Understanding the Electric Vehicle Market: A Primer
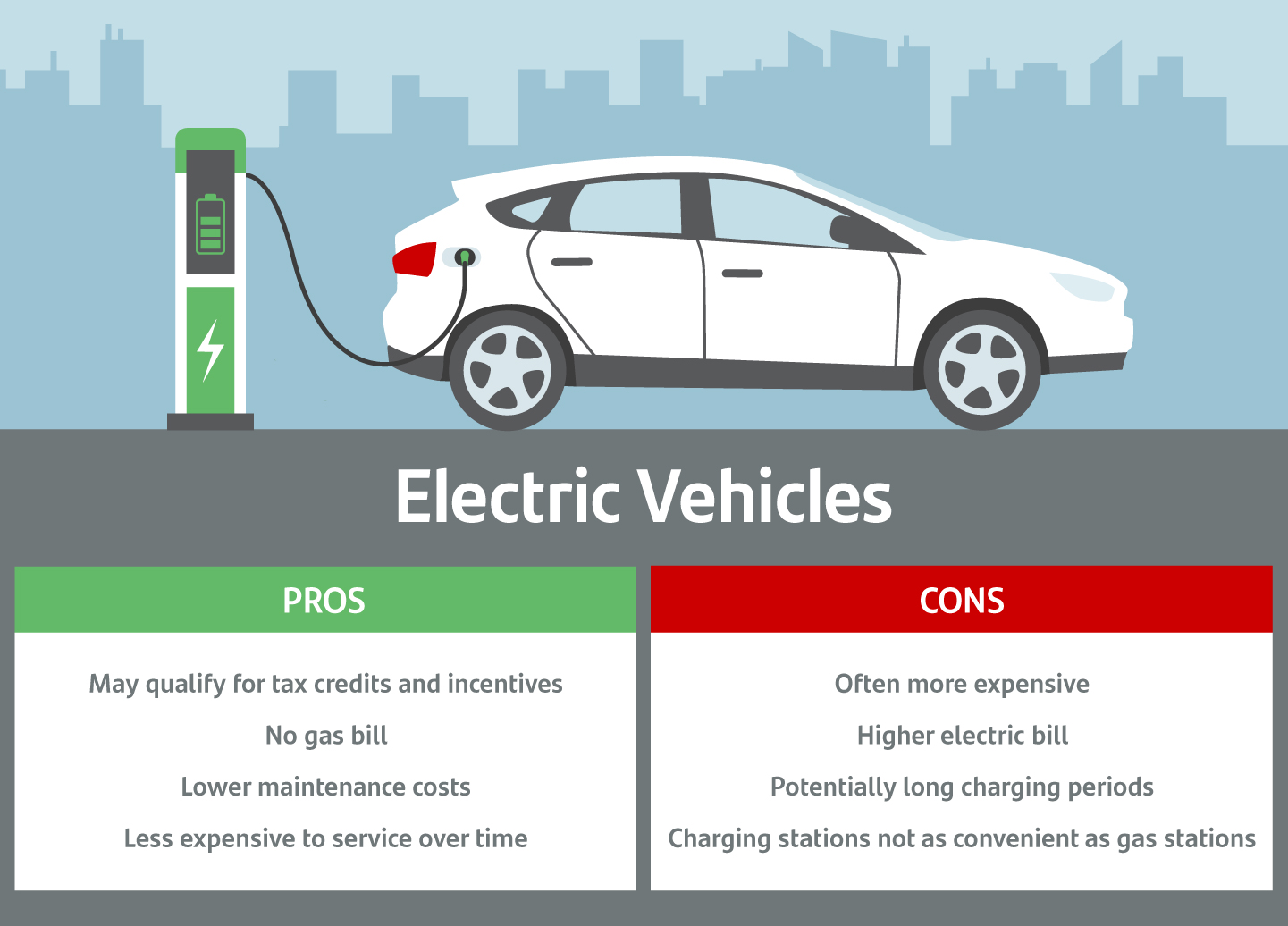
The electric vehicle (EV) market has experienced rapid growth in recent years, driven by increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions. As governments and consumers become more environmentally conscious, the EV industry is poised for continued expansion. However, to fully understand the competitive landscape of the EV market, it is essential to analyze the industry’s structure and dynamics. This is where Porter’s Five Forces analysis comes into play, providing a framework for evaluating the competitive forces that shape the EV market. By applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis to the EV industry, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into the market’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation. The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a crucial tool for understanding the EV market’s competitive landscape and making informed strategic decisions.
