What is Lean Startup Methodology and Why Does it Matter
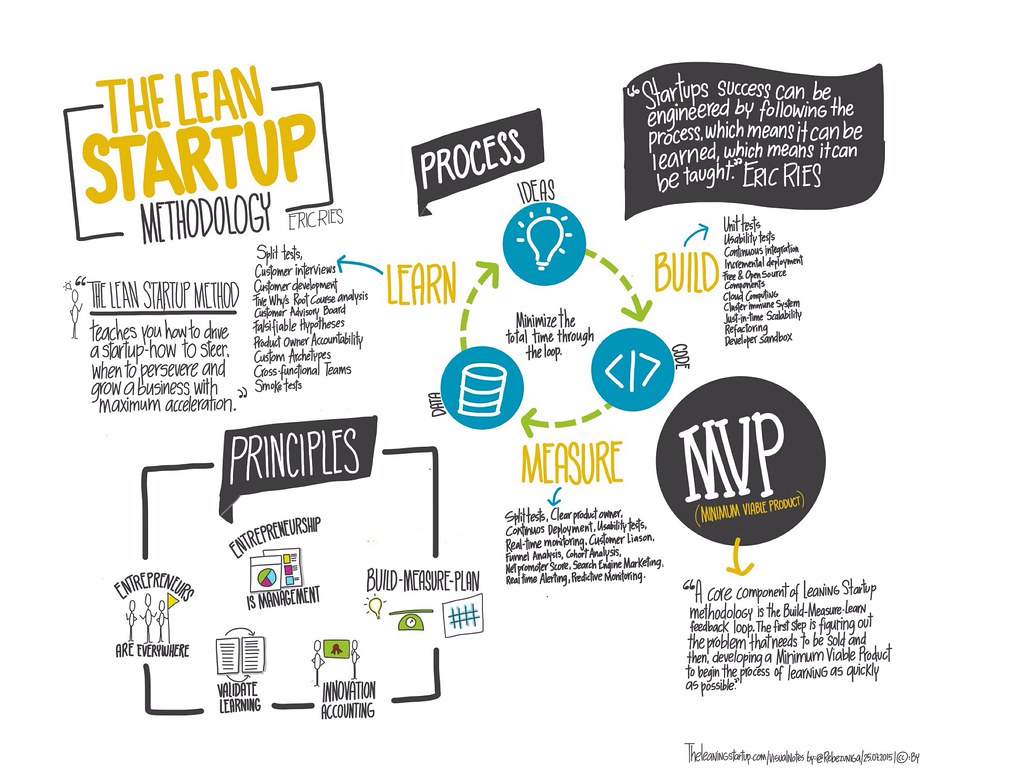
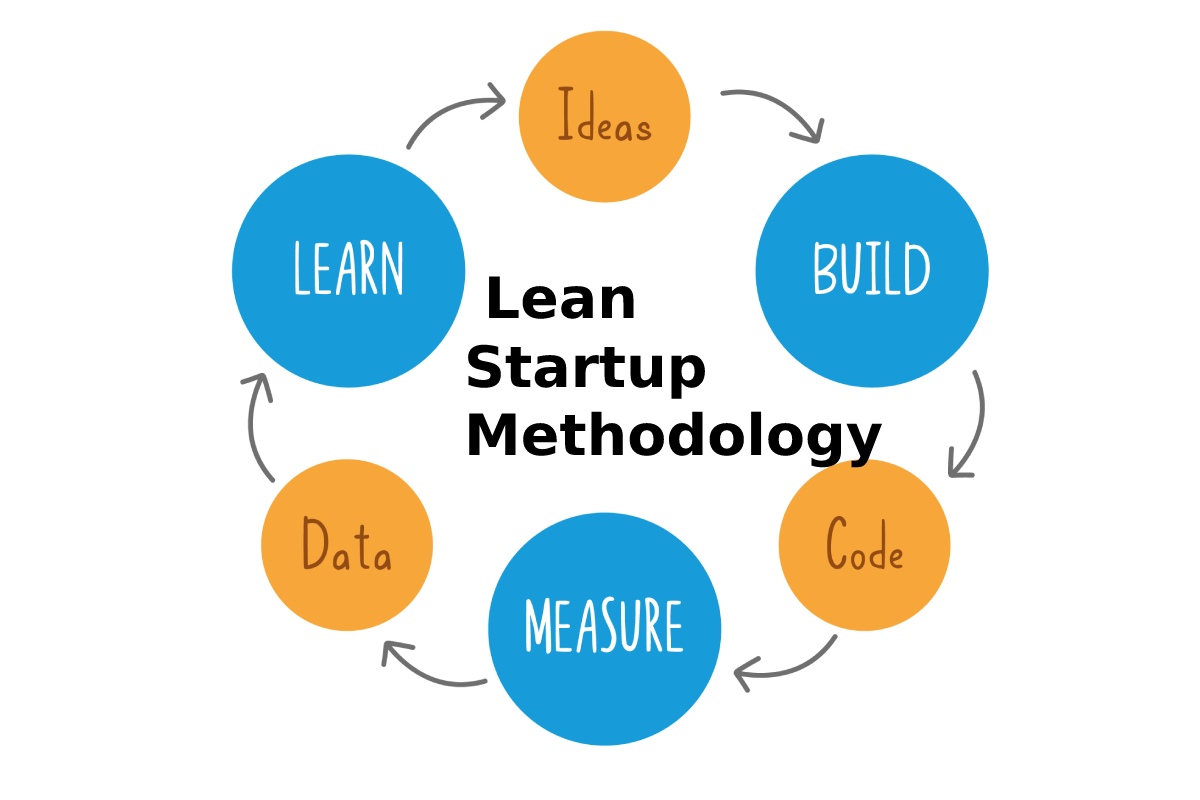
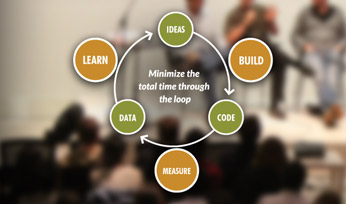
Lean startup methodology is a revolutionary approach to building and launching successful startups. This innovative framework, popularized by Eric Ries, emphasizes rapid experimentation, customer-centricity, and continuous iteration. By adopting lean startup principles, entrepreneurs can reduce the risk of launching a new product or service, and increase their chances of success in a rapidly changing market.
At its core, lean startup methodology is about embracing uncertainty and using data-driven decision making to drive innovation. This approach is in stark contrast to traditional startup methods, which often rely on elaborate business plans and a “build it and they will come” mentality. By focusing on lean startup principles, entrepreneurs can create a more agile and adaptable organization, better equipped to respond to changing customer needs and market conditions.
One of the key benefits of lean startup methodology is its emphasis on rapid experimentation. By building and testing a minimum viable product (MVP), entrepreneurs can quickly validate assumptions about their product or service, and make data-driven decisions about how to proceed. This approach also encourages a culture of continuous iteration, where entrepreneurs are constantly seeking feedback from customers, and using that feedback to improve and refine their offering.
Lean startup methodology is not just a buzzword or a passing fad. It’s a proven approach that has been successfully adopted by many of the world’s most innovative and successful startups. By embracing lean startup principles, entrepreneurs can create a more sustainable and scalable business model, and increase their chances of long-term success.
So, why does lean startup methodology matter? In today’s fast-paced and competitive startup landscape, it’s more important than ever to be agile, adaptable, and customer-centric. By adopting lean startup principles, entrepreneurs can stay ahead of the curve, and build a successful and sustainable business that meets the needs of their customers.
How to Apply Lean Startup Principles to Your Business
