The Tax Implications of Withdrawing from a 401k
Withdrawing from a 401k before age 59 1/2 can have significant tax implications. The IRS imposes a 10% penalty on early withdrawals, in addition to income tax on the withdrawn amount. This can result in a substantial reduction in the individual’s retirement savings. For example, if an individual withdraws $10,000 from their 401k at age 40, they may be subject to a 10% penalty of $1,000, plus income tax on the withdrawn amount. This can leave the individual with only $8,000 to $9,000, depending on their tax bracket.
The tax implications of withdrawing from a 401k can be severe, and individuals should carefully consider their options before making a withdrawal. It is essential to understand the tax implications and explore alternative solutions to avoid depleting retirement savings. For instance, individuals may consider taking a loan from their 401k or exploring other sources of emergency funding. By understanding the tax implications and exploring alternative solutions, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement savings.
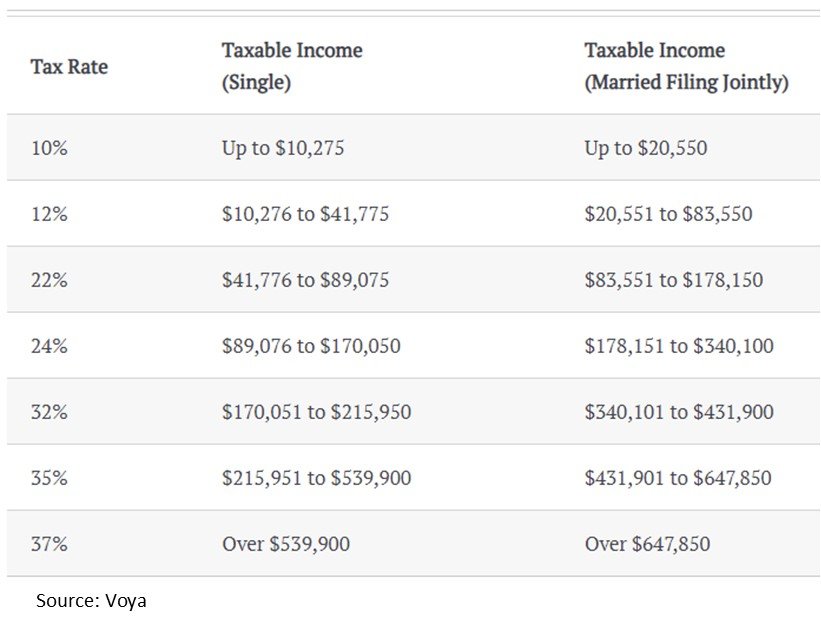
In addition to the 10% penalty, individuals may also be subject to income tax on the withdrawn amount. The tax rate will depend on the individual’s tax bracket, and the withdrawn amount will be added to their taxable income. For example, if an individual withdraws $10,000 from their 401k and is in the 24% tax bracket, they may be subject to an additional $2,400 in income tax. This can result in a total tax liability of $3,400, including the 10% penalty.
It is crucial to note that the tax implications of withdrawing from a 401k can vary depending on individual circumstances. Individuals should consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to understand the specific tax implications of their situation. By seeking professional advice, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement savings and avoid unnecessary tax penalties.
What are the tax penalties for withdrawing from a 401k? The answer is complex and depends on individual circumstances. However, one thing is clear: withdrawing from a 401k before age 59 1/2 can have significant tax implications. By understanding the tax implications and exploring alternative solutions, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement savings and avoid depleting their nest egg.
How to Avoid Tax Penalties on 401k Withdrawals
How to Avoid Tax Penalties on 401k Withdrawals
Avoiding tax penalties on 401k withdrawals requires careful planning and consideration of available options. One strategy is to wait until age 59 1/2, when the 10% penalty no longer applies. This allows individuals to withdraw from their 401k without incurring the penalty, although they will still be subject to income tax on the withdrawn amount.
Another strategy is to use the rule of 55, which allows individuals to withdraw from their 401k without penalty if they leave their job or retire at age 55 or older. This rule applies to 401k plans, but not to IRAs. For example, if an individual leaves their job at age 55 and needs to access their 401k funds, they can do so without incurring the 10% penalty.
Substantially equal payments (SEPP) are another option for avoiding tax penalties on 401k withdrawals. SEPP allows individuals to take a series of substantially equal payments from their 401k over a period of time, typically five years or more. This can provide a steady stream of income while avoiding the 10% penalty. However, SEPP requires careful planning and calculation to ensure that the payments are substantially equal and meet the IRS requirements.
