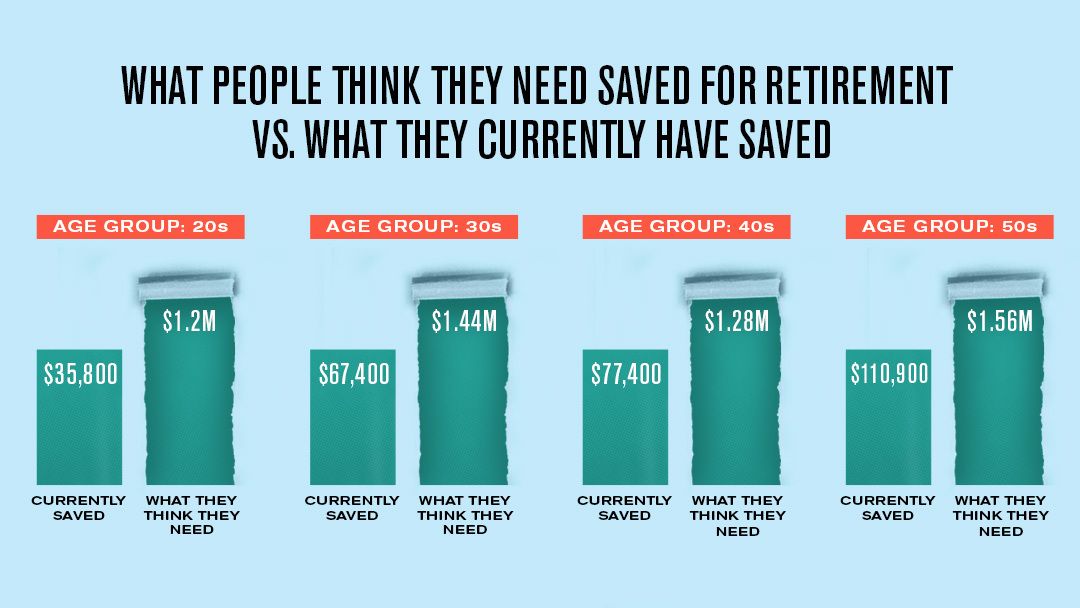
When Can You Expect to Retire: Understanding the Average Retirement Age
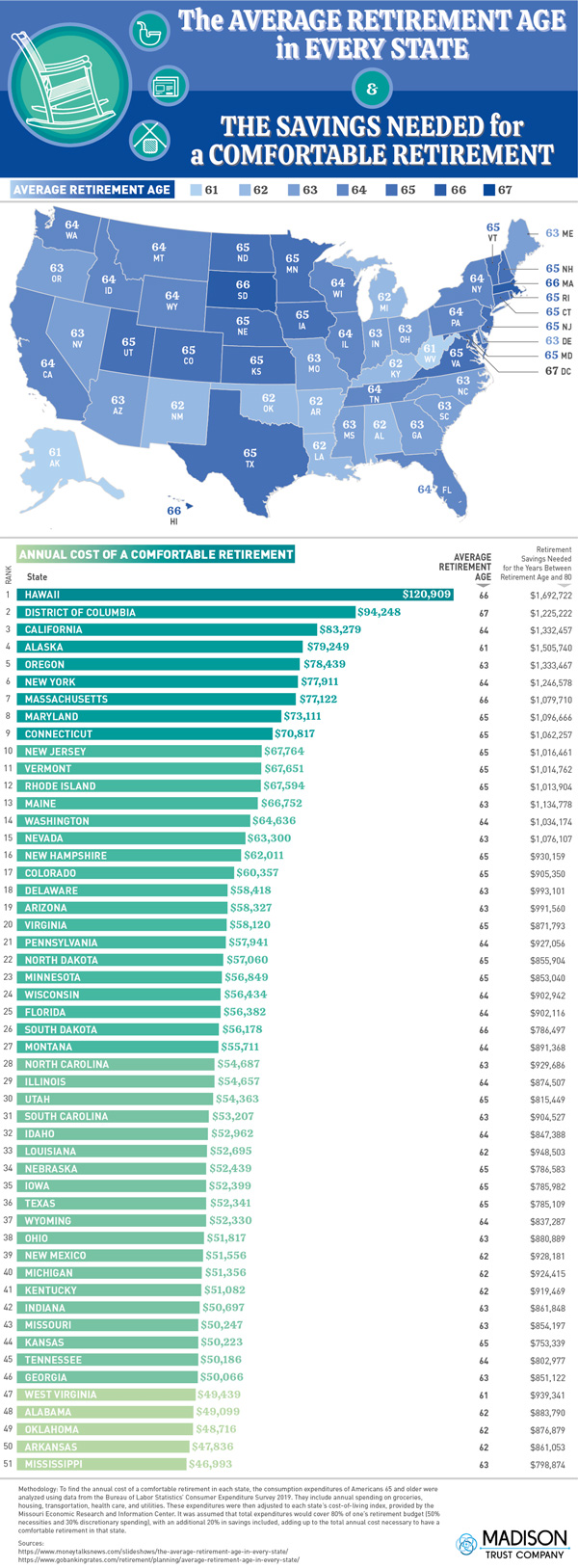
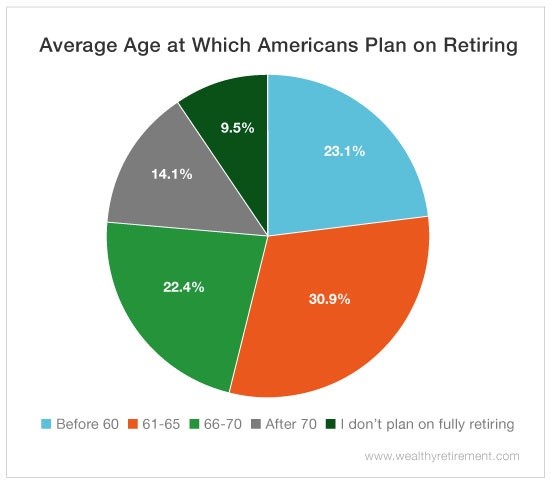
The concept of average retirement age in the US is a complex one, influenced by a multitude of factors including occupation, health, and financial preparedness. As the US population ages, understanding the average retirement age is crucial for individuals, policymakers, and employers. According to data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, the average retirement age in the US is around 64 years old. However, this number varies significantly depending on factors such as education level, income, and occupation.
For instance, workers in the public sector tend to retire earlier, with an average retirement age of 62, compared to private sector workers who retire at an average age of 65. Additionally, individuals with higher levels of education and income tend to retire later, often in their late 60s or even 70s. This is likely due to the fact that these individuals have more financial resources and better access to healthcare, allowing them to continue working longer.
Health is another critical factor influencing the average retirement age. Individuals with chronic health conditions or disabilities may be forced to retire earlier, while those with better health may be able to continue working longer. Financial preparedness also plays a significant role, as individuals who have saved adequately for retirement may be able to retire earlier, while those who have not may need to continue working longer.
Understanding the average retirement age in the US is essential for individuals planning for their retirement. By considering factors such as occupation, health, and financial preparedness, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement goals and develop a plan to achieve them. In the next section, we will explore the factors that influence an individual’s ideal retirement age and provide tips on how to determine a suitable retirement age.
How to Determine Your Ideal Retirement Age: Factors to Consider
