Understanding the Basics of 401k Plans
A 401k plan is a type of employer-sponsored retirement savings plan that allows employees to contribute a portion of their salary to a tax-deferred investment account. The plan is named after the relevant section of the U.S. tax code, and it has become a popular way for individuals to save for retirement. There are two main types of 401k plans: Traditional and Roth. Understanding the basics of 401k plans is essential to making informed decisions about retirement savings.
The primary purpose of a 401k plan is to provide a tax-advantaged way for employees to save for retirement. Contributions to a 401k plan are made before taxes, reducing an individual’s taxable income for the year. The funds are then invested in a variety of assets, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds, and grow tax-deferred over time. This means that the funds are not subject to taxes until they are withdrawn in retirement.
Both Traditional and Roth 401k plans offer benefits, including higher contribution limits compared to individual retirement accounts (IRAs). In 2022, the annual contribution limit for 401k plans is $19,500, with an additional $6,500 catch-up contribution allowed for individuals 50 and older. Additionally, many employers offer matching contributions to their 401k plans, which can help employees save even more for retirement.
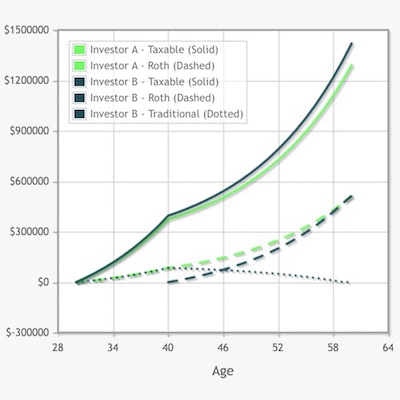
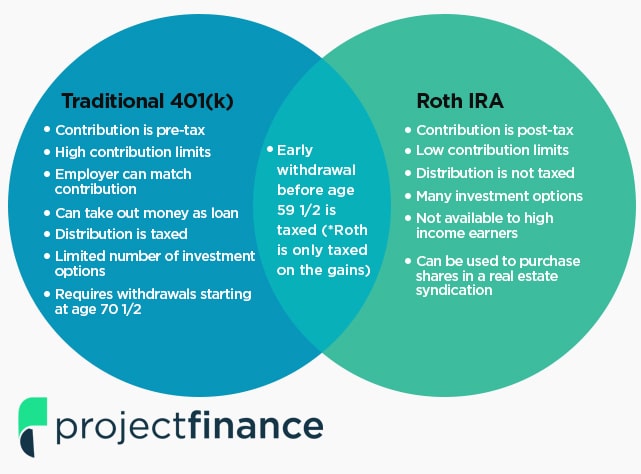
When considering a 401k plan, it’s essential to understand the key differences between Traditional and Roth plans. Traditional 401k plans offer tax-deferred growth, meaning that contributions are made before taxes, and withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income. Roth 401k plans, on the other hand, require after-tax contributions, but withdrawals are tax-free in retirement. This fundamental difference can significantly impact an individual’s retirement savings strategy.
In the next section, we’ll delve deeper into the key differences between Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans, including tax implications, contribution limits, and withdrawal rules. By understanding these differences, individuals can make informed decisions about which type of 401k plan is best for their needs and goals.
How to Choose Between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k
When it comes to choosing between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k, there are several key differences to consider. Both types of plans offer benefits, but they cater to different needs and goals. Understanding the pros and cons of each type of plan can help individuals make an informed decision about which one is best for their retirement savings strategy.
