The Impact of Image Dimensions on Website Performance
When it comes to website performance, image dimensions play a crucial role in determining page load times, user experience, and search engine rankings. Large image files can significantly slow down page loading, leading to a higher bounce rate and lower search engine rankings. In fact, according to Google, a one-second delay in page loading can result in a 7% reduction in conversions. To mitigate this, it’s essential to reduce image dimensions without losing quality, ensuring a seamless user experience and improved search engine optimization (SEO).
Images account for a significant portion of the average webpage’s file size, with some estimates suggesting that images make up around 60% of the total file size. By optimizing image dimensions, website owners can reduce the file size of their images, resulting in faster page loading times and improved website performance. This, in turn, can lead to increased user engagement, higher conversion rates, and improved search engine rankings.
Moreover, search engines like Google take into account page loading times when ranking websites. A website with optimized image dimensions is more likely to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) than a website with large, unoptimized images. By reducing image dimensions without losing quality, website owners can improve their website’s visibility, drive more traffic, and increase their online presence.
In addition to improving website performance and SEO, reducing image dimensions can also enhance user experience. Faster page loading times and optimized images can lead to increased user engagement, lower bounce rates, and higher conversion rates. By providing a seamless and efficient user experience, website owners can build trust with their audience, establish their brand as an authority in their industry, and drive business growth.
In conclusion, optimizing image dimensions is crucial for website performance, SEO, and user experience. By reducing image dimensions without losing quality, website owners can improve page loading times, increase user engagement, and drive business growth. In the next section, we’ll explore the difference between image compression and resizing, and how they affect image quality.
Understanding Image Compression and Resizing
When it comes to reducing image dimensions without losing quality, it’s essential to understand the difference between image compression and resizing. Both techniques can help decrease the file size of an image, but they work in distinct ways and have different effects on image quality.
Image compression reduces the file size of an image by eliminating unnecessary data. This can be achieved through various algorithms, such as Huffman coding, arithmetic coding, or LZ77. Compression can be lossless, where the original data is preserved, or lossy, where some data is discarded to achieve a smaller file size. Lossy compression is commonly used for images, as it can significantly reduce the file size while maintaining acceptable quality.
On the other hand, image resizing involves changing the dimensions of an image, either by increasing or decreasing its width and height. Resizing can be done using various interpolation methods, such as nearest-neighbor, bilinear, or bicubic interpolation. When reducing image dimensions, it’s crucial to use a high-quality interpolation method to avoid pixelation and maintain image sharpness.
When to use each technique depends on the specific requirements of the image. If the goal is to reduce the file size of an image without changing its dimensions, compression is the way to go. However, if the image needs to be resized to fit a specific layout or design, resizing is the better option. In some cases, a combination of both compression and resizing may be necessary to achieve the desired result.
For example, if you have a high-resolution image that needs to be displayed on a website, you may want to resize it to a smaller dimension to reduce the file size and improve page load times. However, if you need to maintain the original dimensions of the image, compression can be used to reduce the file size without sacrificing quality.
By understanding the difference between image compression and resizing, you can make informed decisions about how to reduce image dimensions without losing quality. This knowledge will help you optimize your images for various applications, from web design to digital marketing, and ensure that your visuals look their best while maintaining a reasonable file size.
How to Reduce Image Dimensions without Losing Quality
Reducing image dimensions without losing quality requires a combination of the right techniques and tools. In this section, we will provide step-by-step instructions on how to reduce image dimensions using popular image editing software, such as Adobe Photoshop and GIMP.
**Step 1: Open the Image in Adobe Photoshop or GIMP**
Open the image you want to reduce in Adobe Photoshop or GIMP. Make sure the image is in a format that can be edited, such as PSD or TIFF.
