What Makes a Photo High Resolution?
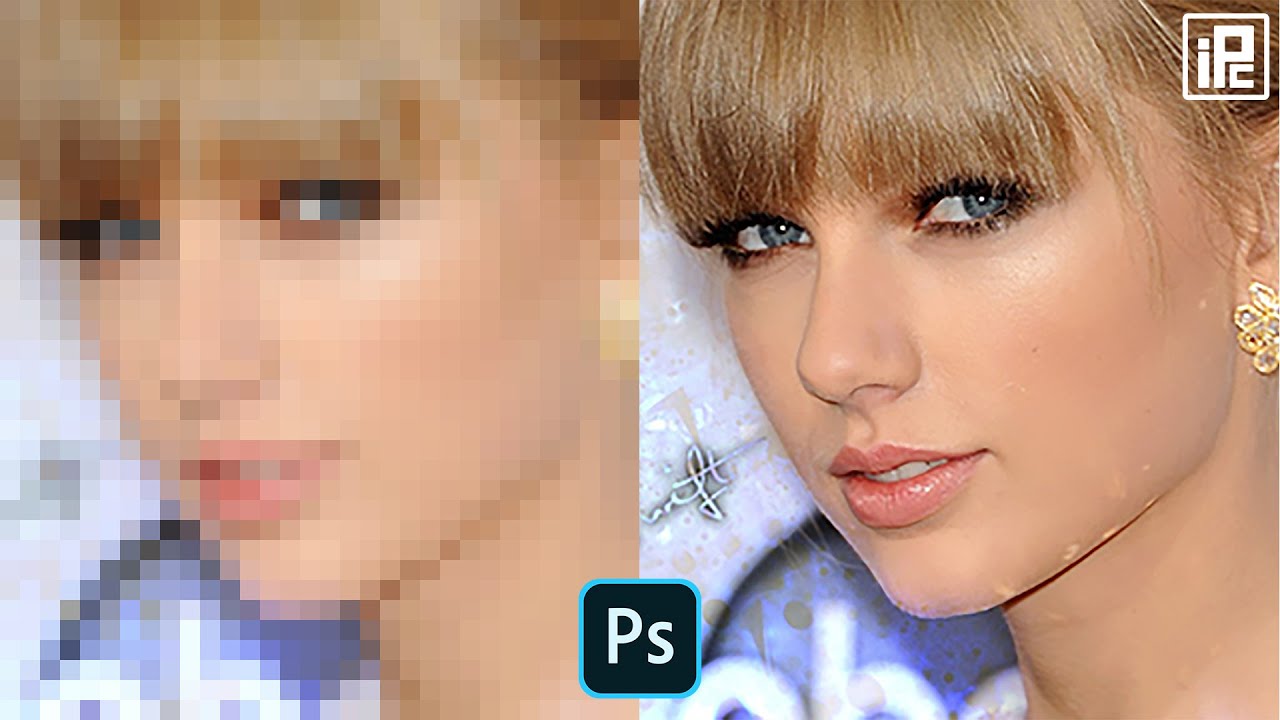
Image resolution is a critical factor in determining the quality of a photo. It refers to the number of pixels that make up an image, with higher resolutions indicating a greater number of pixels. A high-resolution image is typically characterized by a high pixel density, which enables it to display fine details and subtle color gradations. But what exactly makes a photo high resolution, and how can you determine if an image meets this standard?
In general, a high-resolution image is one that has a high pixel count, typically in the range of several million pixels. For example, a 12-megapixel camera can capture images with a resolution of 4000 x 3000 pixels, while a 24-megapixel camera can capture images with a resolution of 6000 x 4000 pixels. However, pixel count alone is not the only factor that determines image resolution. Other factors, such as the image sensor size, lens quality, and image processing algorithms, also play a crucial role in determining the overall quality of the image.
