The Importance of Operational Planning in Achieving Strategic Goals
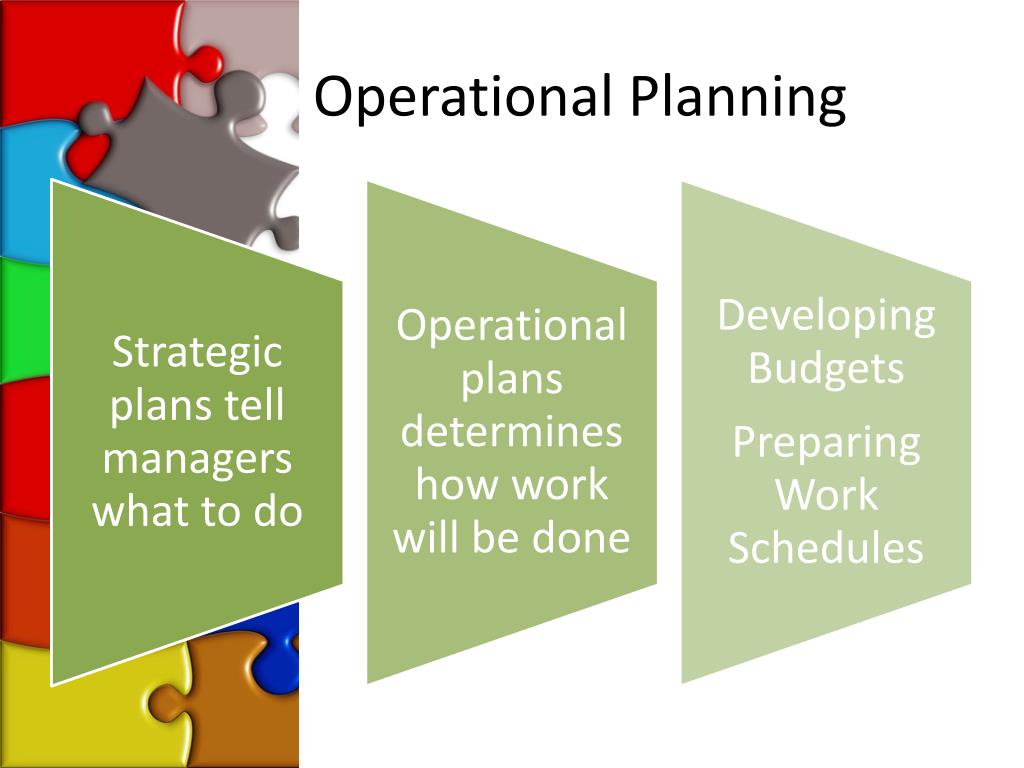
Operational planning is a critical component of business strategy, enabling organizations to achieve their goals and objectives. By developing an operational plan, businesses can create a roadmap for success, outlining the steps necessary to achieve their vision. Effective operational planning involves aligning resources, processes, and systems to support the organization’s overall strategy. This, in turn, enables businesses to increase efficiency, improve productivity, and enhance competitiveness.
A well-crafted operational plan provides a clear direction for the organization, ensuring that all departments and teams are working towards the same objectives. It also facilitates the allocation of resources, enabling businesses to prioritize investments and optimize resource utilization. Furthermore, operational planning enables organizations to identify potential risks and opportunities, allowing them to develop strategies to mitigate or capitalize on them.
Operational plan development is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and evaluation. As the business environment evolves, operational plans must adapt to ensure the organization remains competitive. By regularly reviewing and revising their operational plan, businesses can ensure that they are on track to achieve their strategic goals.
In today’s fast-paced business environment, operational planning is more important than ever. With the rise of digital technologies and increasing global competition, businesses must be agile and responsive to changing market conditions. A well-developed operational plan enables organizations to navigate these challenges, ensuring that they remain competitive and achieve their strategic objectives.
By investing time and effort into operational plan development, businesses can reap numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, increased productivity, and enhanced competitiveness. As such, operational planning is an essential component of business strategy, enabling organizations to achieve their goals and objectives.