**Step 2: Resize the Image**
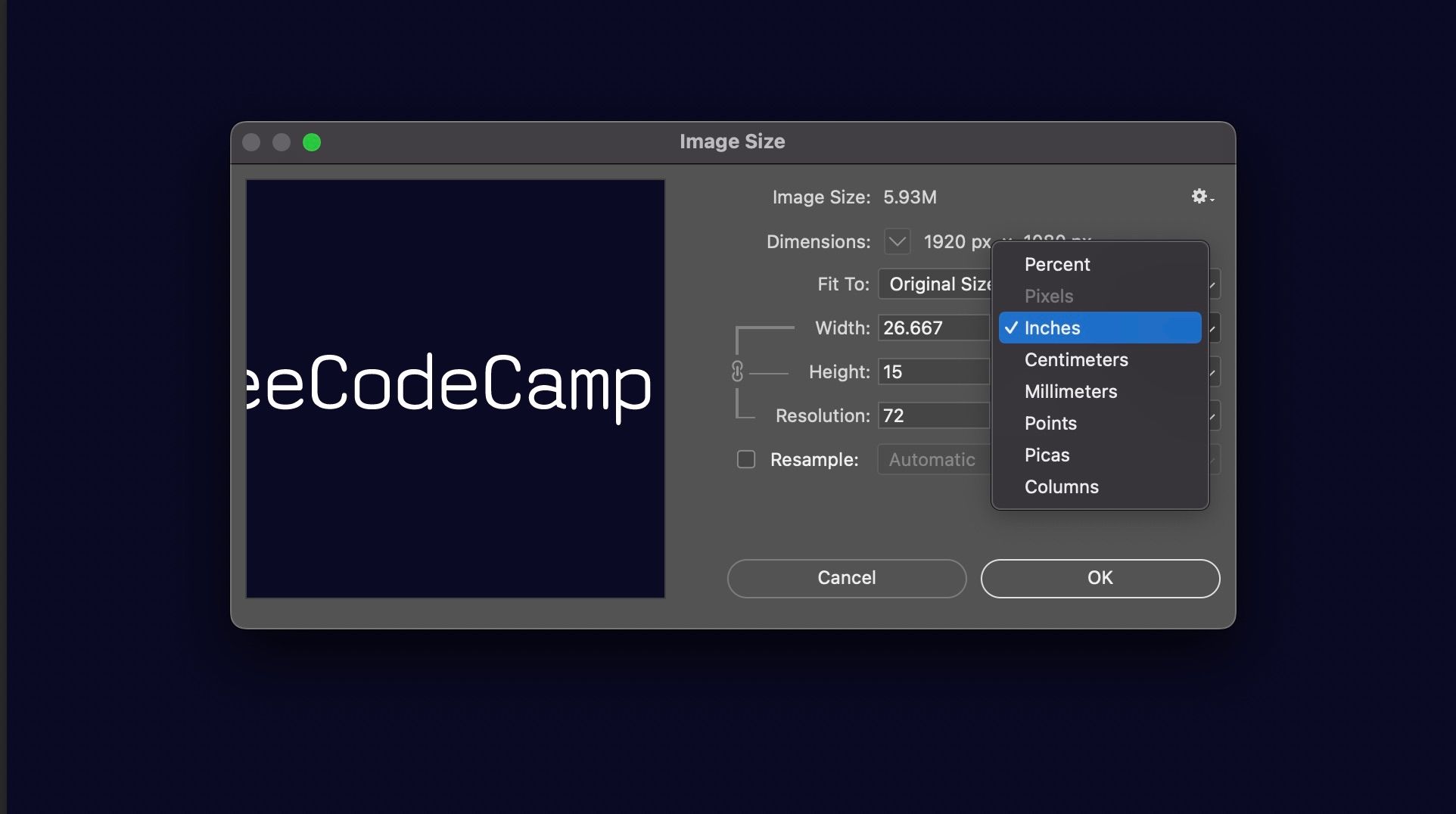
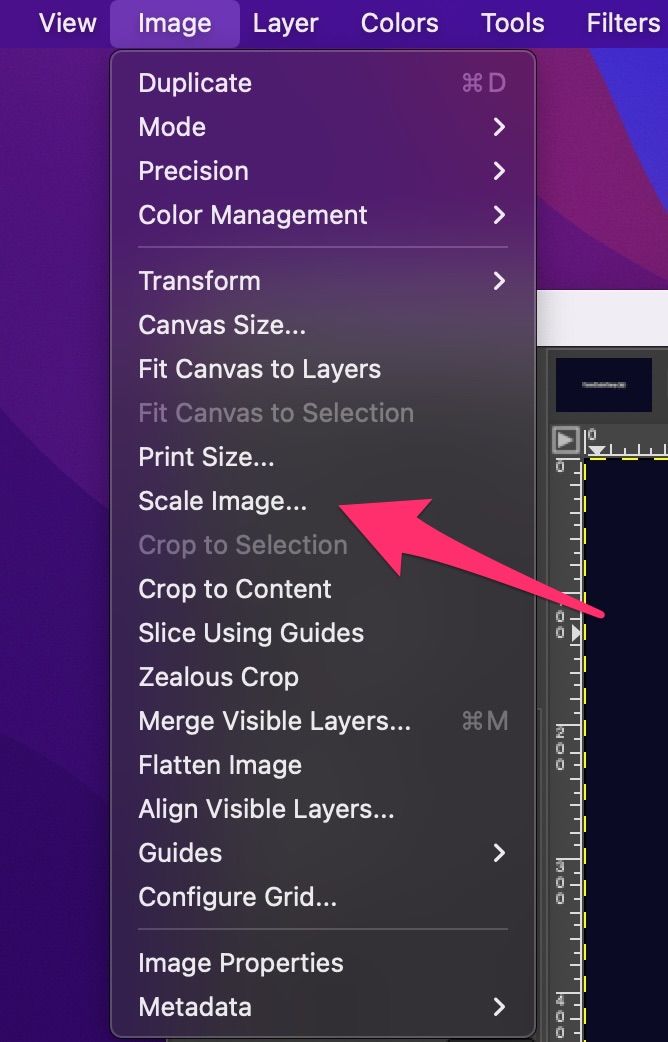
In Adobe Photoshop, go to Image > Image Size and enter the new dimensions for the image. Make sure to select the “Constrain Proportions” checkbox to maintain the aspect ratio. In GIMP, go to Image > Scale Image and enter the new dimensions.
**Step 3: Choose the Right Resampling Method**
When resizing an image, it’s essential to choose the right resampling method to maintain image quality. In Adobe Photoshop, select the “Bicubic Sharper” resampling method, which is suitable for reducing image dimensions. In GIMP, select the “Cubic” resampling method.
**Step 4: Apply Compression**
Once the image is resized, apply compression to reduce the file size. In Adobe Photoshop, go to File > Export > Save for Web (Legacy) and select the “JPEG” format. Adjust the quality settings to achieve the desired balance between image size and quality. In GIMP, go to File > Export As and select the “JPEG” format. Adjust the quality settings to achieve the desired balance between image size and quality.
**Step 5: Save the Image**
Save the image in the desired format, such as JPEG or PNG. Make sure to choose the right format for your image, depending on the intended use.
**Tips for Selecting the Right Compression Algorithm and Quality Settings**
When applying compression, it’s essential to select the right compression algorithm and quality settings to maintain image quality. For JPEG images, use the “Baseline” compression algorithm and adjust the quality settings to achieve the desired balance between image size and quality. For PNG images, use the “Deflate” compression algorithm and adjust the quality settings to achieve the desired balance between image size and quality.
By following these steps and tips, you can reduce image dimensions without losing quality, achieving a balance between image size and quality that is suitable for various applications, from web design to digital marketing.
The Role of Image Format in Dimension Reduction
When it comes to reducing image dimensions without losing quality, the image format plays a crucial role. Different image formats have varying levels of compression and suitability for dimension reduction. In this section, we will discuss the most common image formats and their suitability for dimension reduction.
**JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)**
JPEG is a popular image format that uses lossy compression, which means that some of the image data is discarded to reduce the file size. JPEG is suitable for photographs and images with many colors, as it can compress these types of images effectively without significant loss of quality. However, JPEG is not suitable for images with text, logos, or graphics, as the lossy compression can cause these elements to become distorted.
**PNG (Portable Network Graphics)**
PNG is a lossless image format that is suitable for images with text, logos, or graphics. PNG uses a combination of Huffman coding and LZ77 compression to reduce the file size without losing any image data. PNG is also suitable for images with transparent backgrounds, as it supports alpha channels. However, PNG files can be larger than JPEG files, especially for photographs.
**GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)**
GIF is a lossless image format that is suitable for images with a limited color palette, such as logos, icons, or graphics. GIF uses a combination of Huffman coding and LZW compression to reduce the file size without losing any image data. GIF is also suitable for animations, as it supports multiple frames. However, GIF is not suitable for photographs, as it can cause the image to become distorted.
**Choosing the Right Image Format**
When choosing an image format for dimension reduction, consider the type of image and its intended use. If the image is a photograph, JPEG may be the best choice. If the image has text, logos, or graphics, PNG may be the best choice. If the image is a logo or icon, GIF may be the best choice.
**Tips for Converting Image Formats**
When converting image formats, it’s essential to consider the potential loss of quality. If converting from a lossless format to a lossy format, such as from PNG to JPEG, some image data may be lost. To minimize the loss of quality, use a high-quality conversion tool and adjust the compression settings accordingly.
By choosing the right image format and considering the potential loss of quality, you can reduce image dimensions without losing quality and achieve a balance between image size and quality that is suitable for various applications, from web design to digital marketing.
Tools for Reducing Image Dimensions without Quality Loss
There are several tools and software available that can help reduce image dimensions without losing quality. In this section, we will review some popular tools and compare their features, pricing, and effectiveness.
**TinyPNG**
TinyPNG is a popular online tool that uses advanced compression algorithms to reduce image file sizes without losing quality. It supports JPEG, PNG, and WebP formats and can compress images up to 90% without visible loss of quality. TinyPNG offers a free plan that allows users to compress up to 20 images per day, as well as a paid plan that starts at $25 per month.
**ImageOptim**
ImageOptim is a free online tool that uses advanced compression algorithms to reduce image file sizes without losing quality. It supports JPEG, PNG, GIF, and WebP formats and can compress images up to 80% without visible loss of quality. ImageOptim also offers a desktop app for Mac and Windows users.
**ShortPixel**
ShortPixel is a popular online tool that uses advanced compression algorithms to reduce image file sizes without losing quality. It supports JPEG, PNG, GIF, and WebP formats and can compress images up to 90% without visible loss of quality. ShortPixel offers a free plan that allows users to compress up to 100 images per month, as well as a paid plan that starts at $4.99 per month.
**Comparison of Features, Pricing, and Effectiveness**
All three tools offer advanced compression algorithms and support multiple image formats. However, TinyPNG and ShortPixel offer more features, such as batch compression and image resizing, than ImageOptim. In terms of pricing, ImageOptim is free, while TinyPNG and ShortPixel offer both free and paid plans. In terms of effectiveness, all three tools can compress images without visible loss of quality, but TinyPNG and ShortPixel offer more aggressive compression options.
**Tips for Using Image Compression Tools**
When using image compression tools, it’s essential to consider the type of image and its intended use. For example, if the image is a photograph, a more aggressive compression setting may be suitable. However, if the image has text or graphics, a more conservative compression setting may be necessary to avoid losing quality. Additionally, it’s essential to test the compressed image to ensure that it meets the desired quality standards.
By using the right image compression tool and following best practices, you can reduce image dimensions without losing quality and achieve a balance between image size and quality that is suitable for various applications, from web design to digital marketing.
Best Practices for Dimension Reduction in Web Design
When it comes to reducing image dimensions without losing quality in web design, there are several best practices to follow. These guidelines will help web designers optimize their images for better website performance, user experience, and search engine rankings.
**Image Placement and Sizing**
When placing images on a website, it’s essential to consider the image size and placement. Images should be placed in a way that they do not overwhelm the content or slow down the page load time. Use CSS to control the image size and placement, and avoid using images that are too large or too small for the content area.
**Compression and Quality Settings**
When compressing images, it’s essential to find the right balance between image size and quality. Use image compression tools to reduce the image file size without sacrificing quality. Adjust the quality settings to achieve the desired balance between image size and quality.
**Image Format and Type**
Choose the right image format and type for the content. For example, use JPEG for photographs, PNG for graphics and logos, and GIF for animations. Avoid using images with unnecessary metadata or EXIF data, as this can increase the image file size.
