Understanding the Amazon Business Model
Amazon’s business model is a complex and multifaceted system that has evolved over the years to become the e-commerce giant it is today. At its core, Amazon is a platform that connects buyers and sellers from all over the world. By providing a marketplace for third-party sellers to list and sell their products, Amazon has created a vast and diverse ecosystem that generates billions of dollars in revenue each year.
One of the key factors that contribute to Amazon’s success is its diversified revenue streams. In addition to retail sales, Amazon earns revenue from advertising, services, and other sources. This diversification allows Amazon to maintain a stable and profitable business model, even in times of economic uncertainty.
For sellers, Amazon’s business model offers a unique opportunity to reach a massive customer base and increase their sales. By leveraging Amazon’s logistics and fulfillment capabilities, sellers can focus on what they do best: creating and marketing their products. However, to fully understand how Amazon makes money from sellers, it’s essential to delve deeper into the various fees and revenue streams that Amazon generates from its seller base.
As a platform, Amazon charges sellers a range of fees, including selling plan fees, shipping fees, and fulfillment fees. These fees contribute significantly to Amazon’s revenue and are a crucial part of its business model. In the next section, we’ll take a closer look at how Amazon makes money from seller fees and explore ways for sellers to minimize their costs.
Amazon’s business model is also driven by its advertising options, which provide sellers with a range of tools to promote their products and increase their visibility on the platform. By understanding how Amazon’s advertising options work and how they contribute to the company’s revenue, sellers can make informed decisions about their marketing strategies and optimize their ad spend for maximum ROI.
Furthermore, Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program is a key revenue driver for the company. By providing sellers with a range of logistics and fulfillment services, Amazon earns revenue from storage fees, shipping fees, and customer service costs. In the following sections, we’ll explore the benefits and costs of FBA and examine how it contributes to Amazon’s revenue.
Finally, Amazon’s commission structure is an essential part of its business model. By charging sellers a commission on each sale, Amazon earns revenue from the transactions that take place on its platform. In the next section, we’ll take a closer look at Amazon’s commission structure and explore ways for sellers to optimize their pricing strategies and maximize their earnings.
How Amazon Makes Money from Seller Fees
Amazon charges sellers a range of fees to use its platform, including selling plan fees, shipping fees, and fulfillment fees. These fees contribute significantly to Amazon’s revenue and are a crucial part of its business model. In this section, we’ll break down the various fees Amazon charges sellers and explore ways for sellers to minimize their costs.
Amazon’s selling plan fees are charged to sellers who use the platform to sell their products. There are two main selling plans: Individual and Professional. The Individual plan costs $0.99 per sale, while the Professional plan costs $39.99 per month. Sellers who use the Professional plan can sell an unlimited number of products and have access to additional features such as inventory management and performance reports.
Shipping fees are another significant source of revenue for Amazon. Sellers can choose to use Amazon’s shipping services, which include Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Merchant Fulfilled. FBA allows sellers to store their products in Amazon’s warehouses and have Amazon handle the shipping and customer service. Merchant Fulfilled, on the other hand, allows sellers to handle their own shipping and customer service.
Fulfillment fees are charged to sellers who use Amazon’s FBA program. These fees include a base fee, a weight-based fee, and a shipping fee. The base fee is $2.41 per unit, while the weight-based fee ranges from $0.45 to $1.15 per pound. The shipping fee ranges from $2.41 to $4.71 per unit, depending on the shipping speed and destination.
To minimize their costs, sellers can optimize their shipping options and use Amazon’s FBA program strategically. For example, sellers can use Amazon’s shipping services to reduce their shipping costs and improve their delivery times. Additionally, sellers can use Amazon’s FBA program to store their products in Amazon’s warehouses and have Amazon handle the shipping and customer service.
By understanding the various fees Amazon charges sellers, sellers can make informed decisions about their pricing strategies and optimize their costs to maximize their earnings. In the next section, we’ll explore Amazon’s advertising options and how they contribute to the company’s revenue.
Amazon’s fees are an essential part of its business model, and understanding how they work is crucial for sellers who want to succeed on the platform. By optimizing their shipping options and using Amazon’s FBA program strategically, sellers can minimize their costs and maximize their earnings. As we’ll see in the next section, Amazon’s advertising options are another key revenue stream for the company.
The Power of Advertising on Amazon
Amazon’s advertising options are a key revenue stream for the company, and a crucial tool for sellers to promote their products and increase their visibility on the platform. In this section, we’ll explore Amazon’s advertising options, including Sponsored Products, Sponsored Brands, and Sponsored Display Ads.
Sponsored Products are a popular advertising option on Amazon, allowing sellers to promote their products to customers who are searching for similar items. These ads are displayed on product detail pages, search results pages, and category pages, and are designed to drive traffic and sales to the seller’s product page.
Sponsored Brands are another advertising option on Amazon, allowing sellers to promote their brand and products to customers who are searching for similar items. These ads are displayed on search results pages and category pages, and are designed to drive traffic and sales to the seller’s product page.
Sponsored Display Ads are a newer advertising option on Amazon, allowing sellers to promote their products to customers who are browsing the platform. These ads are displayed on product detail pages, search results pages, and category pages, and are designed to drive traffic and sales to the seller’s product page.
Amazon earns revenue from these advertising options through a cost-per-click (CPC) model, where sellers pay a fee each time a customer clicks on their ad. The CPC model allows Amazon to generate revenue from its advertising options, while also providing sellers with a cost-effective way to promote their products.
To maximize their earnings on Amazon, sellers can leverage the platform’s advertising options to promote their products and increase their visibility. By optimizing their ad campaigns and targeting the right customers, sellers can drive traffic and sales to their product page, and increase their earnings on the platform.
