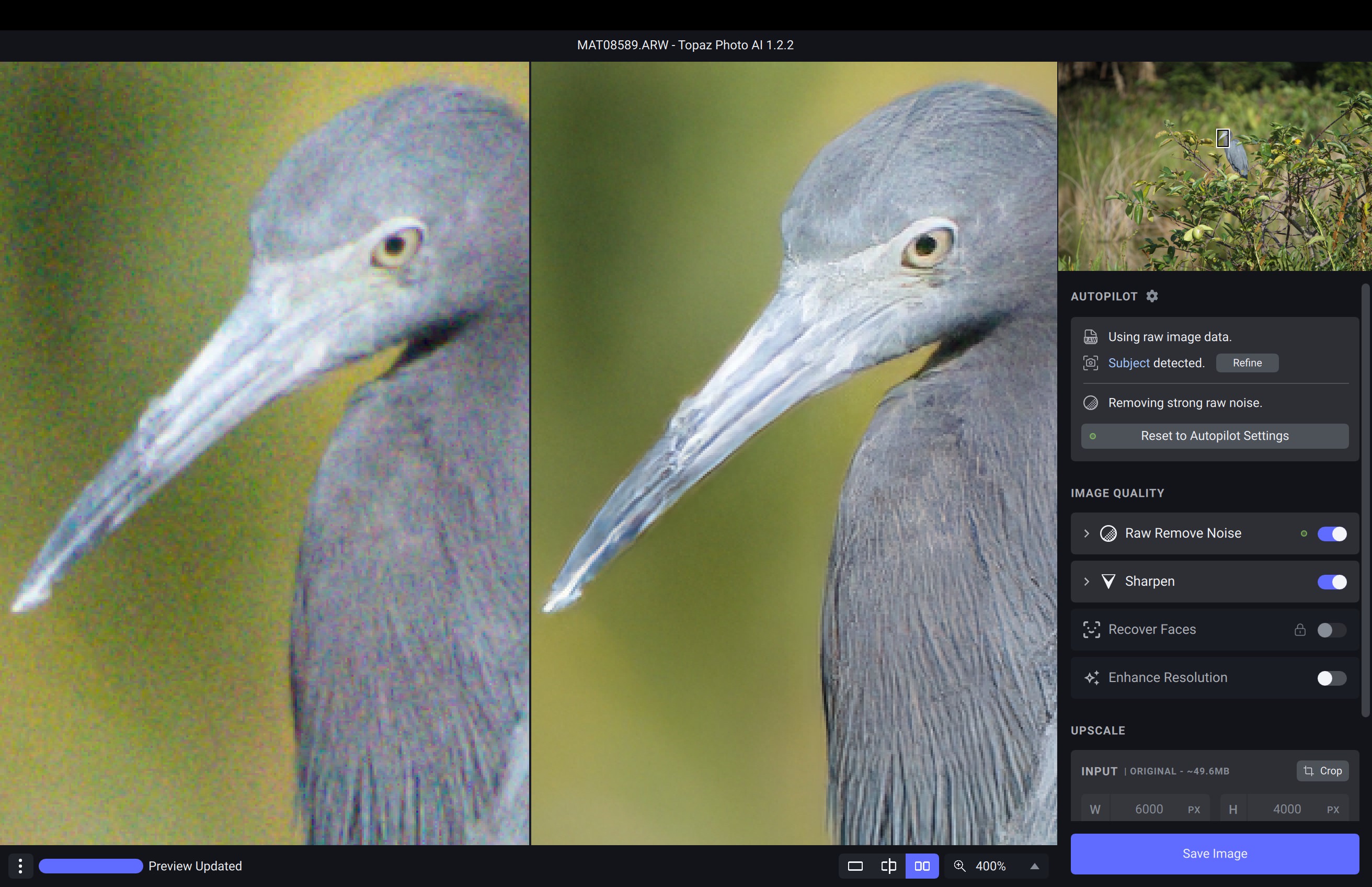
The Dilemma of Image Enlargement: Balancing Size and Clarity
When it comes to digital images, size matters. Whether you’re a professional photographer, graphic designer, or social media enthusiast, you’ve likely encountered the problem of how to increase the size of an image without losing quality. It’s a delicate balancing act, as enlarging an image can quickly lead to pixelation, distortion, and a loss of clarity. The consequences can be disastrous, resulting in blurry or unprofessional-looking images that fail to convey the intended message. Understanding how to increase the size of an image without sacrificing its quality is crucial in today’s visually-driven world. In this article, we’ll explore the best practices and techniques for enlarging images while maintaining their pixel density and integrity, ensuring that your visuals remain sharp and stunning.
Understanding Image Resolution: The Key to Enlargement Success
When it comes to increasing the size of an image without losing quality, understanding image resolution is crucial. Image resolution refers to the number of pixels per unit of length in an image, typically measured in pixels per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI). A higher resolution means a more detailed and clearer image, making it ideal for enlargement. For example, a high-resolution image with 300 DPI or 300 PPI will retain its quality when enlarged, whereas a low-resolution image with 72 DPI may become pixelated or blurry.
