Understanding Image Resolution and Quality
Image resolution and quality are crucial factors to consider when working with digital images. Resolution refers to the number of pixels that make up an image, while quality refers to the overall clarity and detail of the image. When an image is resized, its resolution and quality can be affected, leading to a loss of detail and clarity. This is why it’s essential to understand how to resize an image without losing quality.
In digital imaging, pixels are the building blocks of an image. The more pixels an image has, the higher its resolution and the more detailed it will be. However, when an image is resized, the number of pixels can change, affecting the image’s resolution and quality. To preserve image quality, it’s crucial to use the correct resizing techniques and algorithms.
Resizing an image can be a complex process, especially when trying to maintain its quality. When an image is enlarged, new pixels are created, which can lead to a loss of detail and clarity. On the other hand, when an image is reduced in size, pixels are discarded, which can also affect the image’s quality. To avoid these issues, it’s essential to use image editing software that can resize images without losing quality.
One of the most common mistakes people make when resizing images is using the wrong software or techniques. This can lead to a loss of image quality, making the image look pixelated or blurry. To avoid this, it’s crucial to use image editing software that can resize images using advanced algorithms, such as bicubic or bilinear interpolation. These algorithms can help preserve image quality by creating new pixels that match the surrounding pixels, reducing the loss of detail and clarity.
In addition to using the correct software and techniques, it’s also essential to understand the different file formats and their compression algorithms. File formats like JPEG, PNG, and TIFF use different compression algorithms that can affect image quality. For example, JPEG uses a lossy compression algorithm that discards some of the image data, which can lead to a loss of quality. On the other hand, PNG uses a lossless compression algorithm that preserves the image data, making it a better choice for images that require high quality.
By understanding image resolution, quality, and the different file formats and compression algorithms, you can resize images without losing quality. This is especially important when working with images for web and print, where image quality can make a significant difference in the overall appearance of the image.
Choosing the Right Image Editing Software
When it comes to resizing images without losing quality, the right image editing software can make all the difference. There are many software options available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. In this section, we’ll explore some of the most popular image editing software and their capabilities.
Adobe Photoshop is one of the most widely used image editing software, and for good reason. It offers a wide range of features and tools, including advanced resizing algorithms and support for multiple file formats. Photoshop is particularly useful for resizing images for print, as it allows for precise control over resolution and color mode.
GIMP is another popular image editing software that offers many of the same features as Photoshop, but at a lower cost. It’s a great option for those on a budget or who don’t need all the advanced features of Photoshop. GIMP also supports multiple file formats and offers a range of resizing algorithms.
Canva is a cloud-based image editing software that’s designed specifically for non-designers. It’s easy to use and offers a range of templates and design tools. Canva is a great option for those who need to resize images for web use, as it allows for easy export to various file formats and resolutions.
When choosing an image editing software, it’s essential to consider your specific needs and goals. If you’re resizing images for print, you’ll want software that offers precise control over resolution and color mode. If you’re resizing images for web use, you’ll want software that allows for easy export to various file formats and resolutions.
Regardless of which software you choose, it’s essential to understand how to use it effectively. This includes learning about the different resizing algorithms and how to apply them to your images. By choosing the right software and learning how to use it, you can ensure that your images are resized without losing quality.
In the next section, we’ll explore the step-by-step process of resizing an image using your chosen software. We’ll cover the importance of using the correct resizing algorithm and how to apply it to your images.
