Understanding the Concept of Tax Withholding
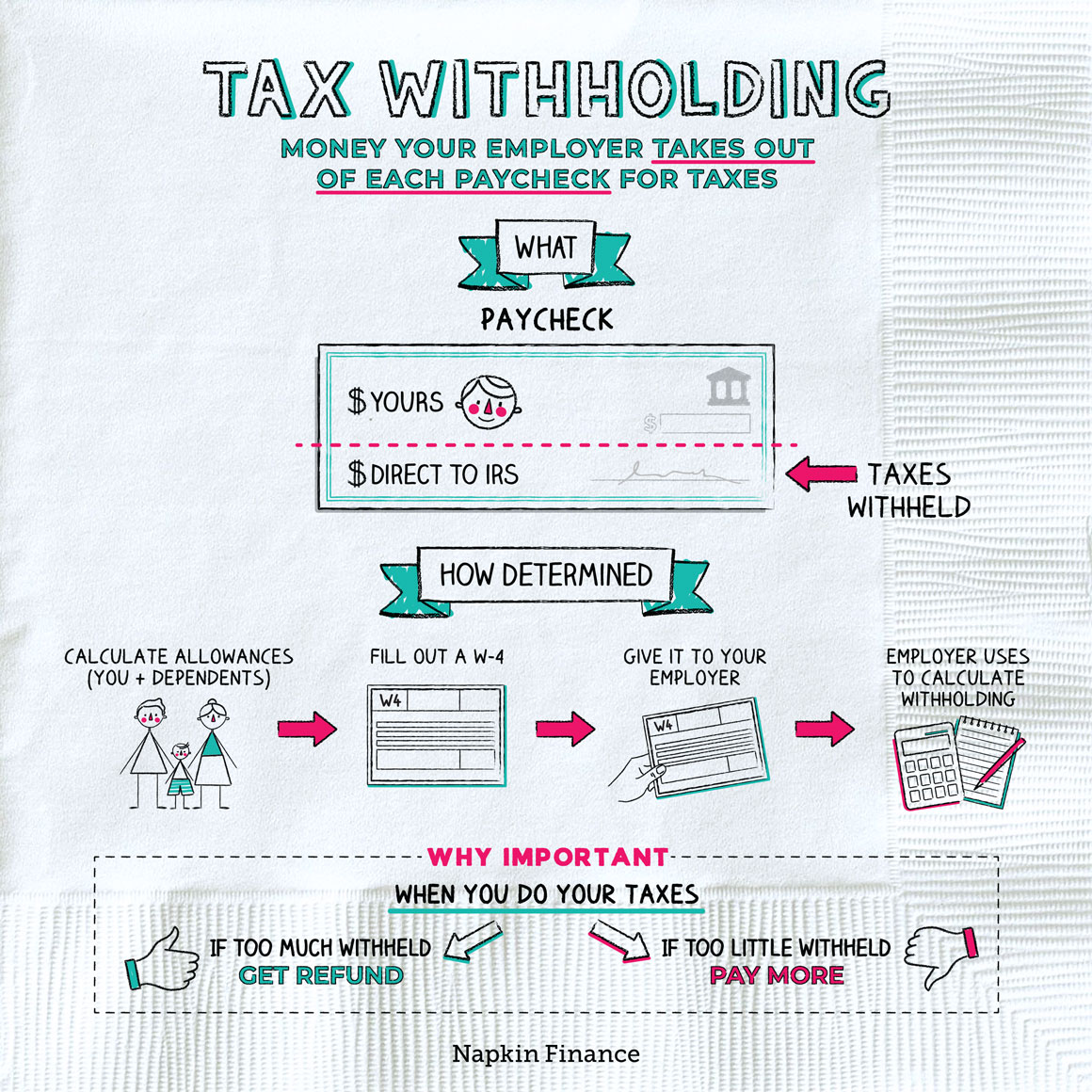
Tax withholding is a crucial aspect of the tax system, and understanding its concept is essential for individuals and businesses alike. So, what does tax withholding mean? In simple terms, tax withholding refers to the process of deducting a portion of an employee’s wages or income and setting it aside for tax payments. This process is typically handled by employers, who are required to withhold a certain amount of taxes from their employees’ paychecks and remit it to the government on their behalf.
The purpose of tax withholding is to ensure that individuals and businesses meet their tax obligations throughout the year, rather than having to pay a large amount of taxes at the end of the year. This approach helps to prevent tax evasion and ensures that the government receives a steady stream of revenue. Tax withholding also helps to reduce the burden of tax payments on individuals and businesses, as it spreads the cost of taxes over several months or quarters.
