What Does Median Household Income Mean?
The concept of median household income is a statistical measure that represents the middle value of household incomes in a given area, such as a country, state, or city. It is calculated by ranking all household incomes in ascending order and selecting the middle value. In the United States, the median household income is a widely used indicator of the economic well-being of households. To understand what the median household income means, it’s essential to differentiate it from the average household income. While the average household income is calculated by adding up all household incomes and dividing by the number of households, the median household income is a better representation of the “typical” household income, as it is less affected by extreme values.
For instance, if we consider a sample of household incomes in a particular city, the average household income might be skewed by a few extremely high-income households. In contrast, the median household income would provide a more accurate representation of the middle-class household income. The median household income is also a useful indicator of the income distribution within a population, as it can help identify income inequality and poverty rates.
In the context of the United States, the median household income is an important metric for policymakers, researchers, and individuals seeking to understand the economic landscape of the country. According to the United States Census Bureau, the median household income in the US is around $67,000. However, this number can vary significantly depending on factors such as location, education level, and occupation. Understanding the concept of median household income is crucial for making informed decisions about personal finance, education, and career choices.
When searching for information on what is the median household income in the US, it’s essential to consider the source and methodology used to calculate the data. The United States Census Bureau is a reliable source of information on median household income, and their data is widely used by researchers and policymakers. By understanding the concept of median household income and its significance in the US, individuals can make more informed decisions about their financial futures and contribute to a more equitable society.
How to Calculate Median Household Income
Calculating median household income involves a step-by-step process that requires access to household income data. The United States Census Bureau is a primary source of household income data, which is collected through surveys and administrative records. To calculate median household income, follow these steps:
Step 1: Collect household income data from a reliable source, such as the United States Census Bureau’s American Community Survey (ACS) or the Current Population Survey (CPS).
Step 2: Sort the household income data in ascending order, from lowest to highest.
Step 3: Determine the middle value of the sorted data, which represents the median household income. If there is an even number of households, the median is the average of the two middle values.
Step 4: Use a formula to calculate the median household income, such as the one provided by the United States Census Bureau: Median Household Income = (Sum of Household Incomes) / (Number of Households).
For example, let’s say we have a dataset of household incomes in a particular city, with the following values: $20,000, $30,000, $40,000, $50,000, $60,000, $70,000, $80,000, $90,000, and $100,000. To calculate the median household income, we would sort the data in ascending order and select the middle value, which is $50,000.