How to Develop an Effective Operational Plan from Scratch
Developing an operational plan from scratch requires a structured approach to ensure that all critical components are included. The process begins with identifying key objectives, which should align with the organization’s overall strategy. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), providing a clear direction for the operational plan.
Once the objectives are established, the next step is to assess the resources required to achieve them. This includes evaluating the organization’s human resources, financial resources, and technological resources. It is essential to identify any gaps or limitations in these resources and develop strategies to address them.
With the objectives and resources in place, the next step is to establish performance metrics to measure operational success. This includes identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) and benchmarking against industry standards. Performance metrics should be measurable, achievable, and relevant to the organization’s objectives.
The operational plan should also include a detailed implementation plan, outlining the steps required to achieve the objectives. This plan should include timelines, milestones, and responsible personnel. It is essential to establish a clear chain of command and communication plan to ensure that all stakeholders are informed and engaged throughout the implementation process.
Operational plan development is an iterative process that requires continuous monitoring and evaluation. As the business environment evolves, the operational plan must adapt to ensure the organization remains competitive. Regular review and revision of the operational plan are essential to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
By following these steps, organizations can develop an effective operational plan from scratch, providing a solid foundation for business success. A well-crafted operational plan enables organizations to achieve their strategic goals, increase efficiency, and improve productivity.
In addition to these steps, it is essential to consider the following best practices when developing an operational plan:
- Involve all stakeholders in the planning process to ensure that everyone is aligned and engaged.
- Use data and analytics to inform the planning process and make data-driven decisions.
- Establish a clear and concise communication plan to ensure that all stakeholders are informed and engaged throughout the implementation process.
- Regularly review and revise the operational plan to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
By incorporating these best practices into the operational plan development process, organizations can ensure that their operational plan is effective, efficient, and aligned with their strategic goals.
Understanding the Key Components of an Operational Plan
An operational plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the steps necessary to achieve an organization’s strategic objectives. It is a critical component of operational plan development, as it provides a roadmap for success and ensures that all stakeholders are aligned and working towards the same goals.
There are three essential components of an operational plan: situation analysis, strategy formulation, and implementation and control.
Situation analysis is the process of analyzing the internal and external environment in which the organization operates. This includes identifying strengths and weaknesses, recognizing opportunities and threats, and assessing the organization’s current situation. The situation analysis provides a foundation for the operational plan, as it helps to identify the key objectives and strategies that will drive success.
Strategy formulation is the process of developing a clear and concise strategy that aligns with the organization’s overall mission and vision. This includes identifying the key objectives, establishing performance metrics, and developing a plan for achieving the objectives. The strategy formulation component of the operational plan provides a clear direction for the organization and ensures that all stakeholders are working towards the same goals.
Implementation and control is the process of putting the operational plan into action. This includes allocating resources, establishing timelines and milestones, and monitoring progress. The implementation and control component of the operational plan ensures that the organization is on track to achieve its objectives and makes adjustments as needed.
By understanding the key components of an operational plan, organizations can develop a comprehensive and effective plan that drives success. The situation analysis, strategy formulation, and implementation and control components work together to provide a roadmap for achieving strategic objectives and ensuring that the organization remains competitive in the market.
In addition to these components, operational plans should also include a clear and concise communication plan, a plan for monitoring and evaluating progress, and a plan for addressing risks and opportunities. By incorporating these elements, organizations can ensure that their operational plan is effective, efficient, and aligned with their strategic goals.
Operational plan development is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and evaluation. As the business environment evolves, the operational plan must adapt to ensure the organization remains competitive. Regular review and revision of the operational plan are essential to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Conducting a Situation Analysis to Inform Your Operational Plan
A situation analysis is a critical component of operational plan development, as it provides a comprehensive understanding of the internal and external environment in which the organization operates. This analysis helps to identify the organization’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as the opportunities and threats that exist in the market.