So, how do you know if a photo is high resolution? One way to determine this is to check the image’s pixel dimensions. If the image has a high pixel count and is displayed at a reasonable size, it is likely to be a high-resolution image. Another way to check is to look for images that are labeled as “high resolution” or “high res” by the photographer or image provider. Additionally, you can use online tools or image editing software to check the image’s resolution and determine if it meets your needs.
High-resolution images are often necessary for certain applications, such as printing, cropping, or enlarging. For example, if you want to print a large poster or billboard, you will need a high-resolution image to ensure that the image remains clear and detailed. Similarly, if you want to crop a portion of an image or enlarge it to a larger size, a high-resolution image will provide the necessary detail and clarity.
In contrast, low-resolution images are often sufficient for web use or other applications where image size is not critical. However, even in these cases, using high-resolution images can provide a number of benefits, including improved image quality, increased flexibility, and enhanced visual impact.
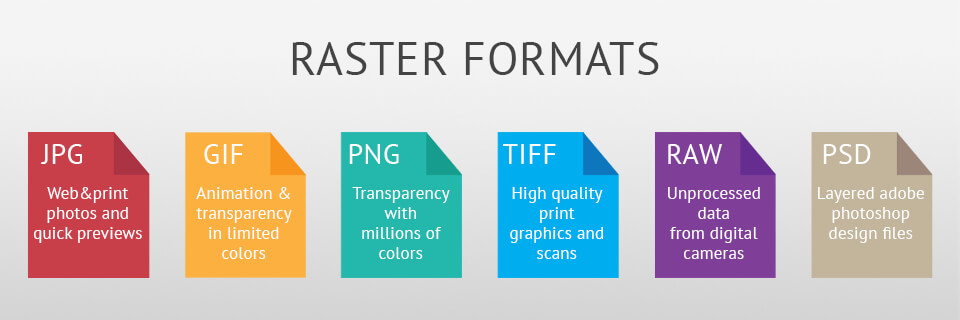
Understanding Image File Formats
When it comes to working with high-resolution images, understanding the different image file formats is crucial. Each format has its own strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right one can significantly impact the quality of the final image. In this section, we’ll explore the most common image file formats, including JPEG, TIFF, and PNG, and discuss their pros and cons.
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group) is one of the most widely used image file formats. It’s ideal for web use, as it compresses images to reduce file size while maintaining acceptable image quality. However, JPEG compression can lead to a loss of detail and color accuracy, making it less suitable for high-end printing or professional applications.
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is a popular choice among professional photographers and graphic designers. It’s an uncompressed format, which means it retains all the image data, resulting in a higher quality image. However, TIFF files are typically larger in size, making them more difficult to share and store.
PNG (Portable Network Graphics) is a versatile format that’s ideal for web use and graphic design. It’s a lossless format, which means it retains all the image data, and it supports transparent backgrounds, making it perfect for logos and icons. However, PNG files can be larger in size than JPEGs, and they may not be suitable for high-end printing.
Other image file formats, such as PSD (Photoshop Document) and RAW, are also worth mentioning. PSD is a proprietary format used by Adobe Photoshop, and it’s ideal for editing and manipulating images. RAW, on the other hand, is a format that captures the raw data from the camera’s sensor, providing maximum flexibility during post-processing.
When choosing an image file format, consider the intended use of the image. If you’re sharing images online, JPEG or PNG may be a good choice. However, if you’re printing high-end images or working with professional applications, TIFF or PSD may be a better option. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each format, you can ensure that your images look their best, regardless of the application.
It’s also worth noting that some image file formats are more compatible with certain software or devices than others. For example, some cameras may only support JPEG or RAW, while others may support multiple formats. By understanding the compatibility of each format, you can avoid compatibility issues and ensure that your images are always accessible.
How to Check the Resolution of a Photo
Checking the resolution of a photo is a straightforward process that can be done using various methods. In this section, we’ll explore how to check the resolution of a photo using image editing software, online tools, and camera settings.
