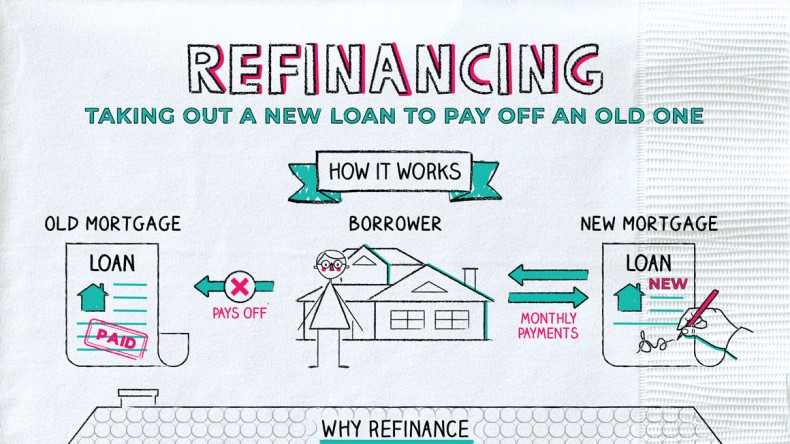
Understanding the Refinancing Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Refinancing a house can be a complex and overwhelming process, but it can also be a great way to save money, tap into home equity, or switch to a more favorable loan term. To help homeowners navigate this process, it’s essential to understand the basics of refinancing, including the reasons why people refinance, the benefits of refinancing, and the different types of refinancing options available.
So, how do you refinance a house? The refinancing process typically begins with a decision to refinance, often motivated by a desire to lower monthly mortgage payments, switch from an adjustable-rate to a fixed-rate loan, or tap into home equity to fund home improvements or pay off debt. Homeowners may also refinance to remove private mortgage insurance (PMI) or to take advantage of lower interest rates.
There are several types of refinancing options available, including rate-and-term refinancing, cash-out refinancing, and cash-in refinancing. Rate-and-term refinancing involves replacing an existing loan with a new loan that has a different interest rate or repayment term. Cash-out refinancing involves taking out a new loan that is larger than the existing loan, allowing homeowners to tap into their home equity. Cash-in refinancing involves paying down the loan balance with a new loan that has a lower balance.
When considering refinancing, it’s essential to weigh the benefits against the costs. Refinancing can save homeowners money on interest payments, reduce monthly mortgage payments, or provide access to cash for home improvements or debt repayment. However, refinancing also involves costs, such as origination fees, appraisal fees, and closing costs.
By understanding the refinancing process and the different types of refinancing options available, homeowners can make informed decisions about whether refinancing is right for them. Whether you’re looking to save money, tap into home equity, or switch to a more favorable loan term, refinancing can be a great way to achieve your financial goals.
Assessing Your Financial Situation: Are You Ready to Refinance?
Before diving into the refinancing process, it’s essential to assess your financial situation to determine if refinancing is right for you. This involves evaluating several key factors, including your credit score, income, debt, and equity in the home.
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining the interest rate you’ll qualify for and whether you’ll be approved for refinancing. A good credit score can help you qualify for lower interest rates, while a poor credit score may lead to higher interest rates or even loan rejection. To improve your credit score, focus on paying bills on time, reducing debt, and avoiding new credit inquiries.
Income is another critical factor in the refinancing process. Lenders will typically require proof of income to ensure you can afford the new loan payments. If you’re self-employed or have a variable income, you may need to provide additional documentation to support your income claims.
Debt is also a significant consideration when refinancing. High levels of debt can make it challenging to qualify for refinancing, as lenders may view you as a higher risk. To improve your chances of approval, focus on reducing debt by paying off high-interest loans and credit cards.
Equity in the home is also essential when refinancing. If you have a significant amount of equity in your home, you may be able to tap into it through a cash-out refinance. However, if you have little equity, you may not qualify for refinancing or may be required to pay private mortgage insurance (PMI).
By carefully evaluating your financial situation, you can determine if refinancing is right for you and make informed decisions about the refinancing process. Remember to consider all the costs involved, including interest rates, fees, and closing costs, to ensure you’re making the best decision for your financial situation.
When considering how to refinance a house, it’s essential to take a holistic approach, considering all aspects of your financial situation. By doing so, you can make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes that can impact your financial well-being.
Choosing the Right Refinancing Option: Fixed-Rate, Adjustable-Rate, or Cash-Out?
When it comes to refinancing a house, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is choosing the right refinancing option. With so many options available, it can be overwhelming to determine which one is best for your situation. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of refinancing options, including fixed-rate, adjustable-rate, and cash-out refinancing, to help you make an informed decision.