Determining the ideal retirement age is a personal decision that depends on various factors, including financial readiness, health, and personal goals. While the average retirement age in the US is around 64, some individuals may choose to retire earlier or later, depending on their unique circumstances.
Financial readiness is a critical factor in determining the ideal retirement age. Individuals who have saved adequately for retirement, have a steady income stream, and have paid off debts may be able to retire earlier. On the other hand, those who are still paying off mortgages, credit cards, or other debts may need to continue working longer to ensure a secure financial future.
Health is another essential factor to consider when determining the ideal retirement age. Individuals with chronic health conditions or disabilities may need to retire earlier, while those with better health may be able to continue working longer. Additionally, personal goals and aspirations can also influence the ideal retirement age. Some individuals may choose to retire earlier to pursue hobbies, travel, or spend time with family, while others may prefer to continue working to stay engaged and active.
To determine the ideal retirement age, individuals should assess their financial readiness, health, and personal goals. They should consider factors such as their retirement savings, income streams, debts, and expenses, as well as their health and wellness. They should also think about their personal goals and aspirations, and how they want to spend their time in retirement.
Here are some tips to help individuals determine their ideal retirement age:
- Assess your financial readiness: Calculate your retirement savings, income streams, debts, and expenses to determine if you have enough resources to support your retirement goals.
- Evaluate your health: Consider your physical and mental health, and how it may impact your ability to work or enjoy retirement.
- Reflect on your personal goals: Think about what you want to achieve in retirement, and how you want to spend your time.
- Consider your occupation: Certain occupations may require earlier or later retirement, depending on the physical demands or stress levels involved.
By considering these factors and tips, individuals can determine their ideal retirement age and create a plan to achieve their retirement goals.
