Understanding the 28/36 Rule: A Benchmark for Housing Expenses
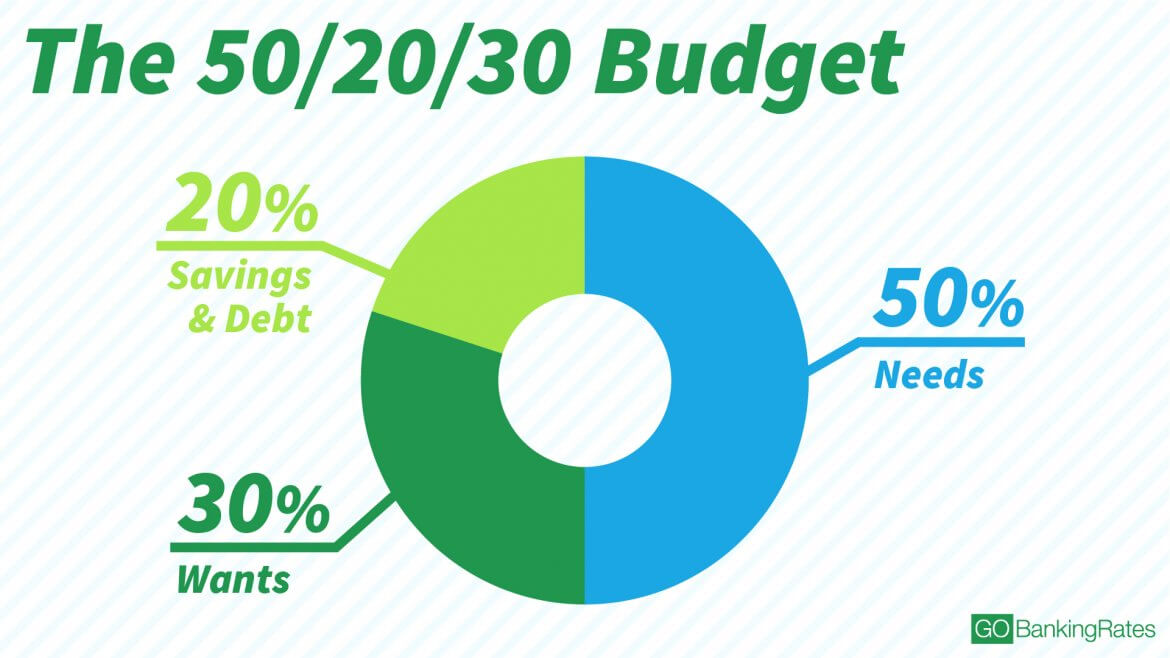
When it comes to determining how much to spend on housing, the 28/36 rule is a widely accepted guideline. This rule suggests that individuals should spend no more than 28% of their gross income on housing expenses, such as rent or mortgage payments, property taxes, and insurance. Additionally, the rule recommends that total debt payments, including housing expenses, credit cards, student loans, and other debt obligations, should not exceed 36% of gross income.
The 28/36 rule serves as a benchmark for making informed decisions about housing expenses. By following this guideline, individuals can ensure that they are not overextending themselves financially and can maintain a comfortable standard of living. It’s essential to note that this rule is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and individual circumstances may vary. However, as a general guideline, the 28/36 rule provides a useful framework for evaluating housing expenses.
For example, let’s consider an individual with a gross income of $4,000 per month. According to the 28/36 rule, their housing expenses should not exceed $1,120 per month (28% of $4,000). This amount includes rent or mortgage payments, property taxes, and insurance. By staying within this limit, the individual can ensure that they have sufficient funds for other expenses, savings, and debt repayment.
While the 28/36 rule is a useful guideline, it’s essential to consider individual circumstances and adjust the ratio accordingly. For instance, individuals with high-interest debt or those who are saving for specific financial goals may need to adjust their housing expenses to accommodate these priorities. Ultimately, the key is to find a balance between housing expenses and other financial obligations to maintain a stable financial foundation.
The Pros and Cons of Spending More on Housing
When considering how much to spend on housing, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of allocating a larger portion of your income towards housing. On one hand, investing in a more expensive home can have its advantages. For instance, a more expensive home may appreciate in value over time, providing a potential long-term investment opportunity. Additionally, a more expensive home may offer better amenities, such as a larger yard, a pool, or a more desirable location.