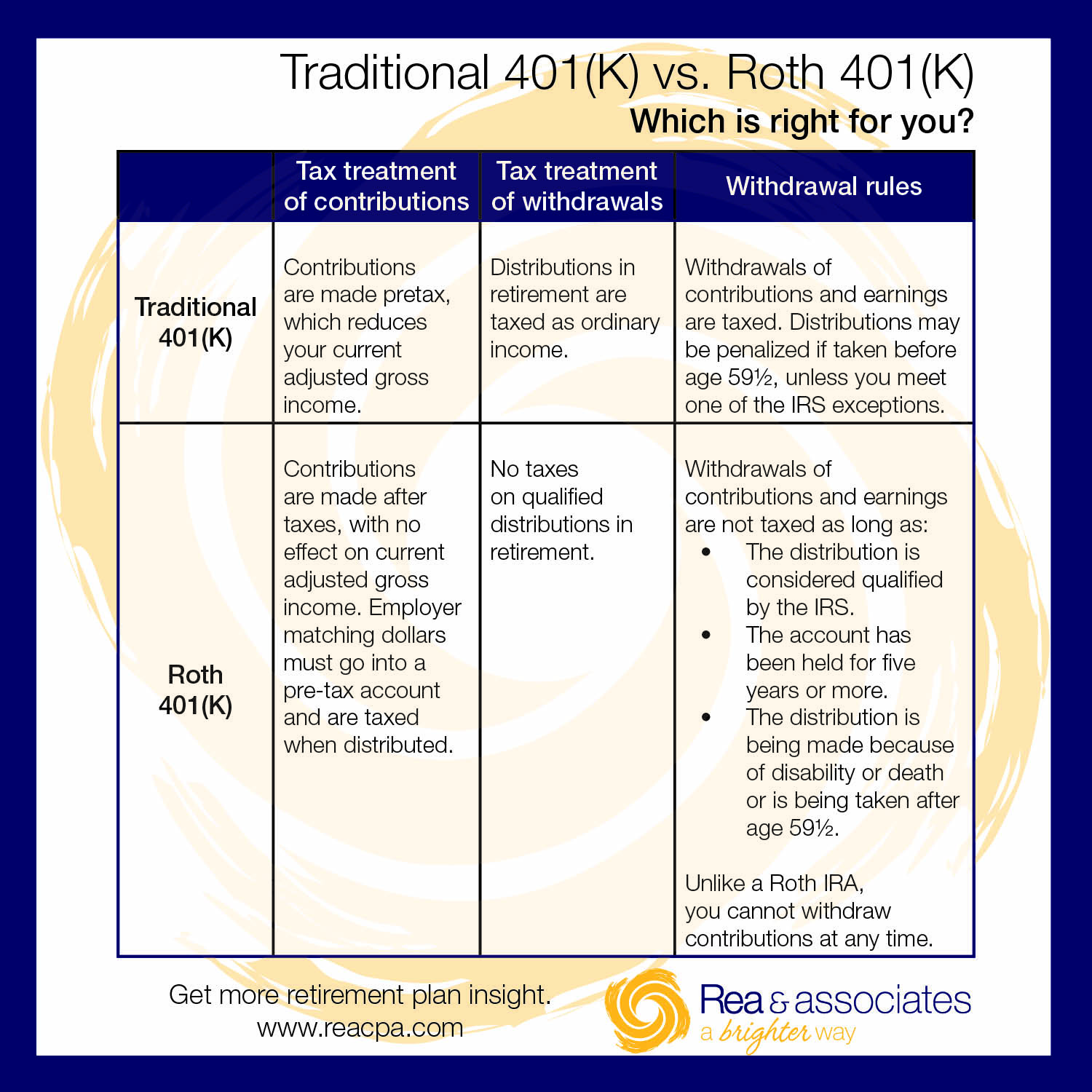
One of the primary differences between Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans is the tax treatment of contributions and withdrawals. Traditional 401k plans offer tax-deferred growth, meaning that contributions are made before taxes, and withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income. Roth 401k plans, on the other hand, require after-tax contributions, but withdrawals are tax-free in retirement. This fundamental difference can significantly impact an individual’s retirement savings strategy.
Another key difference between Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans is the contribution limits and income restrictions. Both types of plans have the same annual contribution limit of $19,500 in 2022, with an additional $6,500 catch-up contribution allowed for individuals 50 and older. However, Roth 401k plans have income restrictions that may limit or eliminate an individual’s ability to contribute to a Roth 401k plan.
In terms of withdrawal rules, Traditional 401k plans require individuals to take required minimum distributions (RMDs) starting at age 72, while Roth 401k plans do not have RMDs during the account owner’s lifetime. Additionally, Roth 401k plans have a 5-year rule, which requires individuals to wait at least five years from the date of their first Roth 401k contribution before they can withdraw earnings tax-free.
When deciding between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k, individuals should consider their current tax situation, retirement goals, and income expectations. If an individual expects to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement, a Roth 401k may be a better option. On the other hand, if an individual expects to be in a lower tax bracket in retirement, a Traditional 401k may be a better option.
Ultimately, the decision between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k depends on individual circumstances and goals. By understanding the key differences between these two types of plans, individuals can make an informed decision about which one is best for their retirement savings strategy.
Tax Implications: Roth 401k vs Traditional 401k
One of the most significant differences between Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans is the tax implications of contributions and withdrawals. Understanding these tax implications is crucial to making informed decisions about which type of plan is best for individual needs and goals.
Roth 401k contributions are made with after-tax dollars, meaning that individuals have already paid income tax on the money they contribute to the plan. As a result, Roth 401k contributions are not tax-deductible. However, the earnings on Roth 401k contributions grow tax-free, and withdrawals are tax-free in retirement, provided certain conditions are met.