How to Resize an Image without Losing Quality
Resizing an image without losing quality requires careful consideration of the resizing algorithm and technique used. The goal is to maintain the image’s original detail and clarity while adjusting its size. To achieve this, follow these steps:
Step 1: Choose the Right Resizing Algorithm
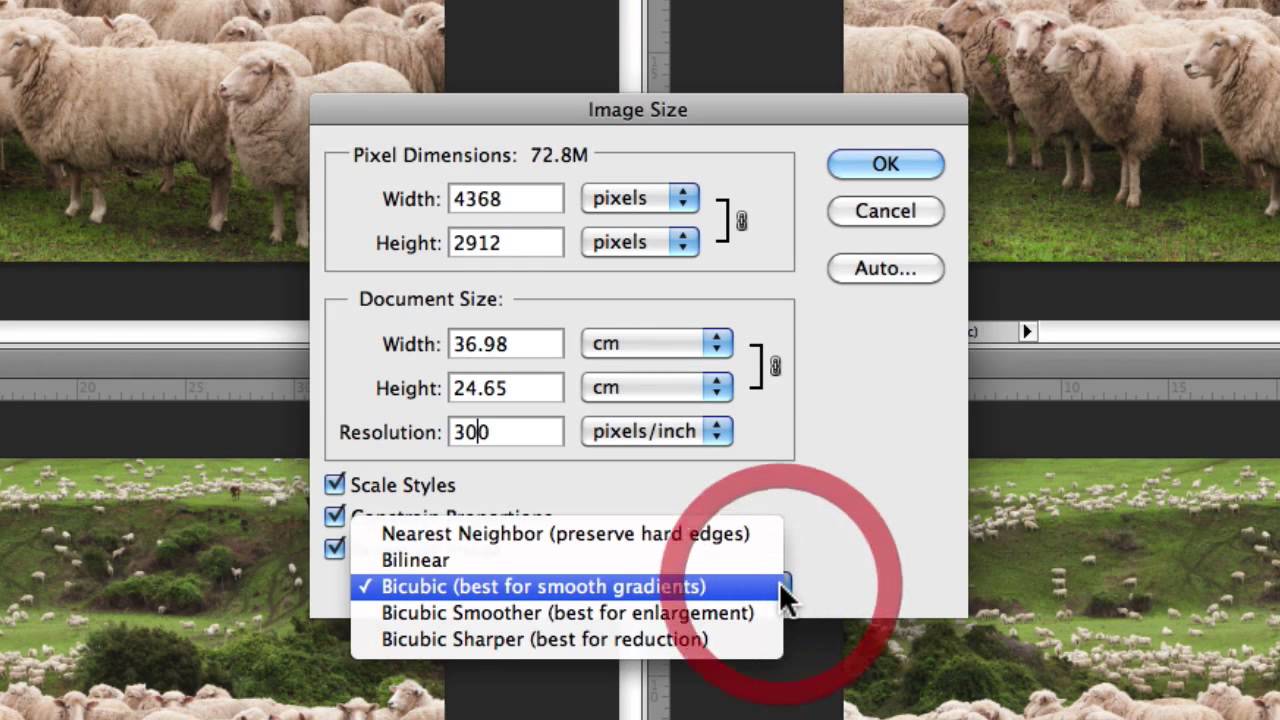
Most image editing software offers various resizing algorithms, including nearest neighbor, bilinear, and bicubic interpolation. Bicubic interpolation is generally considered the best option for resizing images without losing quality, as it produces smoother and more detailed results.
Step 2: Select the Correct Resampling Method
When resizing an image, it’s essential to select the correct resampling method. The resampling method determines how the image is resized, and the wrong method can lead to a loss of quality. The most common resampling methods are:
- Nearest Neighbor: This method is fast but can produce a “blocky” or “pixelated” effect.
- Bilinear: This method is a good balance between speed and quality, but may not produce the best results for large resizing operations.
- Bicubic: This method is the most accurate and produces the best results, but can be slower than the other methods.
