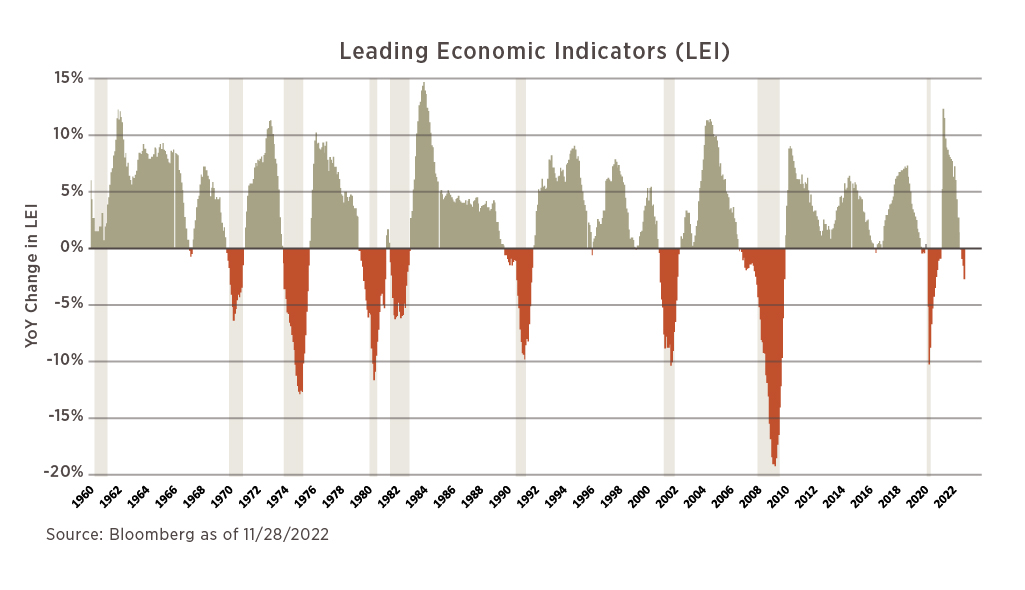
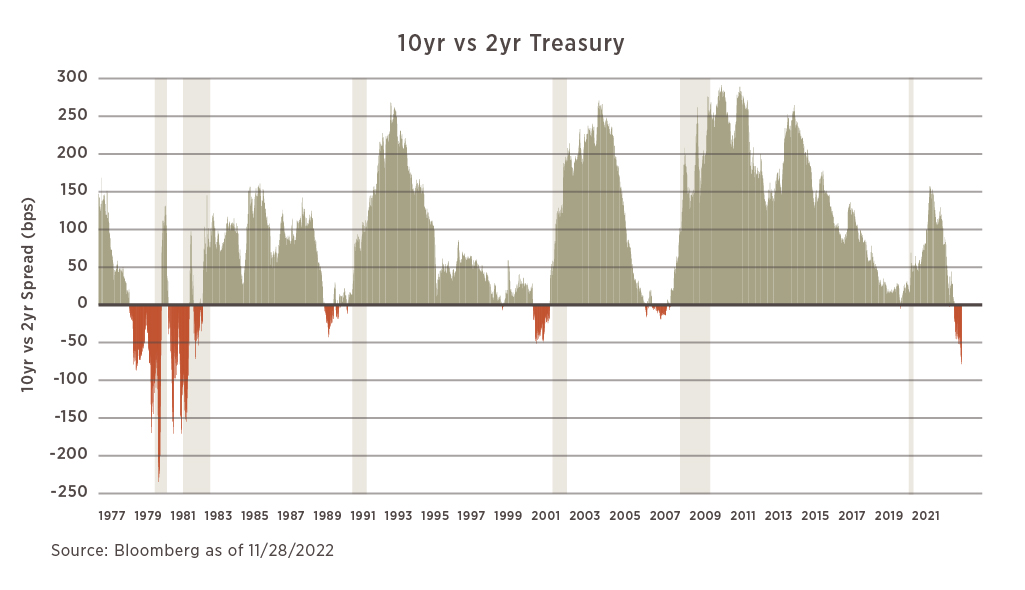
What is a Recession and How is it Defined?
A recession is a period of economic decline, typically defined as a decline in gross domestic product (GDP) for two or more consecutive quarters. Recessions are often characterized by a decline in economic activity, including a decrease in production, employment, and income. The National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) is the official arbiter of recessions in the United States, and it defines a recession as “a significant decline in economic activity spread across the economy, lasting more than a few months.”