Fixed-rate refinancing is a popular option for homeowners who want to lock in a low interest rate for the life of the loan. With a fixed-rate loan, your interest rate and monthly payment will remain the same for the entire term of the loan, typically 15 or 30 years. This can provide stability and predictability, making it easier to budget and plan for the future.
Adjustable-rate refinancing, on the other hand, offers a lower interest rate for a set period of time, typically 3-7 years. After the introductory period, the interest rate can adjust based on market conditions, which can result in higher monthly payments. Adjustable-rate loans can be a good option for homeowners who plan to sell or refinance their home before the introductory period ends.
Cash-out refinancing allows homeowners to tap into their home’s equity and receive a lump sum of cash at closing. This can be a good option for homeowners who need to fund home improvements, pay off debt, or cover unexpected expenses. However, cash-out refinancing typically comes with a higher interest rate and fees, so it’s essential to carefully consider the costs and benefits before making a decision.
When deciding how to refinance a house, it’s essential to consider your financial goals and situation. If you’re looking for stability and predictability, a fixed-rate loan may be the best option. If you’re looking for a lower interest rate and are willing to take on some risk, an adjustable-rate loan may be a good choice. If you need to tap into your home’s equity, a cash-out refinance may be the way to go.
Ultimately, the right refinancing option for you will depend on your individual circumstances and goals. By carefully considering your options and seeking the advice of a financial professional, you can make an informed decision and achieve your financial objectives.
How to Shop for Refinancing Rates: Tips and Tricks
Shopping for refinancing rates can be a daunting task, but with the right strategies, you can find the best rates and save thousands of dollars on your mortgage. When considering how to refinance a house, it’s essential to compare rates from multiple lenders to ensure you’re getting the best deal.
Start by researching and comparing rates from different types of lenders, including banks, credit unions, and online mortgage lenders. You can use online tools, such as mortgage rate comparison websites, to get an idea of the current rates and terms offered by various lenders.
When comparing rates, make sure to consider the annual percentage rate (APR), which includes the interest rate, points, and fees. Also, pay attention to the loan terms, including the loan duration, payment schedule, and any prepayment penalties.
Negotiating with lenders is also a crucial part of the refinancing process. Don’t be afraid to ask lenders to match or beat a competitor’s rate, or to waive certain fees. Remember, lenders want your business, and they may be willing to work with you to get it.
Another tip is to consider working with a mortgage broker, who can help you shop for rates and negotiate with lenders on your behalf. Mortgage brokers often have access to multiple lenders and can help you find the best rates and terms.
Finally, be sure to read the fine print and understand all the terms and conditions of the loan before signing. This includes understanding any fees associated with the loan, such as origination fees, appraisal fees, and closing costs.
By following these tips and tricks, you can find the best refinancing rates and save thousands of dollars on your mortgage. Remember to always do your research, compare rates, and negotiate with lenders to get the best deal.
When refinancing a house, it’s essential to be patient and persistent. Don’t rush into a decision, and make sure you understand all the terms and conditions of the loan. By taking the time to shop for rates and negotiate with lenders, you can find the best refinancing option for your situation.
Understanding Refinancing Fees: What to Expect
When considering how to refinance a house, it’s essential to understand the various fees associated with the process. Refinancing fees can add up quickly, and it’s crucial to know what to expect to avoid any surprises. In this article, we’ll break down the different types of fees associated with refinancing and provide guidance on how to minimize them.
Origination fees are one of the most common fees associated with refinancing. These fees are typically charged by the lender to cover the costs of processing the loan. Origination fees can range from 0.5% to 1% of the loan amount, and they can be negotiated with the lender.
Appraisal fees are another type of fee associated with refinancing. An appraisal is an independent evaluation of the value of your home, and it’s typically required by the lender to ensure that the loan amount is not more than the value of the property. Appraisal fees can range from $300 to $1,000, depending on the location and type of property.
Closing costs are also a significant expense associated with refinancing. Closing costs can include fees such as title insurance, escrow fees, and recording fees. These fees can range from 2% to 5% of the loan amount, and they can be negotiated with the lender.
To minimize refinancing fees, it’s essential to shop around and compare rates and fees from different lenders. You can also negotiate with the lender to waive or reduce certain fees. Additionally, consider working with a mortgage broker who can help you navigate the refinancing process and negotiate with lenders on your behalf.
When refinancing a house, it’s also important to consider the long-term costs of the loan. While refinancing fees may seem like a significant expense upfront, they can be offset by the long-term savings of a lower interest rate or lower monthly payments.
By understanding the different types of fees associated with refinancing and taking steps to minimize them, you can save thousands of dollars on your mortgage and achieve your financial goals.
Refinancing with Bad Credit: Options and Considerations
Refinancing a house with bad credit can be a challenging and daunting task. However, it’s not impossible. Homeowners with poor credit can still refinance their mortgage, but they may face higher interest rates, stricter loan terms, and additional fees. Understanding the options and considerations for refinancing with bad credit can help homeowners make informed decisions and avoid costly mistakes.
