Understanding the Importance of Accurate W4 Filing
Accurate completion of the W4 form is crucial for both employees and employers. The W4 form, also known as the Employee’s Withholding Certificate, determines the amount of federal income tax withheld from an employee’s paycheck. Filling out the form correctly ensures that the right amount of taxes is withheld, avoiding potential penalties and fines. Inaccurate filing can lead to underpayment or overpayment of taxes, resulting in a larger tax bill or a smaller refund. Moreover, incorrect W4 filing can also impact an employee’s take-home pay, affecting their financial planning and budgeting.
The best way to fill out W4 involves understanding the form’s purpose and the consequences of incorrect filing. The W4 form is used to determine an employee’s filing status, number of allowances, and additional income or deductions. By accurately completing the form, employees can ensure that their tax withholding is correct, and they receive the right amount of take-home pay. Employers also benefit from accurate W4 filing, as it helps them comply with tax laws and regulations, reducing the risk of penalties and fines.
In addition to the financial implications, accurate W4 filing also affects an employee’s eligibility for certain tax credits and deductions. For example, the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and the Child Tax Credit require accurate W4 filing to determine eligibility. By filling out the form correctly, employees can ensure they receive the tax credits and deductions they are eligible for, reducing their tax liability and increasing their refund.
Overall, accurate W4 filing is essential for both employees and employers. By understanding the importance of accurate filing and following the best way to fill out W4, individuals can ensure they receive the right amount of take-home pay, avoid potential penalties and fines, and receive the tax credits and deductions they are eligible for.
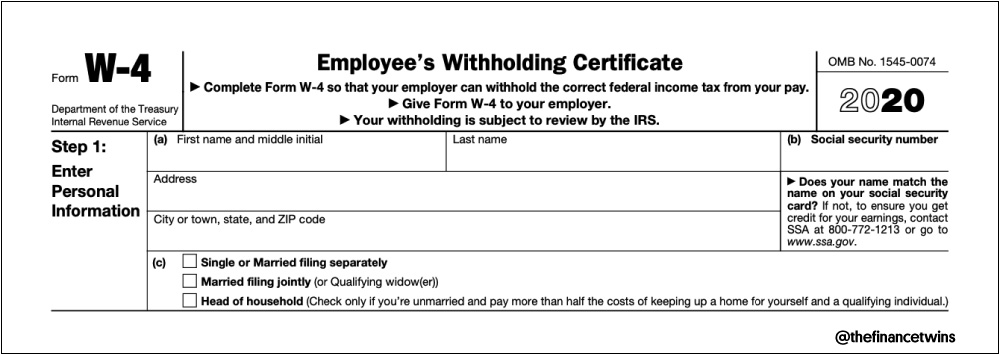
Breaking Down the W4 Form: A Section-by-Section Guide
The W4 form is a crucial document that determines the amount of taxes withheld from an employee’s paycheck. To ensure accurate tax withholding, it’s essential to understand the different sections of the W4 form and provide the required information. In this section, we’ll break down the W4 form into its various components and explain the purpose of each section.
The W4 form is divided into five main sections: Personal Information, Filing Status, Number of Allowances, Additional Income, and Dependents. Each section requires specific information that will help determine the correct amount of taxes to withhold.
Section 1: Personal Information
This section requires basic personal information, including the employee’s name, address, Social Security number, and date of birth. This information is used to identify the employee and ensure that the correct tax withholding is applied.
Section 2: Filing Status
In this section, the employee must indicate their filing status, which can be single, married, head of household, or qualifying widow(er). The filing status determines the tax withholding tables used to calculate the amount of taxes withheld. It’s essential to choose the correct filing status to avoid under or over-withholding.
Section 3: Number of Allowances
The number of allowances claimed determines the amount of taxes withheld. An allowance is a fixed amount of money that is exempt from taxation. The more allowances claimed, the less taxes will be withheld. Employees can claim allowances for themselves, their spouse, and dependents.
