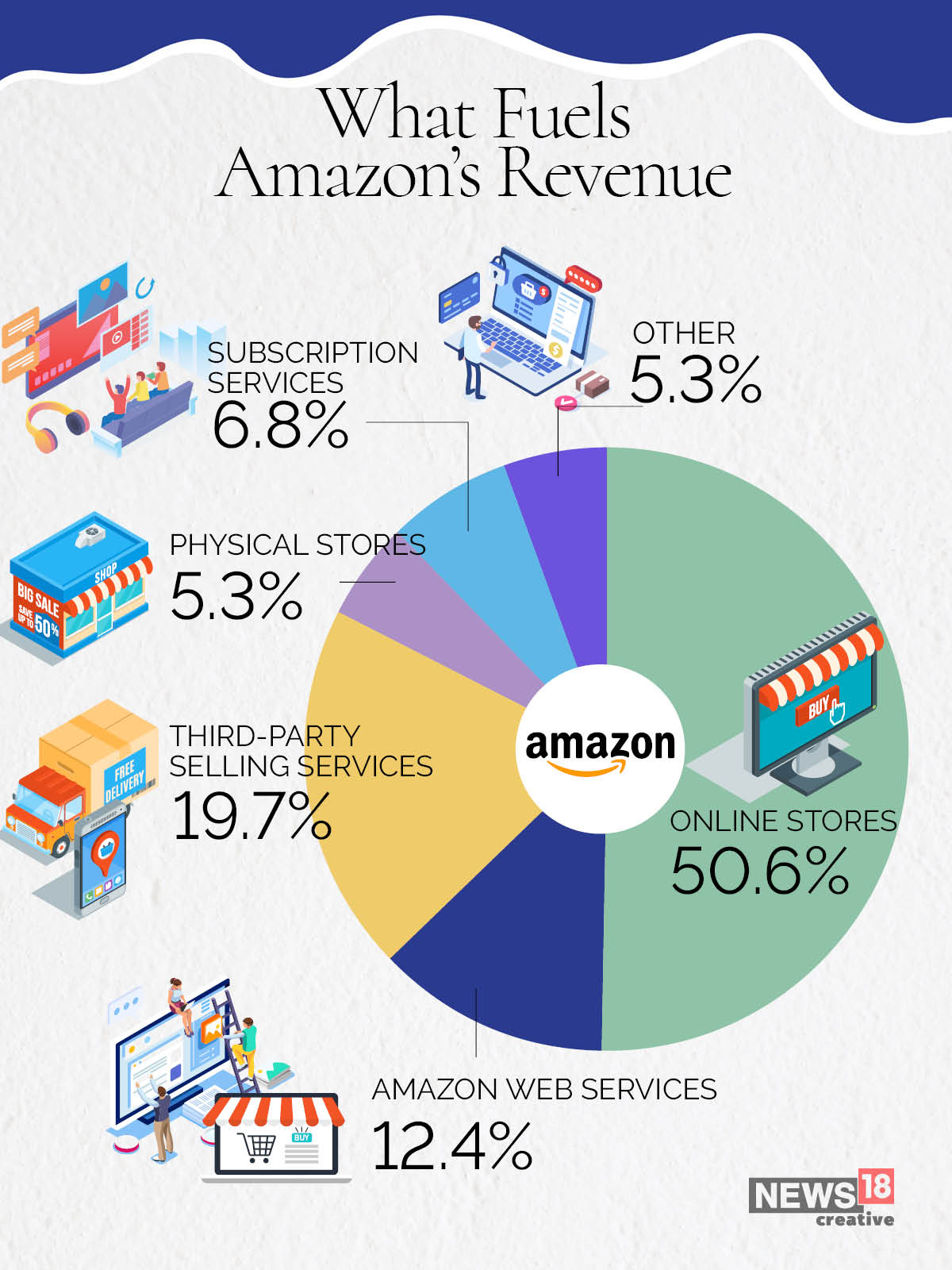
The Amazon Business Model: Understanding the Basics
Amazon’s business model is a complex and multifaceted system that generates revenue from various sources. At its core, Amazon is an e-commerce platform that connects buyers with sellers, providing a marketplace for individuals and businesses to sell their products. However, Amazon’s revenue streams extend far beyond just transaction fees. The company has developed a robust ecosystem that includes advertising, subscription services, and cloud computing, among other offerings.
One of the primary ways Amazon makes money from sellers is through various fees associated with selling on the platform. These fees can include selling plan fees, shipping fees, and fulfillment fees, among others. For example, Amazon’s selling plan fees can range from 8% to 15% of the sale price, depending on the category and type of product. Additionally, Amazon charges shipping fees to sellers, which can range from $2.50 to $10.00 per unit, depending on the weight and dimensions of the product.