Applying lean startup methodology to your business requires a structured approach. The first step is to define a problem statement, which clearly articulates the problem you’re trying to solve and the target market you’re trying to serve. This statement should be concise, yet meaningful, and should guide all subsequent decisions.
Next, identify your target market and create buyer personas to better understand their needs and pain points. This will help you develop a minimum viable product (MVP) that meets their needs and provides a unique value proposition. The MVP should be a simplified version of your product or service, designed to test assumptions and gather feedback from early adopters.
Once you’ve developed your MVP, it’s essential to create a feedback loop that allows you to collect and analyze data from your target market. This can be achieved through surveys, user testing, and analytics tools. The feedback loop should be continuous, with regular iterations and improvements made to the product or service based on customer feedback.
Another critical aspect of lean startup methodology is the concept of pivoting. Pivoting involves making significant changes to your business model or product based on customer feedback and data analysis. This can be a challenging process, but it’s essential to remain agile and adaptable in a rapidly changing market.
To illustrate the application of lean startup principles, consider the example of a startup that develops a mobile app for food delivery. The problem statement might be “to provide a convenient and efficient way for customers to order food from local restaurants.” The target market might be busy professionals who value convenience and speed. The MVP might be a simplified app that allows customers to order from a limited number of restaurants, with a feedback loop that collects data on customer preferences and pain points.
By following these steps and embracing the principles of lean startup methodology, businesses can reduce the risk of launching a new product or service and increase their chances of success in a rapidly changing market.
The Role of Customer Feedback in Lean Startup
Customer feedback is a crucial component of lean startup methodology. It provides valuable insights into customer needs, preferences, and pain points, allowing startups to iterate and improve their product or service. In a lean startup, customer feedback is not just a nicety, but a necessity. It’s the fuel that drives the innovation engine, enabling startups to build products that meet the needs of their target market.