The Impact of Retirement Age on Social Security Benefits
The retirement age has a significant impact on Social Security benefits, and understanding how it affects these benefits is crucial for individuals planning for retirement. The Social Security Administration (SSA) uses a formula to calculate benefits based on an individual’s earnings history, and the retirement age plays a critical role in determining the benefit amount.
Retiring early, typically before the age of 62, can result in reduced Social Security benefits. This is because the SSA reduces the benefit amount by a certain percentage for each year an individual retires before their full retirement age. For example, if an individual retires at 62, their benefit amount may be reduced by 30% compared to their full retirement benefit.
On the other hand, delaying retirement can result in increased Social Security benefits. For each year an individual delays retirement beyond their full retirement age, their benefit amount increases by a certain percentage. For example, if an individual delays retirement until 70, their benefit amount may increase by 24% compared to their full retirement benefit.
It’s essential to note that the full retirement age varies depending on the individual’s birth year. For individuals born between 1943 and 1954, the full retirement age is 66. For those born between 1955 and 1959, the full retirement age increases gradually to 66 and 10 months. For individuals born in 1960 or later, the full retirement age is 67.
Here are some examples of how different retirement ages can impact Social Security benefits:
- Retiring at 62: 30% reduction in benefits compared to full retirement benefit
- Retiring at 65: 13% reduction in benefits compared to full retirement benefit
- Retiring at 66 (full retirement age): 100% of full retirement benefit
- Retiring at 67: 108% of full retirement benefit
- Retiring at 70: 124% of full retirement benefit
Understanding how the retirement age affects Social Security benefits is crucial for individuals planning for retirement. By considering their retirement age and its impact on benefits, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement goals and develop a plan to maximize their benefits.
Retirement Savings Strategies for a Secure Future
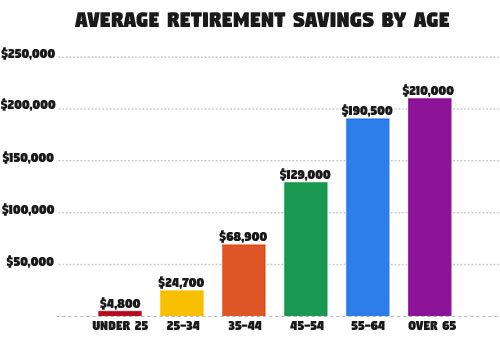
Retirement savings is a critical component of planning for a secure retirement. With the average retirement age in the US being around 64, it’s essential to start saving early and consistently to ensure a comfortable retirement. Here are some retirement savings strategies to help you achieve your goals:
1. Start Early: The power of compound interest can work in your favor when you start saving early. Even small, consistent contributions can add up over time, providing a significant nest egg for retirement.
2. Take Advantage of Employer Matching: Many employers offer 401(k) or other retirement plans that match employee contributions. This is essentially free money that can help your retirement savings grow faster.
3. Diversify Your Investments: Spread your retirement savings across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, to minimize risk and maximize returns.
4. Utilize Retirement Accounts: Utilize tax-advantaged retirement accounts such as 401(k), IRA, or Roth IRA to save for retirement. These accounts offer tax benefits that can help your savings grow faster.
5. Automate Your Savings: Set up automatic transfers from your paycheck or bank account to your retirement account to make saving easier and less prone to being neglected.
Retirement accounts such as 401(k) and IRA play a crucial role in helping individuals save for retirement. Here’s a brief overview of these accounts:
401(k): A 401(k) is a employer-sponsored retirement plan that allows employees to contribute a portion of their salary to a retirement account on a pre-tax basis. The funds are invested and grow tax-deferred until withdrawal.
IRA: An IRA (Individual Retirement Account) is a self-directed retirement plan that allows individuals to contribute a portion of their income to a retirement account on a tax-deductible basis. The funds are invested and grow tax-deferred until withdrawal.
Roth IRA: A Roth IRA is a type of IRA that allows individuals to contribute after-tax dollars to a retirement account. The funds grow tax-free and are withdrawn tax-free in retirement.
By following these retirement savings strategies and utilizing retirement accounts, you can create a secure financial foundation for your retirement and achieve your long-term goals.