The EV market is characterized by a complex interplay of factors, including technological advancements, regulatory policies, and shifting consumer preferences. As the market continues to evolve, it is essential to stay ahead of the curve and anticipate future developments. By examining the EV market through the lens of Porter’s Five Forces analysis, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation. The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a powerful tool for navigating the EV market’s complex landscape and making informed strategic decisions.
One of the key drivers of the EV market’s growth is the increasing demand for sustainable transportation solutions. As consumers become more environmentally conscious, they are seeking alternatives to traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. The EV market is well-positioned to meet this demand, with a range of models available to suit different needs and preferences. However, the EV market is not without its challenges, and stakeholders must be aware of the competitive forces that shape the industry. By applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis to the EV market, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
In conclusion, the EV market is a complex and dynamic industry, driven by a range of factors, including technological advancements, regulatory policies, and shifting consumer preferences. By applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis to the EV market, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation. The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a powerful tool for navigating the EV market’s complex landscape and making informed strategic decisions.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis: A Framework for Evaluating Competition
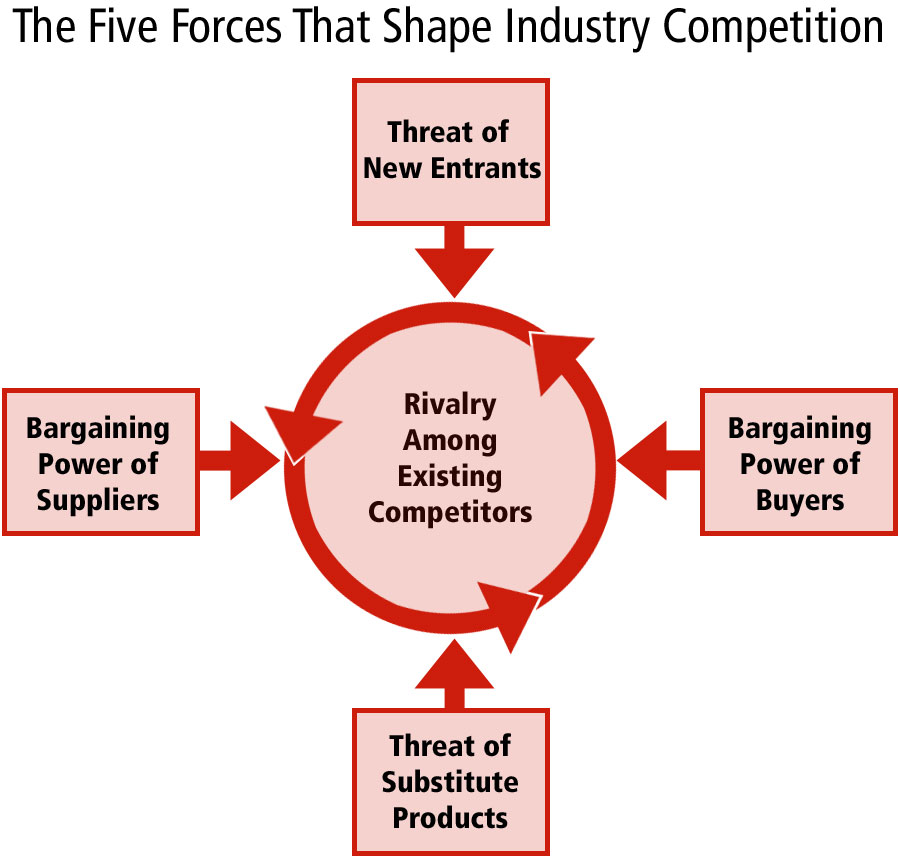
Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a widely used framework for assessing the competitive structure of an industry. Developed by Michael Porter, this framework provides a comprehensive approach to analyzing the competitive forces that shape an industry. The five forces include the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of suppliers, the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of substitute products, and the competitive rivalry among existing competitors. By applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis to the electric vehicle (EV) market, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a powerful tool for evaluating the competitive landscape of the EV market. By examining the five forces, stakeholders can assess the attractiveness of the industry and identify potential threats and opportunities. For example, the threat of new entrants in the EV market is relatively low due to high capital requirements and technological expertise. However, the bargaining power of suppliers, particularly those providing critical components such as batteries and electric motors, can have a significant impact on the industry’s competitive dynamics.
