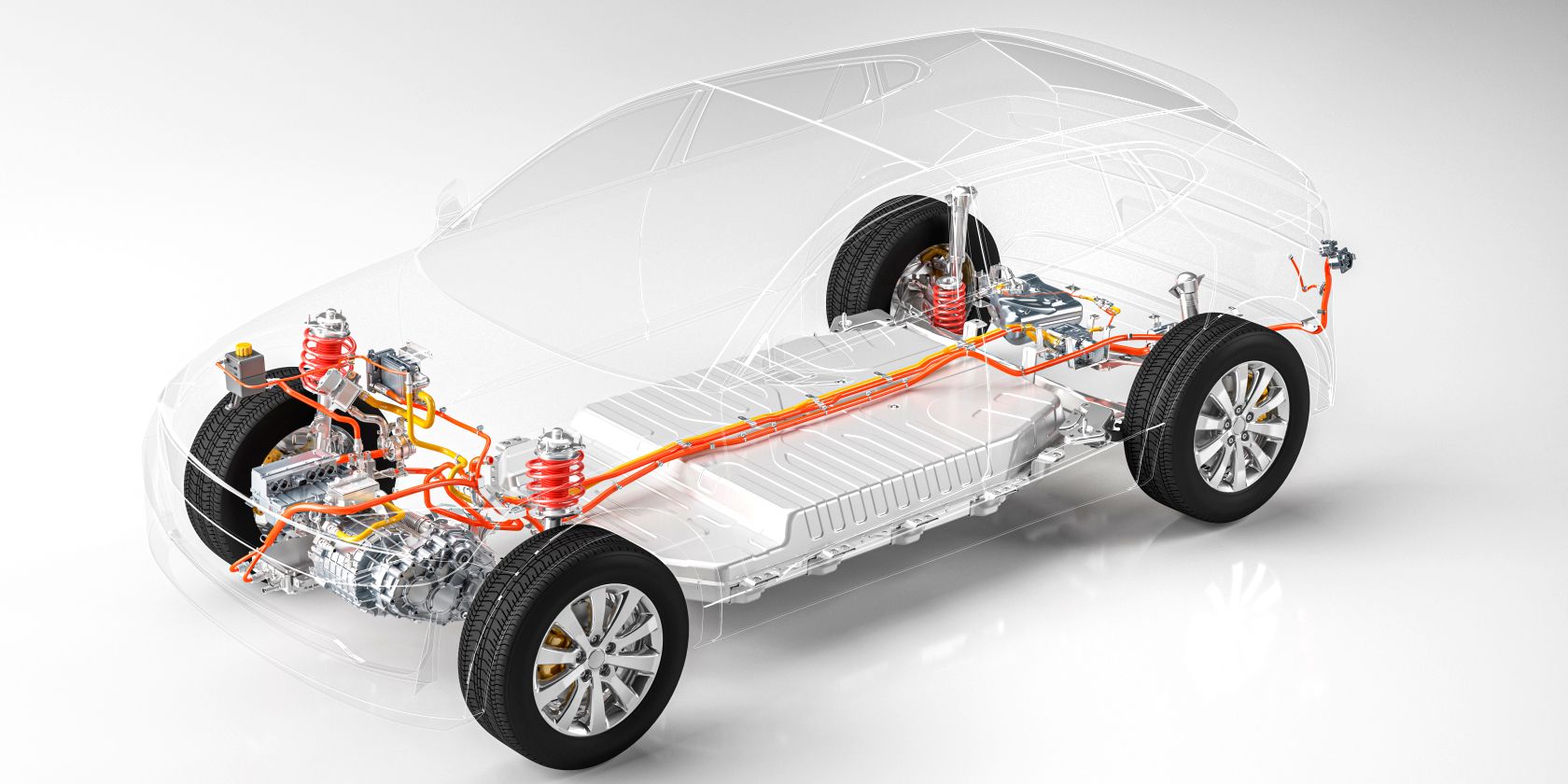
Understanding the Importance of Standardization in Electric Motors
Standardization is a crucial aspect of the electric vehicle (EV) industry, particularly when it comes to electric motors. The benefits of standardization in electric motors are numerous, including improved safety, efficiency, and interoperability. By standardizing electric motor components and systems, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet specific safety and performance requirements, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. Moreover, standardization enables the widespread adoption of electric vehicles by facilitating the development of compatible charging infrastructure and promoting economies of scale in manufacturing.