For example, let’s say an employee earns a monthly salary of $5,000. Their employer may be required to withhold 20% of their salary for federal income taxes, which would be $1,000. This amount would be deducted from the employee’s paycheck and remitted to the government on their behalf. The employee would then receive their net pay, which would be $4,000 ($5,000 – $1,000).
Tax withholding can be applied to various types of income, including wages, salaries, tips, and commissions. It can also be applied to other types of income, such as interest, dividends, and capital gains. The amount of taxes withheld depends on several factors, including the type of income, the amount of income, and the tax rates applicable to the individual or business.
In addition to federal income taxes, tax withholding can also be applied to state and local taxes. The rules and regulations surrounding tax withholding vary from state to state, so it’s essential to understand the specific requirements in your area.
Overall, tax withholding is an essential aspect of the tax system, and understanding its concept is crucial for individuals and businesses. By grasping the basics of tax withholding, you can better navigate the tax system and ensure that you meet your tax obligations throughout the year.
How to Calculate Tax Withholding: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating tax withholding can be a complex process, but it’s essential to get it right to avoid penalties and interest. To help you understand how to calculate tax withholding, we’ll break down the process into a step-by-step guide.
Step 1: Determine Your Tax Filing Status
Your tax filing status plays a significant role in determining your tax withholding. You can file as single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, or qualifying widow(er). Each filing status has its own tax rates and deductions, so it’s essential to choose the correct one.
Step 2: Calculate Your Gross Income
Your gross income includes all the income you earn from various sources, such as wages, salaries, tips, and commissions. You’ll need to calculate your gross income to determine how much tax withholding is required.
Step 3: Determine Your Tax Deductions and Exemptions
Tax deductions and exemptions can reduce your taxable income, which in turn affects your tax withholding. You may be eligible for deductions such as the standard deduction, mortgage interest, and charitable donations. You may also be eligible for exemptions such as the personal exemption and dependent exemptions.
Step 4: Use Tax Withholding Tables and Charts
Tax withholding tables and charts can help you determine how much tax withholding is required based on your income and filing status. These tables and charts are usually provided by the IRS and can be found on their website.
Step 5: Calculate Your Tax Withholding
Using the information from the previous steps, you can calculate your tax withholding. You’ll need to multiply your gross income by the tax withholding rate, which is usually a percentage of your income. You can use the tax withholding tables and charts to determine the correct withholding rate.
Example:
Let’s say you’re single and have a gross income of $50,000 per year. You’re eligible for the standard deduction of $12,000 and have no exemptions. Using the tax withholding tables and charts, you determine that your tax withholding rate is 22%. You would multiply your gross income by the withholding rate to get your total tax withholding.
50,000 x 0.22 = 11,000
In this example, your total tax withholding would be $11,000 per year, or approximately $917 per month.
By following these steps, you can calculate your tax withholding and ensure that you’re meeting your tax obligations. Remember to review and adjust your tax withholding regularly to avoid penalties and interest.
The Importance of Accurate Tax Withholding
Accurate tax withholding is crucial for individuals and businesses to avoid penalties and interest. When tax withholding is incorrect, it can lead to a range of problems, from underpayment of taxes to overpayment of taxes. In this section, we’ll explore the importance of accurate tax withholding and how it can benefit individuals and businesses.
Consequences of Under-Withholding
Under-withholding occurs when an individual or business withholds too little tax from their income. This can result in a tax bill at the end of the year, which can be a significant financial burden. Additionally, under-withholding can lead to penalties and interest, which can further increase the tax bill.
For example, let’s say an individual has a tax liability of $10,000 but only withholds $8,000 throughout the year. At the end of the year, they will owe $2,000 in taxes, plus penalties and interest. This can be a significant financial burden, especially if the individual is not prepared to pay the tax bill.
Consequences of Over-Withholding
Over-withholding occurs when an individual or business withholds too much tax from their income. This can result in a large tax refund at the end of the year, but it can also mean that the individual or business has given the government an interest-free loan throughout the year.
For example, let’s say an individual has a tax liability of $8,000 but withholds $10,000 throughout the year. At the end of the year, they will receive a tax refund of $2,000. While this may seem like a good thing, it means that the individual has given the government an interest-free loan of $2,000 throughout the year.