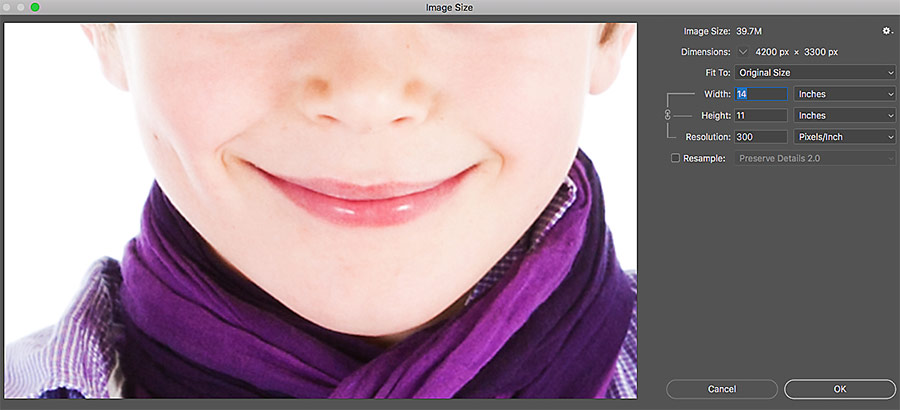
Using Image Editing Software:
Most image editing software, such as Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom, allows you to check the resolution of a photo by viewing the image’s metadata. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Open the image in your image editing software.
2. Go to the “File” menu and select “Properties” or “Metadata.”
3. Look for the “Resolution” or “Image Size” section, which will display the image’s pixel dimensions and resolution.
Using Online Tools:
There are several online tools available that allow you to check the resolution of a photo without having to download any software. One popular tool is the “Image Size” tool on the website ResizeImage.net. To use this tool, follow these steps:
1. Go to ResizeImage.net and click on the “Image Size” tool.
2. Upload your image to the website or enter the image’s URL.
3. The tool will display the image’s pixel dimensions and resolution.
Using Camera Settings:
If you’re using a digital camera, you can check the resolution of a photo by viewing the camera’s settings. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Go to the camera’s menu and select the “Image Size” or “Resolution” option.
2. Look for the current resolution setting, which will be displayed in pixels (e.g. 4000 x 3000).
By using one of these methods, you can easily check the resolution of a photo and determine if it’s high resolution or not. Remember, if you’re unsure about the resolution of a photo, you can always check the image’s metadata or use an online tool to verify the resolution.
Now that you know how to check the resolution of a photo, you can use this knowledge to ensure that your images are always high quality and suitable for your intended use. Whether you’re a professional photographer or just starting out, understanding image resolution is an essential skill that will help you take your photography to the next level.
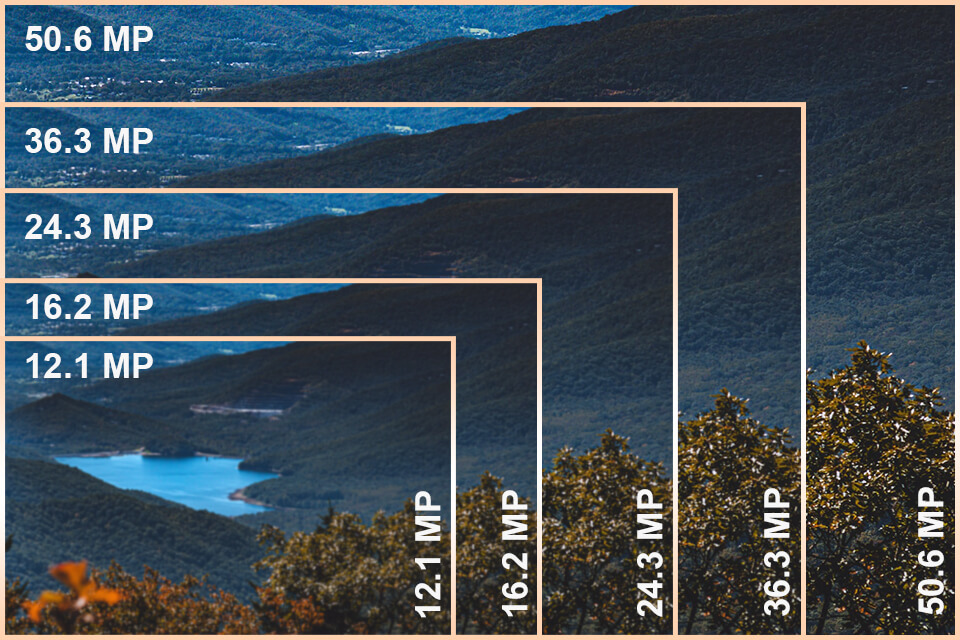
The Role of Megapixels in Image Resolution
Megapixels are a key factor in determining the resolution of an image. But what exactly are megapixels, and how do they impact image quality? In this section, we’ll explore the relationship between megapixels and image resolution, and discuss how megapixels affect the quality of a photo.
