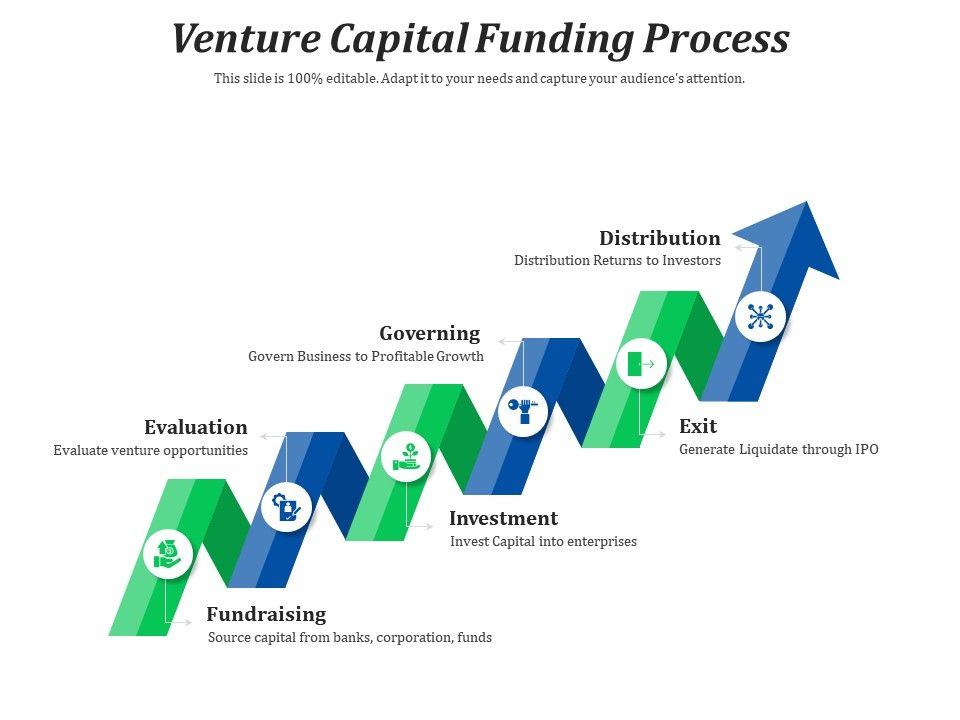
Understanding the Anatomy of a Term Sheet: Key Components and Their Implications
A venture capital term sheet is a critical document that outlines the terms and conditions of an investment in a startup. It is essential to understand the different sections of a typical term sheet, as each component can have a significant impact on the startup’s future. A well-structured term sheet can provide a solid foundation for a successful partnership between the startup and the investor, while a poorly negotiated term sheet can lead to costly mistakes and conflicts down the line.
The valuation section of the term sheet is one of the most critical components, as it determines the value of the startup and the ownership stake of the investor. A fair valuation is essential to ensure that the startup is not over- or undervalued, which can impact the investor’s return on investment and the startup’s ability to raise future funding. The valuation section should include a clear definition of the pre-money and post-money valuation, as well as any applicable discounts or premiums.
The equity section of the term sheet outlines the ownership structure of the startup, including the number of shares issued to the investor and the voting rights associated with those shares. It is essential to understand the implications of different equity structures, such as common stock, preferred stock, and convertible notes, and how they can impact the startup’s control and decision-making processes.
The voting rights section of the term sheet determines the level of control and influence the investor has over the startup’s decision-making processes. This section should outline the specific voting rights associated with the investor’s shares, including any protective provisions or veto rights. It is essential to understand the implications of different voting rights structures and how they can impact the startup’s ability to make key decisions.
The exit clauses section of the term sheet outlines the conditions under which the investor can exit the investment, including IPOs, acquisitions, and secondary sales. It is essential to understand the implications of different exit clauses and how they can impact the startup’s ability to raise future funding or achieve a successful exit.
By understanding the different sections of a typical venture capital term sheet, startups can better navigate the negotiation process and ensure a successful partnership with their investors. A well-structured term sheet can provide a solid foundation for a successful investment, while a poorly negotiated term sheet can lead to costly mistakes and conflicts down the line. By taking the time to understand the key components and their implications, startups can ensure a successful venture capital term sheet negotiation and set themselves up for long-term success.
Pre-Negotiation Strategies: How to Prepare for a Successful Term Sheet Discussion
Before entering into venture capital term sheet negotiations, it is essential to prepare thoroughly to ensure a successful outcome. Preparation is key to navigating the complex world of startup funding and securing a fair deal. By researching potential investors, understanding their investment thesis, and developing a clear understanding of the startup’s goals and limitations, founders can set themselves up for success.