Amazon’s business model is designed to be highly scalable and efficient, allowing the company to generate significant revenue from its vast network of sellers. By providing a platform for sellers to reach a massive customer base, Amazon is able to collect fees and commissions on each sale. This model has proven to be highly successful, with Amazon generating over $280 billion in revenue in 2020 alone.
Understanding how Amazon makes money from sellers is crucial for anyone looking to sell on the platform. By grasping the various revenue streams and fees associated with selling on Amazon, sellers can better optimize their strategies and maximize their earnings. Whether you’re a seasoned seller or just starting out, it’s essential to have a solid understanding of Amazon’s business model and how it impacts your bottom line.
As Amazon continues to grow and expand its offerings, it’s likely that the company will find new and innovative ways to generate revenue from its sellers. By staying informed and adapting to these changes, sellers can stay ahead of the curve and continue to thrive on the platform. Whether you’re looking to increase your sales, improve your margins, or simply better understand the Amazon ecosystem, understanding how Amazon makes money from sellers is a crucial step in achieving your goals.
How Amazon Makes Money from Sellers: A Breakdown of Fees
Amazon charges sellers various fees for using its platform, which can eat into their profit margins. Understanding these fees is crucial for sellers to optimize their pricing and maximize their earnings. The main types of fees Amazon charges sellers include selling plan fees, shipping fees, and fulfillment fees.
Selling plan fees are charged to sellers based on the type of plan they have. The Individual plan costs $0.99 per sale, while the Professional plan costs $39.99 per month. Sellers who opt for the Professional plan can sell an unlimited number of products, while those on the Individual plan are limited to 40 sales per month.
Shipping fees are another significant cost for sellers. Amazon charges sellers a shipping fee based on the weight and dimensions of the product. For example, a product that weighs 1 pound and measures 10 inches by 10 inches by 10 inches would cost $2.50 to ship. Sellers can also opt for Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) service, which includes shipping and handling fees.
Fulfillment fees are charged to sellers who use Amazon’s FBA service. These fees include the cost of storing and shipping products, as well as customer service and returns. The fulfillment fee for a standard-sized product is $2.41, while the fee for an oversized product is $8.13.
Other fees that Amazon charges sellers include referral fees, which range from 8% to 15% of the sale price, depending on the category and type of product. Sellers are also charged a variable closing fee, which ranges from $0.15 to $1.80 per sale.
Understanding how Amazon makes money from sellers is crucial for optimizing pricing and maximizing earnings. By factoring in the various fees charged by Amazon, sellers can ensure they are making a profit on their sales. For example, if a seller is selling a product for $20, they need to factor in the selling plan fee, shipping fee, and fulfillment fee to determine their net earnings.
By understanding the fees associated with selling on Amazon, sellers can make informed decisions about their pricing and inventory management. This can help them to maximize their earnings and stay competitive in the Amazon marketplace.
The Power of Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA): Benefits and Costs
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a game-changer for sellers on the platform. By leveraging Amazon’s logistics and shipping expertise, sellers can increase their shipping efficiency and customer trust. However, FBA also comes with costs that sellers need to consider.
One of the main benefits of FBA is increased shipping efficiency. Amazon’s vast network of warehouses and shipping centers allows for fast and reliable shipping, which can lead to higher customer satisfaction and more positive reviews. Additionally, FBA sellers can take advantage of Amazon’s trusted brand, which can increase customer trust and loyalty.
However, FBA also comes with costs. Sellers need to pay a fulfillment fee, which ranges from $2.41 to $8.13 per unit, depending on the weight and dimensions of the product. Additionally, sellers need to pay a storage fee, which ranges from $0.45 to $2.40 per cubic foot, depending on the type of storage and the time of year.
Despite the costs, many sellers find that FBA is worth it. By outsourcing their shipping and logistics to Amazon, sellers can focus on other aspects of their business, such as marketing and product development. Additionally, FBA sellers can take advantage of Amazon’s customer service and returns handling, which can save time and reduce hassle.
For example, a seller who uses FBA can expect to pay around $3.50 per unit in fulfillment fees, plus an additional $0.50 per unit in storage fees. However, this seller can also expect to see an increase in sales and customer satisfaction, as well as a reduction in shipping and logistics costs.
Overall, FBA is a powerful tool for sellers on Amazon. By understanding the benefits and costs of FBA, sellers can make informed decisions about whether to use the service and how to optimize their FBA strategy.