To put this into perspective, consider the following scenarios where high-resolution images are necessary: printing large-format prints, creating detailed product images, or showcasing high-quality textures. In these cases, a high-resolution image is essential to ensure that the enlarged image remains clear and detailed. On the other hand, low-resolution images are suitable for web use, where file size and loading speed are more important than image quality.
Moreover, understanding the relationship between pixels and image size is vital. When an image is enlarged, the number of pixels remains the same, but the pixels are spread out over a larger area, resulting in a decrease in pixel density. This decrease in pixel density can lead to a loss of image quality, making it essential to use image editing software to preserve pixel density while enlarging the image. By doing so, you can ensure that your enlarged image maintains its quality and clarity, meeting your desired outcome of how to increase size of image without losing quality.
The Role of File Formats in Image Enlargement
When it comes to enlarging images, the file format plays a crucial role in maintaining image quality. Different file formats have unique strengths and weaknesses that affect the outcome of image enlargement. Understanding the characteristics of each format is essential to avoid sacrificing image quality. JPEG, PNG, and TIFF are the most common file formats used in image editing, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is the most widely used file format for photographic images. It uses lossy compression, which reduces the file size but also compromises image quality. While JPEG is suitable for web use, it’s not ideal for image enlargement, as the lossy compression can lead to a softening of the image. When enlarging a JPEG image, the quality may degrade significantly, resulting in a pixelated or blurry output.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics) is a lossless format, making it a better choice for images that require transparency, such as logos or graphics. PNG files are larger in size compared to JPEGs, but they maintain their quality even when enlarged. However, PNGs may not be suitable for photographic images, as they can result in large file sizes, which can be challenging to manage.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is a lossless format that’s commonly used in professional photography and printing. TIFF files are uncompressed, resulting in large file sizes, but they maintain the highest level of image quality. TIFF is an excellent choice for image enlargement, as it preserves the original quality of the image. However, due to its uncompressed nature, TIFF files can be slow to upload and download, making them less suitable for web use.
When deciding on a file format for image enlargement, consider the intended use of the image. If you need to enlarge a photographic image for web use, a JPEG with minimal compression might be suitable. For images that require transparency or high-quality printing, PNG or TIFF might be a better choice. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each file format, you can ensure that your enlarged images maintain their quality and meet your specific needs.
In the quest to increase size of image without losing quality, choosing the right file format is crucial. By understanding the characteristics of each format, you can avoid common mistakes and produce high-quality enlarged images that meet your requirements. Whether you’re a professional photographer or a graphic designer, selecting the appropriate file format will help you achieve the desired outcome and preserve the integrity of your images.
How to Increase Image Size Without Losing Quality Using Adobe Photoshop
When it comes to enlarging images without sacrificing quality, Adobe Photoshop is a popular choice among professionals and enthusiasts alike. With its advanced features and intuitive interface, Photoshop provides a range of options to increase image size while preserving clarity and detail. To get started, follow these steps:
1. Open your image in Adobe Photoshop and make sure it’s in a format that can be edited, such as a PSD or JPEG file.
2. Go to Image > Image Size, and in the “Image Size” dialog box, uncheck the “Constrain Proportions” option to allow for independent width and height adjustments.
3. In the “Width” and “Height” fields, enter the desired dimensions for your enlarged image. You can also enter a percentage value to scale the image up or down.
4. In the “Resample” section, select the “Preserve Details” option to enable Photoshop’s advanced resampling algorithm. This feature helps maintain image quality by reducing noise and preserving edges.
5. Adjust the “Reduce Noise” and “Sharpen Details” sliders to fine-tune the resampling process. These settings can make a significant difference in the quality of your enlarged image.
6. Click “OK” to apply the changes and view the enlarged image. If necessary, make further adjustments to the image size, resampling settings, or noise reduction and sharpening sliders to achieve the desired result.
By following these steps and leveraging Photoshop’s advanced features, you can successfully increase the size of your image without losing quality. Remember to work on a copy of your original image and save the enlarged version in a suitable format, such as JPEG or TIFF, to ensure optimal results.
When using Photoshop to enlarge images, it’s essential to understand how to increase size of image without losing quality. By doing so, you can create high-quality images that are suitable for various applications, from digital displays to print media.
Whether you’re a professional graphic designer, photographer, or simply looking to enhance your digital images, Photoshop provides a robust platform for image enlargement and editing. By mastering its features and techniques, you can unlock the full potential of your images and produce stunning results that captivate your audience.
Alternative Methods for Enlarging Images: Free and Paid Options
While Adobe Photoshop is a powerful tool for image enlargement, it’s not the only option available. Fortunately, there are alternative methods that can help you increase the size of your image without losing quality, whether you’re on a budget or prefer a different workflow. When exploring alternative methods, it’s essential to understand how to increase size of image without losing quality, as each software or tool has its strengths and weaknesses.