**Responsive Design and Image Scaling**
Use responsive design techniques to ensure that images scale properly on different devices and screen sizes. Use CSS media queries to define different image sizes and scaling factors for different devices and screen sizes.
**Testing and Optimization**
Test and optimize images regularly to ensure that they are optimized for better website performance, user experience, and search engine rankings. Use image compression tools and web performance optimization tools to analyze and optimize images.
**Tips for Web Designers**
When reducing image dimensions without losing quality in web design, consider the following tips:
- Use image compression tools to reduce image file size without sacrificing quality.
- Choose the right image format and type for the content.
- Use CSS to control image size and placement.
- Test and optimize images regularly.
- Use responsive design techniques to ensure that images scale properly on different devices and screen sizes.
By following these best practices and tips, web designers can reduce image dimensions without losing quality and achieve a balance between image size and quality that is suitable for various applications, from web design to digital marketing.
Common Mistakes to Avoid when Reducing Image Dimensions
When reducing image dimensions, there are several common mistakes to avoid in order to maintain image quality and achieve the desired results. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common mistakes to avoid when reducing image dimensions.
**Over-Compression**
One of the most common mistakes to avoid when reducing image dimensions is over-compression. Over-compression can result in a significant loss of image quality, making the image appear pixelated or distorted. To avoid over-compression, it’s essential to find the right balance between image size and quality. Use image compression tools to reduce the image file size without sacrificing quality.
**Incorrect Formatting**
Another common mistake to avoid when reducing image dimensions is incorrect formatting. Incorrect formatting can result in images that are not optimized for the web, leading to slow page load times and poor user experience. To avoid incorrect formatting, it’s essential to choose the right image format for the content. For example, use JPEG for photographs, PNG for graphics and logos, and GIF for animations.
**Neglecting to Test Images**
Neglecting to test images is another common mistake to avoid when reducing image dimensions. Testing images is essential to ensure that they are optimized for the web and meet the desired quality standards. Use image testing tools to analyze and optimize images for better website performance, user experience, and search engine rankings.
**Using Low-Quality Images**
Using low-quality images is another common mistake to avoid when reducing image dimensions. Low-quality images can result in a poor user experience and negatively impact website performance and search engine rankings. To avoid using low-quality images, it’s essential to use high-quality images that are optimized for the web.
**Tips for Avoiding Common Mistakes**
When reducing image dimensions, consider the following tips to avoid common mistakes:
- Avoid over-compression by finding the right balance between image size and quality.
- Choose the right image format for the content.
- Test images regularly to ensure that they are optimized for the web.
- Use high-quality images that are optimized for the web.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can reduce image dimensions without losing quality and achieve a balance between image size and quality that is suitable for various applications, from web design to digital marketing.
Conclusion: Optimizing Image Dimensions for a Better User Experience
In conclusion, reducing image dimensions without losing quality is crucial for website performance, user experience, and search engine rankings. By understanding the difference between image compression and resizing, choosing the right image format, and using the right tools and techniques, web designers can optimize image dimensions without sacrificing quality.
**Final Tips for Achieving a Balance between Image Size and Quality**
To achieve a balance between image size and quality, consider the following final tips:
- Use image compression tools to reduce image file size without sacrificing quality.
- Choose the right image format for the content.
- Test images regularly to ensure that they are optimized for the web.
- Use high-quality images that are optimized for the web.
- Avoid over-compression, incorrect formatting, and neglecting to test images.
**The Importance of Optimizing Image Dimensions**
Optimizing image dimensions is essential for website performance, user experience, and search engine rankings. By reducing image dimensions without losing quality, web designers can improve page load times, enhance user experience, and increase search engine rankings.
**The Future of Image Optimization**
As technology continues to evolve, image optimization will become even more important. With the rise of mobile devices and high-speed internet, users expect fast and seamless online experiences. By optimizing image dimensions, web designers can stay ahead of the curve and provide users with the best possible online experience.
By following these tips and best practices, web designers can reduce image dimensions without losing quality and achieve a balance between image size and quality that is suitable for various applications, from web design to digital marketing.