The Foundation of Operational Excellence
Operational planning is a critical component of achieving business objectives, as it enables organizations to establish a clear direction, allocate resources effectively, and measure progress towards their goals. A well-developed operational plan serves as a roadmap for success, outlining the steps necessary to achieve strategic objectives and drive business growth. By investing time and effort into operational plan development, businesses can reap numerous benefits, including increased efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness.
One of the primary advantages of operational planning is its ability to promote efficiency and productivity. By streamlining processes, eliminating waste, and optimizing resource allocation, businesses can reduce costs, improve quality, and enhance customer satisfaction. Moreover, operational planning enables organizations to respond quickly to changing market conditions, customer needs, and competitive pressures, thereby maintaining a competitive edge.
Another significant benefit of operational planning is its impact on competitiveness. In today’s fast-paced business environment, companies must be agile and adaptable to stay ahead of the competition. A well-developed operational plan enables businesses to anticipate and respond to changes in the market, identify new opportunities, and capitalize on emerging trends. By doing so, organizations can differentiate themselves from competitors, establish a strong market presence, and drive long-term success.
Furthermore, operational planning plays a crucial role in driving business growth. By establishing clear goals, objectives, and key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can measure progress, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions. This enables organizations to allocate resources effectively, prioritize initiatives, and focus on high-impact activities that drive growth and profitability.
Effective operational planning also involves aligning business objectives with operational capabilities. By assessing organizational strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, businesses can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to address them. This enables organizations to build on their strengths, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities, ultimately driving business success.
How to Develop a Comprehensive Operational Plan
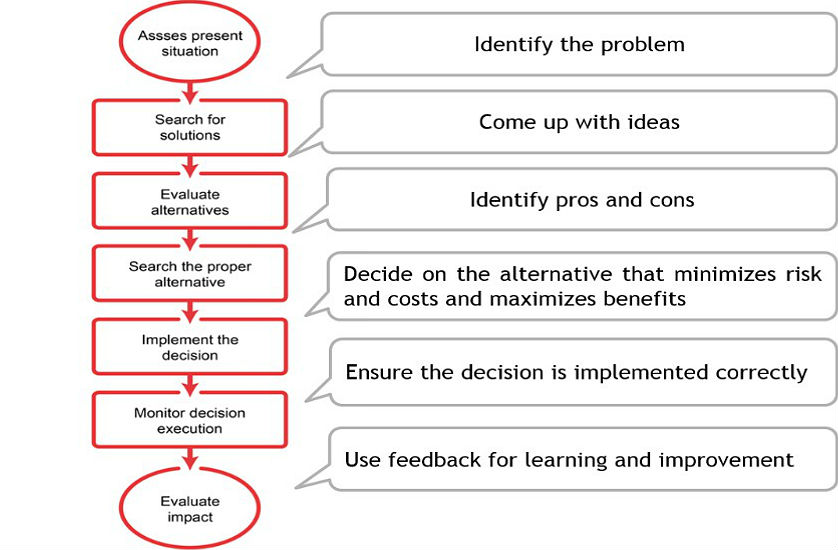
Developing a comprehensive operational plan is a critical step in achieving business success. A well-crafted operational plan serves as a roadmap for the organization, outlining the steps necessary to achieve strategic objectives and drive business growth. In this section, we will provide a step-by-step guide on creating an operational plan, including defining goals and objectives, identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), and establishing a timeline for implementation.
Step 1: Define Goals and Objectives
The first step in developing an operational plan is to define the organization’s goals and objectives. This involves identifying the key outcomes that the organization wants to achieve, and establishing clear and measurable objectives. Goals and objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), and should align with the organization’s overall strategy.
Step 2: Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Once the goals and objectives have been defined, the next step is to identify the key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure progress. KPIs should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the organization’s goals and objectives. Examples of common KPIs include customer satisfaction, productivity, and quality metrics.
Step 3: Establish a Timeline for Implementation
The final step in developing an operational plan is to establish a timeline for implementation. This involves identifying the key milestones and deadlines that must be met in order to achieve the organization’s goals and objectives. The timeline should be realistic and achievable, and should take into account any potential roadblocks or obstacles that may arise.
Best Practices for Operational Plan Development
When developing an operational plan, there are several best practices to keep in mind. First, the plan should be aligned with the organization’s overall strategy and goals. Second, the plan should be specific, measurable, and achievable. Third, the plan should be flexible and adaptable, and should be able to respond to changing market conditions and customer needs. Finally, the plan should be regularly reviewed and updated, in order to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When developing an operational plan, there are several common mistakes to avoid. First, the plan should not be too vague or general. Second, the plan should not be too rigid or inflexible. Third, the plan should not be developed in isolation, but should involve input and feedback from key stakeholders. Finally, the plan should not be neglected or ignored, but should be regularly reviewed and updated.