One popular free option is Canva, a graphic design platform that also offers image editing capabilities. Canva’s image enlargement feature allows you to upload your image and adjust the dimensions while maintaining quality. Another free option is GIMP, a free and open-source image editing software that rivals Adobe Photoshop in many ways. GIMP offers advanced features like content-aware scaling and perspective crop, making it an excellent alternative for those on a budget.
If you’re willing to invest in paid software, Skylum Luminar and ON1 Photo Raw are excellent options. Skylum Luminar is a photo editing software that offers AI-powered tools for image enlargement, noise reduction, and sharpening. ON1 Photo Raw, on the other hand, is a professional-grade image editing software that provides advanced features like dynamic contrast and local adjustments. Both software options are designed to help you increase the size of your image without losing quality, making them ideal for photographers and graphic designers.
When exploring alternative methods, it’s crucial to consider the file format of your original image. If you’re working with a JPEG file, you may want to consider software that specializes in JPEG enlargement, like izumu or PhotoZoom Pro. These software options use advanced algorithms to enlarge JPEG files while preserving quality.
In the end, the choice of software or method depends on your specific needs and preferences. Whether you opt for free online tools, paid software, or a combination of both, understanding how to increase size of image without losing quality is key to achieving professional results. By exploring alternative methods and mastering the techniques outlined in this article, you’ll be well on your way to creating high-quality enlarged images that impress.
The Importance of Noise Reduction and Sharpening in Image Enlargement
When it comes to enlarging images, noise reduction and sharpening are two crucial steps that can make all the difference in preserving image quality. Noise reduction helps to eliminate unwanted grain or pixels that can appear when an image is enlarged, while sharpening enhances the overall clarity and definition of the image.
In order to effectively reduce noise, it’s essential to understand the different types of noise that can affect an image. There are two main types: luminance noise, which appears as grain or speckles, and chrominance noise, which appears as color flecks. Both types of noise can be reduced using various techniques and tools, such as applying filters, adjusting brightness and contrast, and using noise reduction software.
Sharpening, on the other hand, is a delicate process that requires a keen eye for detail. Over-sharpening can lead to an unnatural, “crunchy” appearance, while under-sharpening can result in a soft, lackluster image. To sharpen an image effectively, it’s essential to adjust the sharpness settings according to the image’s content and intended use.
In Adobe Photoshop, the “Unsharp Mask” filter is a popular tool for sharpening images. This filter allows users to adjust the amount of sharpening, radius, and threshold to achieve the desired level of sharpness. Additionally, the “Smart Sharpen” filter uses advanced algorithms to automatically detect and sharpen the image.
When enlarging images, it’s essential to apply noise reduction and sharpening techniques in moderation. Over-reliance on these techniques can lead to an unnatural, over-processed appearance. By striking the right balance between noise reduction and sharpening, you can enlarge your images with confidence, preserving their quality and clarity.
Remember, when aiming to increase the size of an image without losing quality, attention to detail is key. By understanding the importance of noise reduction and sharpening, and applying these techniques effectively, you can achieve high-quality, professionally-looking images that impress.
Best Practices for Saving and Exporting Enlarged Images
After successfully enlarging an image without sacrificing quality, it’s essential to save and export it correctly to maintain its integrity. This step is crucial, as it can make or break the image’s usability. When saving and exporting enlarged images, consider the following best practices to ensure optimal results.
File compression is a critical aspect of image saving. To minimize file size without compromising quality, use lossless compression formats like TIFF or PNG. These formats retain the image’s original data, making them ideal for printing or editing. For web use, JPEG compression is suitable, but be cautious not to over-compress, which can lead to a loss of quality.
Color profile management is another vital consideration. Embedding the correct color profile ensures that the image’s colors remain accurate and consistent across different devices and platforms. Failure to do so can result in washed-out or distorted colors. In Adobe Photoshop, go to “Edit” > “Color Settings” to assign the correct color profile.
When exporting images for web use, it’s essential to optimize them for faster loading times. Use the “Save for Web” option in Adobe Photoshop or equivalent features in other software to compress the image while maintaining its quality. This step is critical for enhancing user experience and search engine optimization.
Finally, consider the image’s intended use and adjust the file format and resolution accordingly. For example, if the image is destined for print, use a high-resolution TIFF or PSD file. For online use, a lower-resolution JPEG or PNG file is sufficient. By following these best practices, you can ensure that your enlarged images retain their quality and meet their intended purpose.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Enlarging Images
When it comes to increasing the size of an image without sacrificing quality, there are several common mistakes to avoid. Over-compression, for instance, can lead to a loss of detail and pixelation. Another mistake is using the wrong file format for the job, such as attempting to enlarge a low-resolution JPEG. Failure to apply noise reduction and sharpening techniques can also result in subpar image quality. Additionally, neglecting to adjust the image resolution and dpi settings during the enlargement process can lead to a distorted or blurry image. To avoid these pitfalls, it’s essential to understand how to increase the size of an image without losing quality, using techniques like those outlined in this article. By doing so, you’ll be able to produce high-quality enlarged images that maintain their clarity and detail.