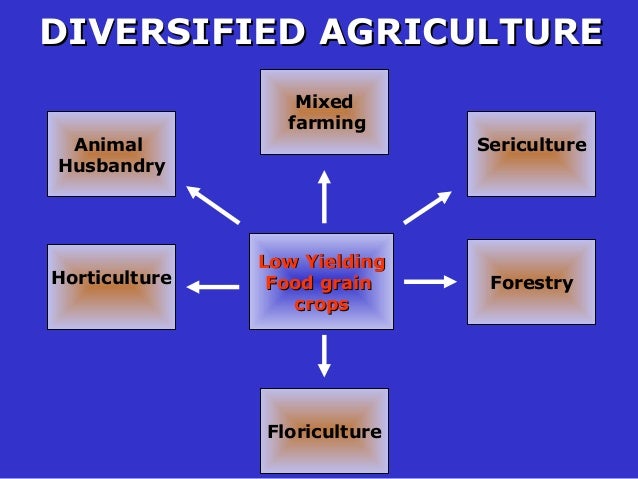
What Do You Call a Farmer? Uncovering Synonyms and Alternatives
The term “farmer” is often used to describe individuals who work in agriculture, but it’s not the only title used to describe these professionals. In fact, there are many alternative names for farmers, each with its own unique connotations and implications. For example, an agriculturalist is a person who specializes in the science and practice of agriculture, while an agronomist is a scientist who studies the relationship between crops, soil, and climate.
Other synonyms for farmers include cultivators, who focus on the cultivation of crops, and ranchers, who specialize in the raising of livestock. These titles are often used in different contexts and industries, and can provide a more nuanced understanding of the various roles and responsibilities of farmers. For instance, a permaculture practitioner is a type of farmer who uses sustainable and regenerative practices to cultivate crops and raise livestock.
In addition to these titles, there are many other alternative names for farmers, each with its own unique characteristics and connotations. Some examples include agricultural entrepreneur, farm manager, and crop specialist. These titles can provide a more detailed understanding of the various roles and responsibilities of farmers, and can help to highlight the diversity and complexity of the agricultural industry.
Using alternative names for farmers can also help to avoid confusion and miscommunication. For example, the term “farmer” is often associated with small-scale, family-owned farms, while the term “agriculturalist” may be more commonly used to describe large-scale, commercial farming operations. By using more specific and nuanced language, we can gain a deeper understanding of the various roles and responsibilities of farmers, and can better appreciate the diversity and complexity of the agricultural industry.
Another name for a farmer might be a person who works in agricultural research and development, or a person who specializes in agricultural education and outreach. These titles can provide a more detailed understanding of the various roles and responsibilities of farmers, and can help to highlight the diversity and complexity of the agricultural industry.
The Art of Cultivation: How to Become a Successful Agricultural Expert
Becoming a successful farmer or agricultural expert requires a combination of education, training, and hands-on experience. While formal education can provide a solid foundation in agricultural science and practices, it is essential to supplement this knowledge with practical experience and continuous learning. Many successful farmers and agricultural experts start their careers by working on family farms or internships, where they can gain hands-on experience and learn from experienced professionals.
In addition to formal education and practical experience, staying up-to-date with industry developments is crucial for success in agriculture. This can be achieved by attending conferences and workshops, participating in online forums and discussions, and reading industry publications. By staying informed about the latest technologies, techniques, and best practices, farmers and agricultural experts can stay ahead of the curve and adapt to changing market conditions and environmental challenges.
Another essential aspect of becoming a successful agricultural expert is developing strong business and management skills. This includes understanding financial management, marketing, and human resources, as well as being able to analyze data and make informed decisions. Many farmers and agricultural experts also develop strong relationships with suppliers, buyers, and other stakeholders, which can help to build a strong reputation and secure business opportunities.
For those interested in pursuing a career in agriculture, there are many different paths to explore. From crop science and animal husbandry to agricultural engineering and environmental science, the options are diverse and exciting. Whether you’re interested in working on a large commercial farm or starting your own small-scale operation, there’s never been a better time to get involved in the world of agriculture.
By combining formal education, practical experience, and continuous learning, farmers and agricultural experts can develop the skills and knowledge needed to succeed in this rewarding and challenging field. Whether you’re just starting out or looking to advance your career, the art of cultivation is a lifelong journey that requires dedication, hard work, and a passion for the land and the people who work it.
