What Affects Your Electricity Bill: Factors to Consider
When it comes to understanding your electricity bill, there are several factors to consider. The average cost of electricity per month can vary significantly depending on your location, usage patterns, and types of appliances. For instance, households in regions with high temperatures or extreme weather conditions may experience higher electricity bills due to increased cooling or heating needs. Similarly, homes with multiple refrigerators, air conditioning units, or electric water heaters can drive up energy consumption and costs.
Another crucial factor influencing electricity bills is the type of appliances used. Energy-efficient appliances, such as those with the ENERGY STAR label, can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower electricity costs. On the other hand, older appliances or those with lower energy efficiency ratings can increase energy consumption and lead to higher bills.
In addition to these factors, the time of day and season can also impact electricity costs. Peak usage hours, typically during the afternoon and early evening, can result in higher rates due to increased demand on the grid. Conversely, off-peak hours, such as late at night or early in the morning, may offer lower rates. Understanding these factors can help you better manage your energy consumption and reduce your average cost of electricity per month.
Furthermore, the size and layout of your home can also affect your electricity bill. Larger homes or those with multiple stories may require more energy to heat, cool, and power appliances, leading to higher electricity costs. Conversely, smaller homes or those with energy-efficient designs can reduce energy consumption and lower bills.
By considering these factors, you can gain a better understanding of what affects your electricity bill and take steps to reduce your energy consumption and lower your average cost of electricity per month.
How to Calculate Your Average Electricity Cost: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating your average electricity cost can help you better understand your energy consumption and identify areas for improvement. To calculate your average electricity cost, follow these steps:
Step 1: Read Your Meter
Start by reading your electricity meter to determine your current energy consumption. Most meters display the total amount of energy consumed in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Take note of the current reading and compare it to your previous reading to determine your energy consumption for the billing period.
Step 2: Understand Your Rate Plan
Next, review your electricity rate plan to determine your rate per kWh. This information can usually be found on your electricity bill or by contacting your utility company. Take note of any additional charges, such as transmission and distribution fees, that may be included in your rate plan.
Step 3: Calculate Your Total Energy Consumption
Using the information from steps 1 and 2, calculate your total energy consumption for the billing period. Multiply the total amount of energy consumed (in kWh) by your rate per kWh to determine your total energy cost.
Step 4: Factor in Additional Charges
In addition to your energy cost, you may be charged additional fees, such as transmission and distribution fees, taxes, and surcharges. Factor these charges into your total energy cost to determine your average cost of electricity per month.
Example Calculation:
Let’s say your electricity meter reads 1,000 kWh for the billing period, and your rate plan charges 12 cents per kWh. Your total energy cost would be:
1,000 kWh x 12 cents/kWh = $120
If you also have a transmission and distribution fee of $10, your total energy cost would be:
$120 (energy cost) + $10 (transmission and distribution fee) = $130
By following these steps, you can calculate your average electricity cost and gain a better understanding of your energy consumption. This information can help you identify areas for improvement and make informed decisions about your energy usage.
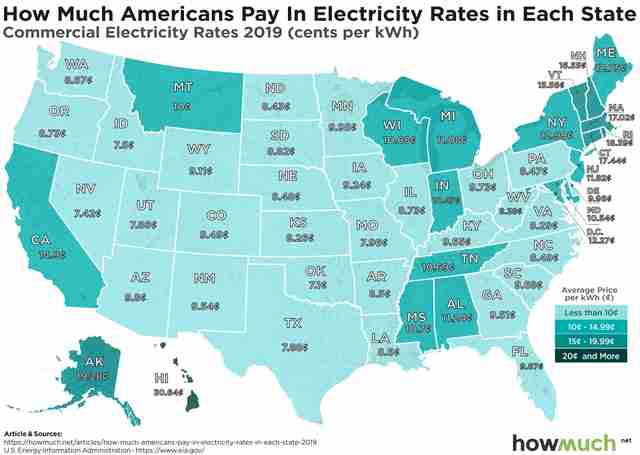
Average Electricity Costs Across the United States: A Regional Breakdown
The average cost of electricity per month varies significantly across the United States, depending on the region, state, and even city. Understanding these regional differences can help you better navigate the complex world of electricity costs and make informed decisions about your energy usage.