Recessions can be caused by a variety of factors, including a decline in consumer spending, a decrease in business investment, and a disruption in global trade. They can also be triggered by external shocks, such as a global pandemic or a major financial crisis. The effects of a recession can be far-reaching, impacting not only the economy but also individuals and communities.
For example, during the 2007-2009 recession, the US economy experienced a significant decline in GDP, with a peak-to-trough decline of 5.1%. The recession also led to a significant increase in unemployment, with the unemployment rate rising from 5.0% in December 2007 to 10.0% in October 2009. The recession had a major impact on various industries, including the housing market, the automotive industry, and the financial sector.
As the US economy continues to evolve, it’s essential to understand the signs of a potential recession. Is the U.S in a recession? The answer is complex, and it’s crucial to examine the current economic indicators to determine the likelihood of a recession. By understanding the definition of a recession and its causes, individuals and businesses can better prepare for potential economic downturns.
Historically, recessions have occurred in the US approximately every 8-10 years, with the most recent recession occurring in 2020. However, the COVID-19 pandemic has created unprecedented economic conditions, making it challenging to predict the likelihood of a recession. As the economy continues to recover, it’s essential to monitor economic indicators and be prepared for potential changes in the economic landscape.
Current Economic Indicators: A Mixed Bag
The current state of the US economy is a complex and multifaceted issue, with various economic indicators sending mixed signals. One of the most closely watched indicators is GDP growth, which has been steadily increasing over the past few years. However, the rate of growth has been slowing down, with the latest quarter showing a growth rate of 2.1%, down from 3.2% in the previous quarter.
Inflation is another key indicator, and it has been relatively stable, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) increasing by 2.3% over the past 12 months. However, some economists are concerned that the recent increase in wages and raw materials could lead to higher inflation in the future.
The labor market is also an important indicator, and it has been showing signs of strength, with the unemployment rate remaining low at 3.6%. However, some economists are concerned that the low unemployment rate could lead to higher wages and inflation, which could potentially trigger a recession.
Consumer spending is another crucial indicator, and it has been relatively stable, with the latest data showing a 0.3% increase in consumer spending. However, some economists are concerned that the recent increase in consumer debt could lead to a decrease in consumer spending in the future.
So, is the U.S in a recession? The answer is not clear-cut, and it’s essential to examine the current economic indicators to determine the likelihood of a recession. While some indicators are showing signs of strength, others are sending warning signals. It’s crucial to monitor these indicators closely and be prepared for potential changes in the economic landscape.
The Federal Reserve has been closely monitoring the economic indicators and has been taking steps to promote economic growth and stability. However, some economists are concerned that the Fed’s actions could potentially trigger a recession. It’s essential to understand the role of monetary policy in shaping the economy and how it can impact the likelihood of a recession.
In conclusion, the current state of the US economy is a mixed bag, with various economic indicators sending different signals. While some indicators are showing signs of strength, others are sending warning signals. It’s crucial to monitor these indicators closely and be prepared for potential changes in the economic landscape.
How to Identify Recession Warning Signs
Identifying recession warning signs is crucial for investors, consumers, and businesses to prepare for potential economic downturns. While it’s impossible to predict with certainty when a recession will occur, there are several indicators that can signal a potential recession. Here are some tips and strategies for identifying recession warning signs:
1. Slowing Economic Growth: A decline in economic growth is often a precursor to a recession. Monitor GDP growth rates, industrial production, and other economic indicators to identify slowing growth.
2. Declining Business Confidence: Business confidence is a key indicator of economic health. Monitor surveys such as the National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB) Small Business Optimism Index and the Conference Board’s Consumer Confidence Index to identify declining confidence.
3. Increasing Debt Levels: High levels of debt can make it difficult for consumers and businesses to weather economic downturns. Monitor debt-to-income ratios, credit card debt, and other debt indicators to identify increasing debt levels.
4. Yield Curve Inversions: A yield curve inversion occurs when short-term interest rates exceed long-term interest rates. This can be a sign of a potential recession. Monitor the yield curve to identify inversions.
5. Decreasing Consumer Spending: Consumer spending is a key driver of economic growth. Monitor consumer spending data, such as retail sales and personal consumption expenditures, to identify decreasing spending.