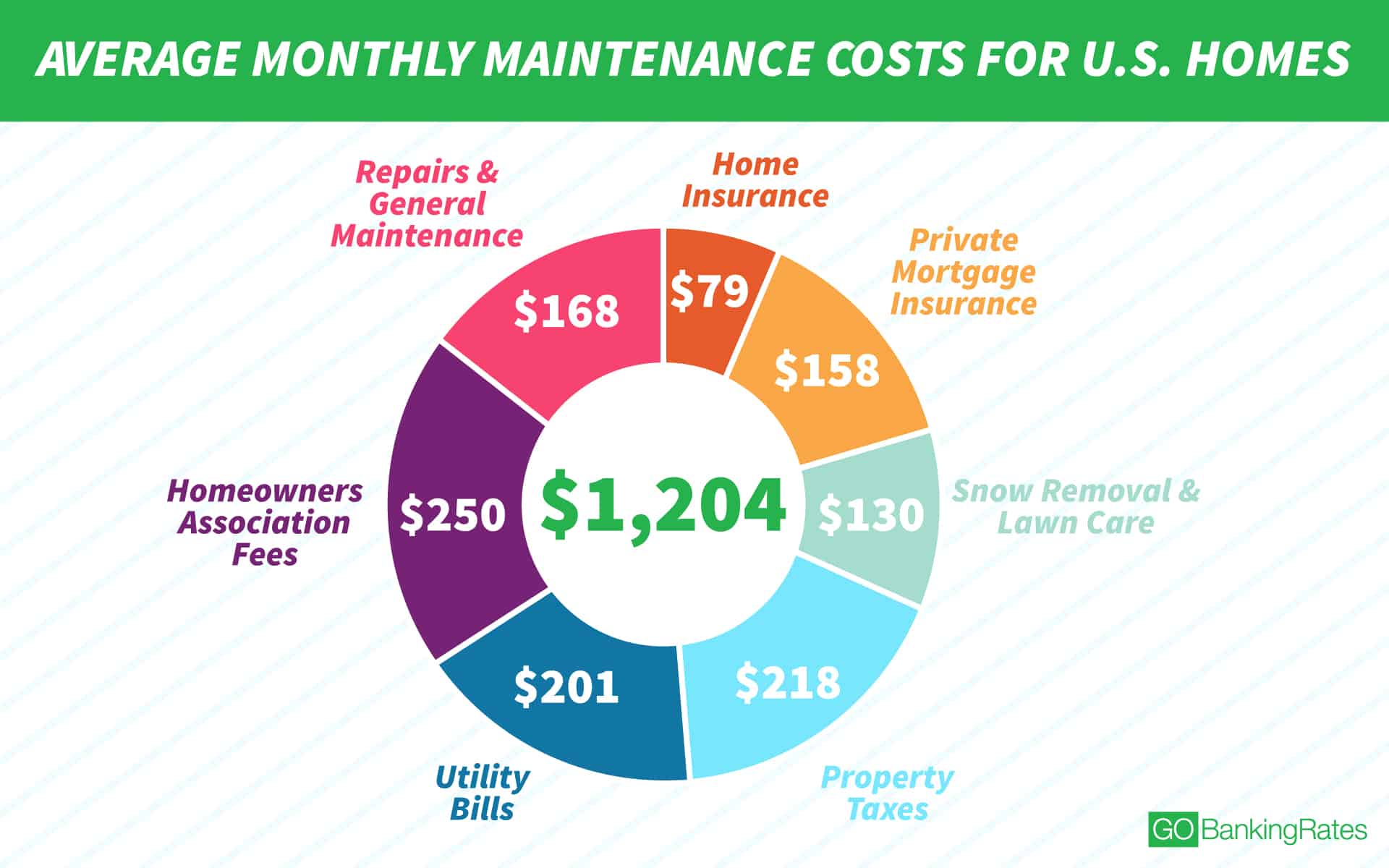
On the other hand, spending more on housing can also have its drawbacks. For example, allocating a larger portion of your income towards housing may leave you with less money for other expenses, such as food, transportation, and entertainment. Furthermore, a more expensive home may also come with higher maintenance and repair costs, which can add up over time.
It’s also important to consider the opportunity cost of spending more on housing. For instance, if you allocate a larger portion of your income towards housing, you may have to sacrifice other financial goals, such as saving for retirement or paying off debt. Therefore, it’s essential to carefully consider your financial priorities and determine whether spending more on housing aligns with your overall financial goals.
Ultimately, the decision of how much to spend on housing depends on your individual circumstances and financial priorities. While investing in a more expensive home may have its advantages, it’s essential to carefully weigh the pros and cons and consider the potential impact on your overall finances. By asking yourself “how much should you spend on housing” and considering your individual circumstances, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals.