There are several key steps involved in conducting a situation analysis, including:
- Identifying internal strengths and weaknesses, such as the organization’s mission, vision, and values, as well as its financial resources and human capital.
- Analyzing external opportunities and threats, such as changes in the market, industry trends, and competitor activity.
- Evaluating the organization’s current situation, including its products or services, target market, and competitive position.
- Assessing the organization’s resources, including its financial, human, and technological resources.
By conducting a thorough situation analysis, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of their internal and external environment, and develop a more effective operational plan. This analysis helps to identify areas for improvement, and provides a foundation for developing strategies that drive success.
A situation analysis can be conducted using a variety of tools and techniques, including SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, and Porter’s Five Forces analysis. These tools help to identify the key factors that affect the organization’s success, and provide a framework for developing a comprehensive operational plan.
For example, a SWOT analysis can help to identify the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This analysis can be used to develop a comprehensive operational plan that leverages the organization’s strengths, addresses its weaknesses, and capitalizes on opportunities in the market.
In addition to these tools and techniques, organizations can also use data and analytics to inform their situation analysis. This can include analyzing customer data, market trends, and competitor activity to gain a deeper understanding of the market and develop a more effective operational plan.
By incorporating a situation analysis into the operational plan development process, organizations can ensure that their plan is comprehensive, effective, and aligned with their strategic goals. This analysis provides a foundation for developing a plan that drives success, and helps to ensure that the organization remains competitive in the market.
Setting SMART Objectives to Drive Operational Success
Setting SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) objectives is a critical component of operational plan development. SMART objectives provide a clear direction for the organization, ensuring that all stakeholders are working towards the same goals. By setting SMART objectives, organizations can drive operational success, increase efficiency, and improve productivity.
A SMART objective is specific, meaning it clearly defines what the organization wants to achieve. For example, “Increase sales revenue by 10% within the next 12 months” is a specific objective. A SMART objective is also measurable, meaning it can be quantified and tracked. For example, “Reduce customer complaints by 20% within the next 6 months” is a measurable objective.
Achievability is another key component of SMART objectives. The objective should be challenging, yet achievable, based on the organization’s resources and capabilities. For example, “Increase market share by 50% within the next 12 months” may be an unrealistic objective for a small business with limited resources.
Relevance is also critical, as the objective should align with the organization’s overall mission and vision. For example, “Increase sales revenue by 10% within the next 12 months” is a relevant objective for a business that wants to increase its market share.
Finally, SMART objectives are time-bound, meaning they have a specific deadline for completion. For example, “Increase sales revenue by 10% within the next 12 months” is a time-bound objective.
Examples of well-crafted SMART objectives include:
- Increase sales revenue by 10% within the next 12 months
- Reduce customer complaints by 20% within the next 6 months
- Improve employee engagement by 15% within the next 9 months
By setting SMART objectives, organizations can ensure that their operational plan is effective, efficient, and aligned with their strategic goals. SMART objectives provide a clear direction for the organization, ensuring that all stakeholders are working towards the same goals.
In addition to setting SMART objectives, organizations should also establish a system for tracking and measuring progress. This can include regular progress reports, performance metrics, and benchmarking. By tracking and measuring progress, organizations can ensure that they are on track to achieve their objectives and make adjustments as needed.