One option for refinancing with bad credit is subprime refinancing. Subprime lenders specialize in lending to borrowers with poor credit, but they often charge higher interest rates and fees to compensate for the increased risk. Homeowners with bad credit may also consider alternative credit scoring models, such as the VantageScore, which can provide a more accurate picture of their creditworthiness.
Another option is to work with a mortgage broker who specializes in bad credit refinancing. These brokers often have relationships with multiple lenders and can help homeowners shop around for the best rates and terms. Additionally, homeowners with bad credit may want to consider a co-signer with good credit to help qualify for a better interest rate.
It’s essential to note that refinancing with bad credit can be more expensive than refinancing with good credit. Homeowners with poor credit may face higher origination fees, appraisal fees, and closing costs. However, refinancing can still be a viable option for homeowners who need to lower their monthly payments, tap into their home’s equity, or switch from an adjustable-rate to a fixed-rate mortgage.
To improve their chances of refinancing with bad credit, homeowners should focus on improving their credit scores. This can be achieved by paying bills on time, reducing debt, and avoiding new credit inquiries. Homeowners can also consider a credit repair service to help identify and correct errors on their credit report.
When refinancing with bad credit, it’s crucial to carefully review the loan terms and conditions. Homeowners should pay attention to the interest rate, fees, and repayment terms to ensure they understand the total cost of the loan. It’s also essential to work with a reputable lender and avoid predatory lending practices.
In summary, refinancing a house with bad credit requires careful consideration and planning. Homeowners with poor credit should explore their options, work with a mortgage broker, and focus on improving their credit scores. By understanding the options and considerations for refinancing with bad credit, homeowners can make informed decisions and achieve their financial goals.
Refinancing and Taxes: What You Need to Know
Refinancing a house can have significant tax implications, and it’s essential to understand these implications to make informed decisions. When refinancing a mortgage, homeowners can deduct the interest paid on the loan, as well as property taxes, from their taxable income. However, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) has introduced some changes to the tax laws that affect refinancing and taxes.
One of the most significant changes is the limit on state and local taxes (SALT) deductions. The TCJA limits SALT deductions to $10,000 per year, which can impact homeowners who refinance their mortgage and pay high property taxes. Additionally, the TCJA has suspended the deduction for home equity loan interest, unless the loan is used to buy, build, or substantially improve the primary residence.
Despite these changes, refinancing can still provide tax benefits. Homeowners can deduct the interest paid on the refinanced loan, as well as points paid on the loan, from their taxable income. Points are prepaid interest that can be deducted in the year they are paid. However, homeowners must meet certain requirements to deduct points, such as using the loan to purchase or improve their primary residence.
Another tax implication of refinancing is the potential for recapture of depreciation. If homeowners have taken depreciation deductions on their primary residence, they may be subject to recapture when they refinance or sell the property. Recapture is the process of paying back the depreciation deductions taken on the property, and it can increase the homeowner’s taxable income.
To navigate the tax implications of refinancing, homeowners should consult with a tax professional or financial advisor. They can help homeowners understand the tax laws and regulations that apply to their specific situation and provide guidance on how to minimize their tax liability. Additionally, homeowners should keep accurate records of their refinancing costs, including interest paid and points paid, to ensure they can deduct these expenses on their tax return.
In summary, refinancing a house can have significant tax implications, and it’s essential to understand these implications to make informed decisions. Homeowners should consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to navigate the tax laws and regulations that apply to their specific situation. By understanding the tax implications of refinancing, homeowners can minimize their tax liability and achieve their financial goals.
When considering how do you refinance a house, it’s essential to factor in the tax implications of the refinancing process. By understanding the tax laws and regulations that apply to refinancing, homeowners can make informed decisions and achieve their financial goals. Whether you’re looking to lower your monthly payments, tap into your home’s equity, or switch from an adjustable-rate to a fixed-rate mortgage, refinancing can be a viable option. However, it’s crucial to consider the tax implications of refinancing to ensure you’re making the best decision for your financial situation.
Common Refinancing Mistakes to Avoid
Refinancing a house can be a complex and time-consuming process, and it’s easy to make mistakes that can cost you money and time. To avoid common refinancing mistakes, it’s essential to understand the refinancing process and take the necessary steps to ensure a smooth and successful transaction. Here are some common refinancing mistakes to avoid:
Not Shopping Around for Rates: One of the most significant mistakes homeowners make when refinancing is not shopping around for rates. Different lenders offer different interest rates, and not comparing rates can result in paying more than necessary. Homeowners should research and compare rates from multiple lenders to find the best deal.
Not Considering All Costs: Refinancing involves more than just interest rates. Homeowners should also consider other costs, such as