How to Create a Sustainable Retirement Income Stream
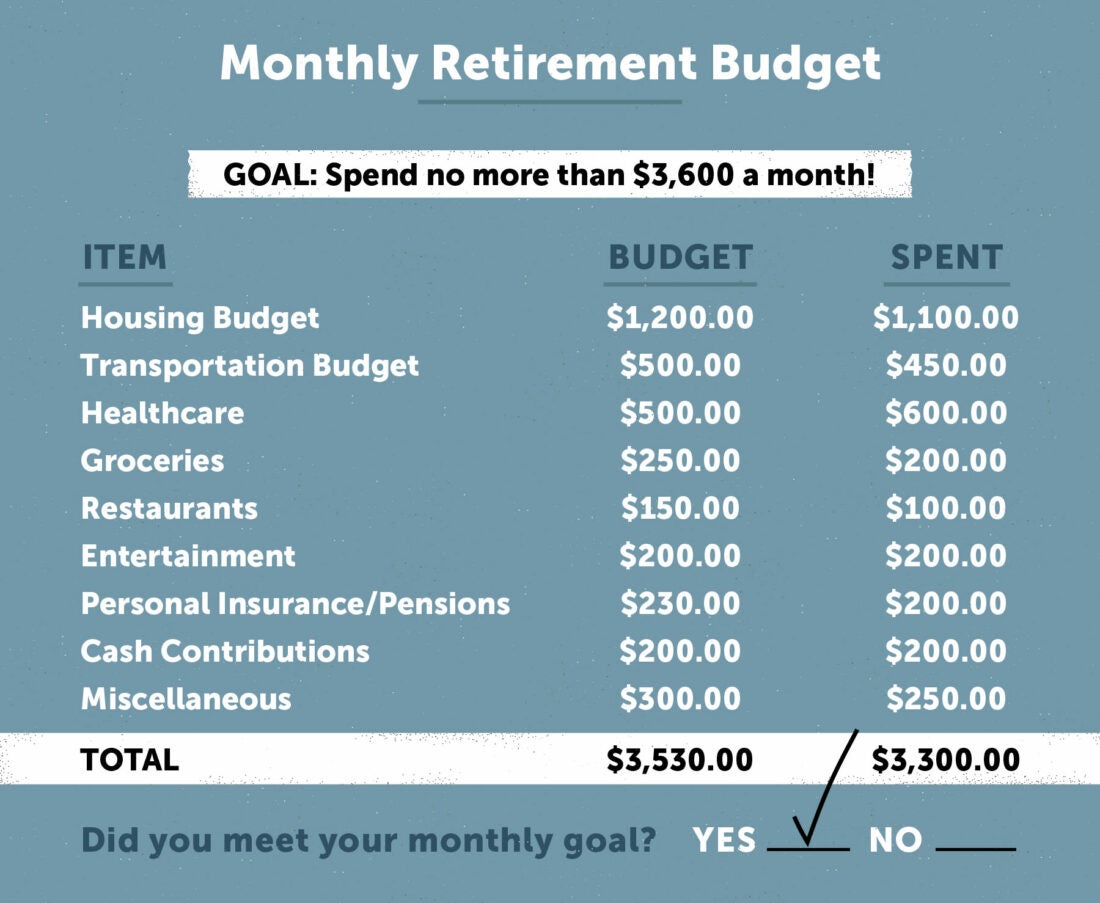
Creating a sustainable retirement income stream is crucial for ensuring a comfortable and secure retirement. A sustainable income stream can help individuals maintain their standard of living, cover expenses, and enjoy their retirement years without financial stress. Here are some strategies for generating income from investments, pensions, and other sources:
1. Diversify Your Investments: Spread your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, to minimize risk and maximize returns.
2. Consider Annuities: Annuities can provide a guaranteed income stream for a set period or for life, helping to ensure a predictable income in retirement.
3. Utilize Pensions: If you have a pension, consider how it can be used to generate income in retirement. You may be able to take a lump sum or receive regular payments.
4. Create a Bond Ladder: A bond ladder can provide a regular income stream by investing in a series of bonds with staggered maturity dates.
5. Consider Dividend-Paying Stocks: Dividend-paying stocks can provide a regular income stream through dividend payments.
6. Rent Out a Property: If you have a rental property, consider renting it out to generate additional income in retirement.
7. Create a Retirement Income Plan: Develop a comprehensive plan that outlines your income sources, expenses, and goals for retirement. This can help you create a sustainable income stream and ensure a comfortable retirement.
Allocating assets for a steady income flow is also crucial for creating a sustainable retirement income stream. Here are some tips for allocating assets:
1. Allocate 40% to 60% of Your Portfolio to Income-Generating Assets: Consider allocating a significant portion of your portfolio to income-generating assets, such as bonds, annuities, and dividend-paying stocks.
2. Allocate 20% to 40% of Your Portfolio to Growth Assets: Consider allocating a portion of your portfolio to growth assets, such as stocks and real estate, to help your portfolio grow over time.
3. Allocate 10% to 20% of Your Portfolio to Cash and Cash Equivalents: Consider allocating a portion of your portfolio to cash and cash equivalents, such as money market funds and CDs, to provide liquidity and flexibility.
