Understanding the Credit Score Landscape
Credit scores play a vital role in determining an individual’s financial health and creditworthiness. A good credit score can unlock better loan terms, lower interest rates, and increased credit limits, making it essential to understand the credit score landscape. In the United States, credit scores are calculated by the three major credit reporting agencies: Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. These agencies use different credit scoring models, such as FICO and VantageScore, to evaluate an individual’s creditworthiness.
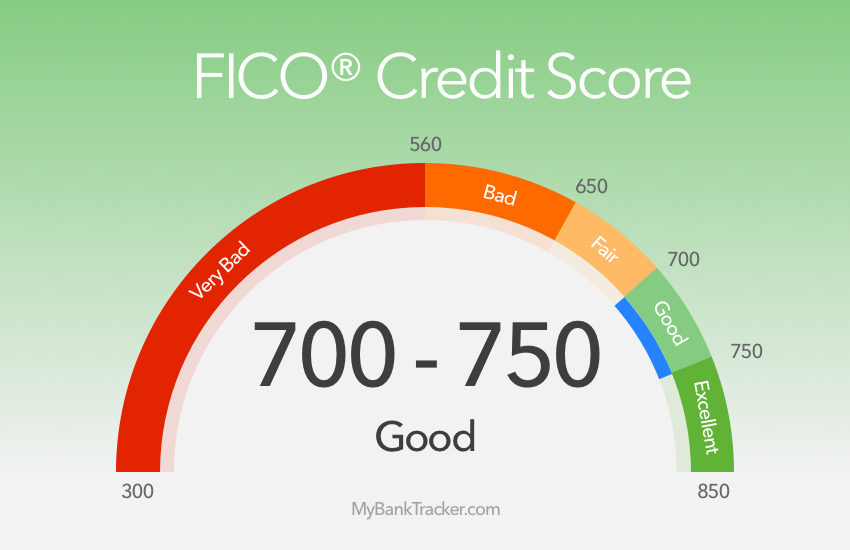
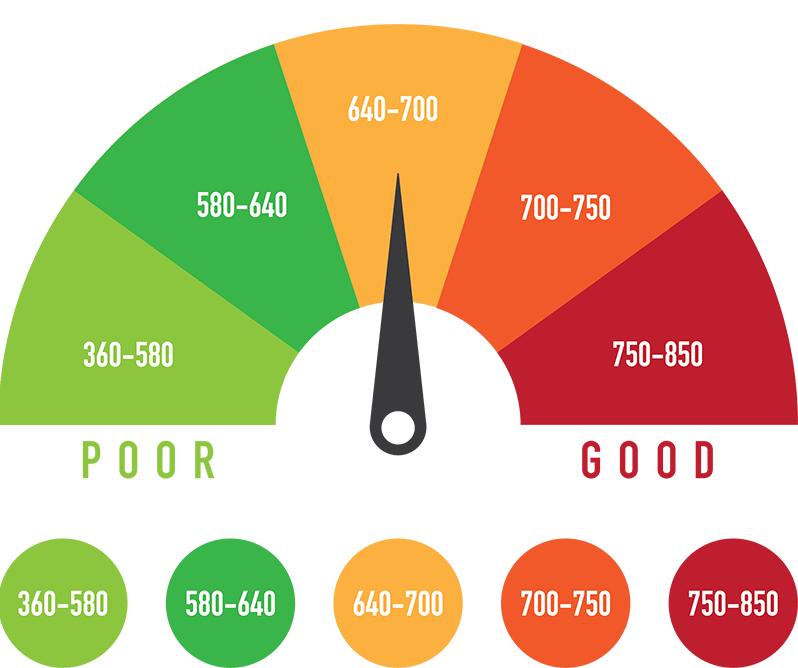
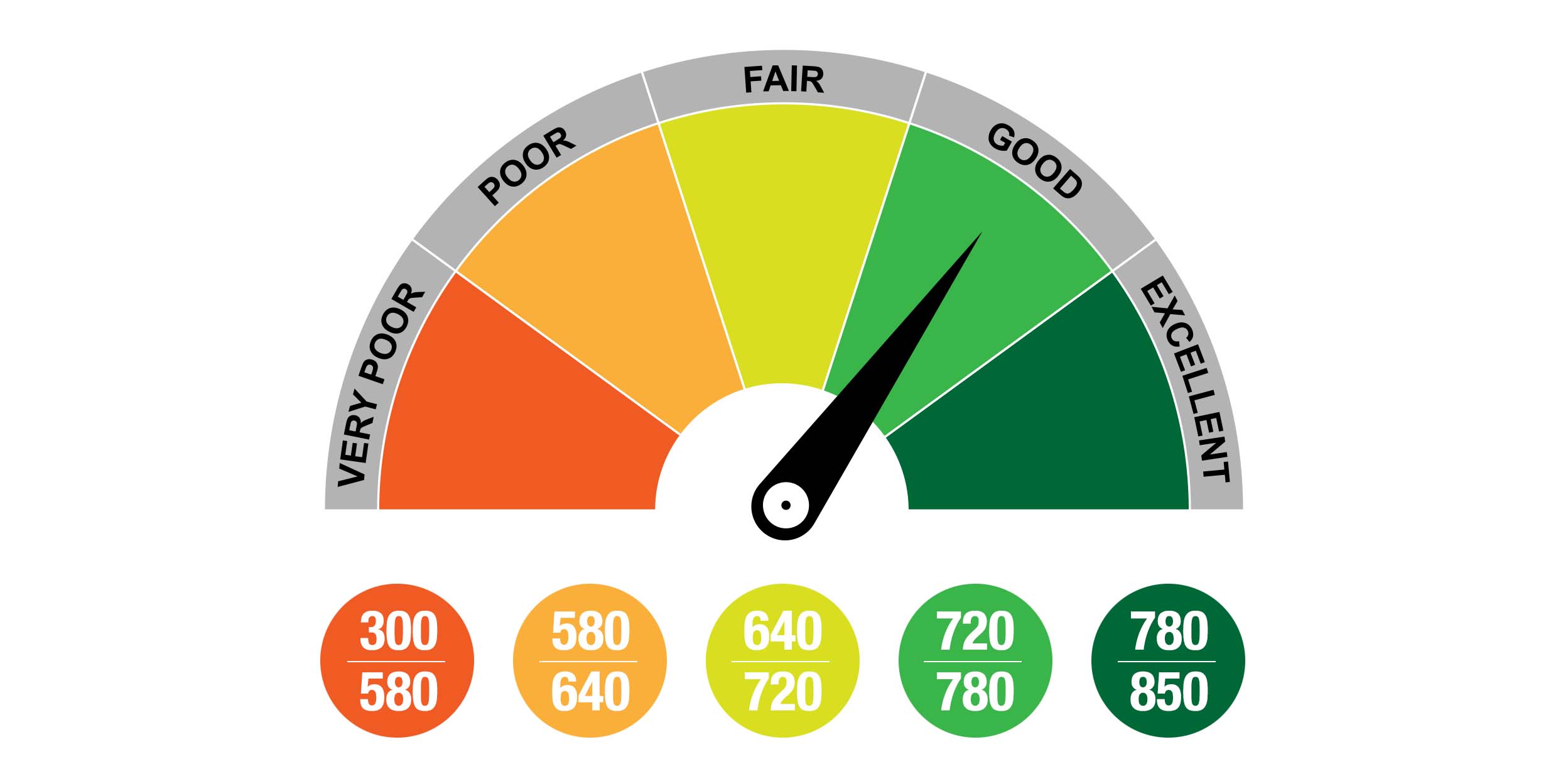
The most widely used credit scoring model is the FICO score, which ranges from 300 to 850. A good credit score is generally considered to be 700 or higher, although this can vary depending on the lender and the type of credit being applied for. Understanding the different credit scoring models and their ranges is crucial in determining what a good credit score is and how to achieve it.