Section 4: Additional Income
This section requires employees to report any additional income that is not subject to withholding, such as self-employment income, investments, or retirement accounts. This information is used to determine the correct amount of taxes to withhold.
Section 5: Dependents
In this section, employees can claim dependents, such as children or elderly parents, who are eligible for tax credits. The number of dependents claimed can affect the amount of taxes withheld.
By understanding the different sections of the W4 form and providing accurate information, employees can ensure that the correct amount of taxes is withheld from their paycheck. This will help avoid under or over-withholding, which can result in penalties or a large tax bill at the end of the year. The best way to fill out W4 is to carefully review each section and provide accurate information to ensure accurate tax withholding.
How to Determine Your Filing Status: A Crucial Step in W4 Completion
Determining the correct filing status is a crucial step in completing the W4 form accurately. The filing status affects the tax withholding tables used to calculate the amount of taxes withheld from an employee’s paycheck. In this section, we’ll discuss the different filing statuses and provide guidance on how to determine which one applies to the employee.
The IRS recognizes five main filing statuses: Single, Married Filing Jointly, Married Filing Separately, Head of Household, and Qualifying Widow(er). Each filing status has its own set of rules and requirements, and choosing the correct one is essential to ensure accurate tax withholding.
Single Filing Status
The single filing status applies to employees who are unmarried or separated and do not qualify for any other filing status. This is the most common filing status, and it’s used as the default status for most employees.
Married Filing Jointly Filing Status
The married filing jointly filing status applies to employees who are married and file their taxes jointly with their spouse. This filing status is used when both spouses agree to file their taxes together and report their combined income and deductions.
Married Filing Separately Filing Status
The married filing separately filing status applies to employees who are married but file their taxes separately from their spouse. This filing status is used when spouses do not want to file their taxes jointly or when they have different tax obligations.
Head of Household Filing Status
The head of household filing status applies to employees who are unmarried or separated and have dependents, such as children or elderly parents. This filing status is used when the employee is the primary breadwinner and provides more than half of the household’s income.
Qualifying Widow(er) Filing Status
The qualifying widow(er) filing status applies to employees who have lost their spouse and have dependents. This filing status is used when the employee is eligible for the same tax rates as married filing jointly and has dependents who qualify for tax credits.
To determine the correct filing status, employees should consider their marital status, dependents, and income. The best way to fill out W4 is to carefully review the different filing statuses and choose the one that applies to their situation. By choosing the correct filing status, employees can ensure accurate tax withholding and avoid any potential penalties or issues with their tax return.
Claiming Allowances: A Key Factor in Tax Withholding
Claiming allowances is a crucial step in completing the W4 form accurately. Allowances are exemptions from income tax withholding, and they can significantly impact the amount of taxes withheld from an employee’s paycheck. In this section, we’ll discuss the different types of allowances and provide guidance on how to claim them accurately.
What are Allowances?
An allowance is a fixed amount of money that is exempt from income tax withholding. The IRS allows employees to claim allowances for themselves, their spouse, and dependents. The number of allowances claimed determines the amount of taxes withheld from an employee’s paycheck.
Types of Allowances
There are several types of allowances that employees can claim, including:
Personal Allowance
A personal allowance is an exemption from income tax withholding for the employee themselves. All employees are eligible for at least one personal allowance.
Dependent Allowance
A dependent allowance is an exemption from income tax withholding for dependents, such as children or elderly parents. Employees can claim one dependent allowance for each dependent they support.
Mortgage Interest Allowance
A mortgage interest allowance is an exemption from income tax withholding for employees who pay mortgage interest on their primary residence. This allowance can be claimed in addition to the personal and dependent allowances.
Other Allowances
There are other allowances that employees can claim, such as allowances for student loan interest, moving expenses, and charitable donations. These allowances can be claimed in addition to the personal, dependent, and mortgage interest allowances.
