Understanding the Purpose of an Employer Identification Number
An Employer Identification Number (EIN) is a unique nine-digit number assigned to a business or entity by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for tax purposes. Having an EIN is crucial for businesses, as it allows them to open a business bank account, hire employees, and file taxes. In essence, an EIN is a social security number for businesses. It is used to identify the business and its tax accounts with the IRS. To get an EIN, businesses must apply through the IRS, either online, by phone, or by mail. The application process is straightforward, but it requires providing specific information about the business, such as its name, address, and type of entity.
One of the primary reasons businesses need an EIN is to file taxes. The IRS uses the EIN to track the business’s tax accounts and ensure compliance with tax laws. Without an EIN, businesses may face difficulties in filing taxes, and may even be subject to penalties and fines. Additionally, an EIN is required to open a business bank account, which is essential for managing business finances and separating personal and business expenses.
Furthermore, businesses with employees must have an EIN to report employment taxes and comply with labor laws. The EIN is used to identify the business on employment tax returns, such as Form 941, and to report employee wages and taxes withheld. In summary, an EIN is a vital component of a business’s tax compliance and financial management. By understanding the purpose of an EIN, businesses can ensure they are meeting their tax obligations and avoiding potential penalties.
For those wondering how to get an EIN number, the process is relatively simple. The IRS provides an online application, which can be completed in a few minutes. Alternatively, businesses can apply by phone or mail, although these methods may take longer. Regardless of the method chosen, businesses must provide accurate and complete information to ensure their application is processed correctly.
In conclusion, an EIN is a critical component of a business’s tax compliance and financial management. By understanding the purpose of an EIN and how to get one, businesses can ensure they are meeting their tax obligations and avoiding potential penalties. Whether applying online, by phone, or by mail, businesses must provide accurate and complete information to ensure their application is processed correctly.
Who Needs an EIN: Eligibility and Requirements
Not all businesses and entities require an Employer Identification Number (EIN), but most do. To determine if your business needs an EIN, it’s essential to understand the eligibility requirements. Generally, any business or entity that has employees, files taxes, or opens a business bank account needs an EIN. This includes sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and non-profit organizations.
Sole proprietorships, for example, may not need an EIN if they don’t have employees or file taxes separately from their personal tax return. However, if a sole proprietorship has employees or wants to open a business bank account, an EIN is required. Partnerships, on the other hand, always need an EIN, regardless of whether they have employees or not.
Corporations, including S corporations and C corporations, require an EIN for tax purposes. Non-profit organizations, such as charities and churches, also need an EIN to apply for tax-exempt status. Additionally, trusts, estates, and real estate mortgage investment conduits (REMICs) require an EIN.
To obtain an EIN, businesses and entities must meet specific requirements. One of the primary requirements is having a valid business name and address. The business name must be unique and not already in use by another business or entity. The address must be a physical location, not a post office box.
Other requirements for obtaining an EIN include providing the responsible party’s name and Social Security number or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN). The responsible party is the person or entity that owns or controls the business. This information is used to verify the identity of the business and its owners.
When applying for an EIN, businesses and entities must also provide information about the type of business entity they are. This includes the business structure, such as sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation. The application must also include the business’s purpose and the date it was established.
By understanding who needs an EIN and the eligibility requirements, businesses and entities can ensure they are in compliance with tax laws and regulations. If you’re wondering how to get an EIN number, the next step is to gather the required documents and information needed to apply.