Researching potential investors is a critical step in the preparation process. Founders should look into the investor’s portfolio, investment strategy, and track record of success. This information can provide valuable insights into the investor’s motivations, risk tolerance, and expectations. By understanding the investor’s perspective, founders can tailor their approach to meet the investor’s needs and increase the chances of a successful negotiation.
Understanding the investor’s investment thesis is also crucial. The investment thesis outlines the investor’s investment strategy, including the types of companies they invest in, the stages of investment, and the expected returns. By understanding the investment thesis, founders can determine whether the investor is a good fit for their startup and whether the investor’s goals align with their own.
Developing a clear understanding of the startup’s goals and limitations is also essential. Founders should have a clear understanding of their startup’s financial situation, growth prospects, and competitive landscape. This information will help founders to determine their negotiating position and make informed decisions during the negotiation process.
In addition to researching investors and understanding the startup’s goals and limitations, founders should also prepare a comprehensive data room. A data room is a collection of documents and information that provides a detailed overview of the startup’s financial situation, growth prospects, and competitive landscape. By having a comprehensive data room, founders can provide investors with the information they need to make an informed investment decision.
By preparing thoroughly, founders can increase their chances of a successful venture capital term sheet negotiation. By researching potential investors, understanding their investment thesis, and developing a clear understanding of the startup’s goals and limitations, founders can navigate the complex world of startup funding with confidence. A well-prepared founder is better equipped to negotiate a fair deal and secure the funding needed to drive growth and success.
How to Negotiate a Fair Valuation: Tips and Tricks for Founders
Negotiating a fair valuation is a critical component of venture capital term sheet negotiations. A fair valuation ensures that the startup is not over- or undervalued, which can impact the investor’s return on investment and the startup’s ability to raise future funding. To negotiate a fair valuation, founders must understand the different valuation methods, determine a reasonable valuation range, and be prepared to respond to investor pushback.
There are several valuation methods that founders can use to determine a fair valuation, including the comparable company analysis, discounted cash flow analysis, and venture capital method. Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and founders should choose the method that best suits their startup’s needs. For example, the comparable company analysis is useful for startups that have similar financial characteristics to other companies in the industry, while the discounted cash flow analysis is useful for startups that have a clear understanding of their future cash flows.
Once founders have determined a reasonable valuation range, they must be prepared to respond to investor pushback. Investors may try to negotiate a lower valuation to increase their return on investment, but founders should be prepared to defend their valuation. This can be done by providing data and analysis to support the startup’s valuation, such as financial statements, market research, and customer feedback.
Founders should also be prepared to negotiate the valuation cap, which is the maximum valuation at which the investor can invest. A higher valuation cap can provide more flexibility for the startup, but it can also increase the investor’s risk. Founders should carefully consider the valuation cap and negotiate a cap that is reasonable and fair.
In addition to negotiating the valuation, founders should also consider the implications of different valuation structures. For example, a pre-money valuation can provide more flexibility for the startup, but it can also increase the investor’s risk. A post-money valuation, on the other hand, can provide more certainty for the investor, but it can also limit the startup’s flexibility.
By understanding the different valuation methods, determining a reasonable valuation range, and being prepared to respond to investor pushback, founders can negotiate a fair valuation that works for both the startup and the investor. A fair valuation is critical to a successful venture capital term sheet negotiation, and founders should be prepared to defend their valuation and negotiate a fair deal.
The Art of Give-and-Take: Negotiating Equity and Voting Rights
Negotiating equity and voting rights is a delicate balance in venture capital term sheet negotiations. Founders must carefully consider the trade-offs between equity and control, and negotiate a balance that works for both the startup and the investor. This requires a deep understanding of the implications of different equity structures and voting rights, as well as the ability to navigate complex discussions.
Equity is a critical component of venture capital term sheet negotiations, as it determines the ownership stake of the investor and the startup. Founders must carefully consider the amount of equity to offer, as well as the type of equity to issue. For example, common stock provides voting rights and control, while preferred stock provides a higher claim on assets and dividends.
Voting rights are also a critical component of venture capital term sheet negotiations, as they determine the level of control and influence the investor has over the startup. Founders must carefully consider the type of voting rights to grant, as well as the percentage of voting rights to allocate. For example, a majority voting rights structure can provide the investor with significant control over the startup, while a minority voting rights structure can provide the startup with more flexibility.