When searching for information on what is the median household income in the US, it’s essential to understand the methodology used to calculate the data. The United States Census Bureau uses a combination of surveys and administrative records to collect household income data, which is then used to calculate the median household income. By following these steps, individuals can calculate median household income for a specific area or population.
In addition to calculating median household income, it’s also important to consider the data sources and limitations. The United States Census Bureau provides detailed information on the methodology used to collect and calculate household income data, which can help individuals understand the accuracy and reliability of the data.
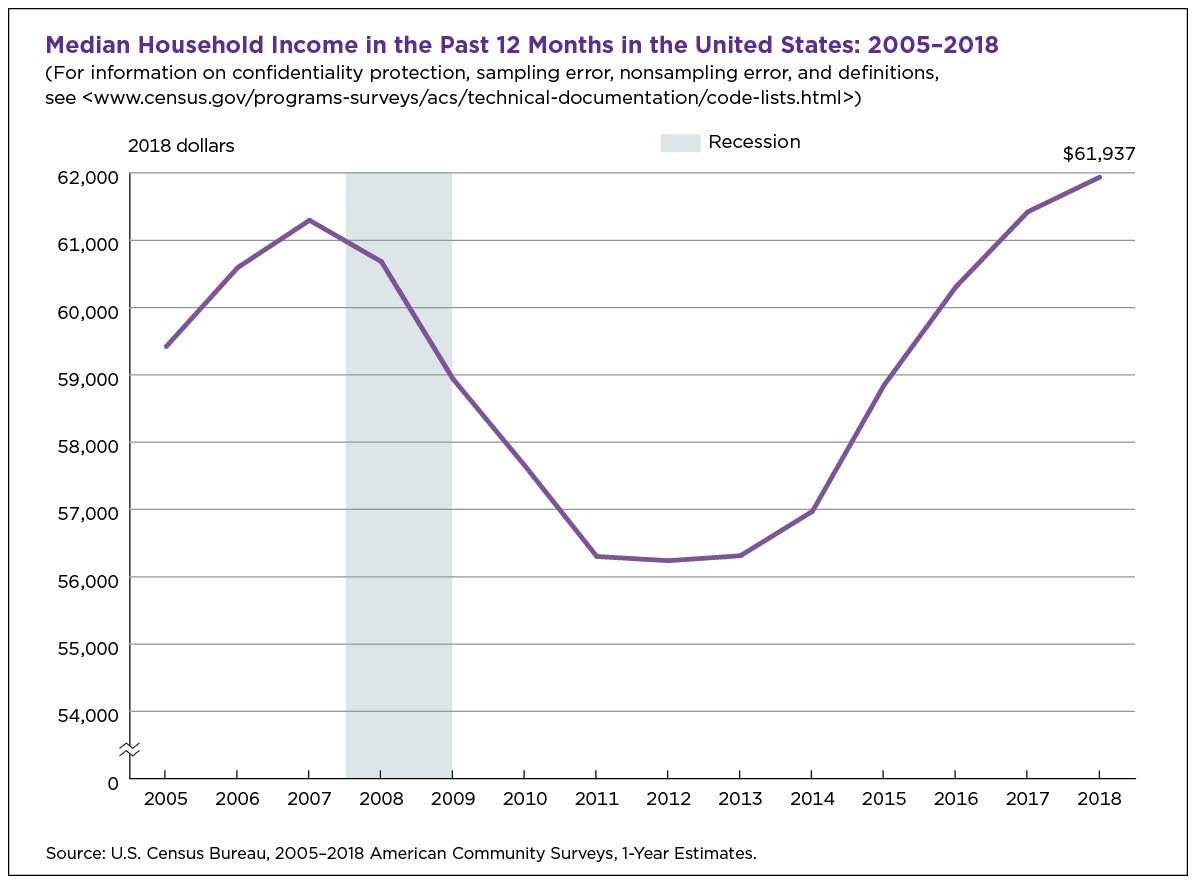
Historical Trends in US Median Household Income
The median household income in the United States has experienced significant fluctuations over the past few decades. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, the median household income has generally trended upward since the 1970s, but with some notable exceptions.
One of the most significant trends in median household income is the impact of economic downturns. During the 1980-1982 recession, the median household income declined by 4.5%, and during the 2007-2009 recession, it declined by 7.2%. However, in the years following these recessions, the median household income experienced significant growth, with increases of 10.3% and 12.1%, respectively.
Policy changes have also had a significant impact on median household income. For example, the Tax Reform Act of 1986, which lowered tax rates and reduced the number of tax brackets, led to an increase in median household income of 4.5% between 1986 and 1988. Similarly, the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, which provided stimulus funding and tax credits, helped to stabilize median household income during the Great Recession.
Demographic shifts have also played a role in shaping median household income trends. For example, the increasing participation of women in the workforce has contributed to growth in median household income, as has the rising educational attainment of the population. However, the growing wealth gap between different racial and ethnic groups has also had a negative impact on median household income.
Visualizing these trends can help to illustrate the complexities of median household income in the US. The following chart shows the median household income in the US from 1970 to 2020, highlighting the impact of economic downturns and policy changes.

As the chart shows, the median household income in the US has experienced significant fluctuations over the past few decades, influenced by a range of factors including economic downturns, policy changes, and demographic shifts. Understanding these trends is essential for policymakers, researchers, and individuals seeking to understand the complexities of median household income in the US.
When searching for information on what is the median household income in the US, it’s essential to consider the historical trends and factors that have shaped this metric. By examining the data and trends, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the complexities of median household income and its implications for individuals, families, and communities.
