Why You Might Want to Remove Your Website from Google
Websites are often created to provide information, promote products or services, or establish a brand’s online presence. However, there may come a time when a website is no longer needed or has become outdated. In such cases, it may be necessary to omit the website from Google search results to prevent users from accessing outdated or irrelevant content. This can be particularly important for businesses that have undergone rebranding or have changed their online strategy. By removing the website from Google’s index, businesses can ensure that users are directed to their new or updated online presence.
Security concerns are another reason why website owners may want to remove their website from Google’s index. If a website has been compromised by malware or has been hacked, it may be necessary to remove it from search results to prevent users from accessing the compromised site. Additionally, website owners may want to remove their website from Google’s index if it contains sensitive or confidential information that should not be publicly accessible.
Furthermore, website owners may want to remove their website from Google’s index if it is no longer relevant or useful to their target audience. This can help to improve the overall user experience and prevent users from accessing outdated or irrelevant content. By removing the website from Google’s index, website owners can ensure that users are directed to more relevant and useful content.
In some cases, website owners may want to omit their website from Google search results temporarily. This can be useful if a website is undergoing maintenance or is being updated. By removing the website from Google’s index, website owners can prevent users from accessing the site while it is being updated, which can help to prevent user frustration and improve the overall user experience.
Overall, there are several reasons why website owners may want to remove their website from Google’s index. Whether it is due to outdated content, security concerns, or a desire to rebrand, removing a website from Google’s index can be an effective way to improve the user experience and prevent users from accessing irrelevant or sensitive content.
Understanding How Google Crawls and Indexes Websites
Google’s crawlers, also known as spiders or bots, are software programs that continuously scan and index the web for new and updated content. The crawling process begins with a list of URLs that Google has discovered through various means, such as sitemaps, links from other websites, and previous crawls. When a crawler visits a website, it reads the HTML content and extracts relevant information, such as keywords, meta tags, and links to other pages.
The crawled data is then sent to Google’s indexing servers, where it is processed and added to the Google index. The index is a massive database that contains information about every webpage that Google has crawled and indexed. When a user submits a search query, Google’s algorithm searches the index to find relevant results and returns them to the user.
Website owners can influence the crawling and indexing process by optimizing their website’s structure and content. This includes creating a clear and concise website hierarchy, using descriptive and keyword-rich meta tags, and ensuring that all pages are accessible to crawlers. Additionally, website owners can submit a sitemap to Google, which helps the crawlers discover new and updated content.
Google’s crawlers also use various signals to determine the frequency and depth of crawling. For example, websites with frequently updated content, such as news sites or blogs, may be crawled more frequently than websites with static content. Similarly, websites with a large number of links from other websites may be considered more authoritative and crawled more deeply.
Understanding how Google crawls and indexes websites is essential for website owners who want to omit their website from Google search results. By knowing how the crawling and indexing process works, website owners can take steps to prevent their website from being crawled and indexed, or to remove their website from the index if it has already been crawled.
It’s worth noting that Google’s crawling and indexing process is continuous, and it can take some time for changes to be reflected in search results. Therefore, website owners who want to omit their website from Google search results should plan ahead and take steps to prevent crawling and indexing, or to remove their website from the index, as soon as possible.
Methods for Removing a Website from Google’s Index
There are several methods that website owners can use to remove their website from Google’s index. The most effective method will depend on the specific circumstances and the reason for removing the website. Here are some of the most common methods:
Using the Google Search Console: The Google Search Console is a free tool that allows website owners to manage their website’s presence in Google’s search results. Website owners can use the Search Console to submit a removal request for their website, which will remove the website from Google’s index. To use the Search Console, website owners must first verify their website ownership, which can be done by adding a meta tag to the website’s HTML header or by uploading an HTML file to the website’s root directory.
Adding a Robots.txt File: A robots.txt file is a text file that is placed in the root directory of a website. The file contains instructions for search engine crawlers, such as Googlebot, on which pages or directories to crawl and index. Website owners can use the robots.txt file to block Googlebot from crawling and indexing their website. To do this, website owners must add a “Disallow” directive to the robots.txt file, which will prevent Googlebot from crawling the website.