Agricultural Specialists: Exploring the Different Types of Farmers
The agricultural industry is diverse and complex, with many different types of farmers contributing to the global food system. From organic farmers who specialize in sustainable and environmentally friendly practices, to permaculture practitioners who focus on regenerative and holistic approaches, each type of farmer brings unique skills and expertise to the table.
Urban farmers, for example, are a growing segment of the agricultural industry, using innovative techniques such as hydroponics and vertical farming to produce fresh produce in urban environments. These farmers often focus on providing locally sourced produce to urban communities, helping to promote food security and support local economies.
Another type of farmer is the regenerative farmer, who focuses on building soil health and biodiversity through practices such as no-till or reduced-till farming, cover cropping, and integrating livestock into crop production. These farmers are helping to promote ecosystem services and mitigate climate change, while also producing high-quality food for consumers.
Permaculture practitioners, on the other hand, take a holistic approach to farming, designing systems that work with nature to produce food and other essential products. These farmers often focus on building diverse and resilient ecosystems, using techniques such as polycultures and agroforestry to promote biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Organic farmers, meanwhile, specialize in producing food without the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or fertilizers. These farmers often focus on building soil health and promoting ecosystem services, using techniques such as crop rotation and composting to maintain soil fertility and structure.
Each of these types of farmers brings unique skills and expertise to the agricultural industry, and plays an important role in promoting food security, sustainability, and ecosystem services. By recognizing and celebrating the diversity of agricultural specialists, we can better appreciate the complexity and richness of the agricultural industry.
Farming as a Career: The Rewards and Challenges of Working in Agriculture
Pursuing a career in agriculture can be a rewarding and challenging experience. On one hand, farming offers the opportunity to work outdoors, be your own boss, and contribute to the global food system. Many farmers find personal satisfaction in seeing their crops grow and flourish, and in knowing that their work is essential to feeding communities around the world.
However, farming is also a physically demanding profession that requires long hours, hard work, and a willingness to adapt to changing weather conditions and market fluctuations. Farmers must also be prepared to deal with the emotional challenges of crop failures, livestock diseases, and other unexpected setbacks.
Despite these challenges, many people find that the rewards of farming far outweigh the drawbacks. For example, farming offers the opportunity to be part of a close-knit community, to work with nature, and to see the tangible results of your labor. Additionally, farming can be a lucrative career, with many farmers earning a good income from their crops and livestock.
Another name for a farmer might be an agricultural entrepreneur, who combines farming with business skills to create a successful and sustainable agricultural enterprise. These individuals must be able to navigate complex market systems, manage finances, and make informed decisions about crop selection, soil management, and other aspects of farm operations.
For those considering a career in agriculture, it’s essential to be aware of the potential challenges and rewards. By understanding the demands and opportunities of farming, individuals can make informed decisions about their career path and prepare themselves for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Ultimately, farming is a career that requires dedication, hard work, and a passion for the land and the people who work it. While it may not be the easiest career path, it can be a highly rewarding one for those who are willing to put in the time and effort required to succeed.
Agricultural Innovators: How Farmers Are Embracing Technology and Sustainability
The agricultural industry is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the need to increase efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and improve crop yields. Farmers are embracing innovative technologies and sustainable practices to stay ahead of the curve and meet the demands of a growing global population.
One example of agricultural innovation is precision agriculture, which uses advanced technologies such as drones, satellite imaging, and precision irrigation to optimize crop growth and reduce waste. This approach allows farmers to target specific areas of the field with the right amount of water, fertilizer, and pesticides, reducing the environmental impact of farming and improving crop yields.
Another example is vertical farming, which involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often in indoor environments. This approach allows for year-round production, regardless of weather conditions, and can increase crop yields by up to 30 times compared to traditional farming methods.
Regenerative agriculture is another innovative approach that focuses on building soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. This approach involves using practices such as no-till or reduced-till farming, cover cropping, and integrating livestock into crop production to promote soil fertility and structure.
These innovative approaches are not only improving crop yields and reducing environmental impact, but also providing new opportunities for farmers to diversify their income streams and improve their livelihoods. For example, some farmers are using precision agriculture to produce high-value crops such as organic produce, while others are using vertical farming to produce leafy greens and other microgreens.
Another name for a farmer might be an agricultural innovator, who combines traditional farming practices with cutting-edge technologies and sustainable approaches to create a more efficient, productive, and environmentally friendly agricultural system.