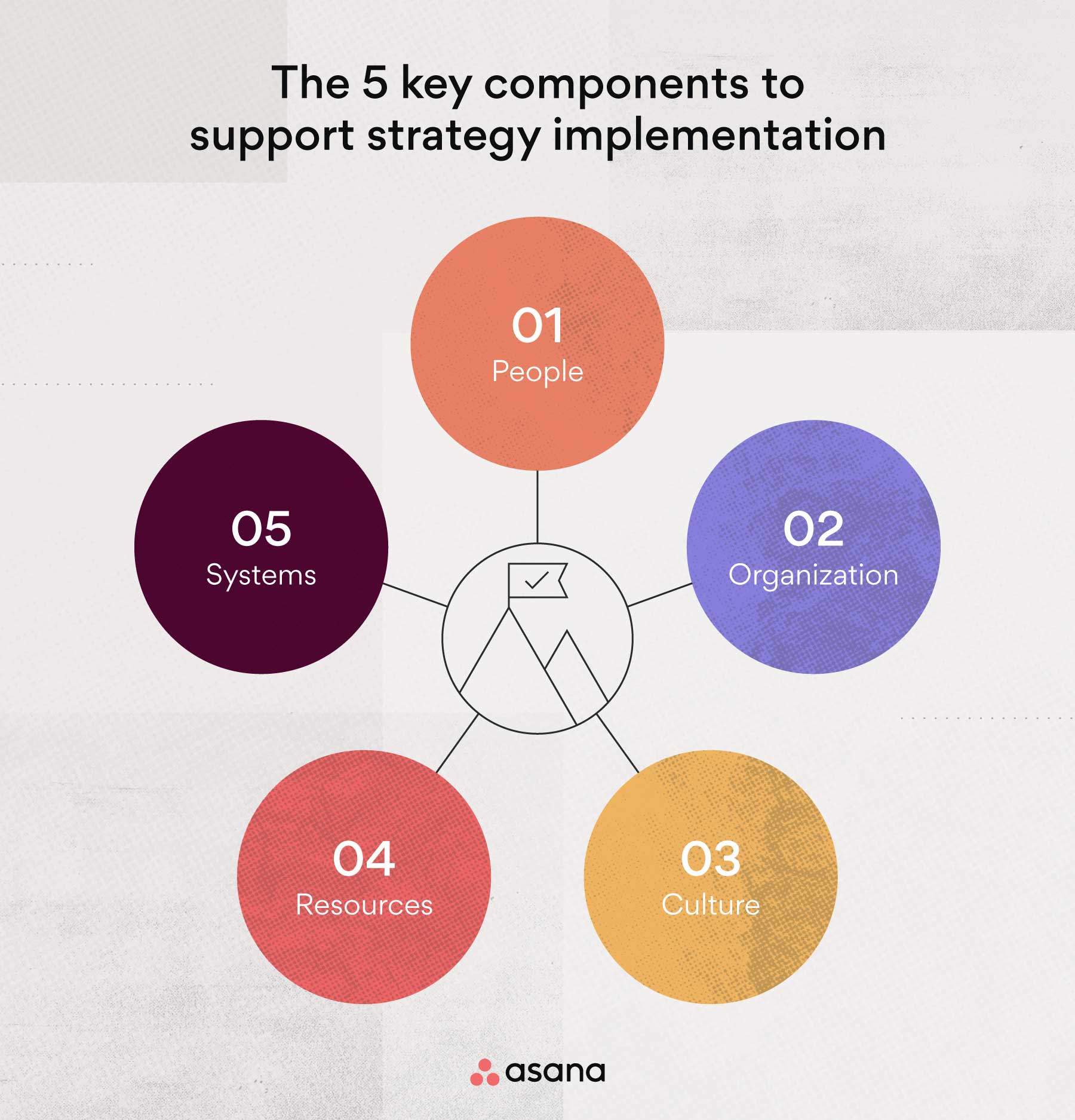
Allocating Resources Effectively to Support Operational Plan Implementation
Allocating resources effectively is a critical component of operational plan implementation. Resources include human resources, financial resources, and technological resources, and must be allocated in a way that supports the achievement of operational objectives.
Human resources are a critical component of operational plan implementation. This includes employees, contractors, and vendors who will be responsible for implementing the operational plan. It is essential to ensure that human resources are allocated effectively, including providing training and development opportunities to ensure that employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to implement the operational plan.
Financial resources are also essential for operational plan implementation. This includes budgeting and allocating funds to support the implementation of the operational plan. It is essential to ensure that financial resources are allocated effectively, including identifying areas where costs can be reduced and allocating funds to support the achievement of operational objectives.