Using the “Noindex” Meta Tag: The “noindex” meta tag is a HTML tag that can be added to a website’s HTML header. The tag instructs search engine crawlers, such as Googlebot, not to index the page. Website owners can use the “noindex” meta tag to prevent Google from indexing their website. To do this, website owners must add the “noindex” meta tag to the HTML header of each page on the website.
Other Methods: There are other methods that website owners can use to remove their website from Google’s index, such as using a website removal tool or contacting Google directly. However, these methods are not always effective and may not be recommended by Google.
It’s worth noting that removing a website from Google’s index can take some time, and it may not be possible to completely remove the website from Google’s index. However, by using one or more of the methods described above, website owners can reduce the visibility of their website in Google’s search results and prevent users from accessing the website.
How to Use the Google Search Console to Remove a Website
The Google Search Console is a powerful tool that allows website owners to manage their website’s presence in Google’s search results. One of the features of the Search Console is the ability to submit a removal request for a website, which can be useful if you want to omit your website from Google search results. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use the Google Search Console to remove a website:
Step 1: Verify Your Website Ownership
To use the Google Search Console, you need to verify your website ownership. This can be done by adding a meta tag to your website’s HTML header or by uploading an HTML file to your website’s root directory. Once you’ve verified your website ownership, you can access the Search Console and submit a removal request.
Step 2: Submit a Removal Request
To submit a removal request, log in to the Google Search Console and navigate to the “Removals” section. Click on the “New removal request” button and enter the URL of the website you want to remove. You’ll need to specify the reason for the removal request and provide any additional information that may be required.
Step 3: Verify the Removal Request
Once you’ve submitted the removal request, Google will review it and verify that the website has been removed from their index. This may take a few days or weeks, depending on the complexity of the request. You can track the status of your removal request in the Search Console.
Step 4: Monitor the Website’s Status
After the removal request has been processed, you should monitor the website’s status to ensure that it has been removed from Google’s index. You can do this by searching for the website in Google and checking that it no longer appears in the search results.
Using the Google Search Console to remove a website is a straightforward process that can be completed in a few steps. By following these steps, you can omit your website from Google search results and prevent users from accessing the website.
Using the Robots.txt File to Block Google Crawlers
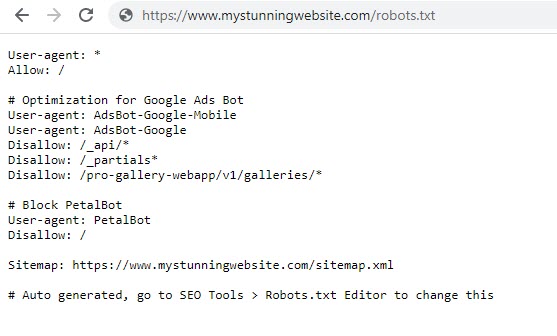
The robots.txt file is a text file that is placed in the root directory of a website. It contains instructions for search engine crawlers, such as Googlebot, on which pages or directories to crawl and index. By using the robots.txt file, website owners can block Google crawlers from accessing their website, which can be useful if they want to omit their website from Google search results.
To create a robots.txt file, website owners can use a text editor to create a new file and add the following lines of code:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /
The first line of code specifies the user agent, which in this case is Googlebot. The second line of code specifies the disallow directive, which tells Googlebot not to crawl or index the website.
Once the robots.txt file has been created, it needs to be uploaded to the root directory of the website. This can be done using an FTP client or by using the website’s file manager.
After the robots.txt file has been uploaded, website owners can test it by using the Google Search Console’s robots.txt tester tool. This tool allows website owners to test their robots.txt file and see how it will be interpreted by Googlebot.
Using the robots.txt file to block Google crawlers is a simple and effective way to omit a website from Google search results. However, it’s worth noting that the robots.txt file is not a foolproof method, and Googlebot may still crawl and index the website if it is linked to from other websites or if it is listed in a sitemap.
Therefore, website owners should use the robots.txt file in conjunction with other methods, such as using the Google Search Console or adding a noindex meta tag, to ensure that their website is completely removed from Google’s index.
Adding a Noindex Meta Tag to Prevent Indexing
The “noindex” meta tag is a HTML tag that can be added to a website’s HTML header to prevent Google from indexing the page. This tag is useful for website owners who want to omit their website from Google search results, as it tells Google not to index the page.