The standardization of electric motors also has a significant impact on the environment. By promoting the use of efficient electric motors, standardization can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the environmental impacts of transportation. Furthermore, standardization can facilitate the development of sustainable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, by enabling the efficient transmission and distribution of electricity.
In addition to its environmental benefits, standardization can also drive innovation in the EV industry. By establishing common standards for electric motors, manufacturers can focus on developing new technologies and improving existing ones, rather than duplicating effort on standardization. This can lead to the development of more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable electric motors, which can help drive the adoption of electric vehicles.
Examples of standardization in electric motors can be seen in the development of industry-wide standards for electric motor components, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60034 series. These standards provide a framework for manufacturers to design and test electric motors, ensuring that they meet specific safety and performance requirements. Similarly, the development of standardized charging systems, such as the Combined Charging System (CCS), has facilitated the widespread adoption of electric vehicles by enabling the efficient transmission of electricity.
In conclusion, standardization is a critical aspect of the electric vehicle industry, particularly when it comes to electric motors. By promoting the use of standardized electric motors, manufacturers can ensure improved safety, efficiency, and interoperability, while also driving innovation and reducing environmental impacts. As the EV industry continues to evolve, the importance of standardization will only continue to grow, enabling the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and promoting a more sustainable transportation sector.
How to Ensure Compliance with Electric Vehicle Safety Standards
Ensuring compliance with electric vehicle safety standards is crucial for manufacturers to guarantee the safety of their products and avoid potential liabilities. The key safety standards for electric vehicles include those related to battery safety, electrical safety, and crashworthiness. In this section, we will provide an overview of these standards and offer guidance on how manufacturers can ensure compliance.
Battery safety is a critical aspect of electric vehicle safety, as lithium-ion batteries can be prone to overheating and fires. To ensure compliance with battery safety standards, manufacturers must adhere to guidelines such as those outlined in the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UNECE) Regulation 100, which sets out requirements for the safety of electric vehicle batteries. This includes testing for electrical, thermal, and mechanical safety, as well as ensuring that batteries are designed and constructed to prevent electrical shock and fire hazards.
Electrical safety is another important consideration for electric vehicle manufacturers. To ensure compliance with electrical safety standards, manufacturers must adhere to guidelines such as those outlined in the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60364 series, which sets out requirements for the electrical safety of electric vehicles. This includes ensuring that electrical systems are designed and constructed to prevent electrical shock and fire hazards, as well as ensuring that electrical components are properly tested and certified.
Crashworthiness is also a critical aspect of electric vehicle safety, as electric vehicles must be designed to withstand crashes and protect occupants. To ensure compliance with crashworthiness standards, manufacturers must adhere to guidelines such as those outlined in the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard (FMVSS) 214, which sets out requirements for the crashworthiness of electric vehicles. This includes testing for frontal, side, and rollover crashes, as well as ensuring that vehicles are designed and constructed to protect occupants in the event of a crash.
To ensure compliance with these safety standards, manufacturers can take several steps. First, they must conduct thorough testing and validation of their products to ensure that they meet the required safety standards. This includes testing for electrical, thermal, and mechanical safety, as well as crash testing to ensure that vehicles can withstand crashes and protect occupants. Second, manufacturers must ensure that their products are designed and constructed to prevent electrical shock and fire hazards, and that electrical components are properly tested and certified. Finally, manufacturers must stay up-to-date with the latest developments in electric vehicle safety standards and regulations, and ensure that their products comply with these requirements.
