Understanding the Basics of Federal Withholding
Federal withholding is a critical component of the US tax system, playing a vital role in ensuring that individuals and businesses comply with their tax obligations. At its core, federal withholding refers to the process by which employers deduct a portion of an employee’s wages and pay them directly to the government as taxes. This includes income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax. The primary purpose of federal withholding is to provide the government with a steady stream of revenue throughout the year, rather than relying on individuals and businesses to pay their taxes in a single lump sum.
The federal withholding system is designed to be a pay-as-you-earn system, where taxes are withheld from an employee’s paycheck and paid to the government on a regular basis. This approach helps to reduce the burden of taxes on individuals and businesses, as they are not required to pay their taxes all at once. Instead, the taxes are withheld gradually, making it easier to manage cash flow and budget for tax expenses.
It’s essential to note that federal withholding is not just limited to income tax. Social Security and Medicare taxes are also withheld from an employee’s paycheck and paid to the government. These taxes are used to fund social security programs and provide healthcare benefits to eligible individuals. The question of whether Social Security and Medicare taxes count as federal withholding is a common one, and it’s essential to understand the answer to this question to ensure compliance with tax laws and regulations.
In the context of federal withholding, it’s crucial to understand the different types of taxes that are withheld and how they impact an individual’s tax liability. By grasping the basics of federal withholding, individuals and businesses can better navigate the tax system and ensure that they are in compliance with all tax laws and regulations. This knowledge can also help to identify potential tax savings opportunities and optimize tax strategies to minimize tax liability.
Do Social Security and Medicare Taxes Count as Federal Withholding?
One of the most common questions regarding federal withholding is whether Social Security and Medicare taxes are considered federal withholding. The answer to this question is yes, Social Security and Medicare taxes do count as federal withholding. According to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS), federal withholding includes all taxes withheld from an employee’s paycheck, including income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax.
The IRS considers Social Security and Medicare taxes to be part of the federal withholding system because they are withheld from an employee’s paycheck and paid to the government on a regular basis. These taxes are used to fund social security programs and provide healthcare benefits to eligible individuals. As a result, they are subject to the same withholding rules and regulations as income tax.
It’s essential to note that the IRS uses the term “federal income tax withholding” to refer to the total amount of taxes withheld from an employee’s paycheck, including Social Security and Medicare taxes. This means that when an employer withholds Social Security and Medicare taxes from an employee’s paycheck, they are considered to be part of the federal withholding system.
Understanding that Social Security and Medicare taxes count as federal withholding is crucial for employees and employers alike. It can help individuals understand how their taxes are being withheld and how it impacts their take-home pay. For employers, it’s essential to ensure that they are withholding the correct amount of taxes, including Social Security and Medicare taxes, to avoid any penalties or fines.
In the context of federal withholding, it’s clear that Social Security and Medicare taxes play a significant role. By understanding how these taxes are withheld and how they impact an individual’s tax liability, individuals and employers can better navigate the tax system and ensure compliance with all tax laws and regulations.
