What are Indexed Pages and Why Do They Matter?
Indexed pages are the backbone of a website’s online presence, playing a crucial role in search engine optimization (SEO) and determining a website’s visibility and ranking. In simple terms, an indexed page is a web page that has been crawled, processed, and stored in a search engine’s massive database, making it searchable and accessible to users. Google’s indexing process is a complex algorithm that involves discovering, crawling, and indexing web pages to provide users with relevant and accurate search results.
When a website’s pages are indexed, it increases the chances of appearing in search engine results pages (SERPs) for relevant keywords and phrases. This, in turn, drives organic traffic, boosts brand awareness, and ultimately, contributes to a website’s online success. However, with millions of websites and web pages competing for attention, it’s essential to understand how to find indexed pages in Google and optimize them for better visibility.
Google’s indexing process involves several stages, including crawling, rendering, and indexing. Crawling involves discovering new and updated content using software programs called “crawlers” or “spiders.” Rendering involves loading the content and executing any scripts to see how the page looks and behaves. Finally, indexing involves storing the crawled and rendered content in massive databases, making it searchable and accessible to users.
Understanding how Google indexes pages is crucial for website owners, marketers, and SEO professionals. By optimizing website structure, content, and meta tags, it’s possible to improve indexing and increase online visibility. In the next section, we’ll explore how to check if specific pages are indexed by Google using various tools and techniques.
How to Check if Your Pages are Indexed by Google
Checking if your pages are indexed by Google is a straightforward process that can be done using various tools and techniques. One of the most effective ways to check indexed pages is by using the Google Search Console (GSC). GSC is a free tool that provides insights into how Google crawls and indexes your website.
To check indexed pages using GSC, follow these steps:
1. Log in to your GSC account and select the property you want to check.
2. Click on the “Coverage” tab and select “Indexed pages” from the dropdown menu.
3. You will see a list of indexed pages, including the URL, title, and meta description.
4. You can also use the “Search Analytics” tab to see how your indexed pages are performing in search results.
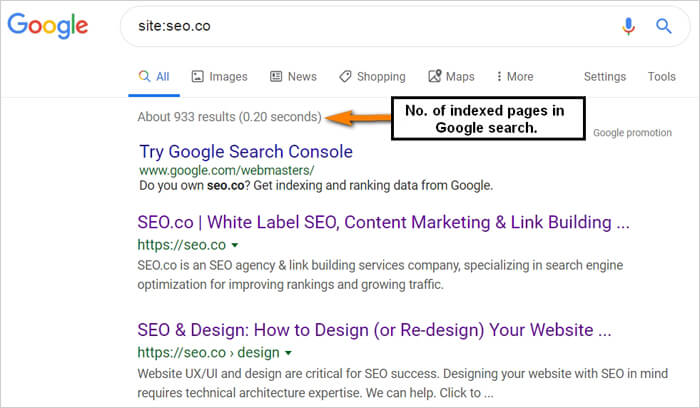
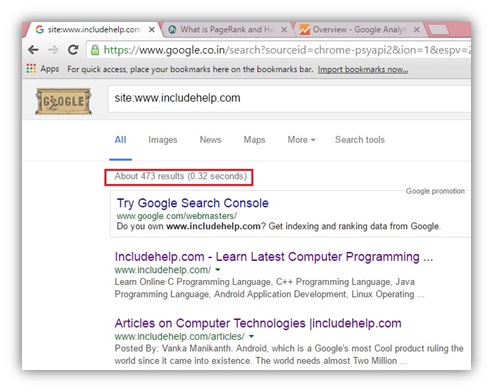
Another way to check indexed pages is by using site operators. Site operators are special commands that can be used to refine search results. To check indexed pages using site operators, follow these steps:
1. Go to Google and type “site:yourwebsite.com” in the search bar.
2. Replace “yourwebsite.com” with your actual website URL.
3. Press enter to see a list of indexed pages from your website.
4. You can also use other site operators, such as “site:yourwebsite.com filetype:pdf” to check indexed PDF files.
In addition to GSC and site operators, you can also use other tools, such as Screaming Frog or Ahrefs, to check indexed pages. These tools provide more advanced features, such as crawling and indexing analysis, to help you optimize your website for better indexing.
By regularly checking indexed pages, you can identify areas for improvement and optimize your website for better visibility and ranking. In the next section, we’ll discuss the different types of indexed pages and how to optimize them for better visibility.
Understanding the Different Types of Indexed Pages
Google indexes a wide range of page types, including HTML pages, PDFs, images, and videos. Each type of page has its own unique characteristics and requirements for indexing. Understanding the different types of indexed pages can help you optimize your website for better visibility and ranking.
HTML pages are the most common type of indexed page. These pages are crawled and indexed by Google’s algorithm, which looks for keywords, meta tags, and other optimization factors. To optimize HTML pages for indexing, focus on creating high-quality, keyword-rich content, and ensure that your meta tags, titles, and descriptions are accurate and descriptive.
PDFs are another type of indexed page. Google can crawl and index PDFs, but they require special handling. To optimize PDFs for indexing, make sure they are text-based and not image-based. You can also use PDF-specific optimization techniques, such as adding keywords to the file name and meta tags.