So, how do you collect and analyze customer feedback in a lean startup? The first step is to establish a feedback loop, which involves creating a system for collecting feedback from customers, analyzing it, and using it to make data-driven decisions. This can be achieved through various channels, such as surveys, user testing, and analytics tools.
When collecting customer feedback, it’s essential to ask the right questions. This involves creating a survey or questionnaire that is designed to gather specific information about customer needs and preferences. For example, you might ask questions like “What do you like about our product?” or “What features would you like to see us add?”
Once you’ve collected customer feedback, the next step is to analyze it. This involves using tools like pivot tables and analytics software to identify patterns and trends in the data. By analyzing customer feedback, you can gain a deeper understanding of customer needs and preferences, and use this information to inform product development decisions.
Using customer feedback to iterate and improve the product or service is a critical component of lean startup methodology. This involves using the insights gained from customer feedback to make data-driven decisions about product development, and to prioritize features and functionality based on customer needs.
For example, let’s say you’re a startup that’s developing a mobile app for food delivery. You collect customer feedback through surveys and user testing, and analyze it using pivot tables and analytics software. Based on the feedback, you discover that customers are looking for a feature that allows them to track the status of their orders in real-time. You use this information to prioritize the development of this feature, and to make data-driven decisions about how to implement it.
By incorporating customer feedback into the lean startup process, startups can build products that meet the needs of their target market, and achieve a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Lean Startup Tools and Techniques for Rapid Experimentation
Rapid experimentation is a critical component of lean startup methodology. It involves testing assumptions and hypotheses through experimentation, and using the results to inform product development decisions. There are several tools and techniques that can be used to facilitate rapid experimentation in a lean startup.
One of the most popular tools for rapid experimentation is A/B testing. A/B testing involves creating two versions of a product or feature, and testing them against each other to see which one performs better. This can be done using tools like Optimizely or VWO, which allow you to create and test different versions of your product or feature.
Another tool that can be used for rapid experimentation is landing pages. Landing pages are standalone web pages that are designed to test a specific hypothesis or assumption. They can be used to test different versions of a product or feature, or to test different marketing messages and value propositions.
Pivot tables are another tool that can be used for rapid experimentation. Pivot tables are a type of data analysis tool that allows you to quickly and easily analyze large datasets. They can be used to analyze customer feedback and behavior, and to identify trends and patterns in the data.
Lean startup also involves using other tools and techniques such as wireframing, prototyping, and usability testing. Wireframing involves creating low-fidelity sketches of a product or feature, and testing them with customers to get feedback. Prototyping involves creating a functional prototype of a product or feature, and testing it with customers to get feedback. Usability testing involves testing a product or feature with customers to see how they interact with it, and to identify any usability issues.
By using these tools and techniques, startups can quickly and easily test assumptions and hypotheses, and use the results to inform product development decisions. This can help to reduce the risk of launching a new product or feature, and increase the chances of success.
For example, let’s say you’re a startup that’s developing a new mobile app. You use A/B testing to test different versions of the app’s user interface, and you use landing pages to test different marketing messages and value propositions. You also use pivot tables to analyze customer feedback and behavior, and to identify trends and patterns in the data. By using these tools and techniques, you can quickly and easily test assumptions and hypotheses, and use the results to inform product development decisions.
Case Studies of Successful Lean Startups
Lean startup methodology has been successfully applied by many startups, resulting in significant growth and success. Here are a few examples of startups that have used lean startup principles to achieve success.
Airbnb is a great example of a startup that has used lean startup methodology to achieve success. Airbnb’s founders, Brian Chesky and Joe Gebbia, started the company by renting out air mattresses in their apartment to attendees of a design conference. They then used the feedback from their customers to iterate and improve their product, eventually expanding to offer a platform for booking entire homes and apartments.
Uber is another example of a startup that has used lean startup methodology to achieve success. Uber’s founders, Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp, started the company by offering a luxury car service in San Francisco. They then used the feedback from their customers to iterate and improve their product, eventually expanding to offer a ride-sharing service that has become a global phenomenon.
Dropbox is a third example of a startup that has used lean startup methodology to achieve success. Dropbox’s founders, Drew Houston and Arash Ferdowsi, started the company by offering a simple file-sharing service. They then used the feedback from their customers to iterate and improve their product, eventually expanding to offer a suite of cloud-based storage and collaboration tools.
In each of these cases, the startups used lean startup methodology to quickly test and validate their assumptions, and to iterate and improve their products based on customer feedback. By using lean startup principles, these startups were able to achieve significant growth and success, and to establish themselves as leaders in their respective markets.