By following these strategies and allocating assets effectively, you can create a sustainable retirement income stream and enjoy a comfortable and secure retirement.
Healthcare and Retirement: Planning for the Unexpected
Healthcare costs are a significant concern for many retirees, and planning for these expenses is crucial for a secure retirement. The average retirement age in the US is around 64, and healthcare costs can be a major expense during this time. Here are some strategies for managing healthcare expenses and leveraging resources such as Medicare and long-term care insurance:
1. Understand Medicare: Medicare is a federal health insurance program that provides coverage for individuals 65 and older. Understanding the different parts of Medicare, including Part A, Part B, and Part D, can help you make informed decisions about your healthcare coverage.
2. Consider Supplemental Insurance: Supplemental insurance, such as Medigap, can help fill the gaps in Medicare coverage. These policies can provide additional coverage for expenses such as copays, deductibles, and coinsurance.
3. Plan for Long-Term Care: Long-term care insurance can provide coverage for expenses related to long-term care, such as nursing home care or home health care. This type of insurance can help protect your assets and ensure that you receive the care you need.
4. Create a Healthcare Budget: Creating a healthcare budget can help you plan for healthcare expenses and ensure that you have enough money set aside for unexpected expenses.
5. Consider Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): HSAs are tax-advantaged accounts that allow you to set aside money for healthcare expenses. These accounts can be used in conjunction with high-deductible health plans to provide additional coverage for healthcare expenses.
6. Prioritize Preventive Care: Preventive care, such as regular check-ups and screenings, can help prevent health problems and reduce healthcare expenses.
7. Consider Alternative Care Options: Alternative care options, such as adult day care or home health care, can provide additional support and care for individuals with chronic health conditions.
By planning for healthcare expenses and leveraging resources such as Medicare and long-term care insurance, you can ensure that you have the coverage you need to maintain your health and well-being in retirement.
Retirement Age and Inflation: What You Need to Know
Inflation can have a significant impact on retirement savings and income, and understanding how to protect against inflation is crucial for maintaining purchasing power in retirement. The average retirement age in the US is around 64, and inflation can erode the value of retirement savings over time.
Here are some strategies for protecting against inflation and maintaining purchasing power in retirement:
1. Invest in Inflation-Indexed Instruments: Inflation-indexed instruments, such as Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS), can provide a hedge against inflation and help maintain purchasing power.
2. Diversify Your Investments: Diversifying your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, can help reduce the impact of inflation on your retirement savings.
3. Consider Inflation-Adjusted Annuities: Inflation-adjusted annuities can provide a guaranteed income stream that increases over time to keep pace with inflation.
4. Plan for Healthcare Costs: Healthcare costs can be a significant expense in retirement, and planning for these costs can help reduce the impact of inflation on your retirement savings.
5. Consider Long-Term Care Insurance: Long-term care insurance can provide coverage for expenses related to long-term care, such as nursing home care or home health care, and can help reduce the impact of inflation on your retirement savings.
6. Review and Adjust Your Retirement Plan: Regularly reviewing and adjusting your retirement plan can help ensure that you are on track to meet your retirement goals and can help reduce the impact of inflation on your retirement savings.
By understanding the impact of inflation on retirement savings and income, and by implementing strategies to protect against inflation, you can help maintain purchasing power in retirement and ensure a secure financial future.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Retirement Future
Planning for a secure retirement requires careful consideration of several factors, including the average retirement age in the US, financial readiness, health, and personal goals. By understanding these factors and taking control of your retirement future, you can ensure a comfortable and secure retirement.
In this article, we have discussed the importance of planning for retirement, including the impact of retirement age on Social Security benefits, retirement savings strategies, and creating a sustainable retirement income stream. We have also addressed the importance of planning for healthcare costs in retirement and the impact of inflation on retirement savings and income.
By following the tips and strategies outlined in this article, you can take control of your retirement future and ensure a secure financial future. Remember to start planning early, take advantage of employer matching, and diversify your investments. Also, consider creating a sustainable retirement income stream, planning for healthcare costs, and protecting against inflation.
Ultimately, planning for a secure retirement requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account your individual circumstances and goals. By taking control of your retirement future, you can ensure a comfortable and secure retirement and enjoy the fruits of your labor.
As you plan for your retirement, remember to stay informed and adapt to changing circumstances. Continuously review and adjust your retirement plan to ensure that you are on track to meet your retirement goals.
By taking control of your retirement future, you can ensure a secure financial future and enjoy a comfortable and fulfilling retirement.