What is Federal Withholding Tax and How Does it Work?
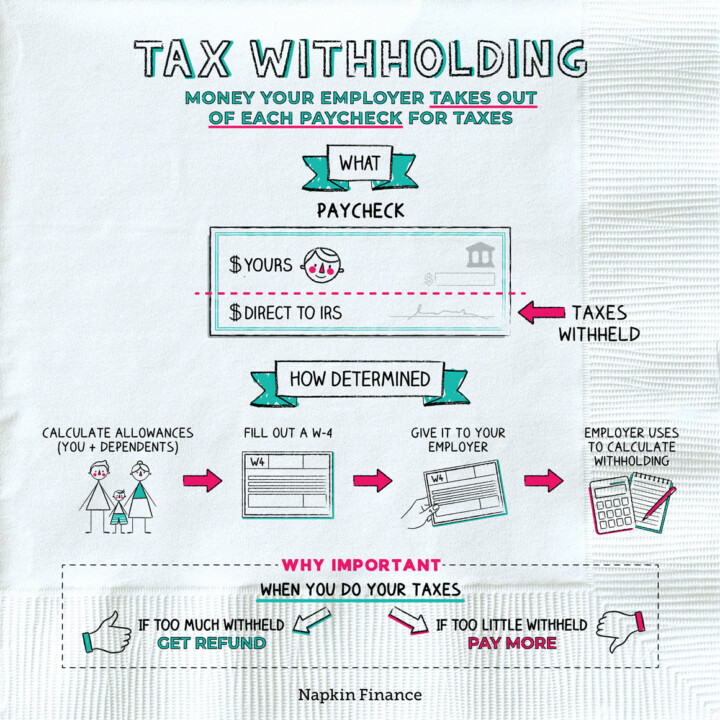
Federal withholding tax is a type of tax that is deducted from an employee’s paycheck and paid to the government on their behalf. The purpose of federal withholding tax is to collect taxes owed to the government throughout the year, rather than requiring individuals to pay a large sum at tax time. The amount of federal withholding tax deducted from an employee’s paycheck is determined by their income level, filing status, and number of dependents.
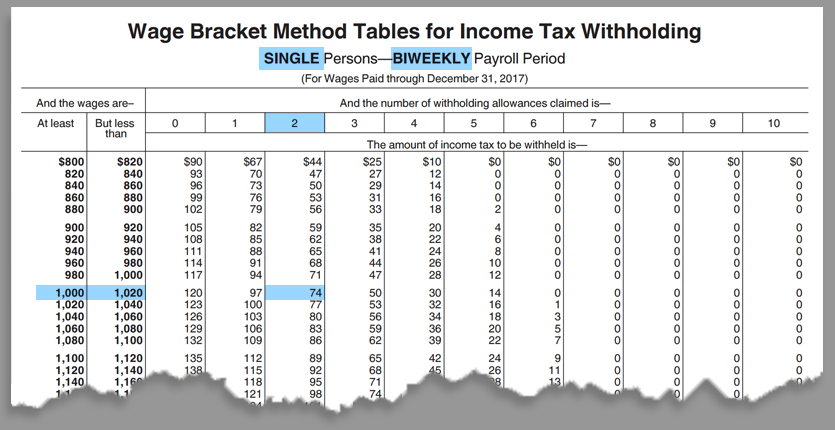
The federal withholding tax rate is calculated based on the information provided by the employee on their W-4 form. The W-4 form asks for information such as filing status, number of dependents, and any additional income or deductions. The employer uses this information to determine the correct amount of federal withholding tax to deduct from the employee’s paycheck.
For example, let’s say John is a single filer with no dependents and earns $50,000 per year. His employer would use the IRS withholding tables to determine the correct amount of federal withholding tax to deduct from his paycheck. Based on the tables, John’s employer would deduct 22% of his income in federal withholding tax, which would be $11,000 per year.
It’s essential to understand that federal withholding tax rates can impact take-home pay. If an employee’s withholding rate is too high, they may be giving the government too much money throughout the year, resulting in a large refund at tax time. On the other hand, if the withholding rate is too low, the employee may owe taxes when they file their tax return.
Employers are required to report the amount of federal withholding tax deducted from an employee’s paycheck to the IRS on a quarterly basis. The IRS uses this information to track the amount of taxes owed by the employee and to ensure that the correct amount of taxes is paid throughout the year.
In addition to federal withholding tax, employees may also have state and local taxes withheld from their paycheck. The amount of state and local taxes withheld varies depending on the state and locality in which the employee lives.