Gathering Required Documents: What You Need to Apply
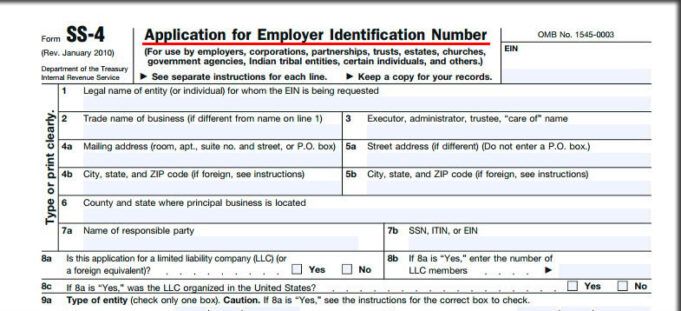
Before applying for an Employer Identification Number (EIN), it’s essential to gather the necessary documents and information required by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This will ensure a smooth and efficient application process. To get an EIN, you’ll need to provide specific information about your business, including its name, address, and type of entity.
The first step is to ensure you have a valid business name and address. The business name must be unique and not already in use by another business or entity. The address must be a physical location, not a post office box. You’ll also need to provide the type of business entity you are, such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or non-profit organization.
In addition to the business name and address, you’ll need to provide information about the responsible party, which is the person or entity that owns or controls the business. This includes the responsible party’s name and Social Security number or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN). If the responsible party is a non-resident alien, they may need to provide additional documentation, such as a copy of their passport or visa.
Other required documents and information may include:
- Business structure: Sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or non-profit organization
- Business purpose: A brief description of the business’s purpose and activities
- Date of establishment: The date the business was established or formed
- State of incorporation: The state where the business is incorporated (if applicable)
It’s also important to note that the IRS may request additional documentation or information to verify the identity of the business and its owners. This may include a copy of the business’s articles of incorporation, a partnership agreement, or a trust agreement.
By gathering the required documents and information, you’ll be well-prepared to apply for an EIN and take the next step in establishing your business. Remember to carefully review the application and ensure all information is accurate and complete to avoid any delays or issues.
Applying for an EIN: Online, Phone, or Mail Options
Once you have gathered the necessary documents and information, you can apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN) through the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). There are three ways to apply for an EIN: online, phone, and mail. Each method has its advantages and disadvantages, which are discussed below.
Online Application: The IRS offers an online application system for EINs, which is available on their website. This is the fastest and most convenient way to apply for an EIN. The online application takes about 10-15 minutes to complete, and you will receive your EIN immediately after submitting the application. To apply online, you will need to provide the required information and documents, including your business name and address, type of business entity, and responsible party’s name and Social Security number or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN).
Phone Application: You can also apply for an EIN by phone by calling the IRS Business and Specialty Tax Line at (800) 829-4933. This method is available from 7:00 a.m. to 7:00 p.m. local time, Monday through Friday. You will need to provide the same information and documents as the online application, and the IRS representative will assist you with the application process. Phone applications are typically processed within 4-6 weeks.
Mail Application: The third option is to apply for an EIN by mail. You can download the EIN application form (Form SS-4) from the IRS website or request one by mail. Once you have completed the form, you can mail it to the IRS address listed on the form. Mail applications are typically processed within 4-6 weeks.
When deciding which method to use, consider the following factors:
- Speed: Online applications are the fastest way to receive an EIN, while mail applications take the longest.
- Convenience: Online applications can be completed at any time, while phone applications are only available during business hours.
- Accuracy: Online applications reduce the risk of errors, as the system checks for accuracy and completeness.
Regardless of the method you choose, make sure to carefully review the application and ensure all information is accurate and complete to avoid any delays or issues. If you’re wondering how to get an EIN number, the next step is to choose the application method that best suits your needs.