Conducting a Situation Analysis for Informed Decision-Making
A situation analysis is a critical step in operational plan development, as it provides a comprehensive understanding of the internal and external factors that can impact the organization’s ability to achieve its goals. By analyzing these factors, organizations can identify opportunities and threats, and develop strategies to capitalize on the former and mitigate the latter.
Internal Factors
Internal factors refer to the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. These factors can include the organization’s culture, values, and mission, as well as its financial resources, human capital, and technological capabilities. By understanding these internal factors, organizations can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to leverage their strengths and address their weaknesses.
External Factors
External factors refer to the market trends, customer needs, and competitive landscape that can impact the organization’s ability to achieve its goals. These factors can include changes in government regulations, shifts in market demand, and the emergence of new competitors. By understanding these external factors, organizations can identify opportunities to innovate and differentiate themselves from their competitors.
Conducting a Situation Analysis
Conducting a situation analysis involves gathering and analyzing data from a variety of sources, including internal reports, market research, and customer feedback. This data can be used to identify patterns and trends, and to develop a comprehensive understanding of the internal and external factors that can impact the organization’s ability to achieve its goals.
Tools and Techniques
There are a variety of tools and techniques that can be used to conduct a situation analysis, including SWOT analysis, PESTEL analysis, and Porter’s Five Forces analysis. These tools can help organizations to identify and prioritize the internal and external factors that can impact their ability to achieve their goals.
Best Practices
When conducting a situation analysis, there are several best practices to keep in mind. First, the analysis should be comprehensive and inclusive, taking into account both internal and external factors. Second, the analysis should be data-driven, using a variety of sources to gather and analyze data. Finally, the analysis should be ongoing, with regular updates and revisions to reflect changes in the internal and external environment.
Setting SMART Goals for Operational Success
Setting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals is a crucial step in operational plan development. SMART goals provide a clear direction and focus for the organization, and help to ensure that everyone is working towards the same objectives.
Why SMART Goals are Important
SMART goals are important because they provide a clear and concise way to communicate the organization’s objectives. They help to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals, and provide a way to measure progress and success. SMART goals also help to prioritize efforts and resources, and provide a way to evaluate the effectiveness of different strategies and tactics.
How to Set SMART Goals
Setting SMART goals involves several steps. First, the organization must identify its overall objectives and priorities. Next, specific goals must be established that are aligned with these objectives. These goals must be measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Finally, the organization must establish a plan for achieving these goals, including identifying the resources and support needed.
Examples of SMART Goals
Here are a few examples of SMART goals:
* Increase customer satisfaction ratings by 10% within the next 6 months by implementing a new customer service training program.
* Reduce production costs by 5% within the next 12 months by implementing a new manufacturing process.
* Increase sales revenue by 15% within the next 12 months by launching a new product line.
Best Practices for Setting SMART Goals
There are several best practices to keep in mind when setting SMART goals. First, goals should be specific and well-defined. Second, goals should be measurable, so progress can be tracked and success can be evaluated. Third, goals should be achievable, but still challenging. Fourth, goals should be relevant to the organization’s overall objectives. Finally, goals should be time-bound, with a specific deadline for completion.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are several common mistakes to avoid when setting SMART goals. First, goals should not be too vague or general. Second, goals should not be too easy or too difficult. Third, goals should not be too focused on short-term gains, but rather on long-term success. Finally, goals should not be set in isolation, but rather in conjunction with other goals and objectives.
Identifying and Mitigating Operational Risks
Operational risks are potential threats to an organization’s ability to achieve its objectives. These risks can arise from various sources, including supply chain disruptions, regulatory changes, talent shortages, and technological failures. Identifying and mitigating operational risks is a critical step in operational plan development, as it helps to ensure that the organization is prepared to respond to potential threats and minimize their impact.
Types of Operational Risks
There are several types of operational risks that organizations should be aware of. These include:
* Supply chain disruptions: Disruptions to the supply chain can have a significant impact on an organization’s ability to deliver products or services to customers.
* Regulatory changes: Changes in regulations can impact an organization’s ability to operate, and can result in significant fines or penalties if not complied with.
* Talent shortages: A shortage of skilled talent can impact an organization’s ability to deliver products or services, and can result in significant recruitment and training costs.
* Technological failures: Technological failures can impact an organization’s ability to operate, and can result in significant downtime and lost productivity.