For instance, a FICO score of 750 or higher is considered excellent, while a score of 650-699 is considered good. On the other hand, a score below 600 is considered poor and may result in higher interest rates or loan rejections. By understanding the credit score landscape, individuals can take the necessary steps to improve their credit scores and achieve better financial health.
In addition to FICO scores, VantageScores are also widely used by lenders. VantageScores range from 501 to 990 and are calculated based on similar factors, including payment history, credit utilization, and credit age. A good VantageScore is generally considered to be 700 or higher, although this can vary depending on the lender and the type of credit being applied for.
Overall, understanding the credit score landscape is essential in determining what a good credit score is and how to achieve it. By knowing the different credit scoring models and their ranges, individuals can take the necessary steps to improve their credit scores and achieve better financial health.
What Makes a Good Credit Score: Breaking Down the Numbers
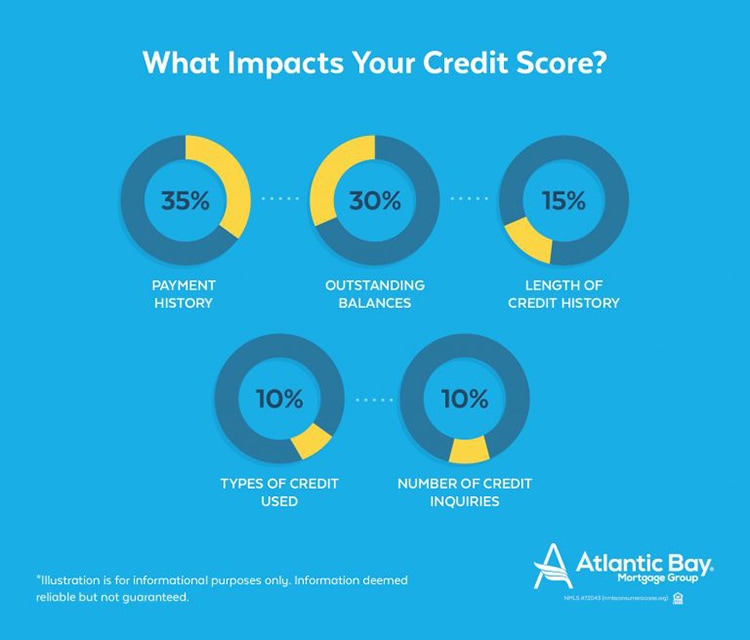
A good credit score is determined by several factors, including payment history, credit utilization, credit age, credit mix, and new credit inquiries. Understanding these factors is crucial in determining what a good credit score is and how to achieve it.
Payment history accounts for 35% of a credit score and is based on an individual’s history of making on-time payments. Late payments, collections, and bankruptcies can negatively impact credit scores, while a history of on-time payments can help improve them. For example, an individual with a history of making on-time payments for several years may have a higher credit score than someone with a history of late payments.
Credit utilization, which accounts for 30% of a credit score, is based on the amount of credit used compared to the amount of credit available. Keeping credit utilization low, ideally below 30%, can help improve credit scores. For instance, an individual with a credit limit of $1,000 and a balance of $300 has a credit utilization ratio of 30%, which is considered good.
Credit age, which accounts for 15% of a credit score, is based on the length of time an individual has had credit. A longer credit history can help improve credit scores, while a short credit history may negatively impact them. For example, an individual who has had credit for 10 years may have a higher credit score than someone who has had credit for only 2 years.
Credit mix, which accounts for 10% of a credit score, is based on the variety of credit types an individual has, such as credit cards, loans, and mortgages. A diverse credit mix can help improve credit scores, while a lack of diversity may negatively impact them. For instance, an individual with a mix of credit cards, loans, and a mortgage may have a higher credit score than someone with only credit cards.
New credit inquiries, which account for 10% of a credit score, are based on the number of new credit applications an individual has made. Applying for too many credit cards or loans in a short period can negatively impact credit scores, while a limited number of applications may not have a significant impact. For example, an individual who applies for several credit cards in a short period may have a lower credit score than someone who applies for only one credit card.