How to Calculate Your Federal Withholding
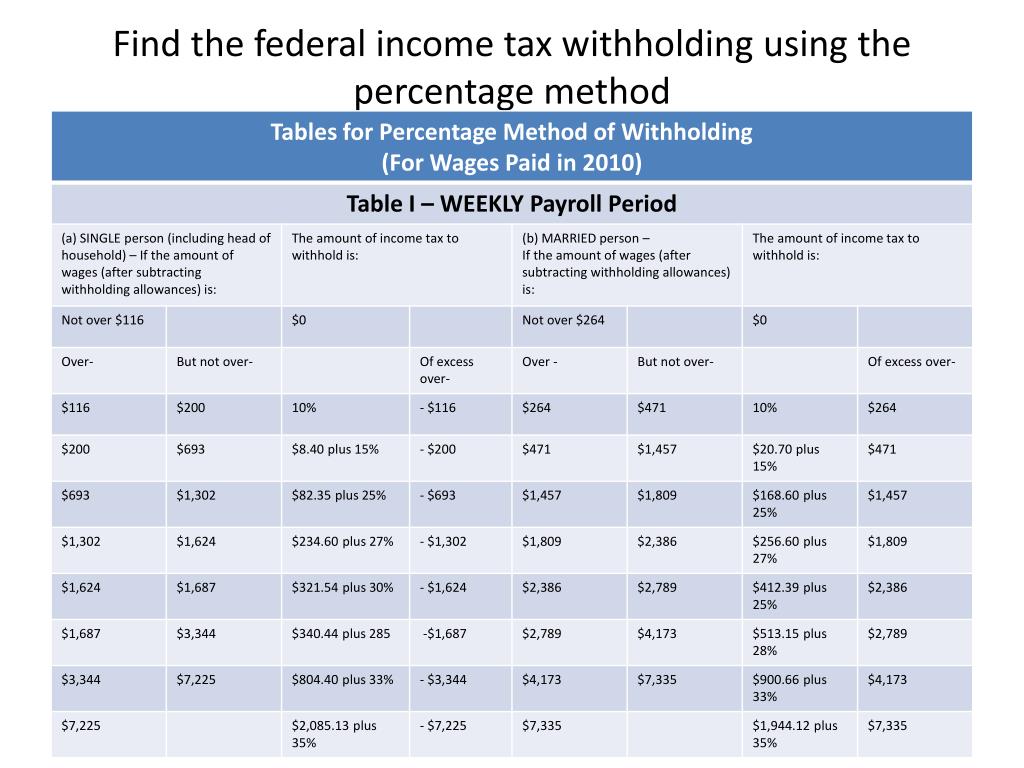
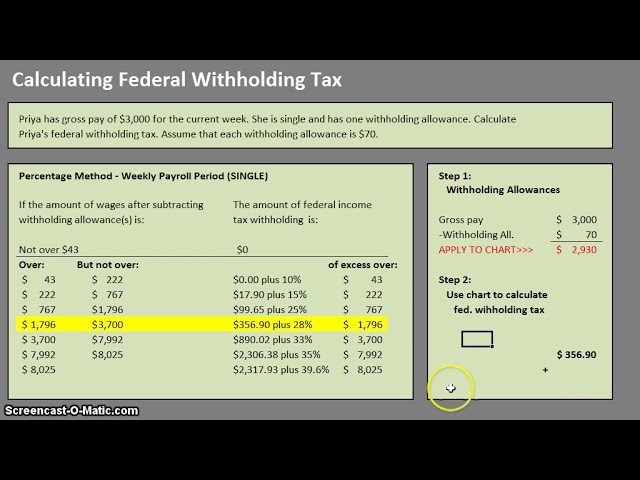
Calculating federal withholding can be a complex process, but it’s essential to understand how it works to ensure that you’re not overpaying or underpaying your taxes. The amount of federal withholding is determined by several factors, including your filing status, number of dependents, and tax deductions.
To calculate your federal withholding, you’ll need to complete a W-4 form, which is used to determine the amount of taxes to withhold from your paycheck. The W-4 form takes into account your filing status, number of dependents, and other factors that affect your tax liability.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to calculating your federal withholding:
1. Determine your filing status: Your filing status will affect the amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck. The most common filing statuses are single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, and qualifying widow(er).
2. Claim your dependents: If you have dependents, you may be eligible for a lower tax rate or additional tax credits. Claiming dependents on your W-4 form can help reduce the amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck.
3. Calculate your tax deductions: Tax deductions can help reduce your taxable income, which in turn can reduce the amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck. Common tax deductions include mortgage interest, charitable donations, and medical expenses.
4. Determine your tax credits: Tax credits can help reduce your tax liability, which can also reduce the amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck. Common tax credits include the earned income tax credit (EITC) and the child tax credit.
5. Complete the W-4 form: Once you’ve determined your filing status, claimed your dependents, calculated your tax deductions, and determined your tax credits, you can complete the W-4 form. The W-4 form will help you determine the amount of taxes to withhold from your paycheck.