These case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of lean startup methodology in achieving success. By using lean startup principles, startups can quickly test and validate their assumptions, and iterate and improve their products based on customer feedback. This approach allows startups to achieve significant growth and success, and to establish themselves as leaders in their respective markets.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Lean Startup Implementation
While lean startup methodology can be a powerful tool for startups, there are several common mistakes that can hinder its effectiveness. Here are some of the most common mistakes to avoid when implementing lean startup methodology:
One of the most common mistakes is neglecting customer feedback. Lean startup methodology is all about customer-centricity, and neglecting customer feedback can lead to a product or service that doesn’t meet the needs of the target market. To avoid this mistake, make sure to collect and analyze customer feedback regularly, and use it to iterate and improve the product or service.
Another common mistake is failing to pivot when necessary. Lean startup methodology is all about rapid experimentation and iteration, and failing to pivot when necessary can lead to stagnation and failure. To avoid this mistake, make sure to regularly assess the product or service and be willing to make changes when necessary.
Not having a clear problem statement is also a common mistake. A clear problem statement is essential for defining the target market and creating a minimum viable product (MVP). To avoid this mistake, make sure to define a clear problem statement and use it to guide the development of the product or service.
Not testing assumptions is another common mistake. Lean startup methodology is all about testing assumptions and iterating based on the results. To avoid this mistake, make sure to test assumptions regularly and use the results to inform product development decisions.
Finally, not maintaining a customer-centric approach is a common mistake. Lean startup methodology is all about customer-centricity, and neglecting this approach can lead to a product or service that doesn’t meet the needs of the target market. To avoid this mistake, make sure to maintain a customer-centric approach throughout the development process.
By avoiding these common mistakes, startups can ensure that they are using lean startup methodology effectively and achieving the best possible outcomes.
Lean Startup and Agile Methodologies: What’s the Difference?
Lean startup and agile methodologies are two popular approaches to product development and project management. While they share some similarities, they have distinct principles and applications. In this section, we’ll explore the differences between lean startup and agile methodologies, and how they can be used together to achieve better outcomes.
Lean startup methodology is a approach to product development that emphasizes rapid experimentation, customer-centricity, and continuous iteration. It’s designed to help startups quickly test and validate assumptions, and to iterate and improve their products based on customer feedback.
Agile methodology, on the other hand, is a approach to project management that emphasizes flexibility, collaboration, and rapid delivery. It’s designed to help teams quickly respond to changing requirements, and to deliver working software in short iterations.
While both lean startup and agile methodologies emphasize rapid iteration and customer-centricity, they have different focuses and applications. Lean startup methodology is primarily focused on product development, while agile methodology is primarily focused on project management.
However, both methodologies can be used together to achieve better outcomes. By combining the principles of lean startup and agile methodologies, teams can quickly test and validate assumptions, and rapidly deliver working software that meets the needs of their customers.
For example, a team might use lean startup principles to develop a minimum viable product (MVP), and then use agile methodologies to iterate and improve the product based on customer feedback. By combining these approaches, teams can quickly deliver working software that meets the needs of their customers, and continuously improve and refine their products over time.
In summary, lean startup and agile methodologies are two distinct approaches to product development and project management. While they share some similarities, they have different focuses and applications. By combining the principles of both methodologies, teams can quickly test and validate assumptions, and rapidly deliver working software that meets the needs of their customers.
Scaling Lean Startup Principles for Growth and Success
As a startup grows and matures, it’s essential to scale lean startup principles to maintain a customer-centric approach and continue to iterate and improve the product or service. Scaling lean startup principles requires a deliberate and structured approach to ensure that the startup remains agile and responsive to changing customer needs.
One key aspect of scaling lean startup principles is to maintain a customer-centric approach. This involves continuing to collect and analyze customer feedback, and using it to inform product development decisions. It’s also essential to ensure that the startup’s organizational structure and processes are aligned with lean startup principles, and that all teams are working together to deliver a seamless customer experience.
Another important aspect of scaling lean startup principles is to continue to iterate and improve the product or service. This involves using data and customer feedback to identify areas for improvement, and prioritizing product development efforts accordingly. It’s also essential to ensure that the startup is using the right tools and technologies to support lean startup principles, such as agile project management software and customer feedback platforms.
Scaling lean startup principles also requires a focus on innovation and experimentation. This involves encouraging a culture of experimentation and learning within the startup, and providing resources and support for teams to test new ideas and approaches. It’s also essential to ensure that the startup is using data and customer feedback to inform innovation efforts, and that all teams are working together to deliver innovative solutions that meet customer needs.
Finally, scaling lean startup principles requires a focus on metrics and measurement. This involves establishing clear metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of lean startup efforts, and using data to inform product development decisions. It’s also essential to ensure that the startup is using the right tools and technologies to support metrics and measurement, such as data analytics software and performance monitoring platforms.
By scaling lean startup principles, startups can maintain a customer-centric approach, continue to iterate and improve the product or service, and drive innovation and experimentation. This can help to drive growth and success, and establish the startup as a leader in its market.