Step 3: Resize the Image
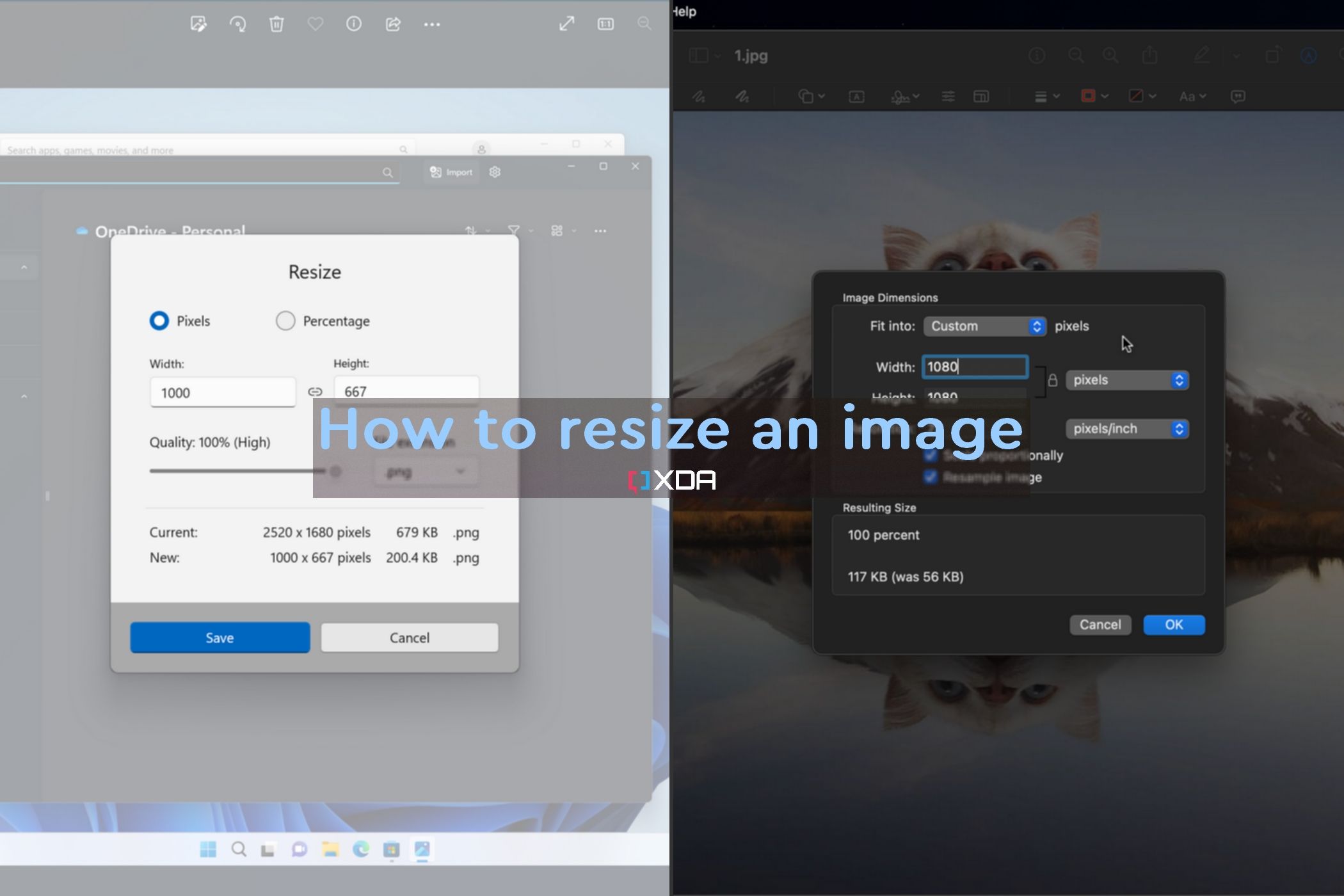
Once you’ve selected the correct resizing algorithm and resampling method, you can resize the image. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open the image in your chosen image editing software.
- Select the “Image” or “Picture” menu and choose “Resize” or “Image Size.”
- Enter the new dimensions for the image, making sure to maintain the original aspect ratio.
- Select the bicubic interpolation algorithm and the correct resampling method.
- Click “OK” to apply the changes.
Step 4: Save the Resized Image
After resizing the image, save it in a format that supports the desired level of compression. JPEG is a good choice for web use, while TIFF or PNG may be better for print or high-quality applications.
By following these steps and using the correct resizing algorithm and technique, you can resize an image without losing quality. Remember to always work with a copy of the original image and avoid over-compressing the resized image to ensure the best possible results. When searching for information on how do I resize an image without losing quality, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project and choose the best approach for your needs.
Understanding Compression and File Formats
When resizing an image, it’s essential to consider the file format and compression algorithm used, as they can significantly impact the image’s quality. Different file formats have varying levels of compression, which can affect the image’s detail and clarity.
Common File Formats for Images
The most common file formats for images are JPEG, PNG, and TIFF. Each format has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of format depends on the intended use of the image.
- JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group): JPEG is a compressed format that uses a lossy compression algorithm, which discards some of the image data to reduce the file size. JPEG is suitable for web use, as it produces relatively small file sizes. However, it’s not ideal for images that require high quality, as the compression can lead to a loss of detail.
- PNG (Portable Network Graphics): PNG is an uncompressed format that uses a lossless compression algorithm, which preserves the image data. PNG is suitable for images that require high quality, such as graphics and logos. However, it produces larger file sizes than JPEG.
- TIFF (Tagged Image File Format): TIFF is an uncompressed format that uses a lossless compression algorithm. TIFF is suitable for high-quality images, such as those used in print or professional photography. However, it produces large file sizes.
Compression Algorithms
Compression algorithms are used to reduce the file size of an image. There are two types of compression algorithms: lossy and lossless.
- Lossy Compression: Lossy compression algorithms discard some of the image data to reduce the file size. JPEG uses a lossy compression algorithm, which can lead to a loss of detail and quality.
- Lossless Compression: Lossless compression algorithms preserve the image data and do not discard any information. PNG and TIFF use lossless compression algorithms, which preserve the image quality.
Choosing the Right File Format and Compression Algorithm
When resizing an image, it’s essential to choose the right file format and compression algorithm to preserve the image quality. If you’re resizing an image for web use, JPEG may be a suitable choice. However, if you’re resizing an image for print or professional use, PNG or TIFF may be a better option.
Best Practices for Compression and File Formats
To preserve image quality when resizing, follow these best practices:
- Use the correct file format for the intended use of the image.
- Use a lossless compression algorithm to preserve the image data.
- Avoid over-compressing the image, as it can lead to a loss of detail and quality.
- Use image editing software that allows you to adjust the compression level and algorithm.
By understanding the different file formats and compression algorithms, you can make informed decisions when resizing an image. Remember to consider the intended use of the image and choose the right file format and compression algorithm to preserve the image quality. When searching for information on how do I resize an image without losing quality, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project and choose the best approach for your needs.
Best Practices for Resizing Images
Resizing images can be a delicate process, and it’s essential to follow best practices to preserve image quality. Here are some tips to help you resize images like a pro:
Work with a Copy of the Original Image
Always work with a copy of the original image, rather than the original itself. This ensures that you can revert to the original image if something goes wrong during the resizing process.
Use the Correct Aspect Ratio
Make sure to maintain the correct aspect ratio when resizing an image. This ensures that the image doesn’t become distorted or stretched. Most image editing software allows you to lock the aspect ratio, making it easier to resize images without compromising their quality.
Avoid Over-Compression
Over-compression can lead to a loss of image quality, making it essential to avoid it when resizing images. Use the correct compression algorithm and adjust the compression level to achieve the desired balance between file size and image quality.
Use Image Editing Software with Advanced Resizing Features
Use image editing software that offers advanced resizing features, such as Adobe Photoshop or GIMP. These software programs allow you to adjust the resizing algorithm, compression level, and other settings to achieve optimal results.
Save Images in the Correct File Format
Save images in the correct file format for the intended use. For example, JPEG is suitable for web use, while PNG or TIFF may be better for print or professional use.
Check Image Quality Before Saving
Always check the image quality before saving the resized image. This ensures that the image meets your quality standards and that you can make any necessary adjustments before saving.
Use Batch Processing for Multiple Images
If you need to resize multiple images, use batch processing to save time and effort. Most image editing software offers batch processing features that allow you to resize multiple images at once.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your resized images maintain their quality and meet your needs. Remember to always work with a copy of the original image, use the correct aspect ratio, and avoid over-compression. When searching for information on how do I resize an image without losing quality, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project and choose the best approach for your needs.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Resizing Images
Resizing images can be a complex process, and it’s easy to make mistakes that can compromise image quality. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when resizing images:
Using the Wrong Software
Using the wrong software can lead to poor image quality and a loss of detail. Make sure to use image editing software that offers advanced resizing features, such as Adobe Photoshop or GIMP.
Ignoring Aspect Ratio
Ignoring the aspect ratio can lead to distorted images that lose their original proportions. Make sure to lock the aspect ratio when resizing images to maintain their original proportions.
Over-Compressing Images
Over-compressing images can lead to a loss of detail and image quality. Make sure to adjust the compression level to achieve the desired balance between file size and image quality.