Understanding federal withholding tax rates is crucial for employees to ensure they are not overpaying or underpaying their taxes throughout the year. By knowing how federal withholding tax works, employees can make informed decisions about their tax withholding and avoid any potential penalties or fines.
So, what is federal withholding tax rate? In simple terms, it’s the percentage of an employee’s income that is deducted and paid to the government on their behalf. By understanding how federal withholding tax rates work, employees can take control of their taxes and ensure they are paying the correct amount throughout the year.
How to Determine Your Federal Withholding Tax Rate
Determining your federal withholding tax rate is crucial to ensure you’re not overpaying or underpaying your taxes throughout the year. Several factors affect federal withholding tax rates, including filing status, number of dependents, and income level. Understanding how these factors impact your withholding rate can help you make informed decisions about your tax withholding.
Filing status is one of the primary factors that affect federal withholding tax rates. The IRS recognizes five filing statuses: single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, and qualifying widow(er). Each filing status has its own set of tax rates and brackets, which can impact your withholding rate.
The number of dependents you claim also affects your federal withholding tax rate. Dependents can include children, relatives, or others who rely on you for financial support. Claiming dependents can reduce your taxable income, which in turn can lower your withholding rate.
Income level is another significant factor that impacts federal withholding tax rates. The IRS uses a progressive tax system, which means that higher income levels are subject to higher tax rates. Understanding how your income level affects your withholding rate can help you make adjustments to minimize your tax liability.
To determine your federal withholding tax rate, you can use the IRS withholding tables or online calculators. The IRS provides a withholding calculator on its website, which can help you estimate your withholding rate based on your income, filing status, and number of dependents.
Alternatively, you can use the IRS withholding tables to determine your withholding rate. The tables provide a range of income levels and corresponding withholding rates for each filing status. By using the tables, you can estimate your withholding rate and make adjustments as needed.
For example, let’s say you’re a single filer with two dependents and earn $60,000 per year. Using the IRS withholding tables, you can determine that your withholding rate is 24%. However, if you claim additional dependents or deductions, your withholding rate may decrease.
Understanding how to determine your federal withholding tax rate is essential to ensure you’re paying the correct amount of taxes throughout the year. By considering your filing status, number of dependents, and income level, you can make informed decisions about your tax withholding and minimize your tax liability.
So, what is federal withholding tax rate? It’s the percentage of your income that’s deducted and paid to the government on your behalf. By understanding how to determine your withholding rate, you can take control of your taxes and ensure you’re paying the correct amount throughout the year.
Federal Withholding Tax Rates: A Breakdown of the Tax Brackets
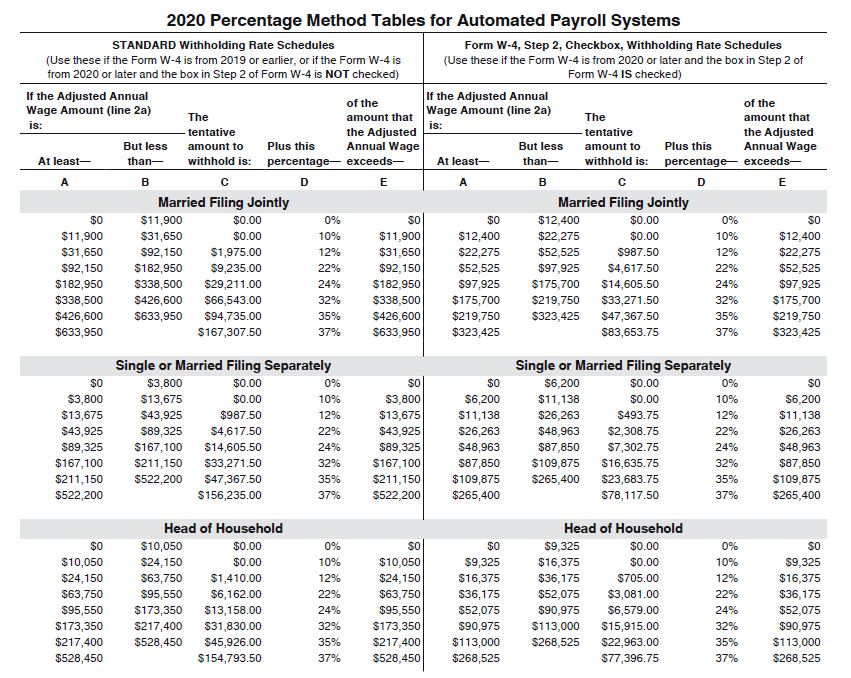
The federal income tax system in the United States is a progressive tax system, meaning that higher income levels are subject to higher tax rates. The tax rates are divided into seven tax brackets, ranging from 10% to 37%. Understanding how the tax brackets work and how they impact withholding rates is essential to managing your federal withholding tax rate.