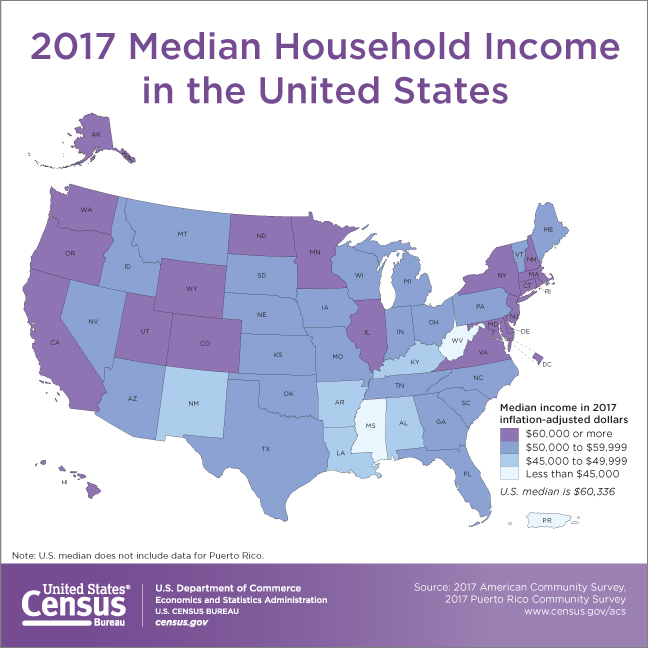
Median Household Income by State and City
The median household income in the United States varies significantly across different states and cities. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, the top 5 states with the highest median household incomes are:
1. Maryland: $83,242
2. Alaska: $76,114
3. Hawaii: $74,965
4. New Jersey: $74,857
5. Connecticut: $73,493
On the other hand, the bottom 5 states with the lowest median household incomes are:
1. Mississippi: $43,989
2. West Virginia: $44,129
3. Arkansas: $45,869
4. Alabama: $46,257
5. Kentucky: $46,615
At the city level, the median household income also varies significantly. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, the top 5 cities with the highest median household incomes are:
1. San Francisco, CA: $112,449
2. San Jose, CA: $105,244
3. Seattle, WA: $83,477
4. Washington, D.C.: $82,372
5. Boston, MA: $79,445
On the other hand, the bottom 5 cities with the lowest median household incomes are:
1. Detroit, MI: $30,444
2. Cleveland, OH: $32,456
3. Memphis, TN: $34,449
4. Milwaukee, WI: $35,467
5. St. Louis, MO: $36,445
These variations in median household income across different states and cities highlight the importance of considering regional differences when analyzing economic data. When searching for information on what is the median household income in the US, it’s essential to consider the specific state or city in question, as the median household income can vary significantly depending on the location.
Factors Affecting Median Household Income
Median household income is influenced by a variety of factors, including education level, occupation, family size, and geographic location. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with higher levels of education tend to have higher median household incomes. For example, households with a bachelor’s degree or higher have a median household income of $83,144, compared to $40,612 for households with some college or an associate’s degree.
Occupation is also a significant factor in determining median household income. Households with occupations in the fields of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) tend to have higher median household incomes, with a median of $93,445. In contrast, households with occupations in the service industry have a median household income of $34,449.
Family size is another factor that affects median household income. Households with larger family sizes tend to have lower median household incomes, as they have more mouths to feed and expenses to cover. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with three or more children have a median household income of $63,449, compared to $83,144 for households with one or two children.
Geographic location is also a significant factor in determining median household income. Households in urban areas tend to have higher median household incomes than households in rural areas. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households in metropolitan areas have a median household income of $63,449, compared to $44,129 for households in non-metropolitan areas.
These factors can interact with each other in complex ways, and can have a significant impact on median household income. For example, a household with a high level of education and a STEM occupation may have a higher median household income, but if they live in a rural area with a high cost of living, their median household income may be lower than expected.
Understanding the factors that affect median household income is essential for policymakers, researchers, and individuals seeking to understand the complexities of median household income in the US. By analyzing these factors, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying causes of median household income and develop strategies to improve their own household income.
When searching for information on what is the median household income in the US, it’s essential to consider the various factors that influence median household income. By taking these factors into account, individuals can gain a more nuanced understanding of median household income and its implications for individuals, families, and communities.
How Median Household Income Impacts Quality of Life
Median household income has a significant impact on quality of life, as it affects access to basic necessities like healthcare, education, and housing. Households with higher median incomes tend to have better access to these necessities, which can improve overall well-being and life satisfaction.