The Porter’s Five Forces analysis framework can be applied to the EV market by examining each of the five forces in turn. The threat of new entrants can be assessed by examining the barriers to entry, such as high capital requirements and technological expertise. The bargaining power of suppliers can be evaluated by examining the impact of suppliers of critical components on the industry’s competitive dynamics. The bargaining power of buyers can be assessed by examining the factors that influence consumer purchasing decisions, such as price, range, and charging infrastructure.
The threat of substitute products can be evaluated by examining the potential impact of alternative fuels, such as hydrogen fuel cells, on the industry’s competitive landscape. Finally, the competitive rivalry among existing competitors can be assessed by examining the market share, product offerings, and strategies of leading players, such as Tesla, Volkswagen, and Nissan. By applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis to the EV market, stakeholders can gain a comprehensive understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a valuable tool for stakeholders seeking to understand the competitive landscape of the EV market. By examining the five forces, stakeholders can assess the attractiveness of the industry and identify potential threats and opportunities. This framework provides a comprehensive approach to analyzing the competitive forces that shape the EV market, and can be used to inform strategic decisions and drive growth and innovation in the industry.
Threat of New Entrants: How Easy is it to Enter the EV Market?
The threat of new entrants in the electric vehicle (EV) market is a crucial aspect of the industry’s competitive landscape. New entrants can bring fresh ideas, innovative technologies, and increased competition to the market, which can be beneficial for consumers. However, the EV market is characterized by high barriers to entry, making it challenging for new players to enter the market.
One of the main barriers to entry in the EV market is the high capital requirement. Establishing a manufacturing facility, developing a distribution network, and creating a brand identity require significant investments. Additionally, new entrants must also comply with regulatory requirements, such as safety and emissions standards, which can be time-consuming and costly.
Another significant barrier to entry is the need for technological expertise. The EV market is driven by advanced technologies, such as battery management systems, electric motors, and power electronics. New entrants must have access to these technologies and the expertise to develop and integrate them into their products.
Furthermore, the EV market is also characterized by regulatory hurdles. Governments around the world have established regulations and incentives to promote the adoption of EVs, but these regulations can also create barriers to entry for new players. For example, new entrants must comply with regulations related to safety, emissions, and charging infrastructure.
Despite these barriers to entry, some new players have successfully entered the EV market. For example, companies like Rivian and Lucid Motors have established themselves as significant players in the market, despite being relatively new entrants. However, these companies have had to overcome significant challenges to establish themselves in the market.
The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis highlights the importance of understanding the threat of new entrants in the EV market. By analyzing the barriers to entry and the strategies used by new entrants, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
In conclusion, the threat of new entrants in the EV market is a significant aspect of the industry’s competitive landscape. While the barriers to entry are high, some new players have successfully entered the market, and the electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis provides a valuable framework for understanding the industry’s competitive dynamics.