Example: Let’s say you’re single and have one dependent. You earn $50,000 per year and have $10,000 in tax deductions. Using the W-4 form, you determine that you need to withhold 25% of your income for federal taxes. Based on this calculation, your employer would withhold $12,500 per year in federal taxes, or approximately $1,042 per month.
By following these steps, you can calculate your federal withholding and ensure that you’re not overpaying or underpaying your taxes. Remember to review and update your W-4 form regularly to ensure that your withholding is accurate and reflects any changes in your tax situation.
The Impact of Social Security and Medicare Taxes on Your Take-Home Pay
Social Security and Medicare taxes can have a significant impact on an employee’s take-home pay. These taxes are withheld from an employee’s paycheck and paid to the government to fund social security programs and provide healthcare benefits to eligible individuals.
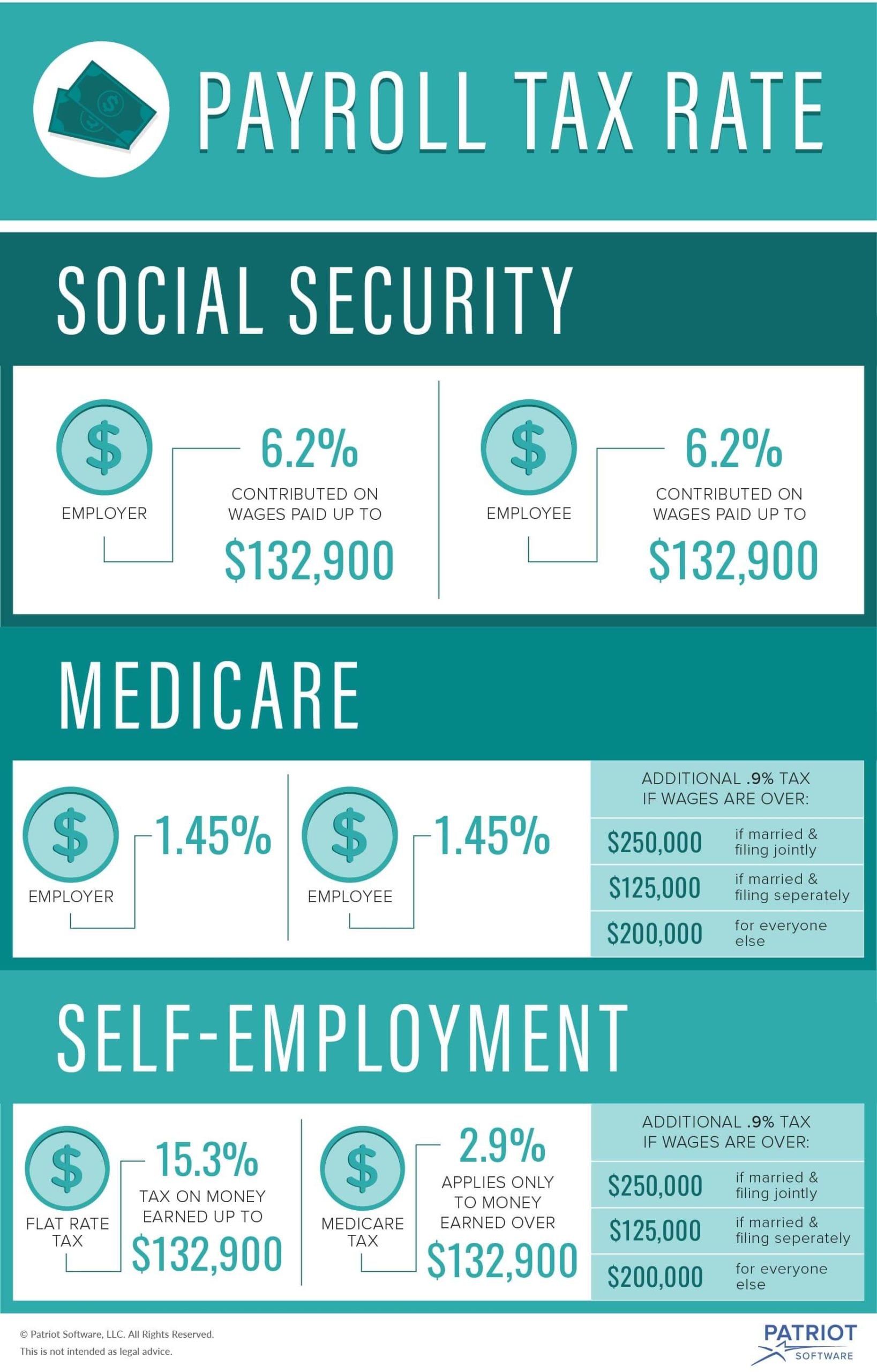
The tax rates for Social Security and Medicare taxes are as follows:
Social Security tax: 6.2% of an employee’s earnings, up to a maximum taxable earnings limit of $147,000 in 2022.
