Understanding the Importance of Accurate Net Profit or Loss Calculations
Accurate calculations of net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C are crucial for self-employed individuals to ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations. The net profit or loss figure is used to determine self-employment tax, business expenses, and overall tax liability. Inaccurate calculations can lead to penalties, fines, and even audits. Therefore, it is essential to understand the significance of accurate net profit or loss calculations and how they impact tax obligations.
The IRS requires self-employed individuals to report their business income and expenses on Schedule C, which is used to calculate net profit or loss. This figure is then used to determine self-employment tax, which is reported on Schedule SE. Accurate calculations of net profit or loss ensure that self-employed individuals pay the correct amount of self-employment tax, which is used to fund Social Security and Medicare.
In addition to self-employment tax, accurate net profit or loss calculations also impact business expenses. Business expenses can be deducted on Schedule C, which reduces the net profit or loss figure. However, inaccurate calculations can lead to incorrect deductions, which can result in penalties and fines. Furthermore, accurate net profit or loss calculations also impact overall tax liability, as it is used to determine the amount of income tax owed.
Self-employed individuals can ensure accurate net profit or loss calculations by maintaining accurate records, including business income, expenses, and depreciation. It is also essential to understand the tax laws and regulations that apply to self-employment income and expenses. By doing so, self-employed individuals can avoid penalties, fines, and audits, and ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations.
In conclusion, accurate calculations of net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C are critical for self-employed individuals to ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations. By understanding the significance of accurate net profit or loss calculations and how they impact tax obligations, self-employed individuals can avoid penalties, fines, and audits, and ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations.
How to Calculate Net Profit or Loss on Schedule C: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating net profit or loss on Schedule C is a crucial step in determining self-employment tax and overall tax liability. To ensure accuracy, follow these steps:
Step 1: Report Business Income
Report all business income on Schedule C, including income from sales, services, and other business activities. This includes income from freelance work, consulting, and any other business ventures.
Step 2: Deduct Business Expenses
Deduct all eligible business expenses on Schedule C, including expenses related to business operations, travel, and equipment. Ensure that expenses are properly categorized and documented to avoid audit issues.
Step 3: Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Calculate COGS by adding the cost of materials, labor, and overhead expenses related to producing goods or services. This will help determine the gross profit margin.
Step 4: Calculate Gross Profit
Calculate gross profit by subtracting COGS from business income. This will provide the gross profit margin, which is used to calculate net profit or loss.
Step 5: Calculate Net Profit or Loss
Calculate net profit or loss by subtracting total business expenses from gross profit. This will provide the net profit or loss figure, which is used to determine self-employment tax and overall tax liability.
Example:
Business Income: $100,000
COGS: $30,000
Gross Profit: $70,000
Business Expenses: $20,000
Net Profit or Loss: $50,000
By following these steps, self-employed individuals can accurately calculate net profit or loss on Schedule C, ensuring compliance with tax laws and regulations.
It’s essential to note that accurate record-keeping is crucial in calculating net profit or loss. Ensure that all business income, expenses, and depreciation are properly documented to avoid audit issues.
In addition to accurate record-keeping, it’s also essential to understand the tax laws and regulations that apply to self-employment income and expenses. By doing so, self-employed individuals can ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations, avoiding penalties and fines.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Calculating Net Profit or Loss
Calculating net profit or loss on IRS Form 1040 Schedule C can be a complex process, and self-employed individuals often make mistakes that can lead to inaccurate calculations and potential audits. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Incorrect Reporting of Business Income
One of the most common mistakes self-employed individuals make is incorrectly reporting business income on Schedule C. This can include failing to report all income, reporting income in the wrong category, or failing to account for income from multiple sources.
Improper Deductions
Self-employed individuals often make mistakes when deducting business expenses on Schedule C. This can include deducting personal expenses, failing to keep accurate records, or deducting expenses that are not eligible for deduction.