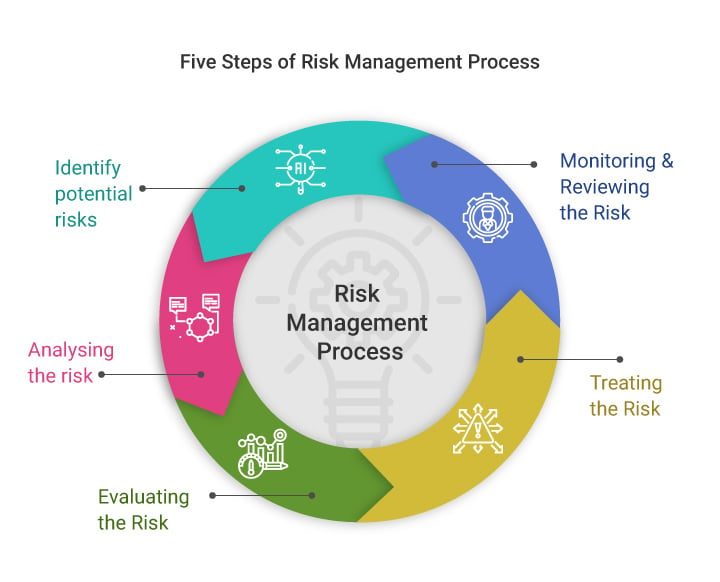
Identifying Operational Risks
Identifying operational risks involves analyzing the organization’s internal and external environment to identify potential threats. This can be done through a variety of methods, including:
* Risk assessments: Conducting regular risk assessments to identify potential threats and assess their likelihood and impact.
* Scenario planning: Developing scenarios to identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
* Stakeholder engagement: Engaging with stakeholders to identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
Mitigating Operational Risks
Mitigating operational risks involves developing strategies to minimize their impact. This can be done through a variety of methods, including:
* Risk avoidance: Avoiding risks by not engaging in certain activities or by developing alternative strategies.
* Risk transfer: Transferring risks to other parties, such as through insurance or outsourcing.
* Risk mitigation: Mitigating risks by developing strategies to minimize their impact, such as through contingency planning or business continuity planning.
Best Practices for Identifying and Mitigating Operational Risks
There are several best practices for identifying and mitigating operational risks. These include:
* Regularly reviewing and updating the risk management plan to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
* Engaging with stakeholders to identify potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them.
* Developing a culture of risk awareness and management throughout the organization.
Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Operational Excellence
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively an organization is achieving its operational objectives. Establishing KPIs is a critical step in operational plan development, as it provides a way to measure progress and identify areas for improvement.
Types of KPIs
There are several types of KPIs that organizations can use to measure operational performance. These include:
* Customer satisfaction KPIs: Measure the level of satisfaction among customers, such as through surveys or feedback forms.
* Productivity KPIs: Measure the efficiency and effectiveness of operational processes, such as through metrics like cycle time or throughput.
* Quality KPIs: Measure the quality of products or services, such as through metrics like defect rates or quality scores.
Benefits of KPIs
Establishing KPIs provides several benefits to organizations, including:
* Improved decision-making: KPIs provide data-driven insights that inform operational decisions.
* Increased efficiency: KPIs help identify areas for improvement, allowing organizations to optimize processes and reduce waste.
* Enhanced customer satisfaction: KPIs help organizations measure and improve customer satisfaction, leading to increased loyalty and retention.
Best Practices for Establishing KPIs
There are several best practices for establishing KPIs, including:
* Aligning KPIs with operational objectives: Ensure that KPIs are aligned with the organization’s operational objectives and goals.
* Making KPIs measurable: Ensure that KPIs are quantifiable and can be measured using data and metrics.
* Establishing targets: Establish targets for KPIs, providing a clear direction for operational improvement.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are several common mistakes to avoid when establishing KPIs, including:
* Focusing on too many KPIs: Focus on a few key KPIs that are aligned with operational objectives, rather than trying to measure too many metrics.
* Not making KPIs actionable: Ensure that KPIs are actionable, providing clear insights and recommendations for improvement.
* Not regularly reviewing KPIs: Regularly review and update KPIs to ensure they remain relevant and effective.
Implementing and Monitoring the Operational Plan
Implementing and monitoring the operational plan is a critical step in operational plan development. This involves putting the plan into action, tracking progress, and making adjustments as needed.
Implementing the Operational Plan
Implementing the operational plan involves several steps, including:
* Assigning tasks and responsibilities to team members
* Establishing a timeline for implementation
* Allocating resources and budget
* Communicating the plan to stakeholders
Monitoring the Operational Plan
Monitoring the operational plan involves tracking progress, identifying areas for improvement, and making adjustments as needed. This can be done through regular progress reviews, feedback mechanisms, and continuous improvement.
Regular Progress Reviews
Regular progress reviews are essential for monitoring the operational plan. These reviews should be held regularly, such as monthly or quarterly, and should involve all team members and stakeholders.