Traditional 401k contributions, on the other hand, are made with pre-tax dollars, meaning that individuals have not yet paid income tax on the money they contribute to the plan. As a result, Traditional 401k contributions are tax-deductible. However, the earnings on Traditional 401k contributions grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income in retirement.
In addition to the tax implications of contributions and withdrawals, Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans also have different rules regarding required minimum distributions (RMDs). Traditional 401k plans require individuals to take RMDs starting at age 72, while Roth 401k plans do not have RMDs during the account owner’s lifetime. This means that individuals with a Roth 401k plan can keep the money in the plan for as long as they want without having to take RMDs.
When considering the tax implications of Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans, individuals should think about their current tax situation and their expected tax situation in retirement. If an individual expects to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement, a Roth 401k plan may be a better option, since the contributions are made with after-tax dollars and the withdrawals are tax-free. On the other hand, if an individual expects to be in a lower tax bracket in retirement, a Traditional 401k plan may be a better option, since the contributions are tax-deductible and the withdrawals are taxed at a lower rate.
Ultimately, the tax implications of Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans are just one factor to consider when deciding which type of plan is best for individual needs and goals. By understanding the tax implications of each type of plan, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement savings strategy.
Contribution Limits and Income Restrictions
Both Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans have contribution limits and income restrictions that may impact an individual’s ability to contribute to a 401k plan. Understanding these limits and restrictions is essential to maximizing retirement savings.
The annual contribution limit for 401k plans is $19,500 in 2022, with an additional $6,500 catch-up contribution allowed for individuals 50 and older. This means that individuals can contribute up to $26,000 to a 401k plan in 2022, if they are 50 or older. However, the contribution limit may be lower for individuals with higher incomes.
Roth 401k plans have income restrictions that may limit or eliminate an individual’s ability to contribute to a Roth 401k plan. In 2022, the income limit for Roth 401k contributions is $137,500 for single filers and $208,500 for joint filers. This means that individuals with incomes above these limits may not be eligible to contribute to a Roth 401k plan.
Traditional 401k plans do not have income restrictions, but the deductibility of contributions may be limited for individuals with higher incomes. In 2022, the income limit for deducting Traditional 401k contributions is $76,000 for single filers and $116,000 for joint filers. This means that individuals with incomes above these limits may not be able to deduct their Traditional 401k contributions from their taxable income.
It’s essential to note that the contribution limits and income restrictions for 401k plans may change over time, so it’s crucial to stay informed about these limits and restrictions to maximize retirement savings. Additionally, individuals should consider their overall financial situation and goals when deciding how much to contribute to a 401k plan.
By understanding the contribution limits and income restrictions for Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement savings strategy. It’s also important to consider other factors, such as tax implications, investment options, and withdrawal rules, when choosing between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k plan.
Withdrawal Rules and Penalties
Both Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans have withdrawal rules and penalties that individuals should be aware of. Understanding these rules and penalties can help individuals avoid unnecessary taxes and penalties.
Roth 401k plans have a 5-year rule, which requires individuals to wait at least five years from the date of their first Roth 401k contribution before they can withdraw earnings tax-free. If an individual withdraws earnings before the 5-year period is up, they may be subject to a 10% penalty, in addition to income tax on the withdrawal.
Traditional 401k plans, on the other hand, require individuals to take required minimum distributions (RMDs) starting at age 72. RMDs are calculated based on the individual’s account balance and life expectancy, and they must be taken annually. If an individual fails to take an RMD, they may be subject to a 50% penalty on the amount that should have been withdrawn.
In addition to RMDs, Traditional 401k plans also have a 10% penalty for withdrawals made before age 59 1/2, unless the individual meets certain exceptions, such as separation from service or disability. Roth 401k plans do not have this penalty, but individuals may still be subject to income tax on withdrawals made before age 59 1/2.
It’s essential to note that the withdrawal rules and penalties for Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans may change over time, so it’s crucial to stay informed about these rules and penalties to avoid unnecessary taxes and penalties. Additionally, individuals should consider their overall financial situation and goals when deciding how to manage their 401k plan withdrawals.
By understanding the withdrawal rules and penalties for Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement savings strategy. It’s also important to consider other factors, such as tax implications, contribution limits, and investment options, when choosing between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k plan.
Investment Options and Portfolios
Both Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans offer a range of investment options and portfolios that individuals can choose from. Understanding these options and how to manage them is crucial to maximizing retirement savings.
Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans typically offer a variety of investment options, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Individuals can choose from a range of pre-set portfolios or create their own custom portfolio using a mix of these investment options.
When selecting investment options, individuals should consider their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and overall financial goals. For example, individuals who are closer to retirement may want to choose more conservative investment options, such as bonds or money market funds, to reduce their risk exposure. On the other hand, individuals who are younger and have a longer investment horizon may want to choose more aggressive investment options, such as stocks or ETFs, to potentially earn higher returns.
In addition to selecting individual investment options, individuals can also choose from pre-set portfolios that are designed to meet specific investment objectives. For example, a conservative portfolio may include a mix of bonds, money market funds, and dividend-paying stocks, while an aggressive portfolio may include a mix of stocks, ETFs, and real estate investment trusts (REITs).
It’s essential to note that the investment options and portfolios available for Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans may vary depending on the plan provider and the individual’s employer. Individuals should review their plan documents and consult with a financial advisor to determine the best investment options and portfolios for their needs and goals.
By understanding the investment options and portfolios available for Roth 401k and Traditional 401k plans, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement savings strategy. It’s also important to consider other factors, such as tax implications, contribution limits, and withdrawal rules, when choosing between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k plan.
Conversion and Rollover Options
When it comes to managing a 401k plan, individuals may need to consider conversion and rollover options. These options can help optimize retirement savings and provide more flexibility in managing one’s portfolio. In the context of the Roth 401k vs Traditional 401k debate, understanding conversion and rollover options is crucial in making informed decisions.
Converting a Traditional 401k to a Roth 401k is a popular option for those who want to take advantage of the tax benefits offered by Roth 401k plans. This process involves transferring funds from a Traditional 401k account to a Roth 401k account, which requires paying taxes on the converted amount. The benefits of converting to a Roth 401k include tax-free growth and withdrawals, as well as no required minimum distributions (RMDs) during the account owner’s lifetime.
On the other hand, rolling over a 401k to an Individual Retirement Account (IRA) is another option available to individuals. This process involves transferring funds from a 401k account to an IRA, which can provide more investment options and flexibility in managing one’s portfolio. When rolling over a 401k to an IRA, it’s essential to consider the type of IRA, as it may impact the tax implications and investment options.
When deciding between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k, it’s essential to consider the conversion and rollover options available. For instance, if an individual expects to be in a higher tax bracket during retirement, converting to a Roth 401k may be a more tax-efficient option. On the other hand, if an individual prefers more investment options and flexibility, rolling over a 401k to an IRA may be a better choice.
In conclusion, conversion and rollover options can play a significant role in optimizing retirement savings. By understanding the options available, individuals can make informed decisions that align with their financial goals and objectives. Whether it’s converting to a Roth 401k or rolling over a 401k to an IRA, it’s essential to consider the tax implications, investment options, and flexibility offered by each option.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best 401k Plan for Your Needs
When it comes to choosing between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k, it’s essential to consider individual needs and goals. Both plans offer unique benefits and drawbacks, and understanding these differences is crucial in making an informed decision. In the debate of Roth 401k vs Traditional 401k, it’s not necessarily a question of which plan is better, but rather which plan is best suited for individual circumstances.
For those who expect to be in a higher tax bracket during retirement, a Roth 401k may be a more tax-efficient option. Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, and withdrawals are tax-free, providing a potential long-term tax savings. On the other hand, those who expect to be in a lower tax bracket during retirement may benefit from a Traditional 401k. Contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, reducing taxable income, and withdrawals are taxed as ordinary income.
Contribution limits and income restrictions are also essential factors to consider when choosing between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k. Both plans have contribution limits, and income restrictions may impact an individual’s ability to contribute to a Roth 401k. Understanding these limits and restrictions can help individuals optimize their retirement savings.
Investment options and portfolios are another critical aspect to consider when choosing between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k. Both plans offer a range of investment options, and individuals can create a diversified portfolio to meet their investment goals. However, it’s essential to consider the fees and expenses associated with each investment option, as these can impact long-term returns.
Ultimately, the decision between a Roth 401k and a Traditional 401k depends on individual circumstances and goals. By considering factors such as tax implications, contribution limits, and investment options, individuals can make an informed decision that aligns with their retirement objectives. Whether it’s a Roth 401k or a Traditional 401k, the key is to start saving early and consistently to maximize retirement savings.
In the Roth 401k vs Traditional 401k debate, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Both plans offer unique benefits and drawbacks, and understanding these differences is crucial in making an informed decision. By considering individual needs and goals, individuals can choose the best plan for their circumstances and optimize their retirement savings.