Founders must also consider the implications of different equity and voting rights structures on the startup’s future. For example, a high equity stake can limit the startup’s ability to raise future funding, while a low equity stake can limit the investor’s return on investment. Similarly, a majority voting rights structure can limit the startup’s ability to make key decisions, while a minority voting rights structure can provide the startup with more flexibility.
To navigate these complex discussions, founders must be prepared to negotiate and compromise. This requires a deep understanding of the investor’s goals and motivations, as well as the ability to communicate effectively and build trust. By taking the time to understand the investor’s perspective and negotiate a fair balance of equity and voting rights, founders can ensure a successful venture capital term sheet negotiation and set their startup up for long-term success.
Some common equity and voting rights structures that founders may encounter include the following:
- Common stock with voting rights: This structure provides the investor with a significant amount of control and influence over the startup.
- Preferred stock with voting rights: This structure provides the investor with a higher claim on assets and dividends, but limits their control and influence over the startup.
- Convertible notes with voting rights: This structure provides the investor with the option to convert their investment into equity at a later date, while also providing voting rights.
By understanding the implications of different equity and voting rights structures, founders can navigate complex discussions and negotiate a fair balance that works for both the startup and the investor.
Protecting Founder Interests: Understanding Exit Clauses and Liquidity Events
Exit clauses and liquidity events are critical components of venture capital term sheet negotiations, as they determine the terms under which the investor can exit the investment and the startup can achieve liquidity. Founders must carefully consider the different types of exit clauses and liquidity events, including IPOs, acquisitions, and secondary sales, and negotiate terms that protect their interests and ensure fair treatment.
Exit clauses are provisions in the term sheet that outline the conditions under which the investor can exit the investment. These clauses can include IPOs, acquisitions, and secondary sales, and can have a significant impact on the startup’s future. For example, an IPO can provide the startup with access to public markets and increased visibility, while an acquisition can provide the startup with access to new resources and expertise.
Liquidity events are events that provide the startup with access to cash and liquidity, such as IPOs, acquisitions, and secondary sales. These events can have a significant impact on the startup’s future, and founders must carefully consider the terms of these events to ensure that they are fair and reasonable.
Founders must also consider the implications of different exit clauses and liquidity events on their ownership and control of the startup. For example, an IPO can dilute the founder’s ownership stake, while an acquisition can result in the loss of control over the startup.
To protect their interests, founders must negotiate exit clauses and liquidity events that are fair and reasonable. This can include negotiating provisions that provide the founder with a seat on the board of directors, or that require the investor to provide notice before exiting the investment.
Some common exit clauses and liquidity events that founders may encounter include:
- IPOs: An IPO is a public offering of stock that provides the startup with access to public markets and increased visibility.
- Acquisitions: An acquisition is the purchase of the startup by another company, which can provide the startup with access to new resources and expertise.
- Secondary sales: A secondary sale is the sale of shares by existing shareholders, which can provide the startup with access to cash and liquidity.
By understanding the different types of exit clauses and liquidity events, and negotiating terms that protect their interests, founders can ensure a successful venture capital term sheet negotiation and set their startup up for long-term success.
Common Term Sheet Negotiation Mistakes to Avoid
Term sheet negotiations can be complex and challenging, and founders often make mistakes that can have significant consequences for their startup. In this section, we will highlight some common mistakes founders make during term sheet negotiations and provide examples of how to avoid these mistakes.
One common mistake founders make is failing to understand the implications of certain clauses. For example, a founder may agree to a valuation cap without fully understanding how it will impact their ownership stake. To avoid this mistake, founders should take the time to carefully review the term sheet and seek advice from a lawyer or other expert if necessary.
Another common mistake founders make is neglecting to negotiate key terms. For example, a founder may focus on negotiating the valuation but neglect to negotiate the voting rights or exit clauses. To avoid this mistake, founders should prioritize the key terms that are most important to their startup and negotiate them aggressively.
Founders may also make the mistake of being too aggressive or confrontational during negotiations. While it is important to be assertive and advocate for the startup’s interests, being too aggressive can damage the relationship with the investor and make it more difficult to reach a mutually beneficial agreement. To avoid this mistake, founders should strive to maintain a professional and respectful tone during negotiations.
Additionally, founders may make the mistake of not considering the long-term implications of the term sheet. For example, a founder may agree to a term sheet that provides a high valuation but also includes restrictive covenants that limit the startup’s ability to operate. To avoid this mistake, founders should carefully consider the long-term implications of the term sheet and negotiate terms that align with their startup’s goals and objectives.