How to Determine Your Comfortable Housing Budget
Determining a comfortable housing budget requires careful consideration of various factors, including your lifestyle, financial priorities, and income. To start, it’s essential to evaluate your income and expenses to understand how much you can afford to spend on housing. Consider your net income, fixed expenses, and variable expenses, such as food, transportation, and entertainment.
Next, consider your financial priorities, such as saving for retirement, paying off debt, or building an emergency fund. You’ll want to ensure that your housing budget aligns with these priorities and doesn’t compromise your ability to achieve your financial goals.
Another crucial factor to consider is transportation costs. If you’re planning to buy a home in a suburban or rural area, you may need to factor in the cost of commuting to work or school. On the other hand, if you’re looking for a home in an urban area, you may be able to walk or bike to work, reducing your transportation costs.
Food expenses are another essential consideration. If you’re planning to buy a home with a large yard or a garden, you may be able to grow some of your own food, reducing your grocery bills. On the other hand, if you’re looking for a home in an area with limited access to grocery stores, you may need to factor in the cost of transportation to buy food.
Entertainment expenses are also important to consider. If you’re planning to buy a home in an area with limited entertainment options, you may need to factor in the cost of traveling to nearby cities or towns for entertainment.
By carefully considering these factors, you can determine a comfortable housing budget that aligns with your lifestyle and financial priorities. Remember to ask yourself “how much should you spend on housing” and consider your individual circumstances to make an informed decision.
The Impact of Housing Costs on Your Overall Finances
Housing costs can have a significant impact on your overall finances, affecting not only your monthly budget but also your long-term financial goals. When determining how much to spend on housing, it’s essential to consider the broader financial implications of your decision.
One of the most significant effects of housing costs is on credit scores. When you take out a mortgage or rent a home, your credit score can be impacted by your payment history and debt-to-income ratio. Missing payments or having a high debt-to-income ratio can negatively affect your credit score, making it more challenging to secure loans or credit in the future.
Housing costs can also impact your savings rate. When you allocate a large portion of your income towards housing, you may have less money available for savings and investments. This can make it more challenging to achieve long-term financial goals, such as retirement or buying a second home.
Retirement planning is another area where housing costs can have a significant impact. When you’re paying a large portion of your income towards housing, you may have less money available for retirement savings. This can make it more challenging to achieve your retirement goals and may require you to work longer or rely on other sources of income.
To balance housing expenses with other financial goals, it’s essential to create a comprehensive budget that accounts for all of your expenses, including housing, transportation, food, and entertainment. You should also prioritize your financial goals and allocate your income accordingly.
For example, if you’re trying to save for retirement, you may want to allocate a larger portion of your income towards retirement savings. On the other hand, if you’re trying to pay off debt, you may want to allocate a larger portion of your income towards debt repayment.
Ultimately, the key to balancing housing expenses with other financial goals is to create a sustainable budget that aligns with your financial priorities. By considering the broader financial implications of your housing costs and prioritizing your financial goals, you can make informed decisions about how much to spend on housing and achieve long-term financial success.
Strategies for Reducing Housing Costs
Reducing housing costs can be a challenging task, but there are several strategies that can help. One of the most effective ways to reduce housing costs is to explore different neighborhoods. By considering neighborhoods that are slightly further away from the city center or that have lower property values, you may be able to find a more affordable option.
Another strategy for reducing housing costs is to consider alternative types of housing. For example, you may want to consider renting a condo or townhouse instead of a single-family home. These types of housing often have lower maintenance costs and may be more affordable than a single-family home.
Negotiating with landlords or sellers is also a great way to reduce housing costs. If you’re renting, you may be able to negotiate a lower rent by signing a longer lease or by offering to pay rent upfront. If you’re buying, you may be able to negotiate a lower price by offering to pay cash or by pointing out flaws in the property.
Additionally, you may want to consider sharing housing costs with a roommate or partner. This can be a great way to split the costs of housing and make it more affordable.
It’s also important to consider the long-term costs of housing, including maintenance and repairs. By choosing a home that is energy-efficient and has a low maintenance cost, you may be able to save money in the long run.
Ultimately, the key to reducing housing costs is to be flexible and open-minded. By considering different neighborhoods, types of housing, and negotiating with landlords or sellers, you may be able to find a more affordable option that meets your needs and budget.
When determining how much to spend on housing, it’s essential to consider all of these factors and strategies. By asking yourself “how much should you spend on housing” and considering your individual circumstances, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your financial goals and priorities.
Long-Term Considerations: How Housing Costs Affect Your Financial Future
Housing costs can have a significant impact on your financial future, affecting your ability to accumulate wealth, repay debt, and achieve financial independence. When determining how much to spend on housing, it’s essential to consider the long-term implications of your decision.