A megapixel is a unit of measurement that represents one million pixels. In the context of digital cameras, megapixels refer to the number of pixels that make up the camera’s image sensor. The more megapixels a camera has, the higher the resolution of the images it produces.
However, it’s essential to note that megapixels are not the only factor that determines image quality. Other factors, such as the camera’s lens quality, image processing algorithms, and sensor size, also play a crucial role in determining the overall quality of the image.
So, how many megapixels do you need to produce high-quality images? The answer depends on the intended use of the image. For example, if you’re shooting for web use, a camera with 12-16 megapixels may be sufficient. However, if you’re shooting for high-end printing or professional applications, a camera with 24-36 megapixels or more may be necessary.
It’s also worth noting that more megapixels don’t always mean better image quality. In fact, having too many megapixels can actually lead to a decrease in image quality due to the increased noise and decreased dynamic range.
For example, landscape photography often requires a high number of megapixels to capture the intricate details of the scene. In this case, a camera with 36-50 megapixels or more may be necessary to produce high-quality images.
On the other hand, portrait photography may not require as many megapixels, as the focus is on capturing the subject’s features and expression rather than the intricate details of the scene. In this case, a camera with 12-24 megapixels may be sufficient.
In conclusion, megapixels play a crucial role in determining the resolution of an image, but they are not the only factor that determines image quality. By understanding the relationship between megapixels and image resolution, you can make informed decisions about the type of camera and equipment you need to produce high-quality images.
Common Misconceptions About High Resolution Images
There are several common misconceptions about high resolution images that can lead to confusion and misinformation. In this section, we’ll address some of these myths and provide examples to debunk them.
Myth #1: All high resolution images are large in file size.
This is not necessarily true. While high resolution images can be larger in file size, it’s not always the case. For example, a high resolution image that is heavily compressed can
Common Misconceptions About High Resolution Images
There are several common misconceptions about high resolution images that can lead to confusion and misinformation. In this section, we’ll address some of these myths and provide examples to debunk them.
Myth #1: All high resolution images are large in file size.
This is not necessarily true. While high resolution images can be larger in file size, it’s not always the case. For example, a high resolution image that is heavily compressed can
Common Misconceptions About High Resolution Images
There are several common misconceptions about high resolution images that can lead to confusion and misinformation. In this section, we’ll address some of these myths and provide examples to debunk them.
Myth #1: All high resolution images are large in file size.
This is not necessarily true. While high resolution images can be larger in file size, it’s not always the case. For example, a high resolution image that is heavily compressed can
Common Misconceptions About High Resolution Images
There are several common misconceptions about high resolution images that can lead to confusion and misinformation. In this section, we’ll address some of these myths and provide examples to debunk them.
Myth #1: All high resolution images are large in file size.
This is not necessarily true. While high resolution images can be larger in file size, it’s not always the case. For example, a high resolution image that is heavily compressed can