According to data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the top 5 states with the lowest average electricity costs per month are:
- Washington: 8.45 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh)
- Idaho: 8.64 cents per kWh
- Utah: 9.15 cents per kWh
- Wyoming: 9.26 cents per kWh
- Montana: 9.33 cents per kWh
On the other hand, the top 5 states with the highest average electricity costs per month are:
- Hawaii: 28.67 cents per kWh
- Alaska: 20.45 cents per kWh
- New York: 18.34 cents per kWh
- Massachusetts: 17.65 cents per kWh
- Connecticut: 17.45 cents per kWh
These regional variations can be attributed to a range of factors, including the availability of renewable energy sources, transmission and distribution costs, and state and local regulations. For example, states with abundant hydroelectric power, such as Washington and Idaho, tend to have lower electricity costs due to the lower cost of generation.
In contrast, states with limited renewable energy sources and high demand for electricity, such as Hawaii and New York, tend to have higher electricity costs. Additionally, states with strict regulations and high transmission and distribution costs, such as Massachusetts and Connecticut, also tend to have higher electricity costs.
By understanding these regional differences, you can better navigate the complex world of electricity costs and make informed decisions about your energy usage. Whether you’re looking to reduce your energy consumption or simply want to understand your electricity bill, knowing the average cost of electricity per month in your region can help you make more informed decisions.
Factors That Influence Electricity Rates: Supply and Demand
Electricity rates are influenced by a variety of factors, including supply and demand. Understanding how these factors impact electricity rates can help you better navigate the complex world of electricity costs and make informed decisions about your energy usage.
Supply and demand play a crucial role in determining electricity rates. When demand for electricity is high, and supply is limited, rates tend to increase. This is because utilities must generate more electricity to meet the increased demand, which can drive up costs. Conversely, when demand is low, and supply is abundant, rates tend to decrease.
Peak usage hours, typically during the afternoon and early evening, can also impact electricity rates. During these times, demand for electricity is high, and utilities must generate more electricity to meet the increased demand. This can drive up costs and result in higher rates.
Seasonal changes can also impact electricity rates. For example, during the summer months, demand for electricity tends to increase due to the use of air conditioning and other cooling appliances. This can drive up rates and result in higher electricity costs. Conversely, during the winter months, demand for electricity tends to decrease, resulting in lower rates.
Weather patterns can also impact electricity rates. Extreme weather conditions, such as heatwaves or cold snaps, can drive up demand for electricity and result in higher rates. Additionally, weather-related events, such as hurricanes or wildfires, can impact electricity generation and transmission, resulting in higher rates.
Understanding how supply and demand impact electricity rates can help you make informed decisions about your energy usage. By reducing your energy consumption during peak usage hours, using energy-efficient appliances, and adjusting your thermostat settings, you can help reduce your average cost of electricity per month.
In addition to supply and demand, other factors can also impact electricity rates, including:
- Fuel costs: The cost of fuel used to generate electricity can impact rates.
- Transmission and distribution costs: The cost of transmitting and distributing electricity can impact rates.
- Regulatory fees: Fees imposed by regulatory agencies can impact rates.
- Taxes: Taxes imposed on electricity generation and transmission can impact rates.
By understanding these factors, you can better navigate the complex world of electricity costs and make informed decisions about your energy usage.
How to Reduce Your Electricity Bill: Simple Tips and Tricks
Reducing your electricity bill can be achieved through a combination of simple changes to your daily habits and investing in energy-efficient appliances. Here are some practical tips and tricks to help you lower your average cost of electricity per month:
1. Switch to energy-efficient lighting: Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with LED or CFL bulbs, which use significantly less energy and last longer.
2. Turn off lights, appliances, and electronics when not in use: This simple habit can make a big difference in your energy consumption. Make sure to turn off lights, TVs, computers, and other appliances when not in use.
3. Adjust your thermostat settings: Lowering your thermostat by just 1-2 degrees can save up to 5% on your heating bill. Consider installing a smart thermostat to optimize your temperature settings.
4. Use power strips: Plug your electronics, such as your TV and computer, into power strips and turn off the strip when not in use to eliminate standby power consumption.
5. Upgrade to energy-efficient appliances: When it’s time to replace your appliances, look for energy-efficient models with the ENERGY STAR label. These appliances use significantly less energy and water than traditional models.
6. Insulate your home: Proper insulation can help reduce heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, which can save you money on your heating and cooling bills.
7. Use natural light: During the day, open your curtains and blinds to let natural light in, which can reduce the need for artificial lighting.
8. Wash clothes in cold water: Washing your clothes in cold water can save up to 90% of the energy used for hot water washing.