How to Claim Allowances
To claim allowances, employees must complete the Allowances section of the W4 form. They must indicate the number of allowances they are claiming and provide documentation to support their claims. The best way to fill out W4 is to carefully review the different types of allowances and claim only those that are eligible.
By claiming allowances accurately, employees can ensure that the correct amount of taxes is withheld from their paycheck. This can help avoid under or over-withholding, which can result in penalties or a large tax bill at the end of the year. By following these guidelines, employees can ensure that they are taking advantage of all the allowances they are eligible for and minimizing their tax liability.
Additional Income and Deductions: How to Report Them on Your W4
Reporting additional income and deductions on the W4 form is crucial to ensure accurate tax withholding. Employees who have additional income or deductions must report them on the W4 form to avoid under or over-withholding. In this section, we’ll discuss how to report additional income and deductions on the W4 form.
What is Additional Income?
Additional income includes any income that is not subject to withholding, such as self-employment income, investments, and charitable donations. Employees who have additional income must report it on the W4 form to ensure accurate tax withholding.
Types of Additional Income
There are several types of additional income that employees can report on the W4 form, including:
Self-Employment Income
Self-employment income includes income from freelance work, consulting, or running a business. Employees who have self-employment income must report it on the W4 form and complete a separate form, Schedule C, to report their business income and expenses.
Investment Income
Investment income includes income from stocks, bonds, and other investments. Employees who have investment income must report it on the W4 form and complete a separate form, Schedule D, to report their investment income and losses.
Charitable Donations
Charitable donations include donations to qualified charitable organizations. Employees who make charitable donations can deduct them on their tax return and report them on the W4 form.
How to Report Additional Income on the W4 Form
To report additional income on the W4 form, employees must complete the Additional Income section of the form. They must indicate the type of additional income they have and provide documentation to support their claims. The best way to fill out W4 is to carefully review the different types of additional income and report only those that are eligible.
Deductions
Deductions include any expenses that can be deducted from an employee’s taxable income. Employees who have deductions must report them on the W4 form to ensure accurate tax withholding.
Types of Deductions
There are several types of deductions that employees can report on the W4 form, including:
Standard Deduction
The standard deduction is a fixed amount that can be deducted from an employee’s taxable income. Employees who do not itemize their deductions can claim the standard deduction.
Itemized Deductions
Itemized deductions include expenses such as mortgage interest, property taxes, and charitable donations. Employees who itemize their deductions must complete a separate form, Schedule A, to report their itemized deductions.
By reporting additional income and deductions on the W4 form, employees can ensure accurate tax withholding and avoid any potential penalties or issues with their tax return. The best way to fill out W4 is to carefully review the different types of additional income and deductions and report only those that are eligible.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filling Out Your W4
When filling out a W4 form, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to incorrect tax withholding, penalties, and even a large tax bill at the end of the year. In this section, we’ll highlight common mistakes employees make when filling out their W4 forms and provide tips on how to avoid them.
Incorrect Filing Status
One of the most common mistakes employees make is choosing the wrong filing status. This can lead to incorrect tax withholding and even affect the employee’s eligibility for certain tax credits. To avoid this mistake, employees should carefully review the different filing statuses and choose the one that applies to their situation.
Insufficient Allowances
Claiming too few allowances can result in too much tax being withheld, while claiming too many allowances can result in too little tax being withheld. Employees should carefully review their income and expenses to determine the correct number of allowances to claim.
Failure to Report Additional Income
Employees who have additional income, such as self-employment income or investments, must report it on their W4 form. Failure to report additional income can result in incorrect tax withholding and even penalties.
Failure to Update the W4 Form
Employees who experience a change in filing status, income, or dependents must update their W4 form to reflect these changes. Failure to update the W4 form can result in incorrect tax withholding and even penalties.
How to Avoid Common Mistakes
To avoid common mistakes when filling out a W4 form, employees should:
Carefully Review the Form
Employees should carefully review the W4 form to ensure they understand what information is required and how to complete it accurately.