Technological resources are also critical for operational plan implementation. This includes hardware, software, and other technology that will be used to support the implementation of the operational plan. It is essential to ensure that technological resources are allocated effectively, including identifying areas where technology can be used to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Effective resource allocation requires a thorough understanding of the operational plan and the resources required to implement it. This includes identifying areas where resources can be allocated more effectively, and making adjustments as needed to ensure that resources are being used efficiently.
Some best practices for allocating resources effectively include:
- Conducting a thorough analysis of the operational plan to identify areas where resources can be allocated more effectively
- Developing a resource allocation plan that outlines the resources required to implement the operational plan
- Identifying areas where costs can be reduced and allocating funds to support the achievement of operational objectives
- Providing training and development opportunities to ensure that employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to implement the operational plan
By allocating resources effectively, organizations can ensure that their operational plan is implemented efficiently and effectively, and that operational objectives are achieved.
In addition to allocating resources effectively, organizations should also regularly review and revise their operational plan to ensure that it remains relevant and effective. This includes monitoring progress, identifying areas for improvement, and making adjustments as needed.
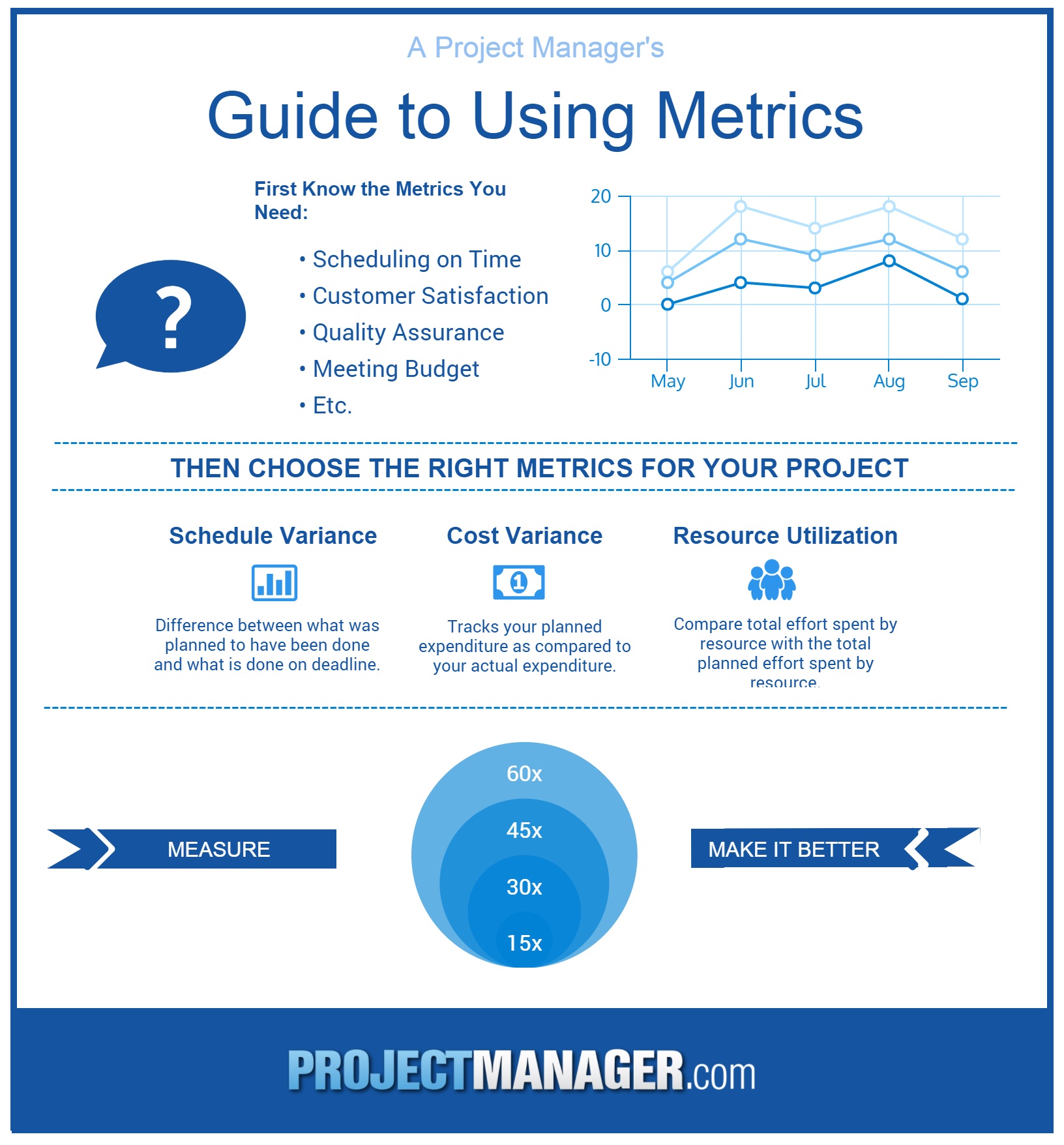
Establishing Performance Metrics to Measure Operational Success
Establishing performance metrics is a critical component of operational plan development, as it enables organizations to measure operational success and make data-driven decisions. Performance metrics provide a clear understanding of how well the organization is performing, and help to identify areas for improvement.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are a type of performance metric that is used to measure operational success. KPIs are quantifiable measures that are used to evaluate the performance of an organization, and are typically aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives.
Examples of KPIs include:
- Revenue growth rate
- Customer satisfaction ratings
- Employee engagement scores
- Return on investment (ROI)
Benchmarking is another important aspect of establishing performance metrics. Benchmarking involves comparing the organization’s performance to that of other organizations in the same industry, or to industry averages. This helps to identify areas where the organization is performing well, and areas where improvement is needed.
Some best practices for establishing performance metrics include:
- Aligning performance metrics with the organization’s strategic objectives