Failure to Account for Depreciation
Depreciation is a complex topic, and self-employed individuals often fail to account for it correctly on Schedule C. This can include failing to calculate depreciation correctly, failing to report depreciation on the correct form, or failing to keep accurate records of depreciation.
Incorrect Calculation of Net Profit or Loss
Self-employed individuals often make mistakes when calculating net profit or loss on Schedule C. This can include failing to account for all business expenses, failing to calculate depreciation correctly, or failing to report net profit or loss on the correct form.
Consequences of Mistakes
Mistakes on Schedule C can have serious consequences, including audits, penalties, and fines. Self-employed individuals can avoid these consequences by taking the time to accurately calculate net profit or loss and seeking professional help when needed.
Best Practices for Avoiding Mistakes
To avoid mistakes on Schedule C, self-employed individuals should follow best practices, including:
Keeping accurate records of business income and expenses
Seeking professional help when needed
Staying up-to-date on tax laws and regulations
Reviewing and revising Schedule C regularly
By following these best practices, self-employed individuals can avoid common mistakes and ensure accurate calculations of net profit or loss on Schedule C.
The Impact of Net Profit or Loss on Self-Employment Tax
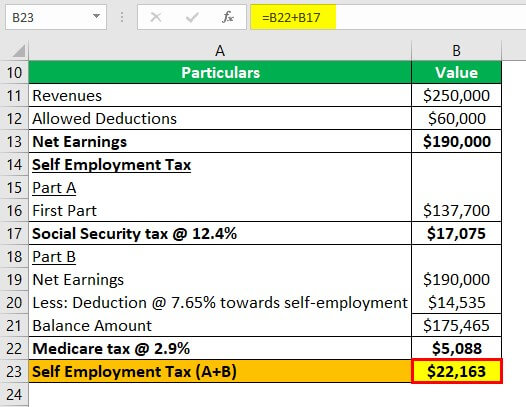
The net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C has a significant impact on self-employment tax. Self-employment tax is used to fund Social Security and Medicare, and it is calculated based on the net earnings from self-employment. The net profit or loss from Schedule C is used to determine the amount of self-employment tax owed.
To calculate self-employment tax, the net profit or loss from Schedule C is multiplied by the self-employment tax rate, which is 15.3% for Social Security and Medicare taxes. This rate includes 12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare. The self-employment tax is typically reported on Schedule SE (Form 1040), and it is due by the tax filing deadline.
The net profit or loss from Schedule C also affects the amount of self-employment tax that can be deducted on Form 1040. The self-employment tax deduction is equal to half of the self-employment tax liability, and it is reported on Line 27 of Form 1040. This deduction can help reduce the overall tax liability.
It is essential to accurately calculate the net profit or loss from Schedule C to ensure that the correct amount of self-employment tax is reported. Underreporting or overreporting self-employment tax can result in penalties and interest. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain accurate records and seek professional help if needed.
In addition to self-employment tax, the net profit or loss from Schedule C also affects the overall tax liability. A net profit will increase the tax liability, while a net loss will reduce the tax liability. Therefore, it is essential to accurately calculate the net profit or loss to ensure that the correct tax liability is reported.
In conclusion, the net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C has a significant impact on self-employment tax. Accurately calculating the net profit or loss is crucial to ensure that the correct amount of self-employment tax is reported, and it also affects the overall tax liability. By understanding the impact of net profit or loss on self-employment tax, self-employed individuals can ensure that they are in compliance with tax laws and regulations.
Business Expense Deductions: What You Need to Know
Accurate calculation of net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C requires a thorough understanding of business expense deductions. Business expenses are a crucial component of Schedule C, as they can significantly impact the net profit or loss. In this section, we will discuss the types of business expenses that can be deducted on Schedule C, how to categorize expenses, what expenses are eligible for deduction, and how to keep accurate records.
Business expenses can be categorized into several types, including cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and capital expenditures. Cost of goods sold includes the direct costs of producing and selling products, such as materials, labor, and overhead. Operating expenses include rent, utilities, salaries, and other expenses necessary to run the business. Capital expenditures include purchases of assets, such as equipment, vehicles, and property.