By monitoring these indicators, investors, consumers, and businesses can identify potential recession warning signs and take steps to prepare. So, is the U.S in a recession? While it’s impossible to predict with certainty, monitoring these indicators can provide valuable insights into the state of the economy.
It’s also essential to understand the role of monetary policy in shaping the economy and how it can impact the likelihood of a recession. The Federal Reserve‘s decisions on interest rates and quantitative easing can have a significant impact on the economy, and understanding these decisions can help investors and consumers make informed decisions.
In addition to monitoring economic indicators, it’s also essential to stay informed about economic trends and recession indicators. Reliable sources of information, such as the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Federal Reserve, can provide valuable insights into the state of the economy.
The Role of Monetary Policy in Shaping the Economy
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in shaping the US economy through its monetary policy decisions. The Fed’s primary objective is to promote maximum employment and price stability, and it uses various tools to achieve these goals. One of the most important tools is setting interest rates, which can influence borrowing costs and spending habits.
When the Fed lowers interest rates, it can stimulate economic growth by making borrowing cheaper and increasing consumer spending. Conversely, when the Fed raises interest rates, it can slow down economic growth by making borrowing more expensive and reducing consumer spending. The Fed also uses quantitative easing, which involves buying or selling government securities to inject liquidity into the economy.
Monetary policy decisions can have a significant impact on the economy, and they can potentially trigger a recession. For example, if the Fed raises interest rates too quickly, it can lead to a slowdown in economic growth and potentially trigger a recession. On the other hand, if the Fed keeps interest rates too low for too long, it can lead to inflation and reduce the purchasing power of consumers.
So, is the U.S in a recession? The answer depends on various factors, including the state of the economy and the Fed’s monetary policy decisions. While the Fed’s decisions can influence the economy, they are not the only factor that determines the state of the economy. Other factors, such as government policies, global events, and technological changes, can also impact the economy.
It’s essential to understand the role of monetary policy in shaping the economy and how it can impact the likelihood of a recession. By monitoring the Fed’s decisions and understanding their impact on the economy, investors and consumers can make informed decisions and prepare for potential economic downturns.
The Fed’s monetary policy decisions are also influenced by its dual mandate, which is to promote maximum employment and price stability. The Fed uses various indicators, such as the unemployment rate and inflation rate, to determine whether the economy is meeting its dual mandate. If the economy is not meeting its dual mandate, the Fed may adjust its monetary policy decisions to stimulate economic growth or reduce inflation.
Expert Insights: What Economists are Saying
Economists and financial experts have varying opinions on the state of the US economy and the potential for a recession. Some experts believe that the economy is strong and that a recession is unlikely, while others believe that the economy is showing signs of weakness and that a recession is possible.
According to a recent survey by the National Association for Business Economics, 60% of economists believe that the US economy will continue to grow in the next year, while 40% believe that a recession is possible. The survey also found that economists are concerned about the impact of trade policies and the rising national debt on the economy.
Janet Yellen, former Chair of the Federal Reserve, has stated that she believes the economy is strong, but that there are risks to the outlook. “I think the economy is in a good place, but I also think that there are risks to the outlook,” she said in a recent interview. “One of the risks is that the economy could slow down more than expected, and that could lead to a recession.”
On the other hand, some economists believe that the economy is already showing signs of weakness and that a recession is possible. “I think the economy is already in a recession,” said David Rosenberg, chief economist at Gluskin Sheff. “The data is already showing signs of weakness, and I think it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
Other experts believe that the economy is in a state of “stagnation,” where growth is slow and uneven. “I think the economy is in a state of stagnation,” said Paul Krugman, Nobel Prize-winning economist. “We’re not seeing the kind of growth that we should be seeing, and I think that’s because of a lack of investment and a lack of demand.”
Overall, the opinions of economists and financial experts on the state of the US economy and the potential for a recession are varied and complex. While some experts believe that the economy is strong, others believe that it is showing signs of weakness and that a recession is possible. So, is the U.S in a recession? The answer depends on who you ask.
Preparing for a Potential Recession: Strategies for Investors and Consumers
While it’s impossible to predict with certainty whether the US will enter a recession, it’s essential for investors and consumers to be prepared. Here are some practical strategies for navigating a potential recession:
For Investors:
Diversify your portfolio: Spread your investments across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and real estate, to minimize risk.