How to Apply for an EIN Online: A Step-by-Step Process
Applying for an Employer Identification Number (EIN) online is a straightforward process that can be completed in a few minutes. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to apply for an EIN online:
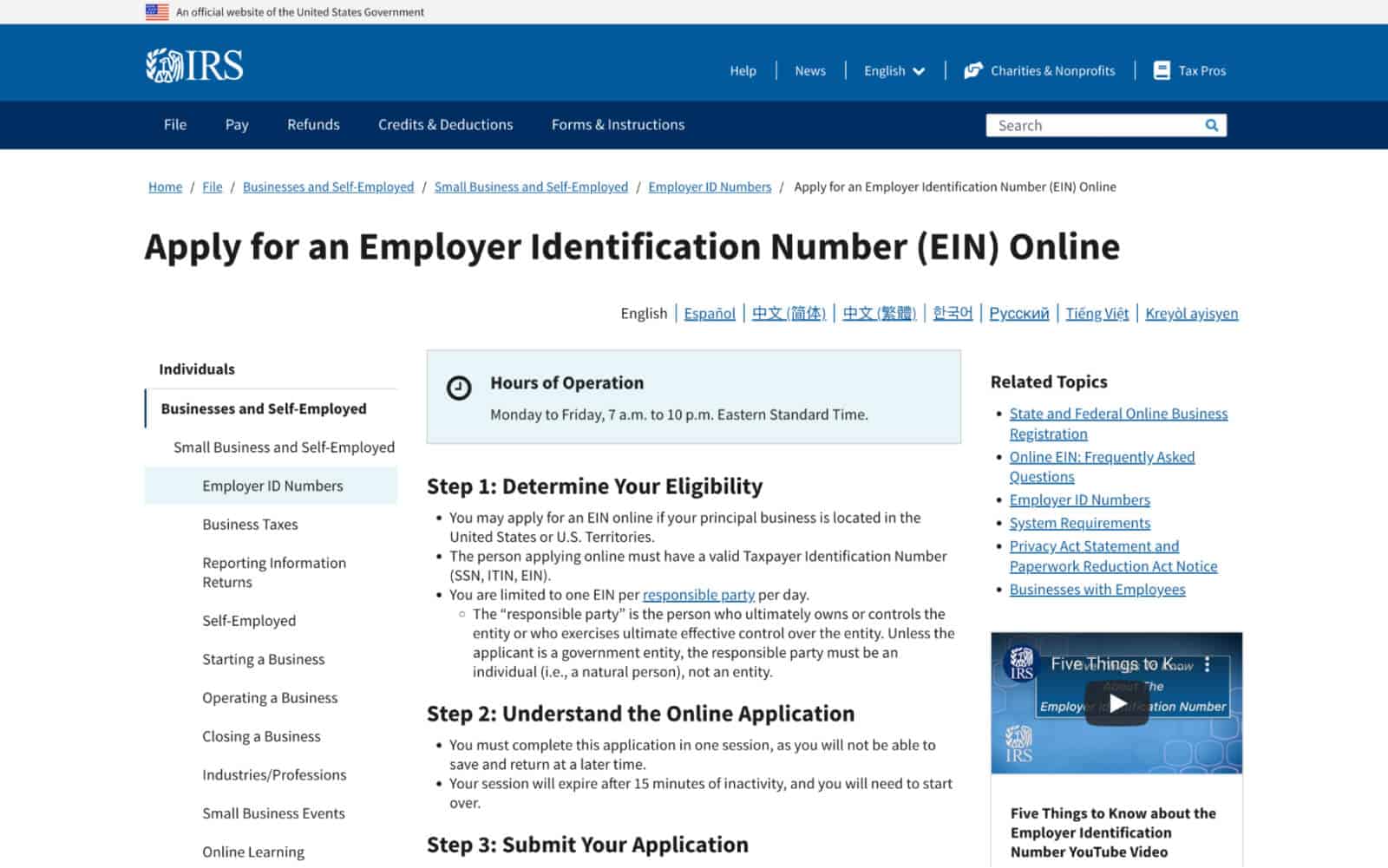
Step 1: Go to the IRS Website
Start by visiting the IRS website at [www.irs.gov](http://www.irs.gov). Click on the “Apply for an Employer Identification Number (EIN)” link, which
Common Errors to Avoid When Applying for an EIN
When applying for an Employer Identification Number (EIN), it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can delay or even reject your application. Here are some common errors to avoid:
Incorrect Business Name or Address
One of the most common mistakes is providing an incorrect business name or address. Make sure to double-check your business name and address to ensure they are accurate and up-to-date. If you have recently changed your business name or address, make sure to update your records with the IRS.