Not Saving Images in the Correct File Format
Not saving images in the correct file format can lead to poor image quality and compatibility issues. Make sure to save images in the correct file format for the intended use, such as JPEG for web use or PNG for print use.
Not Checking Image Quality Before Saving
Not checking image quality before saving can lead to poor image quality and a loss of detail. Make sure to check the image quality before saving to ensure that it meets your quality standards.
Using Low-Quality Images
Using low-quality images can lead to poor image quality and a loss of detail. Make sure to use high-quality images that are suitable for resizing.
Not Considering the Intended Use of the Image
Not considering the intended use of the image can lead to poor image quality and compatibility issues. Make sure to consider the intended use of the image and adjust the resizing settings accordingly.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your resized images maintain their quality and meet your needs. Remember to use the right software, lock the aspect ratio, and avoid over-compressing images. When searching for information on how do I resize an image without losing quality, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project and choose the best approach for your needs.
Resizing Images for Web and Print
Resizing images for web and print requires different approaches, as each medium has its own unique requirements. Understanding these differences is crucial to ensure that your images look their best in both digital and physical formats.
Resizing Images for Web
When resizing images for web use, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Resolution: Web images typically require a lower resolution than print images, as they will be viewed on a screen. A resolution of 72 dpi is standard for web use.
- Color Mode: Web images should be in RGB color mode, as this is the standard for digital displays.
- File Format: JPEG is a popular file format for web use, as it offers a good balance between file size and image quality.
Resizing Images for Print
When resizing images for print use, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Resolution: Print images typically require a higher resolution than web images, as they will be viewed in a physical format. A resolution of 300 dpi is standard for print use.
- Color Mode: Print images should be in CMYK color mode, as this is the standard for physical printing.
- File Format: TIFF or PSD are popular file formats for print use, as they offer high image quality and flexibility.
Key Differences Between Web and Print
The key differences between resizing images for web and print are:
- Resolution: Web images require a lower resolution than print images.
- Color Mode: Web images should be in RGB color mode, while print images should be in CMYK color mode.
- File Format: Web images are typically in JPEG format, while print images are typically in TIFF or PSD format.
Best Practices for Resizing Images for Web and Print
To ensure that your images look their best in both digital and physical formats, follow these best practices:
- Use the correct resolution and color mode for the intended medium.
- Choose the right file format for the intended medium.
- Use image editing software that offers advanced resizing features, such as Adobe Photoshop or GIMP.
By understanding the differences between resizing images for web and print, you can ensure that your images look their best in both digital and physical formats. Remember to use the correct resolution, color mode, and file format for the intended medium, and follow best practices for resizing images. When searching for information on how do I resize an image without losing quality, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your project and choose the best approach for your needs.
Conclusion: Preserving Image Quality through Proper Resizing
Resizing images can be a complex process, but by following the steps and best practices outlined in this article, you can preserve image quality and achieve optimal results. Remember to choose the right image editing software, use the correct resizing algorithm, and avoid common mistakes such as over-compression and ignoring aspect ratio.
Key Takeaways
The key takeaways from this article are:
- Understanding image resolution and quality is essential for preserving image quality when resizing.
- Choosing the right image editing software is crucial for achieving optimal results.
- Using the correct resizing algorithm, such as bicubic or bilinear interpolation, is essential for preserving image quality.
- Avoiding common mistakes such as over-compression and ignoring aspect ratio is crucial for achieving optimal results.
- Resizing images for web and print requires different approaches, and understanding these differences is essential for achieving optimal results.
Final Tips for Achieving Optimal Results
To achieve optimal results when resizing images, follow these final tips:
- Always work with a copy of the original image.
- Use the correct aspect ratio and resolution for the intended medium.
- Avoid over-compression and use the correct file format for the intended medium.
- Use image editing software that offers advanced resizing features, such as Adobe Photoshop or GIMP.
By following these tips and best practices, you can preserve image quality and achieve optimal results when resizing images. Remember to always consider the specific requirements of your project and choose the best approach for your needs. When searching for information on how do I resize an image without losing quality, this article provides a comprehensive guide to help you achieve optimal results.