Feedback Mechanisms
Feedback mechanisms are critical for monitoring the operational plan. These mechanisms should be established to provide regular feedback from team members, stakeholders, and customers.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is essential for operational excellence. This involves regularly reviewing and updating the operational plan to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Best Practices for Implementing and Monitoring the Operational Plan
There are several best practices for implementing and monitoring the operational plan, including:
* Establishing clear goals and objectives
* Assigning tasks and responsibilities clearly
* Establishing a timeline for implementation
* Allocating resources and budget effectively
* Communicating the plan to stakeholders clearly
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are several common mistakes to avoid when implementing and monitoring the operational plan, including:
* Failing to establish clear goals and objectives
* Failing to assign tasks and responsibilities clearly
* Failing to establish a timeline for implementation
* Failing to allocate resources and budget effectively
* Failing to communicate the plan to stakeholders clearly
Sustaining Operational Excellence through Continuous Improvement
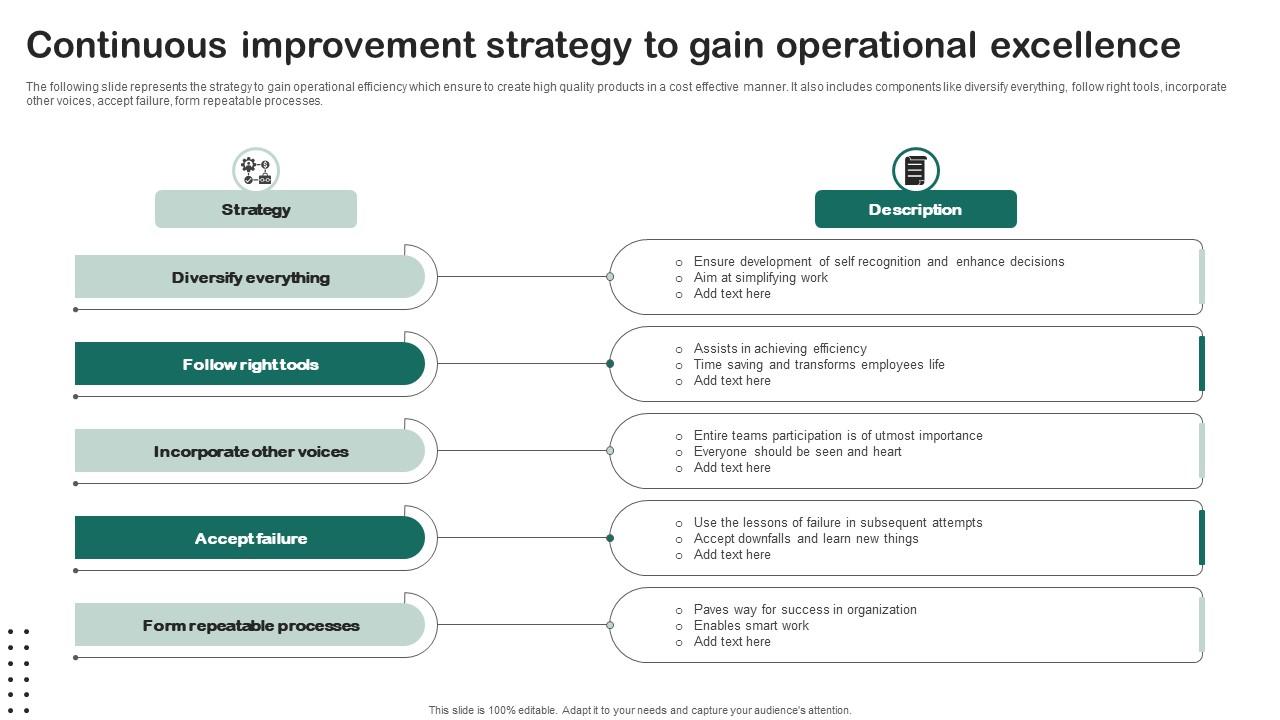
Sustaining operational excellence requires a commitment to continuous improvement. This involves regularly reviewing and updating the operational plan to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Strategies for Encouraging a Culture of Innovation and Experimentation
There are several strategies that organizations can use to encourage a culture of innovation and experimentation, including:
* Encouraging employee feedback and suggestions
* Providing training and development opportunities
* Encouraging experimentation and calculated risk-taking
* Recognizing and rewarding innovation and improvement
Benefits of Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement provides several benefits to organizations, including:
* Improved operational efficiency and effectiveness
* Increased innovation and competitiveness
* Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty
* Improved employee engagement and retention
Best Practices for Sustaining Operational Excellence
There are several best practices for sustaining operational excellence, including:
* Regularly reviewing and updating the operational plan
* Encouraging a culture of innovation and experimentation
* Providing training and development opportunities
* Recognizing and rewarding innovation and improvement
Common Mistakes to Avoid
There are several common mistakes to avoid when sustaining operational excellence, including:
* Failing to regularly review and update the operational plan
* Failing to encourage a culture of innovation and experimentation
* Failing to provide training and development opportunities
* Failing to recognize and reward innovation and improvement