It is essential to note that these strategies may have specific requirements and limitations. For example, the rule of 55 only applies to 401k plans, and SEPP requires careful calculation and planning. Individuals should consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to determine the best strategy for their specific situation and to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
What are the tax penalties for withdrawing from a 401k? By understanding the available strategies for avoiding tax penalties, individuals can make informed decisions about their retirement savings and minimize the impact of taxes on their nest egg. Whether it’s waiting until age 59 1/2, using the rule of 55, or taking substantially equal payments, there are options available to help individuals avoid tax penalties and achieve their retirement goals.
Exceptions to the 10% Penalty Rule
While the 10% penalty for early 401k withdrawals can be a significant deterrent, there are certain exceptions that may allow individuals to avoid this penalty. One such exception is for first-time home purchases. If an individual is using their 401k funds to purchase a primary residence, they may be exempt from the 10% penalty. However, this exception only applies to a maximum of $10,000 in withdrawals.
Another exception to the 10% penalty rule is for qualified education expenses. If an individual is using their 401k funds to pay for qualified education expenses, such as tuition and fees, they may be exempt from the penalty. However, this exception only applies to expenses that are incurred within a certain timeframe, typically within 120 days of the withdrawal.
Qualified disability expenses are also an exception to the 10% penalty rule. If an individual is using their 401k funds to pay for qualified disability expenses, such as medical expenses or long-term care costs, they may be exempt from the penalty. However, this exception only applies to individuals who are deemed disabled by the Social Security Administration.
It is essential to note that these exceptions have specific requirements and limitations. Individuals should consult with a financial advisor or tax professional to determine if they qualify for an exception and to ensure compliance with IRS regulations.
Understanding the exceptions to the 10% penalty rule can help individuals make informed decisions about their 401k withdrawals. By knowing the rules and exceptions, individuals can avoid unnecessary penalties and make the most of their retirement savings.
Impact of Tax Penalties on Retirement Savings
Tax penalties on 401k withdrawals can have a significant impact on retirement savings. The 10% penalty, combined with income tax on the withdrawn amount, can result in a substantial reduction in retirement income. For example, if an individual withdraws $10,000 from their 401k at age 40, they may be subject to a 10% penalty of $1,000, plus income tax on the withdrawn amount. This can leave the individual with only $8,000 to $9,000, depending on their tax bracket.
The long-term impact of tax penalties on retirement savings can be severe. By withdrawing from a 401k early, individuals may be reducing their retirement income and increasing their tax liability. This can result in a lower standard of living in retirement and a reduced ability to achieve long-term financial goals.
Preserving retirement assets is crucial to maintaining a comfortable standard of living in retirement. By avoiding tax penalties and minimizing withdrawals, individuals can help ensure that their retirement savings last throughout their golden years. It is essential to consider the long-term impact of tax penalties on retirement savings and to develop a strategy for minimizing their impact.
What are the tax penalties for withdrawing from a 401k? Understanding the impact of tax penalties on retirement savings can help individuals make informed decisions about their retirement planning. By considering the long-term consequences of tax penalties, individuals can develop a strategy for minimizing their impact and maximizing their retirement income.
It is essential to note that tax penalties are just one consideration when it comes to retirement planning. Individuals should also consider other factors, such as investment returns, inflation, and healthcare costs, when developing their retirement strategy. By taking a comprehensive approach to retirement planning, individuals can help ensure that they achieve their long-term financial goals.
Alternatives to Withdrawing from a 401k
When faced with a financial emergency, it’s essential to consider alternatives to withdrawing from a 401k to avoid the tax penalties and preserve retirement savings. One option is to take a loan from the 401k account. This allows individuals to borrow a portion of their retirement funds, typically up to 50% of the account balance or $50,000, whichever is less. The loan must be repaid with interest, usually through payroll deductions, within a specified period, typically five years.
Another alternative is to explore other sources of emergency funding, such as a home equity loan or line of credit, a personal loan, or a credit card. These options may offer more favorable interest rates and repayment terms compared to a 401k loan. Additionally, individuals may consider reducing expenses, increasing income, or seeking assistance from a non-profit credit counseling agency to address financial difficulties.
It’s also important to note that some employers offer emergency loan programs or financial assistance initiatives that can help employees cover unexpected expenses without tapping into their 401k accounts. Individuals should review their employee benefits package or consult with their HR representative to determine if such programs are available.