By following these steps, manufacturers can ensure compliance with electric vehicle safety standards and guarantee the safety of their products. This is critical for building trust with consumers and promoting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Deciphering Electric Motor Regulations: A Guide for Manufacturers
Electric motor regulations are a critical aspect of the electric vehicle industry, as they govern the performance, efficiency, and safety of electric motors. Manufacturers must navigate a complex landscape of regulations to ensure compliance and avoid potential liabilities. In this section, we will provide an overview of the various regulations governing electric motors, including those related to efficiency, noise, and electromagnetic compatibility.
Efficiency regulations are a key aspect of electric motor regulations, as they govern the energy consumption and environmental impact of electric motors. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 60034 series sets out requirements for the efficiency of electric motors, including minimum efficiency levels and testing procedures. Manufacturers must ensure that their electric motors meet these efficiency requirements to avoid penalties and reputational damage.
Noise regulations are another important consideration for electric motor manufacturers. The IEC 60034 series also sets out requirements for the noise levels of electric motors, including maximum permissible noise levels and testing procedures. Manufacturers must ensure that their electric motors meet these noise requirements to avoid disturbing the environment and affecting human health.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations are also critical for electric motor manufacturers. The IEC 61000 series sets out requirements for the EMC of electric motors, including minimum requirements for electromagnetic emissions and immunity. Manufacturers must ensure that their electric motors meet these EMC requirements to avoid interfering with other electronic devices and affecting their performance.
To navigate the complex landscape of electric motor regulations, manufacturers can take several steps. First, they must stay up-to-date with the latest developments in regulations and standards, including changes to the IEC 60034 and IEC 61000 series. Second, they must conduct thorough testing and validation of their electric motors to ensure compliance with regulations. Third, they must ensure that their electric motors are designed and constructed to meet regulatory requirements, including efficiency, noise, and EMC requirements.
By following these steps, manufacturers can ensure compliance with electric motor regulations and avoid potential liabilities. This is critical for building trust with consumers and promoting the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
In addition to regulatory compliance, manufacturers can also benefit from standardization and certification programs. The IEC 60034 series provides a framework for the standardization of electric motors, including requirements for efficiency, noise, and EMC. Manufacturers can also obtain certification from organizations such as the IEC and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which can help to demonstrate compliance with regulations and improve market access.
The Role of International Standards in Shaping Electric Vehicle Policy
International standards play a crucial role in shaping electric vehicle policy, as they provide a framework for the development of national and regional regulations. Organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) are key players in the development of international standards for electric vehicles.
The IEC is responsible for developing standards for electrical and electronic technologies, including electric vehicles. The IEC 60034 series, for example, sets out requirements for the safety and performance of electric motors, while the IEC 62196 series sets out requirements for electric vehicle charging systems. These standards provide a framework for manufacturers to design and test their products, ensuring that they meet minimum safety and performance requirements.
The ISO is also involved in the development of international standards for electric vehicles, particularly in the areas of safety and environmental sustainability. The ISO 26262 series, for example, sets out requirements for the functional safety of electric vehicles, while the ISO 14040 series sets out requirements for the environmental sustainability of electric vehicles.
These international standards have a significant impact on national and regional regulations, as they provide a framework for policymakers to develop regulations that are consistent with international best practices. In the European Union, for example, the IEC 60034 series is referenced in the EU’s Low Voltage Directive, which sets out requirements for the safety of electrical equipment, including electric vehicles.
In the United States, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) references the IEC 62196 series in its regulations for electric vehicle charging systems. Similarly, in China, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology references the IEC 60034 series in its regulations for electric vehicle safety.
The use of international standards in electric vehicle policy has several benefits, including improved safety, increased efficiency, and reduced costs. By adopting international standards, manufacturers can ensure that their products meet minimum safety and performance requirements, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries. Additionally, international standards can facilitate trade and commerce, as they provide a common language and framework for manufacturers and policymakers to work together.
