather than clicks. This can help increase revenue potential and reduce waste. Advertisers can also use ad extensions to increase ad visibility and improve user engagement.
By understanding the payment terms and conditions for Google Ads, advertisers can manage their payments and resolve any issues that may arise. In the next section, we’ll explore the factors that impact Google Ads revenue for publishers, including ad placement, ad format, and user engagement.
Factors Affecting Google Ads Revenue for Publishers
As a publisher, maximizing Google Ads revenue is crucial to monetizing your online presence. However, several factors can impact your revenue potential, including ad placement, ad format, and user engagement. Understanding these factors can help you optimize your ad inventory and increase your revenue.
Ad placement is a critical factor in determining Google Ads revenue for publishers. The placement of your ads on your website or mobile app can significantly impact your revenue potential. For example, placing ads above the fold or in high-traffic areas can increase your ad visibility and click-through rate (CTR). On the other hand, placing ads in low-traffic areas or below the fold can decrease your ad visibility and CTR.
Ad format is another factor that can impact Google Ads revenue for publishers. Different ad formats, such as display ads, link units, and native ads, can perform differently in terms of revenue potential. For example, display ads can generate higher revenue than link units, but may also have a lower CTR.
User engagement is also a critical factor in determining Google Ads revenue for publishers. Engaging users with high-quality content and interactive experiences can increase your ad visibility and CTR. On the other hand, low-quality content and poor user experiences can decrease your ad visibility and CTR.
So, how can publishers optimize their ad inventory for maximum revenue? The answer lies in understanding their audience and optimizing their ad placement, ad format, and user engagement. By using data and analytics to inform their ad optimization strategies, publishers can increase their revenue potential and achieve their monetization goals.
For example, publishers can use Google Analytics to track their website traffic and ad performance. They can also use Google AdSense to optimize their ad placement and ad format. Additionally, publishers can use user engagement metrics, such as time on site and bounce rate, to optimize their content and user experience.
By optimizing their ad inventory and user experience, publishers can increase their Google Ads revenue and achieve their monetization goals. In the next section, we’ll explore the benchmarks and industry standards for Google Ads revenue, including average CPC, CPM, and conversion rates.
Google Ads Revenue Benchmarks and Industry Standards
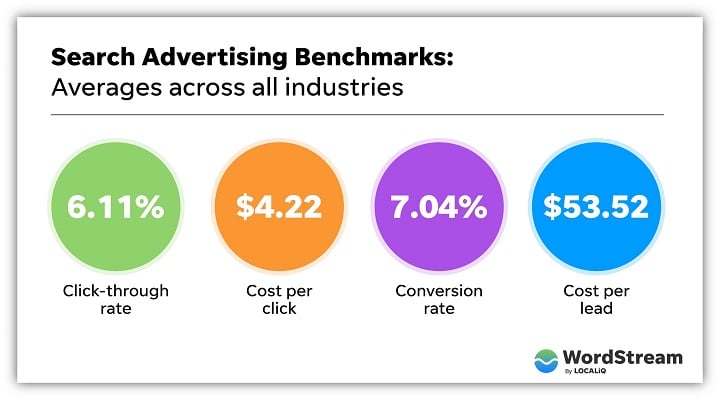
Understanding the benchmarks and industry standards for Google Ads revenue is crucial for advertisers and publishers to evaluate their campaign performance and optimize their strategies. But how much does Google Ads pay its advertisers? The answer lies in understanding the average cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-thousand impressions (CPM), and conversion rates.
According to Google Ads benchmarks, the average CPC for search ads is around $1.16, while the average CPM for display ads is around $0.45. However, these numbers can vary significantly depending on the industry, location, and ad format.
Conversion rates are also an important metric for evaluating Google Ads revenue. According to Google Ads benchmarks, the average conversion rate for search ads is around 2.35%, while the average conversion rate for display ads is around 0.77%.
Advertisers and publishers can use these benchmarks to evaluate their campaign performance and optimize their strategies. For example, if an advertiser’s CPC is higher than the industry average, they may need to adjust their bidding strategy or ad targeting. Similarly, if a publisher’s CPM is lower than the industry average, they may need to optimize their ad placement or ad format.
Industry standards for Google Ads revenue also vary depending on the industry and location. For example, the average CPC for the finance industry is around $3.44, while the average CPC for the retail industry is around $0.86.