Incomplete Application
Another common mistake is submitting an incomplete application. Make sure to fill out all required fields and provide all necessary documentation. If you are unsure about what information is required, you can refer to the IRS website or contact the IRS directly.
Failure to Provide Required Documentation
Failure to provide required documentation is another common mistake. Make sure to provide all necessary documentation, such as your business license, articles of incorporation, or partnership agreement. If you are unsure about what documentation is required, you can refer to the IRS website or contact the IRS directly.
Using an Incorrect Type of Business Entity
Using an incorrect type of business entity is another common mistake. Make sure to select the correct type of business entity, such as sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or non-profit organization. If you are unsure about what type of business entity you should select, you can refer to the IRS website or contact the IRS directly.
Not Providing a Responsible Party’s Name and Social Security Number or ITIN
Not providing a responsible party‘s name and Social Security number or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN) is another common mistake. Make sure to provide the name and Social Security number or ITIN of the responsible party, which is the person or entity that owns or controls the business.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure a smooth and efficient application process for your EIN. If you’re wondering how to get an EIN number, make sure to follow these tips to avoid any delays or issues.
What to Do After Receiving Your EIN: Next Steps
After receiving your Employer Identification Number (EIN), there are several next steps to take to ensure your business is properly set up and compliant with tax laws. Here are some of the key steps to take:
Open a Business Bank Account
One of the first things to do after receiving your EIN is to open a business bank account. This will help you keep your personal and business finances separate, which is essential for tax purposes. You will need to provide your EIN to the bank to open the account.
Obtain Any Necessary Licenses and Permits
Depending on the type of business you have and the state you are in, you may need to obtain licenses and permits to operate. You will need to provide your EIN to obtain these licenses and permits.
Update Business Records
After receiving your EIN, you will need to update your business records to reflect the new number. This includes updating your business license, articles of incorporation, and any other relevant documents.
Apply for a Business Credit Card or Loan
If you need to obtain financing for your business, you can use your EIN to apply for a business credit card or loan. This will help you establish credit for your business and make it easier to obtain financing in the future.
File Taxes
Finally, you will need to use your EIN to file taxes for your business. This includes filing annual tax returns and making quarterly estimated tax payments.
By following these steps, you can ensure your business is properly set up and compliant with tax laws. If you’re wondering how to get an EIN number, the next step is to take these steps to establish your business and start operating.
Maintaining Your EIN: Updating Information and Avoiding Revocation
Once you have obtained an Employer Identification Number (EIN), it’s essential to maintain accurate and up-to-date information associated with the EIN. This includes updating the business name or address, and avoiding EIN revocation due to inactivity or non-compliance.
Updating Business Information
If your business name or address changes, you must update your EIN information with the IRS. You can do this by filing Form 8822, Change of Address or Responsible Party, with the IRS. This form is used to update the business name, address, or responsible party associated with the EIN.
Avoiding EIN Revocation
The IRS can revoke an EIN if the business is inactive or non-compliant with tax laws. To avoid EIN revocation, make sure to file all required tax returns and make timely payments. You should also ensure that your business is compliant with all tax laws and regulations.
Consequences of EIN Revocation
If your EIN is revoked, you will no longer be able to use it to file tax returns or open a business bank account. You may also be subject to penalties and fines for non-compliance. To avoid these consequences, it’s essential to maintain accurate and up-to-date information associated with the EIN.
Best Practices for Maintaining Your EIN
To maintain your EIN and avoid revocation, follow these best practices:
- Update your business information with the IRS if your business name or address changes.
- File all required tax returns and make timely payments.
- Ensure that your business is compliant with all tax laws and regulations.
- Keep accurate and up-to-date records associated with the EIN.
By following these best practices, you can maintain your EIN and avoid revocation. If you’re wondering how to get an EIN number, the next step is to maintain your EIN and ensure compliance with tax laws.