9. Air dry clothes: Instead of using a clothes dryer, hang your clothes to dry, which can save up to 60% of the energy used for drying clothes.
10. Conduct an energy audit: Hire a professional to conduct an energy audit of your home to identify areas of energy inefficiency and provide recommendations for improvement.
By implementing these simple tips and tricks, you can significantly reduce your electricity bill and lower your average cost of electricity per month.
Understanding Your Electricity Rate Plan: Types and Options
When it comes to electricity rate plans, there are several options available to consumers. Understanding the different types of rate plans can help you make informed decisions about your electricity usage and potentially lower your average cost of electricity per month.
Fixed-Rate Plans:
Fixed-rate plans offer a fixed rate per kilowatt-hour (kWh) for a specified period of time, usually 6-12 months. This type of plan provides price stability and protection against rate increases. However, if rates decrease, you may be locked into a higher rate.
Variable-Rate Plans:
Variable-rate plans offer a rate that can change from month to month based on market conditions. This type of plan can provide flexibility and potentially lower rates if market prices decrease. However, rates can also increase if market prices rise.
Time-of-Use (TOU) Plans:
TOU plans offer different rates for different times of the day. For example, rates may be higher during peak hours (usually 7am-7pm) and lower during off-peak hours (usually 7pm-7am). This type of plan can help you save money if you can shift your usage to off-peak hours.
Prepaid Plans:
Prepaid plans require you to pay for your electricity usage in advance. This type of plan can help you budget and avoid surprise bills. However, if you use more electricity than you prepaid for, you may be charged a higher rate for the excess usage.
Renewable Energy Plans:
Renewable energy plans offer electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar or wind power. This type of plan can help you reduce your carbon footprint and support sustainable energy production.
When choosing an electricity rate plan, consider your usage patterns, budget, and personal preferences. It’s essential to read the fine print and understand the terms and conditions of each plan before making a decision.
By understanding the different types of electricity rate plans available, you can make informed decisions about your electricity usage and potentially lower your average cost of electricity per month.
Electricity Cost Comparison: How Does Your Bill Stack Up?
Comparing your electricity bill to others can help you understand whether you’re paying a fair price for your energy usage. In this section, we’ll provide a comparison of average electricity costs across different households, including small, medium, and large homes.
Small Homes (less than 1,000 sqft):
The average cost of electricity per month for small homes is around $100-$150. These homes typically have lower energy usage due to their smaller size and fewer appliances.
Medium Homes (1,000-2,500 sqft):
The average cost of electricity per month for medium homes is around $150-$250. These homes typically have moderate energy usage due to their size and number of appliances.
Large Homes (more than 2,500 sqft):
The average cost of electricity per month for large homes is around $250-$400. These homes typically have higher energy usage due to their larger size and more appliances.
Factors that contribute to these variations include:
- Appliance usage: Homes with more appliances, such as refrigerators, air conditioners, and washing machines, tend to have higher energy usage.
- Insulation and energy efficiency: Well-insulated homes with energy-efficient appliances tend to have lower energy usage.
- Location: Homes in areas with high temperatures or extreme weather conditions tend to have higher energy usage due to increased cooling or heating needs.
By comparing your electricity bill to others, you can gain a better understanding of your energy usage and identify areas for improvement. Remember to consider factors such as appliance usage, insulation, and location when evaluating your energy costs.
Additionally, you can use online tools and resources to compare your electricity bill to others in your area. These tools can provide valuable insights into your energy usage and help you make informed decisions about your energy consumption.