Seek Guidance from a Tax Professional
Employees who are unsure about how to complete their W4 form should seek guidance from a tax professional. A tax professional can provide guidance on how to complete the form accurately and avoid common mistakes.
Use the Best Way to Fill Out W4
The best way to fill out W4 is to carefully review the form and seek guidance from a tax professional if necessary. By avoiding common mistakes, employees can ensure accurate tax withholding and avoid any potential penalties or issues with their tax return.
How to Update Your W4 Form: When and Why You Need to Make Changes
Updating your W4 form is an essential step in ensuring accurate tax withholding and avoiding any potential penalties or issues with your tax return. In this section, we’ll discuss the circumstances under which an employee needs to update their W4 form and provide guidance on how to make changes.
When to Update Your W4 Form
Employees need to update their W4 form in the following circumstances:
Change in Filing Status
If an employee’s filing status changes, such as getting married or divorced, they need to update their W4 form to reflect the change. This will ensure that the correct amount of taxes is withheld from their paycheck.
Change in Income
If an employee’s income changes, such as getting a raise or starting a side job, they need to update their W4 form to reflect the change. This will ensure that the correct amount of taxes is withheld from their paycheck.
Change in Dependents
If an employee’s dependents change, such as having a child or becoming a caregiver for a family member, they need to update their W4 form to reflect the change. This will ensure that the correct amount of taxes is withheld from their paycheck.
How to Update Your W4 Form
To update your W4 form, employees need to follow these steps:
Complete a New W4 Form
Employees need to complete a new W4 form, taking into account the changes in their filing status, income, or dependents.
Submit the Updated Form to Your Employer
Employees need to submit the updated W4 form to their employer, who will update their tax withholding accordingly.
Verify the Changes
Employees should verify that the changes have been made correctly by checking their paycheck stub or contacting their employer’s HR department.
Best Practices for Updating Your W4 Form
To ensure accurate tax withholding and avoid any potential penalties or issues with your tax return, employees should follow these best practices:
Keep Your W4 Form Up-to-Date
Employees should keep their W4 form up-to-date by reviewing and updating it regularly, especially if their filing status, income, or dependents change.
Use the Best Way to Fill Out W4
The best way to fill out W4 is to carefully review the form and seek guidance from a tax professional if necessary. By following these best practices, employees can ensure accurate tax withholding and avoid any potential penalties or issues with their tax return.
Best Practices for W4 Completion: Tips for Employees and Employers
Accurate completion of the W4 form is crucial for both employees and employers. In this section, we’ll provide best practices for W4 completion, including tips for employees on how to accurately fill out the form and guidance for employers on how to facilitate the process and ensure compliance.
Tips for Employees
Employees can follow these best practices to ensure accurate completion of their W4 form:
Review and Update Your W4 Form Regularly
Employees should review and update their W4 form regularly, especially if their filing status, income, or dependents change.
Use the Best Way to Fill Out W4
The best way to fill out W4 is to carefully review the form and seek guidance from a tax professional if necessary.
Keep Accurate Records
Employees should keep accurate records of their income, deductions, and dependents to ensure accurate completion of their W4 form.
Tips for Employers
Employers can follow these best practices to facilitate the W4 completion process and ensure compliance:
Provide Clear Instructions and Guidance
Employers should provide clear instructions and guidance to employees on how to complete their W4 form accurately.
Offer Support and Resources
Employers should offer support and resources to employees who need help completing their W4 form, such as access to tax professionals or online resources.
Verify Employee Information
Employers should verify employee information, such as Social Security numbers and addresses, to ensure accurate completion of the W4 form.
Stay Up-to-Date with Tax Laws and Regulations
Employers should stay up-to-date with tax laws and regulations to ensure compliance and accurate completion of the W4 form.
By following these best practices, employees and employers can ensure accurate completion of the W4 form and avoid any potential penalties or issues with tax withholding.