When considering FBA, sellers should think about their business goals and how FBA can help them achieve those goals. For example, if a seller is looking to increase their shipping efficiency and customer trust, FBA may be a good option. However, if a seller is looking to reduce their costs and increase their profit margins, they may want to consider other options.
Advertising on Amazon: A Key Revenue Stream
Amazon’s advertising platform is a key revenue stream for the company, generating billions of dollars in revenue each year. The platform allows sellers to promote their products to Amazon’s vast customer base, increasing visibility and driving sales.
There are several types of ads available on Amazon, including Sponsored Products and Sponsored Brands. Sponsored Products are ads that promote individual products, while Sponsored Brands are ads that promote a brand as a whole. Both types of ads can be targeted to specific keywords, interests, and demographics, allowing sellers to reach their desired audience.
Amazon’s advertising platform uses a cost-per-click (CPC) model, meaning that sellers only pay for ads that are clicked on by customers. This makes it a cost-effective way for sellers to promote their products and increase sales.
For example, a seller who is selling a product on Amazon can create a Sponsored Products ad to promote that product. The ad will be displayed on Amazon’s search results page and on product detail pages, and the seller will only pay for the ad if a customer clicks on it.
Amazon’s advertising platform also provides a range of tools and metrics to help sellers optimize their ads and improve their return on investment (ROI). These tools include ad performance metrics, such as click-through rate (CTR) and conversion rate, as well as ad targeting options, such as keyword targeting and interest targeting.
By using Amazon’s advertising platform, sellers can increase their visibility and drive sales on the platform. This can be especially effective for sellers who are looking to promote new products or increase sales during peak shopping seasons.
Amazon’s advertising platform is also a key revenue stream for the company, generating billions of dollars in revenue each year. By providing a platform for sellers to promote their products, Amazon is able to generate revenue from advertising, in addition to revenue from sales and other sources.
Amazon’s Subscription Services: Prime and Beyond
Amazon’s subscription services are a key component of the company’s revenue streams. The most well-known of these services is Amazon Prime, which offers customers a range of benefits, including free two-day shipping, streaming of music and video content, and access to exclusive deals and discounts.
Amazon Prime is a highly successful service, with over 150 million subscribers worldwide. The service generates significant revenue for Amazon, both through subscription fees and through increased sales of products to Prime members. In fact, Prime members are more likely to purchase products on Amazon than non-Prime members, and they tend to spend more money on the platform.
In addition to Amazon Prime, the company also offers a range of other subscription services, including Prime Video, Amazon Fresh, and Amazon Music Unlimited. These services provide customers with access to streaming content, fresh groceries, and music, respectively, and generate additional revenue for Amazon.
Amazon’s subscription services also benefit sellers on the platform. For example, Prime members are more likely to purchase products from sellers who offer free two-day shipping, which can increase sales and revenue for those sellers. Additionally, Amazon’s subscription services can help to increase customer loyalty and retention, which can lead to more repeat business for sellers.
For example, a seller who offers free two-day shipping to Prime members may see an increase in sales and revenue as a result. This is because Prime members are more likely to purchase products from sellers who offer fast and free shipping, and they tend to spend more money on the platform.
Amazon’s subscription services are a key component of the company’s revenue streams, and they provide a range of benefits to both customers and sellers. By offering a range of subscription services, Amazon is able to generate significant revenue and increase customer loyalty and retention.
Other Revenue Streams: Amazon Web Services and More
While Amazon’s e-commerce platform is its primary source of revenue, the company has diversified its income streams through various other services. One of the most significant contributors to Amazon’s revenue is Amazon Web Services (AWS), a comprehensive cloud computing platform that provides a wide range of services, including computing power, storage, databases, analytics, machine learning, and more. AWS is used by businesses, governments, and individuals around the world, generating billions of dollars in revenue for Amazon each year.
Another revenue stream for Amazon is Amazon Pay, a digital payment service that allows customers to pay for goods and services online and in-person. Amazon Pay is accepted by thousands of merchants worldwide, and its usage is growing rapidly. Additionally, Amazon has also launched Amazon Go, a chain of convenience stores that use artificial intelligence and computer vision to enable customers to grab items and go without checking out. Amazon Go is still a relatively small contributor to Amazon’s revenue, but it has the potential to disrupt the retail industry and generate significant income for the company in the future.
Amazon has also made significant investments in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and robotics, which are expected to generate new revenue streams in the coming years. For example, Amazon’s acquisition of Whole Foods Market has enabled the company to integrate its AI-powered shopping technology into physical stores, creating new opportunities for revenue growth. Furthermore, Amazon’s development of autonomous delivery drones and robots is expected to reduce shipping costs and increase efficiency, potentially leading to higher profits for the company.