- Using a combination of financial and non-financial metrics to get a comprehensive view of performance
- Establishing clear targets and thresholds for each metric
- Regularly reviewing and revising performance metrics to ensure they remain relevant and effective
By establishing performance metrics, organizations can ensure that they are measuring operational success effectively, and making data-driven decisions to drive improvement.
In addition to establishing performance metrics, organizations should also regularly review and revise their operational plan to ensure continuous improvement. This includes monitoring progress, identifying areas for improvement, and making adjustments as needed.
By combining performance metrics with regular review and revision, organizations can ensure that their operational plan is effective, efficient, and aligned with their strategic goals.
Reviewing and Revising Your Operational Plan for Continuous Improvement
Regularly reviewing and revising your operational plan is essential for ensuring continuous improvement and achieving strategic goals. This process helps to identify areas for improvement, monitor progress, and make adjustments as needed.
There are several reasons why reviewing and revising your operational plan is important:
- Ensures alignment with strategic goals: Regular review and revision of the operational plan ensures that it remains aligned with the organization’s strategic goals and objectives.
- Identifies areas for improvement: Reviewing and revising the operational plan helps to identify areas for improvement, such as inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and opportunities for growth.
- Monitors progress: Regular review and revision of the operational plan helps to monitor progress towards achieving strategic goals and objectives.
- Makes adjustments as needed: Reviewing and revising the operational plan allows for adjustments to be made as needed, ensuring that the organization remains on track to achieve its strategic goals.
Some best practices for reviewing and revising your operational plan include:
- Regularly reviewing and revising the operational plan on a quarterly or annual basis
- Using data and metrics to inform the review and revision process
- Involving key stakeholders in the review and revision process
- Identifying and addressing areas for improvement
By regularly reviewing and revising your operational plan, you can ensure that your organization remains on track to achieve its strategic goals and objectives.
In addition to reviewing and revising your operational plan, it’s also important to regularly review and revise your performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs). This helps to ensure that your performance metrics and KPIs remain relevant and effective in measuring operational success.
By combining regular review and revision of your operational plan with regular review and revision of your performance metrics and KPIs, you can ensure that your organization remains on track to achieve its strategic goals and objectives.