Images are also indexed by Google, and can be optimized for better visibility. To optimize images for indexing, use descriptive file names and alt tags, and ensure that the images are high-quality and relevant to the content on the page.
Videos are also indexed by Google, and can be optimized for better visibility. To optimize videos for indexing, use descriptive titles and descriptions, and ensure that the videos are high-quality and relevant to the content on the page.
Understanding the different types of indexed pages can help you optimize your website for better visibility and ranking. By focusing on creating high-quality, keyword-rich content, and ensuring that your meta tags, titles, and descriptions are accurate and descriptive, you can improve your website’s indexing and ranking.
In addition to understanding the different types of indexed pages, it’s also important to understand how Google crawls and indexes pages. Google uses a complex algorithm to crawl and index pages, which takes into account a wide range of factors, including keywords, meta tags, and link equity.
By understanding how Google crawls and indexes pages, you can optimize your website for better visibility and ranking. In the next section, we’ll discuss common reasons why pages may not be indexed, and provide solutions and best practices for overcoming these issues.
Common Reasons Why Pages May Not Be Indexed
When it comes to indexing pages, Google’s algorithms can be complex and nuanced. Despite best efforts, some pages may not be indexed, leading to reduced visibility and ranking. Understanding the common reasons behind this issue can help website owners and SEO professionals take corrective action. Here are some of the most common reasons why pages may not be indexed by Google:
Crawl Errors: Google’s crawlers may encounter errors while attempting to crawl a website, resulting in pages not being indexed. This can be due to server errors, DNS issues, or faulty website architecture. Regularly monitoring crawl errors using Google Search Console can help identify and resolve these issues.
Duplicate Content: Duplicate content can confuse Google’s algorithms, leading to pages not being indexed. This can occur when multiple pages have similar or identical content, or when content is copied from other websites. Implementing canonical URLs, using meta tags, and creating unique content can help resolve duplicate content issues.
Poor Website Architecture: A poorly designed website architecture can hinder Google’s ability to crawl and index pages. This can include issues such as deep navigation, slow page loading times, and inadequate internal linking. Improving website architecture through techniques such as flat navigation, page speed optimization, and internal linking can help improve indexing.
Meta Tags and Header Tags: Incorrectly configured meta tags and header tags can prevent pages from being indexed. This includes issues such as missing or duplicate title tags, meta descriptions, and header tags. Ensuring that meta tags and header tags are correctly configured and optimized can help improve indexing.
Mobile-Friendliness: With the majority of searches now coming from mobile devices, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly pages in its indexing. Pages that are not mobile-friendly may not be indexed, or may be indexed at a lower priority. Ensuring that websites are mobile-friendly and responsive can help improve indexing.
Over-Optimization: Over-optimization can lead to pages being flagged as spam, resulting in them not being indexed. This includes issues such as keyword stuffing, excessive internal linking, and manipulative anchor text. Ensuring that optimization techniques are used in moderation and in line with Google’s guidelines can help prevent over-optimization issues.
By understanding these common reasons why pages may not be indexed, website owners and SEO professionals can take corrective action to improve indexing and increase visibility. Regularly monitoring crawl errors, optimizing website architecture, and ensuring that meta tags and header tags are correctly configured can help improve indexing and drive more traffic to a website. By following these best practices, it’s possible to find indexed pages in Google and improve overall website performance.
Optimizing Your Website for Better Indexing
Optimizing a website for better indexing is crucial to improve its visibility and ranking on Google. By implementing the right strategies, website owners can increase the chances of their pages being indexed and appearing in search results. Here are some actionable tips to optimize website structure, content, and meta tags for better indexing:
Website Structure: A well-organized website structure is essential for better indexing. This includes creating a clear hierarchy of pages, using descriptive URLs, and ensuring that all pages are easily accessible from the homepage. A flat website architecture can help Google’s crawlers navigate and index pages more efficiently.
Internal Linking: Internal linking is critical for helping Google’s crawlers discover and index new pages. By creating a clear linking structure, website owners can guide crawlers to important pages and improve indexing. This includes using descriptive anchor text, creating a clear navigation menu, and linking to relevant pages from within content.
XML Sitemaps: XML sitemaps are a crucial tool for helping Google’s crawlers discover and index new pages. By creating and submitting a sitemap, website owners can inform Google about new pages, updates, and changes to their website. This can help improve indexing and reduce crawl errors.
Mobile-Friendliness: With the majority of searches now coming from mobile devices, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly pages in its indexing. Website owners can ensure that their website is mobile-friendly by using responsive design, optimizing page loading times, and ensuring that all content is easily accessible on mobile devices.
Content Optimization: High-quality, engaging content is essential for improving indexing. Website owners can optimize their content by using descriptive titles, meta descriptions, and header tags. This can help Google’s crawlers understand the content and context of each page, improving indexing and ranking.
Meta Tags: Meta tags are a crucial element of website optimization. Website owners can optimize their meta tags by using descriptive titles, meta descriptions, and keyword tags. This can help Google’s crawlers understand the content and context of each page, improving indexing and ranking.