To add a “noindex” meta tag to a website, website owners can use a text editor to add the following line of code to the HTML header:
This line of code tells Google not to index the page, and it can be added to the HTML header of each page on the website.
After adding the “noindex” meta tag, website owners can verify its effectiveness by using the Google Search Console‘s “Fetch as Google” tool. This tool allows website owners to see how Googlebot views the page, and it can help them verify that the “noindex” meta tag is working correctly.
Using the “noindex” meta tag is a simple and effective way to prevent Google from indexing a website. However, it’s worth noting that this method may not be foolproof, and Google may still index the website if it is linked to from other websites or if it is listed in a sitemap.
Therefore, website owners should use the “noindex” meta tag in conjunction with other methods, such as using the Google Search Console or adding a robots.txt file, to ensure that their website is completely removed from Google’s index.
In addition to adding a “noindex” meta tag, website owners can also use other meta tags to control how Google indexes their website. For example, the “nofollow” meta tag can be used to prevent Google from following links on the page, and the “nosnippet” meta tag can be used to prevent Google from displaying a snippet of the page in search results.
By using these meta tags, website owners can have more control over how Google indexes their website, and they can ensure that their website is not indexed in a way that they do not want.
What to Expect After Removing a Website from Google’s Index
After removing a website from Google’s index, website owners can expect a few things to happen. First, the website will no longer appear in Google’s search results, which means that users will not be able to find the website by searching for it on Google.
However, it’s worth noting that removing a website from Google’s index does not necessarily mean that the website will be completely removed from the internet. The website may still be accessible by typing in the URL directly, and it may still be indexed by other search engines.
In addition, removing a website from Google’s index can take some time. Google’s crawlers may take several days or even weeks to update their index and remove the website from their search results. During this time, the website may still appear in Google’s search results, even though it has been removed from the index.
Website owners can verify that their website has been removed from Google’s index by using the Google Search Console. The Search Console provides a tool that allows website owners to check the status of their website’s removal request and see when the website was last crawled by Google.
It’s also important to note that removing a website from Google’s index is not a permanent solution. If the website is not properly blocked from Google’s crawlers, it may be reindexed at a later time. To prevent this from happening, website owners should take steps to block Google’s crawlers from accessing their website, such as by adding a robots.txt file or using the “noindex” meta tag.
By understanding what to expect after removing a website from Google’s index, website owners can take the necessary steps to ensure that their website is properly removed and that it does not reappear in Google’s search results.
It’s also worth noting that removing a website from Google’s index can have an impact on the website’s traffic and visibility. If the website is no longer appearing in Google’s search results, it may receive less traffic and visibility. Website owners should consider this when deciding whether to remove their website from Google’s index.
Preventing Reindexing and Ensuring Long-Term Removal
After removing a website from Google’s index, it’s essential to take steps to prevent reindexing and ensure long-term removal. This can be achieved by regularly monitoring the website’s status and making long-term changes to prevent reindexing.
One way to prevent reindexing is to regularly monitor the website’s status using the Google Search Console. The Search Console provides a tool that allows website owners to check the status of their website’s removal request and see when the website was last crawled by Google.
Another way to prevent reindexing is to make long-term changes to the website’s structure and content. This can include removing any links to the website from other websites, updating the website’s robots.txt file, and adding a “noindex” meta tag to the website’s HTML header.
It’s also essential to ensure that the website is not reindexed by Google’s crawlers. This can be achieved by blocking Google’s crawlers from accessing the website using a robots.txt file or by adding a “noindex” meta tag to the website’s HTML header.
Additionally, website owners can use the Google Search Console to submit a removal request for any URLs that may have been reindexed. This can help to ensure that the website is completely removed from Google’s index and prevent reindexing.
By taking these steps, website owners can ensure that their website is completely removed from Google’s index and prevent reindexing. This can help to maintain the website’s online presence and prevent any potential issues that may arise from reindexing.
It’s also worth noting that preventing reindexing and ensuring long-term removal can be a complex process, and it may require ongoing effort and maintenance. However, by following the steps outlined above, website owners can ensure that their website is completely removed from Google’s index and prevent reindexing.