Benefits of Accurate Tax Withholding
Accurate tax withholding can benefit individuals and businesses in several ways. Firstly, it can help avoid penalties and interest, which can save money and reduce financial stress. Secondly, it can help individuals and businesses budget their finances more effectively, as they will have a better understanding of their tax liability throughout the year.
Finally, accurate tax withholding can help individuals and businesses take advantage of tax savings opportunities, such as deductions and credits. By withholding the correct amount of tax, individuals and businesses can ensure that they are taking advantage of all the tax savings opportunities available to them.
In conclusion, accurate tax withholding is crucial for individuals and businesses to avoid penalties and interest. By understanding the consequences of under-withholding and over-withholding, individuals and businesses can take steps to ensure that they are withholding the correct amount of tax throughout the year. This can help reduce financial stress, improve budgeting, and take advantage of tax savings opportunities.
Tax Withholding Tables and Charts: A Helpful Resource
Tax withholding tables and charts are essential tools for individuals and businesses to determine accurate tax withholding. These resources provide a quick and easy way to calculate tax withholding based on income, deductions, and exemptions.
What are Tax Withholding Tables and Charts?
Tax withholding tables and charts are pre-calculated tables and charts that provide the correct tax withholding amount based on income, deductions, and exemptions. These tables and charts are usually provided by the IRS and are updated annually to reflect changes in tax rates, deductions, and exemptions.
How to Use Tax Withholding Tables and Charts
Using tax withholding tables and charts is a straightforward process. First, determine your income, deductions, and exemptions. Then, use the tables and charts to find the correct tax withholding amount based on your income and filing status.
For example, let’s say you have a monthly income of $4,000 and are single. Using the tax withholding tables and charts, you would find that your tax withholding amount is $800 per month.
Benefits of Using Tax Withholding Tables and Charts
Using tax withholding tables and charts can help individuals and businesses determine accurate tax withholding. This can help avoid penalties and interest, reduce financial stress, and improve budgeting.
Additionally, tax withholding tables and charts can help individuals and businesses take advantage of tax savings opportunities, such as deductions and credits. By using these resources, individuals and businesses can ensure that they are withholding the correct amount of tax throughout the year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Tax Withholding Tables and Charts
While tax withholding tables and charts are helpful resources, there are common mistakes to avoid when using them. One common mistake is failing to update the tables and charts annually to reflect changes in tax rates, deductions, and exemptions.
Another common mistake is failing to account for changes in income, deductions, and exemptions throughout the year. This can result in inaccurate tax withholding, which can lead to penalties and interest.
Conclusion
Tax withholding tables and charts are essential tools for individuals and businesses to determine accurate tax withholding. By using these resources, individuals and businesses can avoid penalties and interest, reduce financial stress, and improve budgeting. Remember to update the tables and charts annually and account for changes in income, deductions, and exemptions throughout the year.
Common Tax Withholding Mistakes to Avoid
Tax withholding can be a complex and nuanced topic, and even small mistakes can lead to significant consequences. In this section, we’ll explore some common tax withholding mistakes to avoid, including under-withholding, over-withholding, and failing to account for changes in income or deductions.
Under-Withholding: A Common Mistake
Under-withholding occurs when an individual or business withholds too little tax from their income. This can result in a tax bill at the end of the year, which can be a significant financial burden. To avoid under-withholding, it’s essential to accurately calculate tax withholding based on income, deductions, and exemptions.
Over-Withholding: Another Common Mistake
Over-withholding occurs when an individual or business withholds too much tax from their income. This can result in a large tax refund at the end of the year, but it can also mean that the individual or business has given the government an interest-free loan throughout the year. To avoid over-withholding, it’s essential to accurately calculate tax withholding based on income, deductions, and exemptions.
Failing to Account for Changes in Income or Deductions
Failing to account for changes in income or deductions is another common tax withholding mistake. This can result in inaccurate tax withholding, which can lead to penalties and interest. To avoid this mistake, it’s essential to regularly review and update tax withholding to reflect changes in income or deductions.
Tips for Avoiding Common Tax Withholding Mistakes
To avoid common tax withholding mistakes, it’s essential to:
• Accurately calculate tax withholding based on income, deductions, and exemptions
• Regularly review and update tax withholding to reflect changes in income or deductions
• Use tax withholding tables and charts to determine accurate withholding
• Consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure accurate tax withholding
By following these tips, individuals and businesses can avoid common tax withholding mistakes and ensure accurate tax withholding throughout the year.