In some cases, individuals may be able to delay or reduce expenses, such as mortgage payments or property taxes, to free up funds for emergency expenses. It’s essential to communicate with creditors and service providers to explore available options and avoid late fees or penalties.
When evaluating alternatives to 401k withdrawals, it’s crucial to consider the potential impact on retirement savings and the tax implications of each option. For instance, taking a 401k loan may reduce the account balance, potentially affecting retirement income, while withdrawing from a 401k may trigger tax penalties and income tax on withdrawals. By exploring alternative solutions, individuals can make informed decisions that balance their short-term financial needs with their long-term retirement goals.
Ultimately, avoiding 401k withdrawals and exploring alternative funding sources can help individuals preserve their retirement savings and minimize the tax penalties associated with early withdrawals. By understanding the options available and seeking professional advice when needed, individuals can make informed decisions that support their financial well-being and retirement security.
Planning for Tax-Efficient Retirement Income
As individuals approach retirement, it’s essential to plan for tax-efficient retirement income to minimize taxes and maximize retirement income. A well-planned retirement income strategy can help individuals make the most of their hard-earned savings and ensure a comfortable retirement. One key consideration is the tax implications of retirement income sources, including 401k withdrawals, pensions, and Social Security benefits.
To minimize taxes in retirement, individuals can consider strategies such as tax-loss harvesting, which involves selling securities at a loss to offset gains from other investments. This can help reduce taxable income and lower tax liabilities. Additionally, individuals can consider converting traditional IRA or 401k accounts to Roth accounts, which can provide tax-free growth and withdrawals in retirement.
Another strategy is to prioritize tax-efficient withdrawal sequences from retirement accounts. For example, individuals may consider withdrawing from taxable accounts first, followed by tax-deferred accounts, and finally tax-free accounts. This can help minimize taxes and maximize retirement income. It’s also essential to consider the impact of required minimum distributions (RMDs) on retirement income and taxes.
Individuals can also explore alternative income sources, such as annuities or real estate investment trusts (REITs), which can provide tax-efficient income in retirement. Annuities, for example, can provide a guaranteed income stream for life, while REITs can offer tax-deferred income and potential long-term capital appreciation.
Maximizing retirement income also requires careful consideration of Social Security benefits. Individuals can optimize their Social Security benefits by delaying claims, which can increase monthly benefits by up to 8% per year. Additionally, individuals can consider strategies such as “file and suspend” or “restricted application” to maximize spousal benefits.
Finally, individuals should consider working with a financial advisor or tax professional to develop a comprehensive retirement income plan. These professionals can help individuals navigate the complex tax landscape and create a personalized plan that minimizes taxes and maximizes retirement income.
By planning for tax-efficient retirement income, individuals can ensure a comfortable and sustainable retirement. It’s essential to consider the tax implications of retirement income sources, prioritize tax-efficient withdrawal sequences, and explore alternative income sources. With careful planning and professional guidance, individuals can make the most of their retirement savings and enjoy a secure and fulfilling retirement.
Seeking Professional Advice on 401k Withdrawals
When considering a 401k withdrawal, it is essential to seek professional advice from a financial advisor or tax professional. They can help individuals navigate the complex tax implications and make informed decisions about their retirement savings. A financial advisor can assess an individual’s overall financial situation, including their income, expenses, debts, and financial goals, to determine the best course of action.
A tax professional can provide guidance on the tax implications of a 401k withdrawal, including the 10% penalty and income tax on withdrawals. They can also help individuals understand the exceptions to the 10% penalty rule and how to report the penalty on their tax return. By seeking professional advice, individuals can avoid costly mistakes and ensure that they are making the most tax-efficient decisions for their retirement savings.
Some questions to ask a financial advisor or tax professional when seeking advice on 401k withdrawals include: What are the tax penalties for withdrawing from a 401k in my situation? Are there any exceptions to the 10% penalty rule that I may be eligible for? How will a 401k withdrawal impact my retirement income and overall financial situation? What are the alternatives to withdrawing from a 401k, and which one is best for me?
By seeking professional advice, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the tax implications of a 401k withdrawal and make informed decisions about their retirement savings. This can help them avoid costly mistakes and ensure that they are making the most tax-efficient decisions for their financial future.
In addition to seeking professional advice, individuals can also educate themselves on the tax implications of 401k withdrawals. This can include researching the rules and regulations surrounding 401k withdrawals, as well as understanding the potential impact on their retirement income. By taking a proactive approach to their retirement planning, individuals can ensure that they are making the most of their 401k savings and setting themselves up for long-term financial success.