One of the most significant long-term implications of housing costs is on wealth accumulation. When you allocate a large portion of your income towards housing, you may have less money available for savings and investments. This can make it more challenging to build wealth over time and achieve long-term financial goals.
Debt repayment is another area where housing costs can have a significant impact. When you take out a mortgage or other type of loan to purchase a home, you’ll need to consider the long-term costs of debt repayment. This can include interest payments, fees, and other expenses that can add up over time.
Financial independence is also an important consideration when it comes to housing costs. When you’re paying a large portion of your income towards housing, you may have less money available for other expenses and savings. This can make it more challenging to achieve financial independence and maintain a comfortable standard of living.
Ultimately, the key to making informed decisions about housing costs is to consider the long-term implications of your decision. By asking yourself “how much should you spend on housing” and considering your individual circumstances, you can make a decision that aligns with your financial goals and priorities.
It’s also important to consider the potential risks and benefits of different types of housing investments. For example, investing in a rental property can provide a potential source of passive income, but it also comes with risks such as tenant vacancies and property damage.
By carefully considering the long-term implications of housing costs and making informed decisions, you can create a sustainable housing budget that aligns with your financial goals and priorities.
Creating a Sustainable Housing Budget: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a sustainable housing budget requires careful planning and consideration of your financial goals and priorities. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you create a housing budget that aligns with your financial goals and priorities.
Step 1: Determine Your Income and Expenses
Start by calculating your total monthly income and expenses. Include all sources of income, such as your salary, investments, and any side hustles. Also, include all of your monthly expenses, such as rent or mortgage payments, utilities, groceries, and entertainment.
Step 2: Calculate Your Housing Costs
Next, calculate your housing costs, including rent or mortgage payments, property taxes, and insurance. Also, consider any additional costs, such as maintenance and repairs.
Step 3: Determine Your Housing Budget
Using the 28/36 rule as a guideline, determine how much you can afford to spend on housing. Consider your income, expenses, and financial goals, and adjust the ratio as needed.
Step 4: Prioritize Your Expenses
Once you have determined your housing budget, prioritize your expenses. Consider what expenses are essential, such as rent or mortgage payments, utilities, and groceries. Also, consider what expenses are discretionary, such as entertainment and hobbies.
Step 5: Create a Budget Plan
Using your income, expenses, and housing budget, create a budget plan that outlines projected income and expenses for each month. Be sure to include a buffer for unexpected expenses and emergencies.
Step 6: Monitor and Adjust
Finally, monitor your budget and adjust as needed. Regularly review your income and expenses to ensure that you are staying within your budget. Make adjustments as needed to ensure that you are meeting your financial goals.
By following these steps, you can create a sustainable housing budget that aligns with your financial goals and priorities. Remember to ask yourself “how much should you spend on housing” and consider your individual circumstances to make an informed decision.
Creating a Sustainable Housing Budget: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a sustainable housing budget requires careful planning and consideration of your financial goals and priorities. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you create a housing budget that aligns with your financial goals and priorities.
Step 1: Determine Your Income and Expenses
Start by calculating your total monthly income and expenses. Include all sources of income, such as your salary, investments, and any side hustles. Also, include all of your monthly expenses, such as rent or mortgage payments, utilities, groceries, and entertainment.
Step 2: Calculate Your Housing Costs
Next, calculate your housing costs, including rent or mortgage payments, property taxes, and insurance. Also, consider any additional costs, such as maintenance and repairs.
Step 3: Determine Your Housing Budget
Using the 28/36 rule as a guideline, determine how much you can afford to spend on housing. Consider your income, expenses, and financial goals, and adjust the ratio as needed.
Step 4: Prioritize Your Expenses
Once you have determined your housing budget, prioritize your expenses. Consider what expenses are essential, such as rent or mortgage payments, utilities, and groceries. Also, consider what expenses are discretionary, such as entertainment and hobbies.
Step 5: Create a Budget Plan
Using your income, expenses, and housing budget, create a budget plan that outlines projected income and expenses for each month. Be sure to include a buffer for unexpected expenses and emergencies.
Step 6: Monitor and Adjust
Finally, monitor your budget and adjust as needed. Regularly review your income and expenses to ensure that you are staying within your budget. Make adjustments as needed to ensure that you are meeting your financial goals.
By following these steps, you can create a sustainable housing budget that aligns with your financial goals and priorities. Remember to ask yourself “how much should you spend on housing” and consider your individual circumstances to make an informed decision.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/most-important-factors-investing-real-estate.asp-ADD-FINALjpg-32950329a30d4500b6d7e0fd0ba95189.jpg)