However, the use of international standards in electric vehicle policy also has some challenges, including the need for coordination and cooperation between different countries and organizations. To address these challenges, it is essential to have a clear understanding of the international standards that apply to electric vehicles and to work together to develop regulations that are consistent with these standards.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure: Standards and Regulations
The development of electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, the need for standardized and regulated charging infrastructure becomes increasingly important. In this context, standards and regulations play a vital role in ensuring the safe, efficient, and interoperable charging of electric vehicles.
One of the key standards governing EV charging infrastructure is the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) J1772 standard, which defines the requirements for Level 1 and Level 2 charging. This standard ensures that EVs can be charged safely and efficiently using a standardized connector. Additionally, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 62196 standard provides guidelines for the safety and performance of EV charging systems.
In terms of regulations, the US Department of Energy has established guidelines for EV charging infrastructure, including requirements for charging speed, payment systems, and accessibility. Similarly, the European Union has implemented regulations governing the deployment of EV charging infrastructure, including requirements for charging point operators and network providers.
The standardization of connector types is also an important aspect of EV charging infrastructure. The Combined Charging System (CCS) is a widely adopted standard that enables fast charging of EVs. CCS combines the J1772 connector with a DC Fast Charging connector, allowing for charging speeds of up to 350 kW. Other connector types, such as the Tesla Supercharger and the CHAdeMO connector, are also widely used.
Payment systems are another critical aspect of EV charging infrastructure. Standardized payment systems, such as the Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP), enable seamless communication between charging points and network providers. This allows EV owners to easily pay for charging sessions using a variety of payment methods.
The development of smart charging infrastructure is also becoming increasingly important. Smart charging systems use advanced technologies, such as Wi-Fi and cellular connectivity, to optimize charging sessions and reduce strain on the grid. These systems can also provide real-time information on charging point availability and pricing.
In conclusion, the standardization and regulation of EV charging infrastructure are critical for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. By establishing standardized connector types, payment systems, and safety protocols, governments and industry stakeholders can ensure the safe, efficient, and interoperable charging of electric vehicles. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, the importance of standardized and regulated charging infrastructure will only continue to increase.
Case Study: How Tesla is Driving Electric Vehicle Standardization
Tesla, a pioneer in the electric vehicle (EV) industry, has been at the forefront of driving standardization in the sector. The company’s efforts to promote standardization have been instrumental in shaping the EV landscape and paving the way for widespread adoption. In this case study, we will examine Tesla’s contributions to EV standardization, focusing on charging infrastructure and battery technology.
One of Tesla’s most significant contributions to EV standardization is its development of the Supercharger network. The Supercharger is a fast-charging system that enables Tesla owners to charge their vehicles quickly and efficiently. The Supercharger network has become a de facto standard for fast charging, with many other manufacturers adopting similar technology. Tesla’s commitment to standardizing fast charging has helped to alleviate range anxiety, a major barrier to EV adoption.
Tesla has also played a crucial role in standardizing battery technology. The company’s battery management system (BMS) is widely regarded as one of the most advanced in the industry. Tesla’s BMS has been adopted by other manufacturers, and its technology has helped to drive the development of more efficient and cost-effective battery solutions. Furthermore, Tesla’s efforts to standardize battery formats have enabled the widespread adoption of EVs, as manufacturers can now design vehicles around standardized battery packs.
In addition to its technical contributions, Tesla has also been a vocal advocate for EV standardization. The company has worked closely with regulatory bodies and industry organizations to promote the adoption of EV-friendly policies and standards. Tesla’s efforts have helped to raise awareness about the importance of standardization in the EV industry and have encouraged other manufacturers to follow suit.
Tesla’s commitment to standardization has also extended to its charging connector. The company’s decision to adopt the Combined Charging System (CCS) connector has helped to drive the adoption of this standard across the industry. CCS is now widely regarded as the de facto standard for EV charging, and its adoption has enabled the development of more efficient and cost-effective charging solutions.