Reduce debt: Pay off high-interest debt and avoid taking on new debt to reduce financial stress.
Build an emergency fund: Save 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses in a easily accessible savings account.
Consider alternative investments: Invest in assets that are less correlated with the stock market, such as gold or real estate.
For Consumers:
Reduce expenses: Cut back on discretionary spending and focus on essential expenses.
Build an emergency fund: Save 3-6 months’ worth of living expenses in a easily accessible savings account.
Pay off high-interest debt: Focus on paying off high-interest debt, such as credit card balances, to reduce financial stress.
Consider a recession-proof budget: Create a budget that accounts for reduced income and increased expenses during a recession.
By taking these steps, investors and consumers can prepare for a potential recession and minimize its impact. So, is the U.S in a recession? While it’s impossible to predict with certainty, being prepared can help reduce financial stress and uncertainty.
It’s also essential to stay informed about economic trends and recession indicators. By monitoring reliable sources of information, such as the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Federal Reserve, investors and consumers can make informed decisions and stay ahead of the curve.
In addition, it’s crucial to critically evaluate information and make informed decisions. By considering multiple perspectives and analyzing data, investors and consumers can make informed decisions and navigate a potential recession with confidence.
Historical Context: Past Recessions and Their Impact
The United States has experienced several recessions throughout its history, each with its own unique causes and effects. By examining past recessions, we can gain valuable insights into the current economic situation and better understand the potential risks and opportunities.
One of the most significant recessions in US history was the Great Depression, which lasted from 1929 to 1939. The Great Depression was caused by a combination of factors, including a stock market crash, overproduction, and a decline in international trade. The recession had a devastating impact on the economy, with unemployment rates soaring to over 25% and GDP declining by over 25%.
Another significant recession was the 1981-1982 recession, which was caused by a combination of high interest rates and a decline in oil prices. The recession had a significant impact on the manufacturing sector, with many factories closing and jobs being lost.
The 2007-2009 recession, also known as the Great Recession, was caused by a housing market bubble bursting and a subsequent financial crisis. The recession had a significant impact on the economy, with unemployment rates soaring to over 10% and GDP declining by over 5%.
By examining these past recessions, we can see that each one had its own unique causes and effects. However, there are also some common themes that emerge, such as the importance of monetary policy and the impact of external shocks on the economy.
So, is the U.S in a recession? While it’s impossible to predict with certainty, examining past recessions can provide valuable insights into the current economic situation. By understanding the causes and effects of past recessions, we can better prepare for potential economic downturns and make informed decisions.
In addition to examining past recessions, it’s also essential to stay informed about current economic trends and recession indicators. By monitoring reliable sources of information, such as the Bureau of Labor Statistics and the Federal Reserve, we can stay ahead of the curve and make informed decisions.
By combining historical context with current economic trends and recession indicators, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the economy and make informed decisions. Whether the US is in a recession or not, being prepared and informed is essential for navigating the complex and ever-changing economic landscape.
Staying Informed: How to Track Economic Trends and Recession Indicators
To stay informed about economic trends and recession indicators, it’s essential to rely on credible sources of information. Here are some reliable sources to track:
Government Reports: The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) and the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provide timely and accurate data on employment, inflation, and GDP growth.
Economic Data: Websites like FRED (Federal Reserve Economic Data) and Quandl offer a vast array of economic data, including recession indicators and economic trends.
News Outlets: Reputable news outlets like The Wall Street Journal, Bloomberg, and CNBC provide in-depth coverage of economic trends and recession indicators.
Think Tanks: Organizations like the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) and the Brookings Institution offer expert analysis and research on economic trends and recession indicators.
To critically evaluate information and make informed decisions, consider the following tips:
Verify sources: Ensure that the information comes from credible sources and is supported by data.
Analyze trends: Look for patterns and trends in the data to gain a deeper understanding of the economy.
Consider multiple perspectives: Seek out diverse opinions and insights to form a well-rounded view of the economy.
Stay up-to-date: Regularly check for updates and new information to stay informed about the latest economic trends and recession indicators.
By staying informed and critically evaluating information, you can make informed decisions and navigate the complex and ever-changing economic landscape. So, is the U.S in a recession? While it’s impossible to predict with certainty, staying informed and prepared can help you weather any economic storm.