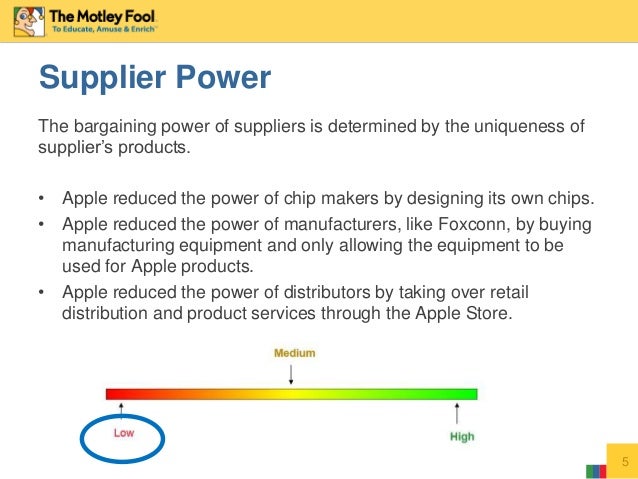
Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Who Holds the Power in the EV Supply Chain?
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical aspect of the electric vehicle (EV) market’s competitive landscape. Suppliers of critical components, such as batteries and electric motors, play a vital role in the production of EVs. The bargaining power of these suppliers can have a significant impact on the industry’s competitive dynamics.
In the EV market, suppliers of batteries and electric motors hold significant bargaining power. These components are critical to the performance and efficiency of EVs, and suppliers have a high degree of control over the supply chain. Companies like Panasonic, LG Chem, and Continental AG are major suppliers of batteries and electric motors to EV manufacturers.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the EV market is influenced by several factors, including the level of differentiation in the market, the cost of switching suppliers, and the presence of substitute products. In the EV market, the level of differentiation is relatively low, as most suppliers offer similar products. However, the cost of switching suppliers can be high, as EV manufacturers often have long-term contracts with their suppliers.
The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis highlights the importance of understanding the bargaining power of suppliers in the EV market. By analyzing the factors that influence the bargaining power of suppliers, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
For example, EV manufacturers can negotiate better prices with their suppliers by leveraging their purchasing power. Additionally, EV manufacturers can also consider vertical integration, where they produce their own batteries and electric motors, to reduce their dependence on suppliers.
However, the bargaining power of suppliers in the EV market is not without its challenges. Suppliers may use their bargaining power to negotiate higher prices or better terms, which can increase the costs of EV manufacturers. Additionally, suppliers may also use their bargaining power to influence the design and development of EVs, which can impact the overall performance and efficiency of the vehicles.
In conclusion, the bargaining power of suppliers is a critical aspect of the EV market’s competitive landscape. By understanding the factors that influence the bargaining power of suppliers, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
Bargaining Power of Buyers: What Do EV Consumers Really Want?
The bargaining power of buyers is a crucial aspect of the electric vehicle (EV) market’s competitive landscape. EV consumers have a significant impact on the industry’s competitive dynamics, and understanding their needs and preferences is essential for EV manufacturers.
EV consumers are primarily driven by factors such as price, range, and charging infrastructure. They want affordable vehicles with a reasonable range and easy access to charging stations. Additionally, EV consumers are also concerned about the environmental impact of their vehicles, and they prefer manufacturers that prioritize sustainability.
The bargaining power of buyers in the EV market is influenced by several factors, including the level of product differentiation, the cost of switching brands, and the presence of substitute products. In the EV market, the level of product differentiation is relatively low, as most EVs offer similar features and performance. However, the cost of switching brands can be high, as EV consumers often have strong brand loyalty.
The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis highlights the importance of understanding the bargaining power of buyers in the EV market. By analyzing the factors that influence the bargaining power of buyers, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
For example, EV manufacturers can focus on developing vehicles with longer ranges and more affordable prices to meet the needs of EV consumers. Additionally, EV manufacturers can also invest in expanding their charging infrastructure to make it more convenient for EV consumers to charge their vehicles.
However, the bargaining power of buyers in the EV market is not without its challenges. EV consumers may use their bargaining power to negotiate better prices or more favorable terms, which can impact the profitability of EV manufacturers. Additionally, EV consumers may also use their bargaining power to influence the design and development of EVs, which can impact the overall performance and efficiency of the vehicles.
In the EV market, companies like Tesla, Volkswagen, and Nissan are well-positioned to meet the needs of EV consumers. These companies have developed a range of EV models with varying price points and features, and they have invested heavily in expanding their charging infrastructure.