By understanding these factors, individuals can take the necessary steps to improve their credit scores and achieve a good credit score. Remember, a good credit score is not just a number, but a reflection of an individual’s financial health and creditworthiness.
How to Achieve a Good Credit Score: Strategies for Success
Achieving a good credit score requires a combination of financial discipline and smart credit management strategies. By following these tips, individuals can improve their credit scores and enjoy better financial health.
Make on-time payments: Payment history is the most significant factor in determining credit scores, accounting for 35% of the total score. Making on-time payments is crucial in maintaining a good credit score. Set up payment reminders or automate payments to ensure timely payments.
Reduce debt: High levels of debt can negatively impact credit scores. Reduce debt by paying off high-interest loans and credit cards, and avoid taking on new debt. Consider consolidating debt into a single, lower-interest loan or credit card.
Monitor credit reports: Credit reports contain information about an individual’s credit history, including payment history, credit utilization, and credit inquiries. Monitor credit reports regularly to ensure accuracy and detect any errors or signs of identity theft.
Keep credit utilization low: Credit utilization is the percentage of available credit being used. Keep credit utilization low, ideally below 30%, to avoid negatively impacting credit scores. Aim to use less than 10% of available credit for the best credit scores.
Avoid applying for too many credit cards: Applying for multiple credit cards in a short period can negatively impact credit scores. Only apply for credit cards when necessary, and space out applications if multiple cards are needed.
Build a long credit history: A longer credit history can help improve credit scores. Consider keeping old accounts open and in good standing to demonstrate responsible credit behavior over time.
Be patient and persistent: Achieving a good credit score takes time and effort. Be patient and persistent in maintaining good credit habits, and avoid getting discouraged by setbacks or slow progress.
By following these strategies, individuals can improve their credit scores and enjoy better financial health. Remember, a good credit score is not just a number, but a reflection of an individual’s financial responsibility and creditworthiness.
The Benefits of a Good Credit Score: Unlocking Better Loan Terms and Lower Interest Rates
A good credit score is the key to unlocking better loan terms and lower interest rates. When lenders see a good credit score, they view the borrower as a lower risk, which can lead to more favorable loan conditions. This can result in significant cost savings over the life of the loan. For example, a borrower with a good credit score may qualify for a lower interest rate on a mortgage, which can save them thousands of dollars in interest payments over the life of the loan.
In addition to lower interest rates, a good credit score can also provide access to better loan terms, such as longer repayment periods or lower fees. This can make it easier to manage debt and reduce the overall cost of borrowing. Furthermore, a good credit score can also increase credit limits, providing borrowers with more flexibility and financial freedom.
So, what constitutes a good credit score? Generally, a credit score of 700 or higher is considered good, although the exact definition of a good credit score can vary depending on the lender and the type of loan. However, by understanding what a good credit score is and how it can benefit borrowers, individuals can take steps to improve their credit score and unlock better loan terms and lower interest rates.
For instance, a good credit score can save individuals money on credit card debt. According to a recent study, borrowers with good credit scores can save up to 10% on credit card interest rates compared to those with poor credit scores. This can result in significant cost savings over time, especially for individuals who carry large credit card balances.
In conclusion, a good credit score is essential for unlocking better loan terms and lower interest rates. By understanding the benefits of a good credit score and taking steps to improve their credit score, individuals can save money, reduce debt, and improve their overall financial health. Whether it’s a mortgage, credit card, or personal loan, a good credit score can provide borrowers with more financial flexibility and freedom.
Common Mistakes That Can Hurt Your Credit Score
While achieving a good credit score requires effort and dedication, it’s equally important to avoid common mistakes that can hurt your credit score. These mistakes can lead to a decline in credit score, making it more challenging to obtain credit or loans in the future. In this section, we’ll discuss some of the most common mistakes that can negatively impact credit scores and provide guidance on how to avoid them.