To be eligible for deduction, business expenses must meet certain criteria. The expense must be ordinary and necessary for the business, and it must be documented with receipts, invoices, or other records. The IRS requires that business expenses be reasonable and not extravagant. For example, a business owner cannot deduct the cost of a luxury car as a business expense unless it is used primarily for business purposes.
Common business expenses that can be deducted on Schedule C include:
- Office expenses, such as supplies, rent, and utilities
- Travel expenses, such as transportation, meals, and lodging
- Equipment and vehicle expenses, such as depreciation and maintenance
- Advertising and marketing expenses
- Insurance premiums, such as liability and property insurance
- Professional fees, such as accounting and legal fees
Accurate record-keeping is essential to support business expense deductions. Business owners should keep receipts, invoices, and other records to document expenses. The IRS requires that records be kept for at least three years in case of an audit. Business owners can use accounting software, such as QuickBooks, to track expenses and generate reports.
In addition to accurate record-keeping, business owners should also be aware of the IRS rules and regulations regarding business expense deductions. The IRS provides guidance on what expenses are eligible for deduction and how to calculate the deduction. Business owners can consult with a tax professional or accountant to ensure that they are taking advantage of all eligible deductions.
In summary, business expense deductions are a critical component of calculating net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C. By understanding the types of business expenses that can be deducted, how to categorize expenses, and what expenses are eligible for deduction, business owners can ensure that they are taking advantage of all eligible deductions and minimizing their tax liability.
Depreciation and Amortization: How to Calculate and Report
Depreciation and amortization are essential components of calculating net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C. These concepts allow self-employed individuals to recover the cost of assets used in their business over time. Accurate calculation and reporting of depreciation and amortization are crucial to ensure compliance with tax laws and to minimize tax liabilities.
Depreciation is the process of allocating the cost of tangible assets, such as equipment, vehicles, and buildings, over their useful life. The IRS provides guidelines for determining the useful life of assets, which can range from 3 to 39 years, depending on the type of asset. To calculate depreciation, self-employed individuals can use the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) or the Alternative Depreciation System (ADS).
MACRS is the most commonly used method, which allows for faster depreciation of assets in the early years. ADS, on the other hand, provides a more gradual depreciation schedule. Self-employed individuals can choose the method that best suits their business needs, but they must use the same method for all assets in the same class.
Amortization is the process of allocating the cost of intangible assets, such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks, over their useful life. The IRS requires self-employed individuals to amortize these assets over a period of 15 years, using the straight-line method.
To report depreciation and amortization on Form 1040 Schedule C, self-employed individuals must complete Form 4562, Depreciation and Amortization. This form requires detailed information about the assets, including their cost, useful life, and depreciation method. The total depreciation and amortization expense is then reported on Schedule C, which is used to calculate net profit or loss.
Accurate calculation and reporting of depreciation and amortization are critical to ensure compliance with tax laws and to minimize tax liabilities. Self-employed individuals should maintain accurate records of their assets, including their cost, useful life, and depreciation method, to support their net profit or loss calculations. By following the IRS guidelines and using the correct forms, self-employed individuals can ensure they are taking advantage of the depreciation and amortization deductions available to them.
Audit-Proof Your Schedule C: Tips for Accurate Record-Keeping
Accurate record-keeping is essential for self-employed individuals to ensure compliance with tax laws and to minimize the risk of audits. When it comes to calculating net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C, maintaining accurate records of business income, expenses, and depreciation is crucial. In this article, we will provide tips on how to maintain accurate records to support net profit or loss calculations.
Business Income Records
Self-employed individuals should keep accurate records of all business income, including invoices, receipts, and bank statements. This includes income from sales, services, and any other business-related activities. It is essential to keep a record of all income, including cash transactions, to ensure accurate reporting on Schedule C.