By understanding the benchmarks and industry standards for Google Ads revenue, advertisers and publishers can optimize their strategies and maximize their revenue potential. In the next section, we’ll explore the tips and strategies for maximizing Google Ads revenue through optimization techniques.
For example, advertisers can use keyword research to optimize their ad targeting and increase their conversion rates. They can also use ad copywriting to improve their ad relevance and increase their CTR. Additionally, publishers can use ad placement optimization to increase their ad visibility and CPM.
By using these optimization techniques, advertisers and publishers can maximize their Google Ads revenue and achieve their marketing goals.
Maximizing Google Ads Revenue through Optimization Techniques
Optimizing Google Ads campaigns is crucial for maximizing revenue and achieving marketing goals. By using various optimization techniques, advertisers and publishers can improve their campaign performance and increase their revenue potential. But how much does Google Ads pay its advertisers? The answer lies in understanding the optimization techniques that can help maximize revenue.
Keyword research is a critical optimization technique for Google Ads campaigns. By conducting thorough keyword research, advertisers can identify relevant and high-performing keywords that can help increase their ad visibility and click-through rate (CTR). Advertisers can use tools like Google Keyword Planner and SEMrush to conduct keyword research and identify high-performing keywords.
Ad copywriting is another important optimization technique for Google Ads campaigns. By writing high-quality and relevant ad copy, advertisers can improve their ad relevance and increase their CTR. Advertisers can use tools like Google Ads Editor and AdWords Script to write and optimize their ad copy.
Bidding strategies are also crucial for optimizing Google Ads campaigns. By using the right bidding strategy, advertisers can maximize their revenue potential and achieve their marketing goals. Advertisers can use tools like Google Ads Bidding Strategies and AdWords Bidding to optimize their bidding strategies.
Additionally, advertisers can use ad extensions to improve their ad visibility and CTR. Ad extensions like site links, callouts, and call extensions can help advertisers provide more value to their users and increase their ad relevance.
By using these optimization techniques, advertisers and publishers can maximize their Google Ads revenue and achieve their marketing goals. In the next section, we’ll explore the common mistakes that advertisers and publishers make when it comes to Google Ads revenue and how to avoid them.
For example, advertisers can use A/B testing to optimize their ad copy and bidding strategies. They can also use Google Ads Analytics to track their campaign performance and identify areas for improvement. Additionally, publishers can use ad placement optimization to increase their ad visibility and CPM.
By avoiding common mistakes and using optimization techniques, advertisers and publishers can maximize their Google Ads revenue and achieve their marketing goals.
Common Google Ads Revenue Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes is crucial to maximizing Google Ads revenue. Advertisers and publishers often make errors that can significantly impact their earnings. By understanding these mistakes, individuals can take proactive steps to optimize their campaigns and increase their revenue.
One of the most significant mistakes is poor ad targeting. Failing to target the right audience can lead to low click-through rates, high bounce rates, and reduced revenue. Advertisers should use specific keywords, demographics, and interests to target their ideal audience. This ensures that ads are shown to users who are most likely to convert, increasing the chances of generating revenue.
Inadequate budgeting is another common mistake. Advertisers often set budgets that are too low, limiting their ad visibility and click-through rates. On the other hand, setting budgets that are too high can lead to wasted spend and reduced ROI. Advertisers should set realistic budgets based on their campaign goals and target audience.
Neglecting ad maintenance is also a significant mistake. Advertisers often set up their campaigns and forget to monitor and optimize them regularly. This can lead to reduced ad performance, lower revenue, and wasted spend. Advertisers should regularly review their campaign metrics, adjust their bids, and update their ad copy to ensure optimal performance.
Not optimizing ad extensions is another mistake that can impact revenue. Ad extensions provide additional information about a business, such as phone numbers, addresses, and reviews. By including ad extensions, advertisers can increase their ad visibility, click-through rates, and conversion rates.
Finally, not tracking conversions is a critical mistake. Advertisers often focus on click-through rates and cost-per-click (CPC) without tracking conversions. This makes it challenging to determine the effectiveness of their campaigns and optimize for maximum ROI. Advertisers should set up conversion tracking to measure the success of their campaigns and make data-driven decisions.
By avoiding these common mistakes, advertisers and publishers can optimize their Google Ads campaigns and increase their revenue. Remember, the key to success lies in understanding how much Google Ads pay and using this knowledge to create targeted, optimized campaigns that drive conversions and revenue.