One of the most significant mistakes that can hurt your credit score is making late payments. Payment history accounts for 35% of your credit score, so missing payments or making late payments can significantly lower your credit score. To avoid this, set up payment reminders or automate your payments to ensure you never miss a payment. Additionally, if you’re having trouble making payments, contact your creditor to discuss possible alternatives, such as a payment plan or temporary hardship program.
Another common mistake is high credit utilization. Credit utilization refers to the amount of credit used compared to the credit limit. Keeping credit utilization below 30% is recommended, as high credit utilization can indicate to lenders that you’re not managing your debt effectively. To avoid high credit utilization, keep your credit card balances low, and avoid applying for multiple credit cards in a short period.
Applying for too many credit cards or loans in a short period can also hurt your credit score. This can indicate to lenders that you’re taking on too much debt, which can increase the risk of default. To avoid this, only apply for credit when necessary, and space out your applications if you need to apply for multiple lines of credit.
Not monitoring your credit report is another mistake that can hurt your credit score. Errors on your credit report can lead to inaccurate credit scores, which can affect your ability to obtain credit. To avoid this, check your credit report regularly, and dispute any errors you find. You can request a free credit report from each of the three major credit reporting agencies (Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax) once a year.
Finally, not paying off debt can also hurt your credit score. While it may be tempting to ignore debt or hope it goes away, this can lead to collection accounts, which can significantly lower your credit score. To avoid this, create a debt repayment plan, and prioritize paying off high-interest debt first.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can maintain a healthy credit profile and achieve a good credit score. Remember, a good credit score requires ongoing effort and attention, but the benefits of better loan terms, lower interest rates, and increased credit limits make it well worth the effort.
Monitoring Your Credit Score: Tools and Resources for Success
Monitoring your credit score is an essential step in maintaining a healthy credit profile. By regularly checking your credit score, you can identify areas for improvement, detect potential errors, and track your progress over time. In this section, we’ll discuss the importance of monitoring your credit score and provide an overview of tools and resources available to help you do so.
Why is monitoring your credit score important? For one, it allows you to detect errors or inaccuracies on your credit report, which can negatively impact your credit score. According to a recent study, one in five credit reports contains errors, which can lead to denied credit applications or higher interest rates. By monitoring your credit score, you can identify these errors and dispute them with the credit reporting agency.
Monitoring your credit score also helps you track your progress over time. By regularly checking your credit score, you can see how your credit habits are impacting your score and make adjustments as needed. This can help you achieve a good credit score, which can unlock better loan terms, lower interest rates, and increased credit limits.
So, how can you monitor your credit score? There are several tools and resources available, including credit monitoring services, mobile apps, and online credit score providers. Credit monitoring services, such as Credit Karma or Credit Sesame, provide free credit scores and reports, as well as alerts and notifications when changes are detected on your credit report.
Mobile apps, such as Credit Scorecard or Credit Monitor, allow you to track your credit score on-the-go, providing real-time updates and alerts. Online credit score providers, such as Experian or TransUnion, offer paid credit monitoring services, which include detailed credit reports and scores, as well as identity theft protection.
In addition to these tools and resources, you can also request a free credit report from each of the three major credit reporting agencies (Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax) once a year. This can help you detect errors or inaccuracies on your credit report and track your credit score over time.
By monitoring your credit score regularly, you can maintain a healthy credit profile, achieve a good credit score, and unlock better loan terms and lower interest rates. Remember, monitoring your credit score is an ongoing process, and by staying on top of your credit score, you can ensure long-term financial health and stability.
Building a Strong Credit History: Tips for New Credit Users
Establishing a strong credit history is crucial for new credit users, as it can impact their ability to obtain credit, loans, and other financial services in the future. A good credit score can unlock better loan terms, lower interest rates, and increased credit limits, making it essential to start building a strong credit history from the outset. In this section, we’ll provide tips and advice for new credit users on how to establish a strong credit history and maintain a good credit score.
One of the most important tips for new credit users is to make on-time payments. Payment history accounts for 35% of your credit score, so making timely payments is crucial for establishing a strong credit history. Set up payment reminders or automate your payments to ensure you never miss a payment.