Understanding how Amazon generates revenue from these various sources is essential for sellers who want to maximize their earnings on the platform. By recognizing the different ways Amazon makes money, sellers can optimize their strategies to take advantage of these revenue streams and increase their own profits. For instance, sellers who use AWS to host their e-commerce websites or store their data can benefit from Amazon’s cloud computing services while also generating revenue for the company. Similarly, sellers who use Amazon Pay to process transactions can benefit from the convenience and security of the service while also contributing to Amazon’s revenue.
In conclusion, Amazon’s revenue streams extend far beyond its e-commerce platform, encompassing a wide range of services, including AWS, Amazon Pay, Amazon Go, and more. By understanding these revenue streams, sellers can optimize their strategies to maximize their earnings on the platform and contribute to Amazon’s continued growth and success.
Maximizing Seller Earnings on Amazon: Tips and Strategies
To maximize earnings on Amazon, sellers need to understand the various profit streams and optimize their strategies accordingly. One key strategy is to optimize product listings to increase visibility and drive sales. This can be achieved by using relevant keywords, high-quality product images, and detailed product descriptions. Additionally, sellers can use Amazon’s advertising platform to promote their products and increase brand awareness.
Another effective strategy is to leverage Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) to streamline shipping and customer service. FBA can help sellers save time and money on shipping, while also providing customers with fast and reliable delivery. Furthermore, FBA can also help sellers increase customer trust and loyalty, leading to repeat business and positive reviews.
Sellers can also maximize their earnings by using Amazon’s subscription services, such as Prime and Amazon Fresh. By offering products that are eligible for Prime shipping, sellers can attract more customers and increase sales. Additionally, sellers can also use Amazon’s subscription services to offer customers a convenient and hassle-free shopping experience.
Moreover, sellers can also use Amazon’s performance metrics, such as sales rank and customer reviews, to optimize their product listings and improve their overall performance. By monitoring these metrics, sellers can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to increase their earnings.
Another important strategy is to diversify product offerings and expand into new markets. By offering a wide range of products, sellers can attract a broader customer base and increase sales. Additionally, sellers can also use Amazon’s global selling program to expand their business into new markets and reach a wider audience.
Finally, sellers can also maximize their earnings by providing excellent customer service and building a strong brand reputation. By responding promptly to customer inquiries and resolving issues quickly, sellers can build trust and loyalty with their customers. Additionally, sellers can also use Amazon’s brand registry program to protect their brand and prevent counterfeiting.
By implementing these strategies, sellers can maximize their earnings on Amazon and achieve long-term success. Whether it’s optimizing product listings, leveraging FBA, or providing excellent customer service, there are many ways for sellers to increase their earnings and grow their business on Amazon.
Conclusion: Amazon’s Profit Streams and Seller Success
In conclusion, Amazon’s profit streams are diverse and complex, with various revenue streams contributing to the company’s overall success. Understanding how Amazon makes money from sellers is crucial for seller success, as it enables them to optimize their strategies and maximize their earnings on the platform.
By recognizing the different types of fees Amazon charges sellers, including selling plan fees, shipping fees, and fulfillment fees, sellers can better manage their costs and increase their profit margins. Additionally, leveraging Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) can help sellers streamline their shipping and customer service, while also increasing customer trust and loyalty.
Amazon’s advertising platform is another key revenue stream for the company, and sellers can benefit from using it to promote their products and increase brand awareness. Furthermore, Amazon’s subscription services, such as Prime and Amazon Fresh, can provide sellers with a steady stream of revenue and help them attract and retain customers.
Other revenue streams, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Amazon Pay, and Amazon Go, also contribute to Amazon’s overall revenue and provide sellers with opportunities to diversify their business and increase their earnings.
To maximize their earnings on Amazon, sellers should focus on optimizing their product listings, using Amazon advertising, and leveraging FBA. By doing so, they can increase their visibility, drive sales, and build a strong brand reputation on the platform.
Ultimately, understanding Amazon’s profit streams and optimizing their strategies accordingly is key to seller success on the platform. By recognizing the various revenue streams and taking advantage of the opportunities they provide, sellers can maximize their earnings and achieve long-term success on Amazon.
As Amazon continues to evolve and expand its services, it is essential for sellers to stay up-to-date with the latest developments and adjust their strategies accordingly. By doing so, they can ensure their continued success on the platform and capitalize on the opportunities that Amazon provides.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1164459206-1021f4903964456d906d54dda7903d2a.jpg)