Medicare tax: 1.45% of an employee’s earnings, with no maximum taxable earnings limit.
For example, let’s say an employee earns $50,000 per year and has a filing status of single. The employee’s Social Security tax would be 6.2% of $50,000, or $3,100 per year. The employee’s Medicare tax would be 1.45% of $50,000, or $725 per year.
These taxes can impact an individual’s overall tax liability, as they are withheld from an employee’s paycheck and paid to the government. However, they also provide important benefits, such as social security and healthcare benefits, to eligible individuals.
It’s essential to note that the impact of Social Security and Medicare taxes on take-home pay can vary depending on an individual’s filing status, number of dependents, and other factors. By understanding how these taxes work and how they impact take-home pay, individuals can better navigate the tax system and make informed decisions about their tax situation.
In addition, individuals can use tax planning strategies to minimize the impact of Social Security and Medicare taxes on their take-home pay. For example, individuals can claim exemptions or adjust their withholding allowances to reduce the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck.
By understanding the impact of Social Security and Medicare taxes on take-home pay, individuals can take control of their tax situation and make informed decisions about their financial future.
Common Misconceptions About Federal Withholding
There are several common misconceptions about federal withholding that can lead to confusion and errors. One of the most common misconceptions is that Social Security and Medicare taxes are not considered federal withholding. However, as we discussed earlier, these taxes are indeed considered federal withholding and are subject to the same withholding rules and regulations as income tax.
Another common misconception is that federal withholding only applies to income tax. However, federal withholding also includes Social Security and Medicare taxes, which are withheld from an employee’s paycheck and paid to the government to fund social security programs and provide healthcare benefits to eligible individuals.
Some individuals may also believe that they can avoid paying federal withholding by claiming exemptions or adjusting their withholding allowances. However, this is not the case. Federal withholding is mandatory, and employers are required to withhold taxes from an employee’s paycheck, regardless of the employee’s filing status or number of dependents.
It’s also important to note that federal withholding is not the same as tax liability. While federal withholding is the amount of taxes withheld from an employee’s paycheck, tax liability refers to the total amount of taxes owed to the government. Federal withholding is just one component of tax liability, and individuals may still owe additional taxes or be eligible for a refund, depending on their individual circumstances.
By understanding these common misconceptions about federal withholding, individuals can avoid errors and ensure that they are in compliance with tax laws and regulations. It’s essential to consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure that you are meeting your federal withholding obligations and minimizing your tax liability.
In addition, individuals can use tax planning strategies to minimize their tax liability and optimize their federal withholding. For example, individuals can claim exemptions or adjust their withholding allowances to reduce the amount of taxes withheld from their paycheck. By taking control of their federal withholding, individuals can ensure that they are meeting their tax obligations and minimizing their tax liability.
How to Adjust Your Federal Withholding for Optimal Tax Savings
Adjusting your federal withholding can help you minimize your tax liability and optimize your tax savings. Here are some tips to help you adjust your federal withholding:
1. Claim exemptions: Claiming exemptions can help reduce the amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck. You can claim exemptions for yourself, your spouse, and your dependents.