By embracing innovation and sustainability, farmers can not only improve their own livelihoods but also contribute to a more food-secure and sustainable future for all.
From Farm to Table: The Importance of Supporting Local Agricultural Experts
Supporting local farmers and agricultural experts is crucial for promoting food security, preserving rural communities, and ensuring the long-term sustainability of the agricultural industry. By buying locally sourced produce, consumers can help to stimulate local economies, promote job creation, and preserve the cultural heritage of rural communities.
Another name for a farmer might be a local food producer, who specializes in growing and producing high-quality, locally sourced produce for the local market. These farmers often use sustainable and regenerative practices to promote soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services, and may also offer educational workshops and tours to promote agricultural literacy and community engagement.
Supporting local farmers and agricultural experts can also help to promote food security, by ensuring that fresh, nutritious produce is available to local communities. This can be especially important for vulnerable populations, such as low-income families, seniors, and individuals with limited access to healthy food options.
In addition to promoting food security and preserving rural communities, supporting local farmers and agricultural experts can also help to promote sustainable agriculture and reduce the environmental impact of farming. By buying locally sourced produce, consumers can help to reduce transportation costs and emissions, and promote more sustainable and regenerative farming practices.
Furthermore, supporting local farmers and agricultural experts can also help to promote agricultural innovation and entrepreneurship, by providing opportunities for farmers to experiment with new crops, technologies, and marketing strategies. This can help to drive economic growth and job creation in rural areas, and promote a more diverse and resilient agricultural industry.
By supporting local farmers and agricultural experts, consumers can help to promote a more sustainable, equitable, and resilient food system, and ensure the long-term health and prosperity of rural communities.
Conclusion: Celebrating the Diversity of Agricultural Experts
The agricultural industry is a complex and diverse field, encompassing a wide range of roles, skills, and expertise. From crop cultivation and livestock management to agricultural entrepreneurship and innovation, the many faces of farming are a testament to the industry’s richness and depth.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of farming and agricultural expertise, highlighting the unique approaches and contributions of different types of farmers. We have also discussed the benefits and challenges of pursuing a career in agriculture, and emphasized the importance of supporting local farmers and agricultural experts.
Another name for a farmer might be a guardian of the land, who works tirelessly to promote soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. These individuals are the backbone of the agricultural industry, and their hard work and dedication are essential to feeding the world’s growing population.
As we celebrate the diversity of agricultural experts, we must also recognize the challenges and opportunities facing the industry. From climate change and soil degradation to technological innovation and market fluctuations, the agricultural industry is constantly evolving and adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
By appreciating and supporting the hard work and dedication of farmers and agricultural experts, we can help to promote a more sustainable, equitable, and resilient food system. We can also help to ensure the long-term health and prosperity of rural communities, and promote a more diverse and vibrant agricultural industry.
In conclusion, the many faces of farming are a testament to the industry’s complexity and diversity. By celebrating the unique approaches and contributions of different types of farmers, we can promote a more sustainable and resilient food system, and ensure the long-term health and prosperity of rural communities.
Conclusion: Celebrating the Diversity of Agricultural Experts
In conclusion, the agricultural industry is a complex and diverse field, encompassing a wide range of roles, skills, and expertise. From crop cultivation and livestock management to agricultural entrepreneurship and innovation, the many faces of farming are a testament to the industry’s richness and depth.
Throughout this article, we have explored the various aspects of farming and agricultural expertise, highlighting the unique approaches and contributions of different types of farmers. We have also discussed the benefits and challenges of pursuing a career in agriculture, and emphasized the importance of supporting local farmers and agricultural experts.
As we celebrate the diversity of agricultural experts, we must also recognize the challenges and opportunities facing the industry. From climate change and soil degradation to technological innovation and market fluctuations, the agricultural industry is constantly evolving and adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
By appreciating and supporting the hard work and dedication of farmers and agricultural experts, we can help to promote a more sustainable, equitable, and resilient food system. We can also help to ensure the long-term health and prosperity of rural communities, and promote a more diverse and vibrant agricultural industry.
Another name for a farmer might be a guardian of the land, who works tirelessly to promote soil health, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. These individuals are the backbone of the agricultural industry, and their hard work and dedication are essential to feeding the world’s growing population.
In the end, the many faces of farming are a reminder of the industry’s complexity and diversity. By celebrating the unique approaches and contributions of different types of farmers, we can promote a more sustainable and resilient food system, and ensure the long-term health and prosperity of rural communities.


.jpg)