Overall, the bargaining power of buyers is a critical aspect of the EV market’s competitive landscape. By understanding the needs and preferences of EV consumers, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
Threat of Substitute Products: Can Alternative Fuels Disrupt the EV Market?
The threat of substitute products is a critical aspect of the electric vehicle (EV) market’s competitive landscape. Alternative fuels, such as hydrogen fuel cells, can potentially disrupt the EV market and impact the industry’s competitive dynamics.
Hydrogen fuel cells are a promising alternative to battery-electric vehicles, offering a range of benefits, including longer driving ranges and faster refueling times. However, the development and deployment of hydrogen fuel cells are still in their infancy, and significant technical and infrastructure challenges must be overcome before they can become a viable substitute for EVs.
The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis highlights the importance of understanding the threat of substitute products in the EV market. By analyzing the potential impact of alternative fuels on the industry’s competitive landscape, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the market’s dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
For example, EV manufacturers can focus on developing vehicles with longer ranges and faster charging times to stay competitive with hydrogen fuel cells. Additionally, EV manufacturers can also invest in expanding their charging infrastructure to make it more convenient for EV consumers to charge their vehicles.
However, the threat of substitute products in the EV market is not without its challenges. Alternative fuels, such as hydrogen fuel cells, may require significant investments in infrastructure and technology, which can be a barrier to entry for new players. Additionally, the development and deployment of alternative fuels may also be impacted by regulatory and policy factors, which can create uncertainty and risk for stakeholders.
In the EV market, companies like Toyota and Honda are already investing in the development of hydrogen fuel cells, which could potentially disrupt the market and impact the competitive dynamics of the industry. However, the adoption of hydrogen fuel cells will depend on a range of factors, including the development of infrastructure, the cost of production, and the availability of hydrogen fuel.
Overall, the threat of substitute products is a critical aspect of the EV market’s competitive landscape. By understanding the potential impact of alternative fuels on the industry’s competitive dynamics, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the market’s dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
Competitive Rivalry Among Existing Competitors: Who’s Leading the EV Pack?
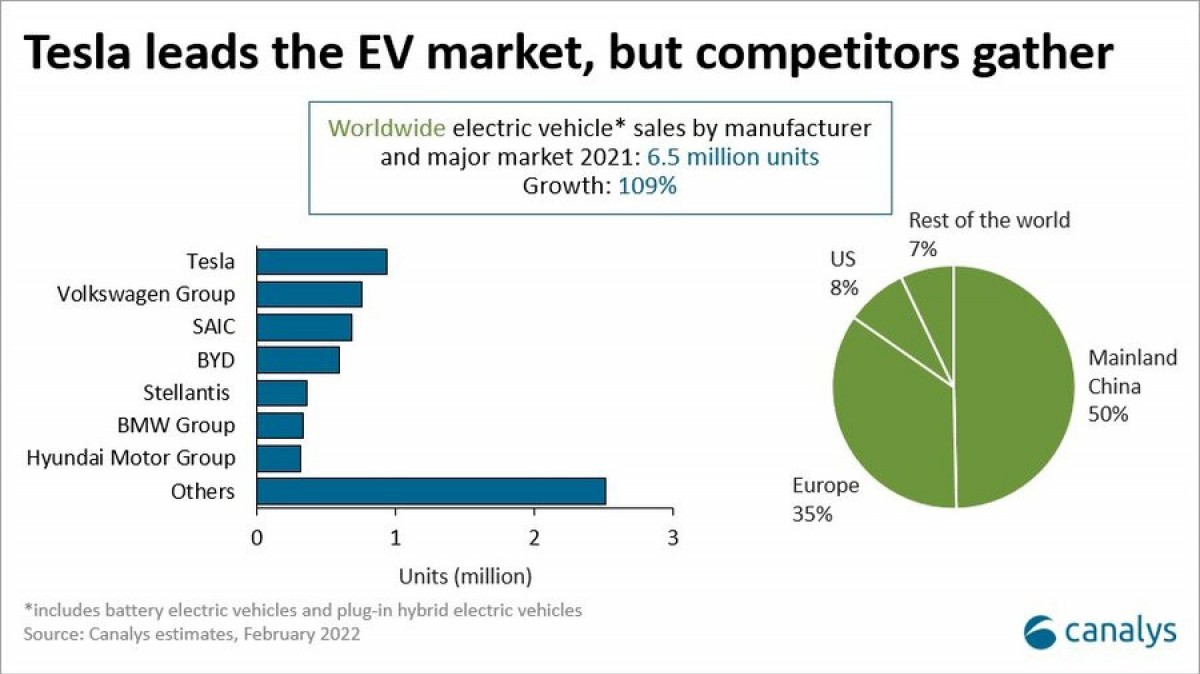
The competitive rivalry among existing competitors in the electric vehicle (EV) market is a critical aspect of the industry’s competitive landscape. The EV market is characterized by a high level of competition among existing players, with companies like Tesla, Volkswagen, and Nissan vying for market share.