2. Adjust withholding allowances: Adjusting your withholding allowances can help you fine-tune your federal withholding. You can adjust your withholding allowances based on your filing status, number of dependents, and other factors that affect your tax liability.
3. Take advantage of tax credits: Tax credits can help reduce your tax liability and increase your tax savings. You can take advantage of tax credits such as the earned income tax credit (EITC), the child tax credit, and the education credits.
4. Review and update your W-4 form: Reviewing and updating your W-4 form can help you ensure that your federal withholding is accurate and up-to-date. You can update your W-4 form to reflect changes in your filing status, number of dependents, and other factors that affect your tax liability.
Example: Let’s say you’re single and have two dependents. You earn $50,000 per year and have a filing status of single. You can claim exemptions for yourself and your dependents, and adjust your withholding allowances to minimize your tax liability. By taking advantage of tax credits and reviewing and updating your W-4 form, you can optimize your federal withholding and increase your tax savings.
By following these tips, you can adjust your federal withholding to minimize your tax liability and optimize your tax savings. Remember to review and update your W-4 form regularly to ensure that your federal withholding is accurate and up-to-date.
In addition, you can use tax planning strategies to minimize your tax liability and optimize your federal withholding. For example, you can use tax-deferred savings vehicles such as 401(k) or IRA accounts to reduce your taxable income. By taking control of your federal withholding and using tax planning strategies, you can minimize your tax liability and maximize your tax savings.
The Role of the W-4 Form in Federal Withholding
The W-4 form is a crucial document in determining federal withholding. It is used to determine the amount of taxes to withhold from an employee’s paycheck, and it is essential to complete the form accurately to avoid any errors or penalties.
The W-4 form asks for information such as filing status, number of dependents, and tax deductions. This information is used to determine the employee’s tax liability and the amount of taxes to withhold from their paycheck.
It is essential to update the W-4 form when necessary, such as when there are changes in filing status, number of dependents, or tax deductions. Failure to update the W-4 form can result in incorrect withholding, which can lead to penalties and fines.
The W-4 form also plays a critical role in determining the amount of Social Security and Medicare taxes to withhold from an employee’s paycheck. As we discussed earlier, Social Security and Medicare taxes are considered federal withholding, and the W-4 form is used to determine the amount of these taxes to withhold.
Example: Let’s say an employee is single and has two dependents. They earn $50,000 per year and have a filing status of single. They complete the W-4 form accurately, claiming exemptions for themselves and their dependents. The W-4 form is used to determine the amount of taxes to withhold from their paycheck, including Social Security and Medicare taxes.
By understanding the importance of the W-4 form in determining federal withholding, employees can ensure that their taxes are withheld accurately and avoid any errors or penalties. It is essential to review and update the W-4 form regularly to ensure that it reflects any changes in filing status, number of dependents, or tax deductions.
In addition, employers can use the W-4 form to determine the amount of taxes to withhold from an employee’s paycheck. By using the W-4 form accurately, employers can ensure that they are withholding the correct amount of taxes and avoiding any penalties or fines.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your Federal Withholding
In conclusion, understanding federal withholding is crucial for individuals to take control of their tax situation. By knowing how federal withholding works, including Social Security and Medicare taxes, individuals can make informed decisions about their tax planning and minimize their tax liability.
As we discussed earlier, Social Security and Medicare taxes are considered federal withholding, and it’s essential to understand how these taxes impact an individual’s take-home pay and overall tax liability.
By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, individuals can adjust their federal withholding to minimize their tax liability and optimize their tax savings. It’s also essential to review and update the W-4 form regularly to ensure that it reflects any changes in filing status, number of dependents, or tax deductions.
Remember, taking control of your federal withholding requires a proactive approach. By understanding how federal withholding works and making informed decisions about your tax planning, you can minimize your tax liability and maximize your tax savings.
Don’t let federal withholding be a mystery to you. Take control of your tax situation today by adjusting your withholding and seeking professional advice when needed. With the right knowledge and planning, you can optimize your tax savings and achieve your financial goals.