Tax Withholding for Freelancers and Independent Contractors
Freelancers and independent contractors face unique tax withholding challenges. Unlike employees who receive a W-2, freelancers and independent contractors receive a 1099-MISC and are responsible for their own tax withholding. In this section, we’ll discuss the tax withholding challenges faced by freelancers and independent contractors and provide guidance on how to navigate these challenges.
The Need for Estimated Tax Payments
Freelancers and independent contractors are required to make estimated tax payments throughout the year. This is because they do not have taxes withheld from their income like employees do. Estimated tax payments are due on a quarterly basis and are used to pay taxes on income that is not subject to withholding.
How to Calculate Estimated Tax Payments
To calculate estimated tax payments, freelancers and independent contractors need to estimate their tax liability for the year. This can be done by using Form 1040-ES, which is the form used for estimated tax payments. The form will ask for information such as income, deductions, and exemptions.
Example:
Let’s say a freelancer has a net income of $50,000 per year and expects to owe $10,000 in taxes. To calculate their estimated tax payments, they would divide their tax liability by 4, which would be $2,500 per quarter.
Tips for Freelancers and Independent Contractors
To navigate the tax withholding challenges faced by freelancers and independent contractors, here are some tips:
• Make estimated tax payments on a quarterly basis to avoid penalties and interest
• Use Form 1040-ES to calculate estimated tax payments
• Keep accurate records of income, deductions, and exemptions to ensure accurate tax withholding
• Consider consulting with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure accurate tax withholding
By following these tips, freelancers and independent contractors can navigate the tax withholding challenges they face and ensure accurate tax withholding throughout the year.
Tax Withholding and Tax Reform: What You Need to Know
Tax reform has had a significant impact on tax withholding, and it’s essential to understand these changes to ensure accurate withholding. In this section, we’ll discuss the impact of tax reform on tax withholding, including changes to tax rates, deductions, and exemptions.
Changes to Tax Rates
Tax reform has resulted in changes to tax rates, which can affect tax withholding. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) reduced tax rates across the board, which can result in lower tax withholding for some individuals and businesses.
Changes to Deductions and Exemptions
Tax reform has also resulted in changes to deductions and exemptions, which can affect tax withholding. The TCJA eliminated or limited certain deductions and exemptions, such as the state and local tax (SALT) deduction and the mortgage interest deduction.
Impact on Tax Withholding
The changes to tax rates, deductions, and exemptions can have a significant impact on tax withholding. Individuals and businesses may need to adjust their tax withholding to reflect these changes. Failure to do so can result in under-withholding or over-withholding, which can lead to penalties and interest.
Example:
Let’s say an individual has a taxable income of $50,000 and is subject to a 24% tax rate. Under the TCJA, their tax rate is reduced to 22%. If they don’t adjust their tax withholding, they may be under-withholding, which can result in penalties and interest.
Tips for Navigating Tax Reform Changes
To navigate the tax reform changes, here are some tips:
• Review and adjust tax withholding to reflect changes to tax rates, deductions, and exemptions
• Consult with a tax professional or financial advisor to ensure accurate tax withholding
• Use tax withholding tables and charts to determine accurate withholding
• Keep accurate records of income, deductions, and exemptions to ensure accurate tax withholding
By following these tips, individuals and businesses can navigate the tax reform changes and ensure accurate tax withholding.
Conclusion: Mastering Tax Withholding for a Stress-Free Tax Season
Understanding tax withholding is crucial for individuals and businesses to avoid penalties and interest. By mastering tax withholding, you can ensure a stress-free tax season and avoid common mistakes that can lead to financial burdens.
Key Takeaways
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve covered the concept of tax withholding, how to calculate tax withholding, the importance of accurate tax withholding, and common tax withholding mistakes to avoid. We’ve also discussed tax withholding tables and charts, tax withholding for freelancers and independent contractors, and the impact of tax reform on tax withholding.
By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, you can take control of your tax withholding and ensure a stress-free tax season. Remember to:
• Understand the concept of tax withholding and its purpose
• Calculate tax withholding accurately using tax withholding tables and charts
• Avoid common tax withholding mistakes, such as under-withholding and over-withholding
• Take advantage of tax savings opportunities, such as deductions and exemptions
• Stay up-to-date with tax reform changes and their impact on tax withholding
By mastering tax withholding, you can ensure a stress-free tax season and avoid financial burdens. Take control of your tax withholding today and start enjoying a more relaxed tax season.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/with-holding-tax-4186749-4d023b8133e443588c8ce795732df79c.jpg)