Amazon’s advertising options are a powerful tool for sellers to promote their products and increase their earnings on the platform. By understanding how these options work, and how to optimize their ad campaigns, sellers can maximize their earnings and achieve success on Amazon.
In addition to its advertising options, Amazon also offers a range of tools and services to help sellers optimize their product listings and improve their performance on the platform. In the next section, we’ll explore Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program, and how it contributes to the company’s revenue.
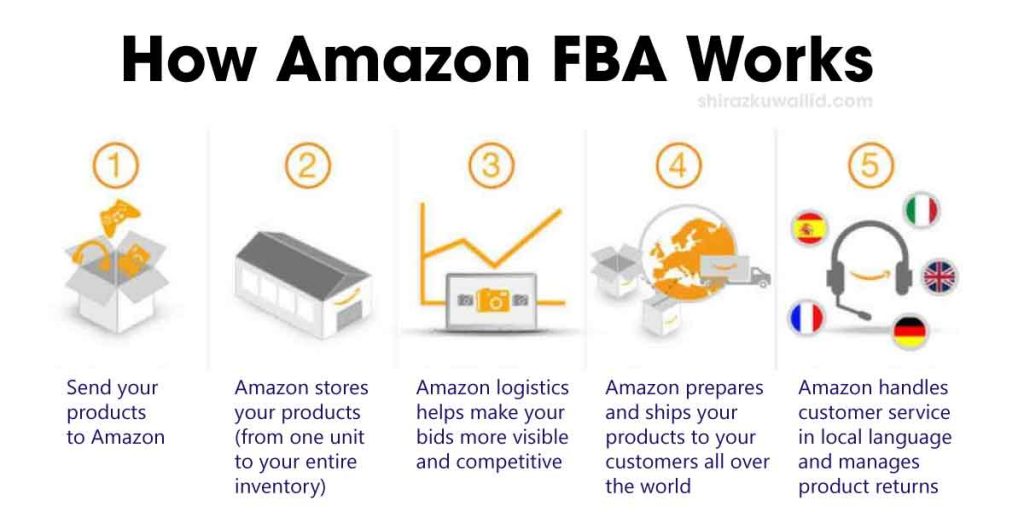
Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) Program: A Key Revenue Driver
Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program is a crucial component of the company’s revenue streams. By leveraging FBA, sellers
Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) Program: A Key Revenue Driver
Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program is a crucial component of the company’s revenue streams. By leveraging FBA, sellers
Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) Program: A Key Revenue Driver
Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program is a crucial component of the company’s revenue streams. By leveraging FBA, sellers
Amazon’s Commission Structure: How Sellers Contribute to Revenue
Amazon’s commission structure is a critical component of its revenue streams. The company earns a commission on every sale made by third-party sellers on its platform. The commission rates vary depending on the product category, with rates ranging from 8% to 15%. For example, Amazon charges a commission rate of 15% on sales of electronics, while the rate for books is 8%.
Sellers can optimize their pricing strategies to minimize the impact of Amazon’s commission rates. One approach is to set prices competitively, taking into account the commission rate and other costs such as shipping and fulfillment. Sellers can also use Amazon’s pricing tools to adjust their prices in real-time and stay competitive.
Amazon’s commission structure is designed to incentivize sellers to provide high-quality products and excellent customer service. Sellers who consistently receive high ratings and reviews from customers are more likely to attract repeat business and increase their sales. This, in turn, contributes to Amazon’s revenue growth.
In addition to commission rates, Amazon also earns revenue from other sources, such as shipping fees and fulfillment fees. Sellers who use Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) program pay a fee for storage, shipping, and customer service. These fees contribute to Amazon’s revenue and help the company maintain its position as a leading e-commerce platform.
Understanding Amazon’s commission structure is essential for sellers who want to maximize their earnings on the platform. By optimizing their pricing strategies and providing excellent customer service, sellers can increase their sales and contribute to Amazon’s revenue growth.
Navigating Amazon’s Policies and Requirements
Amazon has a set of policies and requirements that sellers must comply with to avoid account suspension or termination. These policies include performance metrics, customer reviews, and intellectual property protection.
Performance metrics are used to evaluate a seller’s performance on Amazon. These metrics include order defect rate, cancellation rate, and late shipment rate. Sellers who fail to meet Amazon’s performance standards may face account suspension or termination.
Customer reviews are an essential part of Amazon’s feedback system. Sellers must ensure that they provide excellent customer service and respond promptly to customer inquiries. Sellers who receive consistently low ratings may face account suspension or termination.
Intellectual property protection is also a critical aspect of Amazon’s policies. Sellers must ensure that they do not infringe on other sellers’ intellectual property rights, including trademarks, copyrights, and patents. Sellers who infringe on other sellers’ intellectual property rights may face account suspension or termination.
To ensure compliance with Amazon’s policies and requirements, sellers must regularly review and update their product listings, respond promptly to customer inquiries, and ensure that they do not infringe on other sellers’ intellectual property rights.
Sellers can also use Amazon’s performance metrics and customer review tools to monitor their performance and identify areas for improvement. By regularly reviewing these metrics and making adjustments as needed, sellers can ensure that they remain compliant with Amazon’s policies and requirements.
Additionally, Amazon provides a range of resources and tools to help sellers navigate its policies and requirements. These resources include the Amazon Seller Central dashboard, which provides access to performance metrics and customer review data, as well as the Amazon Seller University, which offers training and support for sellers.
By understanding and complying with Amazon’s policies and requirements, sellers can ensure that they remain successful on the platform and avoid account suspension or termination.