Business Expense Records
Accurate records of business expenses are critical to ensure compliance with tax laws and to minimize tax liabilities. Self-employed individuals should keep receipts, invoices, and bank statements for all business expenses, including supplies, equipment, rent, and utilities. It is essential to categorize expenses correctly to ensure accurate reporting on Schedule C.
Depreciation Records
Depreciation records are essential to calculate net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C. Self-employed individuals should keep records of all assets, including their cost, useful life, and depreciation method. This includes records of depreciation calculations, including the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS) or the Alternative Depreciation System (ADS).
Record-Keeping Tips
To maintain accurate records, self-employed individuals should:
- Keep all records in a designated area, such as a file cabinet or digital storage device.
- Use a accounting software or spreadsheet to track income and expenses.
- Keep receipts and invoices for all business transactions.
- Categorize expenses correctly to ensure accurate reporting on Schedule C.
- Review records regularly to ensure accuracy and completeness.
Benefits of Accurate Record-Keeping
Accurate record-keeping provides several benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of audits and penalties.
- Minimized tax liabilities.
- Improved financial management and decision-making.
- Increased confidence in net profit or loss calculations.
Conclusion
Accurate record-keeping is essential for self-employed individuals to ensure compliance with tax laws and to minimize the risk of audits. By maintaining accurate records of business income, expenses, and depreciation, self-employed individuals can ensure accurate reporting on Schedule C and minimize tax liabilities. By following these tips, self-employed individuals can audit-proof their Schedule C and ensure a smooth tax filing process.
Seeking Professional Help: When to Consult a Tax Professional
Calculating net profit or loss from IRS Form 1040 Schedule C can be a complex and time-consuming process, especially for self-employed individuals with limited tax knowledge. While it’s possible to navigate the process alone, seeking professional help from a tax professional can be beneficial in many situations. In this article, we’ll discuss when it’s necessary to consult a tax professional for help with calculating net profit or loss on Schedule C.
When to Consult a Tax Professional
Self-employed individuals should consider consulting a tax professional in the following situations:
- Complex business structures: If you have a complex business structure, such as a partnership or S corporation, a tax professional can help you navigate the tax laws and ensure accurate reporting.
- High-volume transactions: If you have a high volume of transactions, a tax professional can help you keep track of income and expenses, and ensure accurate reporting on Schedule C.
- Depreciation and amortization: If you have assets that require depreciation or amortization, a tax professional can help you calculate and report these expenses accurately.
- Audit concerns: If you’re concerned about an audit, a tax professional can help you ensure that your records are accurate and complete, and represent you in case of an audit.
Benefits of Consulting a Tax Professional
Consulting a tax professional can provide several benefits, including:
- Accurate reporting: A tax professional can ensure that your net profit or loss is calculated accurately, reducing the risk of errors and penalties.
- Maximized deductions: A tax professional can help you identify and claim all eligible deductions, minimizing your tax liability.
- Reduced stress: Let a tax professional handle the complexity of tax laws and regulations, reducing your stress and workload.
- Increased confidence: With a tax professional on your side, you can have confidence in your net profit or loss calculations and tax reporting.
How to Find a Qualified Tax Professional
To find a qualified tax professional, consider the following:
- Look for certifications: Look for certifications such as Enrolled Agent (EA), Certified Public Accountant (CPA), or Accredited Tax Advisor (ATA).
- Check experience: Check the tax professional’s experience in handling self-employment taxes and Schedule C.
- Ask for referrals: Ask for referrals from friends, family, or colleagues who have used a tax professional in the past.
- Check credentials: Check the tax professional’s credentials, such as their license and certifications.
What to Expect from a Tax Professional
When working with a tax professional, you can expect:
- Personalized service: A tax professional will provide personalized service, tailored to your specific needs and situation.
- Expert knowledge: A tax professional will have expert knowledge of tax laws and regulations, ensuring accurate reporting and maximized deductions.
- Clear communication: A tax professional will communicate clearly and effectively, ensuring that you understand your net profit or loss calculations and tax reporting.
- Representation: A tax professional will represent you in case of an audit, ensuring that your rights are protected.