By implementing these strategies, website owners can improve their website’s indexing and increase its visibility on Google. Remember, indexing is an ongoing process, and regular monitoring and optimization are necessary to ensure that all pages are indexed correctly. By following these best practices, it’s possible to find indexed pages in Google and improve overall website performance.
Using Google Search Console to Monitor Indexed Pages
Google Search Console is a powerful tool that helps website owners monitor and maintain their website’s presence in Google’s search results. One of the key features of Search Console is the ability to monitor indexed pages, track crawl errors, and identify areas for improvement. In this section, we’ll explore how to use Search Console to optimize website performance and find indexed pages in Google.
Setting up Search Console: To get started with Search Console, website owners need to set up an account and verify their website. This can be done by following the instructions provided by Google. Once the account is set up, website owners can access the Search Console dashboard, which provides an overview of their website’s performance.
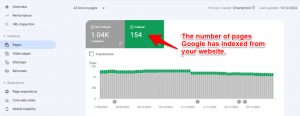
Monitoring Indexed Pages: The “Index” section of Search Console provides information on the number of pages indexed by Google. Website owners can use this section to monitor the number of pages indexed, as well as identify any issues that may be preventing pages from being indexed. This includes crawl errors, duplicate content, and poor website architecture.
Tracking Crawl Errors: The “Crawl” section of Search Console provides information on crawl errors, including errors that prevent Google’s crawlers from accessing pages. Website owners can use this section to identify and fix crawl errors, which can improve indexing and website performance.
Identifying Areas for Improvement: The “Optimization” section of Search Console provides recommendations for improving website performance, including suggestions for improving page speed, mobile-friendliness, and content quality. Website owners can use this section to identify areas for improvement and implement changes to optimize their website.
Using Search Console to Optimize Website Performance: By using Search Console to monitor indexed pages, track crawl errors, and identify areas for improvement, website owners can optimize their website’s performance and improve their visibility in Google’s search results. This includes improving page speed, mobile-friendliness, and content quality, as well as fixing crawl errors and duplicate content issues.
By following these steps and using Search Console to monitor and maintain their website’s presence in Google’s search results, website owners can improve their website’s performance and increase their visibility in search results. Remember, optimizing website performance is an ongoing process, and regular monitoring and maintenance are necessary to ensure that all pages are indexed correctly and performing well.
Advanced Techniques for Finding Indexed Pages
While the methods outlined in the previous sections can help you find indexed pages, there are some advanced techniques that can help you uncover hidden gems and optimize your website content. In this section, we’ll explore some of these advanced techniques, including using Google’s site operator, info operator, and link operator.
Using the Site Operator: The site operator is a powerful tool that allows you to search for indexed pages within a specific website. To use the site operator, simply type “site:” followed by the website’s URL. For example, “site:example.com” will return a list of all indexed pages on the example.com website.
Using the Info Operator: The info operator is another useful tool that provides information about a specific website, including the number of indexed pages. To use the info operator, simply type “info:” followed by the website’s URL. For example, “info:example.com” will return information about the example.com website, including the number of indexed pages.
Using the Link Operator: The link operator is a useful tool that allows you to find indexed pages that link to a specific website. To use the link operator, simply type “link:” followed by the website’s URL. For example, “link:example.com” will return a list of all indexed pages that link to the example.com website.
Using Advanced Search Operators: Google provides a range of advanced search operators that can help you find indexed pages. These operators include “inurl:”, “intitle:”, and “intext:”. By using these operators, you can refine your search results and find specific indexed pages.
Using Third-Party Tools: There are a range of third-party tools available that can help you find indexed pages. These tools include Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Moz. By using these tools, you can gain insights into your website’s indexed pages and optimize your content for better visibility.
By using these advanced techniques, you can gain a deeper understanding of your website’s indexed pages and optimize your content for better visibility. Remember, finding indexed pages is an ongoing process, and regular monitoring and maintenance are necessary to ensure that all pages are indexed correctly and performing well. By following these advanced techniques, you can find indexed pages in Google and improve your website’s visibility and ranking.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Indexed Pages
In conclusion, understanding indexed pages is crucial for any website owner or SEO professional looking to improve their website’s visibility and ranking. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can gain a deeper understanding of indexed pages and how to optimize your website for better indexing.
Remember, indexing is an ongoing process, and regular monitoring and maintenance are necessary to ensure that all pages are indexed correctly and performing well. By using the techniques outlined in this article, you can find indexed pages in Google and improve your website’s visibility and ranking.
Key takeaways from this article include:
- Understanding the concept of indexed pages and their importance in SEO
- Using the Google Search Console to monitor indexed pages and track crawl errors
- Optimizing website structure, content, and meta tags for better indexing
- Using advanced techniques such as site operators, info operators, and link operators to find indexed pages
By implementing these strategies, you can improve your website’s visibility and ranking, and drive more traffic to your site. Remember to stay up-to-date with the latest best practices and algorithm updates to ensure that your website remains optimized for better indexing.
By mastering the art of indexed pages, you can take your website to the next level and achieve greater success in the digital landscape.