Another key tip is to keep credit utilization low. Credit utilization refers to the amount of credit used compared to the credit limit. Keeping credit utilization below 30% is recommended, as high credit utilization can indicate to lenders that you’re not managing your debt effectively. Aim to use less than 30% of your available credit to show lenders you can manage your debt responsibly.
New credit users should also avoid applying for too many credit cards or loans in a short period. This can indicate to lenders that you’re taking on too much debt, which can increase the risk of default. Only apply for credit when necessary, and space out your applications if you need to apply for multiple lines of credit.
Monitoring your credit report is also essential for new credit users. Check your credit report regularly to detect errors or inaccuracies, which can negatively impact your credit score. You can request a free credit report from each of the three major credit reporting agencies (Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax) once a year.
Finally, new credit users should prioritize building a long credit history. A longer credit history can positively impact your credit score, as it shows lenders you have a proven track record of managing debt responsibly. Avoid closing old accounts, as this can negatively impact your credit age and credit utilization.
By following these tips and advice, new credit users can establish a strong credit history and maintain a good credit score. Remember, building a strong credit history takes time and effort, but the benefits of better loan terms, lower interest rates, and increased credit limits make it well worth the effort.
Additionally, new credit users can consider becoming an authorized user on someone else’s credit account, such as a parent or spouse, to start building credit. This can help establish a credit history and improve credit scores over time.
Overall, building a strong credit history requires responsible credit behavior, patience, and persistence. By following these tips and advice, new credit users can set themselves up for long-term financial success and unlock better loan terms and lower interest rates.
Maintaining a Good Credit Score: Long-Term Strategies for Success
Maintaining a good credit score requires ongoing effort and attention. It’s not enough to simply achieve a good credit score; you must also work to maintain it over the long term. In this section, we’ll provide guidance on how to maintain a good credit score, including strategies for managing debt, avoiding credit pitfalls, and staying informed about changes in the credit landscape.
One of the most important strategies for maintaining a good credit score is to manage debt effectively. This means keeping credit utilization low, making on-time payments, and avoiding debt accumulation. Consider implementing a debt snowball or debt avalanche strategy to pay off high-interest debt and reduce your overall debt burden.
Another key strategy is to avoid credit pitfalls, such as late payments, high credit utilization, and applying for too many credit cards. These mistakes can negatively impact your credit score and make it more difficult to maintain a good credit score over the long term. Set up payment reminders, automate your payments, and avoid applying for credit unnecessarily to avoid these pitfalls.
Staying informed about changes in the credit landscape is also crucial for maintaining a good credit score. This means staying up-to-date on changes to credit scoring models, new credit products and services, and shifts in lender requirements. Consider following reputable credit experts and staying informed through online resources and financial news outlets.
Additionally, maintaining a good credit score requires ongoing monitoring and maintenance. Regularly check your credit report to detect errors or inaccuracies, and dispute any issues you find. Consider using credit monitoring services or mobile apps to track your credit score and receive alerts and notifications when changes are detected.
Finally, maintaining a good credit score requires a long-term perspective. Avoid making short-term decisions that may negatively impact your credit score, such as taking on high-interest debt or applying for multiple credit cards. Instead, focus on building a strong credit history and maintaining a good credit score over the long term.
By following these strategies and maintaining a good credit score over the long term, individuals can unlock better loan terms, lower interest rates, and increased credit limits. Remember, maintaining a good credit score requires ongoing effort and attention, but the benefits make it well worth the effort.
In conclusion, maintaining a good credit score is an ongoing process that requires effort, attention, and a long-term perspective. By managing debt effectively, avoiding credit pitfalls, staying informed about changes in the credit landscape, and maintaining a good credit score over the long term, individuals can achieve financial stability and security.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/7-things-you-didnt-know-affect-your-credit-score.aspx-ADD-V2-f87cdc4ddf2c4c7a93d078f56015ed55.jpg)