Tesla is currently the leading player in the EV market, with a significant market share and a strong brand reputation. However, other companies like Volkswagen and Nissan are rapidly gaining ground, with new product offerings and aggressive marketing strategies.
The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis highlights the importance of understanding the competitive rivalry among existing competitors in the EV market. By analyzing the market share, product offerings, and strategies of leading players, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
For example, companies like Tesla and Volkswagen are investing heavily in the development of new EV models, with a focus on improving range, performance, and affordability. Additionally, companies like Nissan are focusing on expanding their charging infrastructure, to make it more convenient for EV consumers to charge their vehicles.
However, the competitive rivalry among existing competitors in the EV market is not without its challenges. Companies must navigate a complex regulatory environment, with varying standards and incentives across different regions. Additionally, companies must also manage the risks associated with the development and deployment of new technologies, such as battery-electric vehicles and hydrogen fuel cells.
In the EV market, companies like Tesla, Volkswagen, and Nissan are well-positioned to compete, with strong brand reputations and significant investments in research and development. However, other companies like Hyundai and Kia are also emerging as significant players, with new product offerings and aggressive marketing strategies.
Overall, the competitive rivalry among existing competitors in the EV market is a critical aspect of the industry’s competitive landscape. By understanding the market share, product offerings, and strategies of leading players, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive dynamics and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
How to Apply Porter’s Five Forces Analysis to the Electric Motor Market
To apply Porter’s Five Forces analysis to the electric motor market, it is essential to identify the key players, assess market trends, and anticipate future developments. The electric motor market is a critical component of the electric vehicle (EV) industry, and understanding its competitive dynamics is crucial for stakeholders.
First, identify the key players in the electric motor market, including companies like Tesla, Volkswagen, and Nissan. These companies are leading the development and deployment of electric motors, and their strategies and market share will have a significant impact on the industry’s competitive dynamics.
Next, assess market trends, including the increasing demand for electric motors, the development of new technologies, and the impact of regulatory policies. The electric motor market is rapidly evolving, and understanding these trends is essential for stakeholders to make informed decisions.
Finally, anticipate future developments, including the potential impact of alternative fuels, such as hydrogen fuel cells, on the electric motor market. The electric motor market is closely tied to the EV industry, and understanding the potential impact of alternative fuels is crucial for stakeholders to anticipate future developments.
The electric vehicle and electric motor Porter’s Five Forces analysis provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the competitive dynamics of the electric motor market. By applying this framework, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive landscape and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.
For example, companies like Tesla and Volkswagen are investing heavily in the development of new electric motor technologies, including advanced materials and designs. Additionally, companies like Nissan are focusing on expanding their electric motor production capacity, to meet the increasing demand for electric vehicles.
However, the electric motor market is not without its challenges. Companies must navigate a complex regulatory environment, with varying standards and incentives across different regions. Additionally, companies must also manage the risks associated with the development and deployment of new technologies, such as battery-electric vehicles and hydrogen fuel cells.
Overall, applying Porter’s Five Forces analysis to the electric motor market provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the industry’s competitive dynamics. By identifying key players, assessing market trends, and anticipating future developments, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the industry’s competitive landscape and identify opportunities for growth and innovation.