In conclusion, Tesla’s efforts to drive EV standardization have been instrumental in shaping the industry. The company’s commitment to standardizing charging infrastructure, battery technology, and connectors has helped to alleviate range anxiety, drive the adoption of EVs, and promote the development of more efficient and cost-effective solutions. As the EV industry continues to evolve, Tesla’s leadership in standardization will remain a critical factor in its success.
The Future of Electric Vehicle Regulations: Trends and Predictions
As the electric vehicle (EV) industry continues to evolve, regulations and standards are expected to play a crucial role in shaping its future. Several trends and predictions are emerging that will impact the development of electric vehicle and electric motor standards and regulations. One of the key trends is the increasing focus on autonomous vehicles, which will require new safety standards and regulations to ensure public safety. Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, which enables EVs to supply energy back to the grid, is another area that will require new standards and regulations to ensure safe and efficient operation.
Sustainable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are also expected to play a larger role in the EV industry, driving the need for new standards and regulations to ensure the efficient integration of these sources into the grid. Additionally, the growing demand for EVs is expected to lead to increased scrutiny of their environmental impact, driving the development of new regulations and standards related to recycling and waste management.
Another trend that is expected to shape the future of EV regulations is the increasing importance of cybersecurity. As EVs become more connected and reliant on software, the risk of cyber threats will grow, requiring new standards and regulations to ensure the security of EV systems. The development of new battery technologies, such as solid-state batteries, is also expected to drive the need for new standards and regulations related to safety and performance.
Furthermore, the growth of the EV industry is expected to lead to increased international cooperation and harmonization of standards and regulations. This will enable manufacturers to design and build EVs that can be sold globally, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) are expected to play a key role in developing global standards for EVs and electric motors.
In terms of predictions, it is expected that the next decade will see significant advancements in EV technology, including the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles and the development of new battery technologies. The growth of the EV industry is also expected to drive increased investment in charging infrastructure, leading to the development of new standards and regulations related to charging systems and payment methods.
Overall, the future of electric vehicle regulations will be shaped by a combination of technological advancements, environmental concerns, and international cooperation. As the industry continues to evolve, it is essential that manufacturers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders work together to develop standards and regulations that promote the safe and efficient development of EVs and electric motors.
Conclusion: Navigating the Evolving Landscape of Electric Vehicle Regulations
In conclusion, the world of electric vehicle regulations is complex and constantly evolving. As the industry continues to grow and mature, it is essential that manufacturers, policymakers, and industry stakeholders stay up-to-date with the latest developments in electric vehicle and electric motor standards and regulations. By understanding the importance of standardization, ensuring compliance with safety standards, and navigating the regulatory landscape, industry players can promote the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and drive the transition to a more sustainable transportation sector.
As we look to the future, it is clear that electric vehicle regulations will play a critical role in shaping the industry’s development. By prioritizing standardization, safety, and sustainability, we can create a regulatory environment that supports the growth of the electric vehicle market and helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Ultimately, the success of the electric vehicle industry will depend on the ability of industry stakeholders to work together to promote the development of a comprehensive and supportive regulatory framework.
By working together, we can create a future where electric vehicles are safe, efficient, and accessible to all. A future where the benefits of electric vehicle technology are realized, and the environmental impact of transportation is minimized. The journey ahead will be complex, but with a deep understanding of electric vehicle and electric motor standards and regulations, we can navigate the evolving landscape and create a brighter future for generations to come.
In the end, the widespread adoption of electric vehicles will require a concerted effort from industry stakeholders, policymakers, and consumers. By prioritizing standardization, safety, and sustainability, we can create a regulatory environment that supports the growth of the electric vehicle market and helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. As we move forward, it is essential that we continue to monitor and adapt to the evolving landscape of electric vehicle regulations, ensuring that we are always working towards a safer, more efficient, and more sustainable transportation sector.