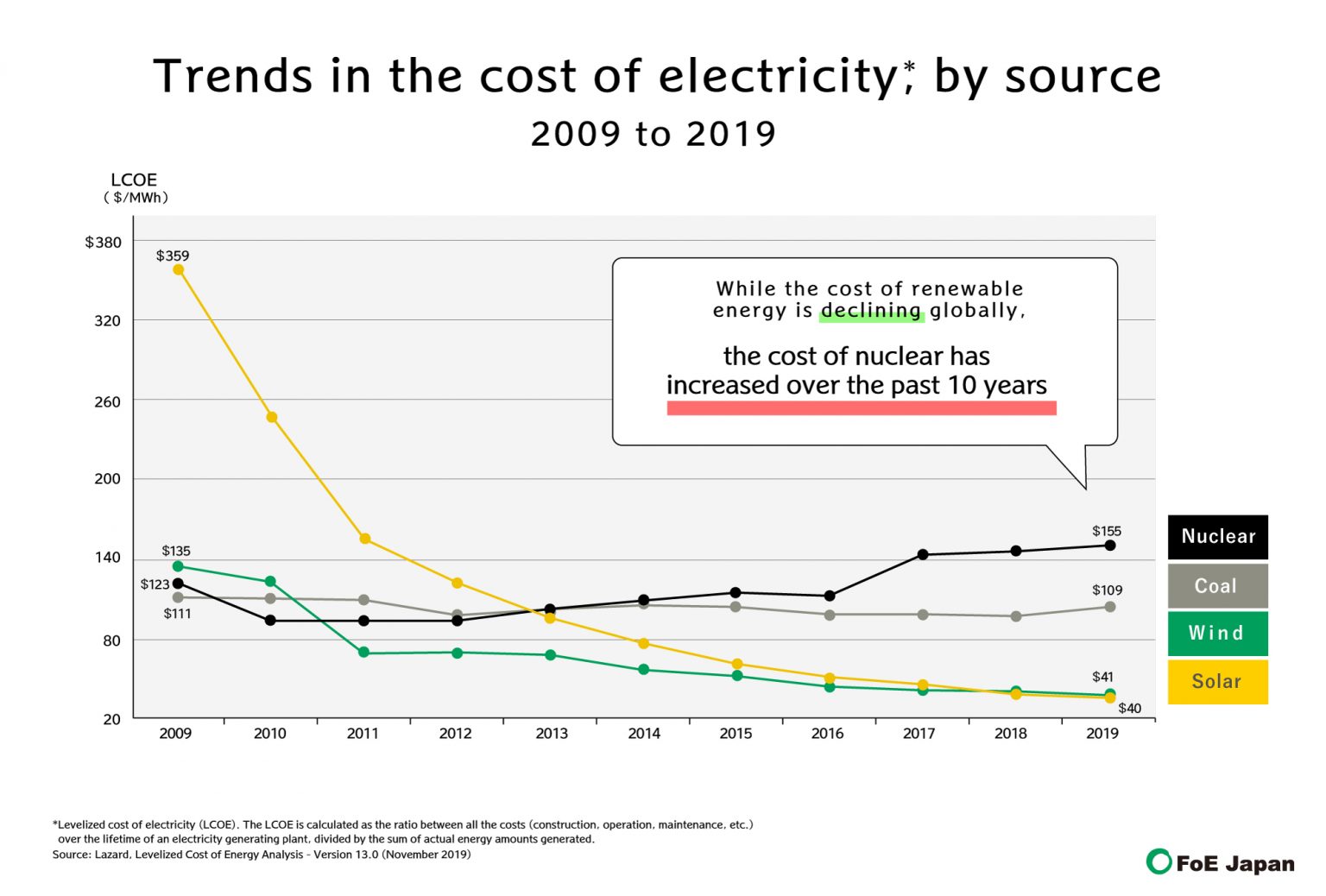
What’s Next for Electricity Costs: Trends and Predictions
The future of electricity costs is likely to be shaped by several trends and predictions, including rate changes, renewable energy adoption, and technological advancements.
Rate Changes:
Electricity rates are expected to continue to fluctuate in response to changes in supply and demand, as well as regulatory policies. In some areas, rates may increase due to the integration of renewable energy sources, while in others, rates may decrease due to the implementation of energy-efficient technologies.
Renewable Energy Adoption:
The adoption of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is expected to continue to grow in the coming years. This trend is likely to lead to a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions and a reduction in electricity costs for consumers who invest in renewable energy systems.
Technological Advancements:
Advances in technology, such as smart grids and energy storage systems, are expected to play a major role in shaping the future of electricity costs. These technologies have the potential to improve the efficiency of the grid, reduce energy waste, and provide consumers with more control over their energy usage.
Electric Vehicles:
The increasing popularity of electric vehicles is expected to have a significant impact on electricity costs. As more consumers switch to electric vehicles, the demand for electricity is likely to increase, leading to higher rates. However, the integration of electric vehicles into the grid also has the potential to provide benefits, such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions and improved energy efficiency.
Energy Storage:
The development of energy storage technologies, such as batteries, is expected to play a major role in shaping the future of electricity costs. These technologies have the potential to provide consumers with more control over their energy usage, reduce energy waste, and improve the efficiency of the grid.
In conclusion, the future of electricity costs is likely to be shaped by several trends and predictions, including rate changes, renewable energy adoption, and technological advancements. As the energy landscape continues to evolve, it’s essential for consumers to stay informed and adapt to the changing market.