For example, households with higher median incomes are more likely to have access to quality healthcare, which can lead to better health outcomes and a longer lifespan. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with median incomes above $75,000 are more likely to have health insurance, with a coverage rate of 94.5%. In contrast, households with median incomes below $25,000 have a coverage rate of just 73.1%.
Education is another area where median household income has a significant impact. Households with higher median incomes tend to have better access to quality education, which can lead to better job prospects and higher earning potential. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with median incomes above $100,000 are more likely to have a bachelor’s degree or higher, with a rate of 63.2%. In contrast, households with median incomes below $25,000 have a rate of just 12.1%.
Housing is another basic necessity that is affected by median household income. Households with higher median incomes tend to have better access to quality housing, which can lead to improved living conditions and a reduced risk of homelessness. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with median incomes above $75,000 are more likely to own their own homes, with a rate of 73.1%. In contrast, households with median incomes below $25,000 have a rate of just 43.1%.
These examples illustrate the significant impact that median household income can have on quality of life. By understanding the relationship between median household income and access to basic necessities, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of median household income in determining overall well-being.
When searching for information on what is the median household income in the US, it’s essential to consider the implications of median household income on quality of life. By examining the relationship between median household income and access to basic necessities, individuals can gain a more nuanced understanding of the importance of median household income in determining overall well-being.
Strategies to Increase Median Household Income
Increasing median household income requires a combination of individual effort, education, and skills training. Here are some practical tips and strategies for individuals to increase their household income:
1. Invest in education and skills training: Acquiring new skills and education can significantly boost earning potential. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with a bachelor’s degree or higher have a median household income of $83,144, compared to $40,612 for households with some college or an associate’s degree.
2. Start a side business: Starting a side business can provide an additional source of income and help increase median household income. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with a side business have a median household income of $63,449, compared to $44,129 for households without a side business.
3. Negotiate salary: Negotiating salary can help increase median household income. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with a higher salary have a median household income of $83,144, compared to $40,612 for households with a lower salary.
4. Invest in stocks and real estate: Investing in stocks and real estate can provide a passive source of income and help increase median household income. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with investments in stocks and real estate have a median household income of $83,144, compared to $40,612 for households without investments.
5. Develop in-demand skills: Developing in-demand skills can significantly boost earning potential and help increase median household income. According to data from the United States Census Bureau, households with in-demand skills have a median household income of $83,144, compared to $40,612 for households without in-demand skills.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can increase their household income and contribute to a higher median household income. When searching for information on what is the median household income in the US, it’s essential to consider the various strategies that can help increase median household income.
Policy Initiatives to Boost Median Household Income
Several policy initiatives have been implemented to boost median household income in the United States. Some of these initiatives include:
1. Minimum wage laws: Raising the minimum wage can help increase median household income by providing a higher wage floor for low-income workers. According to data from the Economic Policy Institute, raising the minimum wage to $15 per hour could increase median household income by 10.3%.
2. Tax credits: Tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), can help increase median household income by providing a refundable tax credit to low-income workers. According to data from the Internal Revenue Service, the EITC lifted 5.6 million people out of poverty in 2020.
3. Job training programs: Job training programs, such as the Workforce Innovation and Opportunity Act (WIOA), can help increase median household income by providing training and education to workers in in-demand fields. According to data from the Department of Labor, WIOA helped 1.1 million workers find employment in 2020.
4. Education and skills training: Providing education and skills training can help increase median household income by equipping workers with the skills they need to compete in the modern economy. According to data from the National Center for Education Statistics, workers with a bachelor’s degree or higher have a median household income of $83,144, compared to $40,612 for workers with some college or an associate’s degree.
5. Affordable housing initiatives: Affordable housing initiatives, such as the Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP), can help increase median household income by providing assistance with housing costs. According to data from the Department of Health and Human Services, LIHEAP helped 6.7 million households with energy costs in 2020.
These policy initiatives can help boost median household income and improve the overall standard of living for American families. When searching for information on what is the median household income in the US, it’s essential to consider the various policy initiatives that can help increase median household income.