Some other common mistakes founders make during term sheet negotiations include:
- Failing to negotiate a clear and concise term sheet
- Not seeking advice from a lawyer or other expert
- Being too focused on the valuation and neglecting other key terms
- Not considering the long-term implications of the term sheet
- Being too aggressive or confrontational during negotiations
By avoiding these common mistakes, founders can ensure a successful venture capital term sheet negotiation and set their startup up for long-term success.
Building Relationships and Trust: The Human Side of Term Sheet Negotiations
When it comes to venture capital term sheet negotiations, the focus is often on the financial and legal aspects of the deal. However, the human side of negotiations is just as crucial in securing a successful investment. Building relationships and trust with investors can make all the difference in navigating the complex world of startup funding.
A strong rapport with investors can help to establish a foundation of trust, which is essential for a successful partnership. This trust can be built by being transparent, responsive, and respectful throughout the negotiation process. Founders should strive to understand the investor’s perspective, goals, and concerns, and be willing to address them in a clear and concise manner.
Effective communication is key to building relationships and trust with investors. Founders should be prepared to clearly articulate their vision, strategy, and financial projections, and be open to feedback and guidance from investors. By doing so, founders can demonstrate their expertise and commitment to the business, which can help to establish credibility and trust with investors.
It’s also important to remember that venture capital term sheet negotiations are not just about the financial terms of the deal, but also about the people involved. Founders should take the time to get to know the investors, their team, and their investment thesis. This can help to identify potential areas of alignment and misalignment, and facilitate a more productive and efficient negotiation process.
In addition to building relationships and trust, founders should also be prepared to navigate difficult conversations during term sheet negotiations. This can include discussions around valuation, equity, and control, which can be sensitive and contentious topics. By approaching these conversations in a calm and professional manner, founders can help to de-escalate tensions and find mutually beneficial solutions.
Ultimately, building relationships and trust with investors is critical to securing a successful venture capital term sheet negotiation. By being transparent, responsive, and respectful, and by taking the time to understand the investor’s perspective, founders can establish a strong foundation for a productive and successful partnership.
By incorporating these strategies into their negotiation approach, founders can increase their chances of securing a fair and favorable venture capital term sheet, and set their startup up for long-term success. Whether it’s a first-time founder or a seasoned entrepreneur, mastering the art of building relationships and trust with investors is essential for navigating the complex world of startup funding.
Post-Negotiation Strategies: How to Ensure a Smooth Investment Process
After the venture capital term sheet negotiation is complete, the next step is to finalize the investment agreement and complete the necessary due diligence. This process can be complex and time-consuming, but with the right strategies, founders can ensure a smooth investment process.
One of the first steps is to review and finalize the investment agreement. This document outlines the terms of the investment, including the amount of funding, valuation, equity, and voting rights. Founders should carefully review the agreement to ensure that it accurately reflects the terms negotiated in the term sheet.
Next, founders should prepare for due diligence, which is the process of verifying the startup’s financial, legal, and operational information. This can include providing financial statements, tax returns, and other documentation to the investor. Founders should be prepared to answer questions and provide additional information as needed.
During the due diligence process, founders should also be prepared to address any concerns or issues that may arise. This can include providing additional information or clarification on certain matters, or negotiating changes to the investment agreement.
Once due diligence is complete, the next step is to close the investment. This typically involves signing the final investment agreement and transferring the funds. Founders should ensure that all necessary documents are in order and that the closing process is completed efficiently.
In addition to these steps, founders should also be prepared to manage the relationship with the investor after the investment is closed. This can include providing regular updates on the startup’s progress, addressing any concerns or issues that may arise, and working collaboratively to achieve the startup’s goals.
By following these post-negotiation strategies, founders can ensure a smooth investment process and set their startup up for success. Whether it’s a first-time founder or a seasoned entrepreneur, mastering the art of venture capital term sheet negotiation and post-negotiation strategies is essential for navigating the complex world of startup funding.
Some key takeaways to keep in mind during the post-negotiation process include:
- Ensure that the investment agreement accurately reflects the terms negotiated in the term sheet.
- Be prepared to provide additional information and answer questions during the due diligence process.
- Address any concerns or issues that may arise during the due diligence process.
- Manage the relationship with the investor after the investment is closed.
By following these tips and strategies, founders can ensure a successful venture capital term sheet negotiation and post-negotiation process, and set their startup up for long-term success.