The tax brackets for the 2022 tax year are as follows:
10%: $0 – $9,875 (single filers), $0 – $19,750 (joint filers), $0 – $14,100 (head of household filers)
12%: $9,876 – $40,125 (single filers), $19,751 – $80,250 (joint filers), $14,101 – $53,700 (head of household filers)
22%: $40,126 – $80,250 (single filers), $80,251 – $171,050 (joint filers), $53,701 – $80,250 (head of household filers)
24%: $80,251 – $164,700 (single filers), $171,051 – $326,600 (joint filers), $80,251 – $164,700 (head of household filers)
32%: $164,701 – $214,700 (single filers), $326,601 – $414,700 (joint filers), $164,701 – $214,700 (head of household filers)
35%: $214,701 – $518,400 (single filers), $414,701 – $622,050 (joint filers), $214,701 – $518,400 (head of household filers)
37%: $518,401 and above (single filers), $622,051 and above (joint filers), $518,401 and above (head of household filers)
These tax brackets are adjusted annually for inflation, so the tax rates and brackets may change from year to year. It’s essential to stay up-to-date on the current tax brackets and rates to ensure accurate withholding rates.
Understanding how the tax brackets work can help you manage your federal withholding tax rate and minimize your tax liability. By knowing which tax bracket you fall into, you can adjust your withholding rate accordingly and avoid overpaying or underpaying your taxes.
So, what is federal withholding tax rate? It’s the percentage of your income that’s deducted and paid to the government on your behalf. By understanding how the tax brackets work and how they impact withholding rates, you can take control of your taxes and ensure you’re paying the correct amount throughout the year.
How to Adjust Your Federal Withholding Tax Rate for Optimal Tax Savings
Adjusting your federal withholding tax rate can help minimize your tax liability and ensure you’re not overpaying or underpaying your taxes throughout the year. Here are some tips on how to adjust your federal withholding tax rate for optimal tax savings:
Claim Exemptions: Claiming exemptions can reduce your taxable income, which in turn can lower your withholding rate. You can claim exemptions for yourself, your spouse, and your dependents. Make sure to review the exemption amounts and adjust your withholding rate accordingly.
Deduct Expenses: Deducting expenses can also reduce your taxable income and lower your withholding rate. You can deduct expenses such as mortgage interest, charitable donations, and medical expenses. Keep track of your expenses throughout the year and adjust your withholding rate accordingly.
Take Advantage of Tax Credits: Tax credits can directly reduce your tax liability, which can lower your withholding rate. You can claim tax credits for education expenses, child care expenses, and retirement savings contributions. Review the tax credits available and adjust your withholding rate accordingly.
Adjust Your Withholding Rate: If you’ve experienced a change in income, filing status, or number of dependents, you may need to adjust your withholding rate. Use the IRS withholding tables or online calculators to determine your new withholding rate and adjust your withholding accordingly.
Consider a Tax Professional: If you’re unsure about how to adjust your federal withholding tax rate or need help with tax planning, consider consulting a tax professional. A tax professional can help you navigate the tax laws and regulations and ensure you’re taking advantage of all the tax savings available to you.
Remember, adjusting your federal withholding tax rate can help minimize your tax liability and ensure you’re not overpaying or underpaying your taxes throughout the year. By following these tips, you can take control of your taxes and ensure you’re paying the correct amount throughout the year.
So, what is federal withholding tax rate? It’s the percentage of your income that’s deducted and paid to the government on your behalf. By adjusting your federal withholding tax rate, you can minimize your tax liability and ensure you’re paying the correct amount throughout the year.
The Impact of Federal Withholding Tax Rates on Your Paycheck
Federal withholding tax rates can have a significant impact on your take-home pay. The amount of taxes withheld from your paycheck can affect your net income, and changes in tax rates or withholding amounts can impact your take-home pay.
For example, let’s say you’re a single filer with a taxable income of $50,000 per year. If your federal withholding tax rate is 22%, your employer will withhold $11,000 in federal income taxes from your paycheck over the course of the year. This means that your take-home pay will be $39,000 per year, or $3,250 per month.
However, if your federal withholding tax rate changes to 24%, your employer will withhold $12,000 in federal income taxes from your paycheck over the course of the year. This means that your take-home pay will be $38,000 per year, or $3,167 per month.
As you can see, changes in federal withholding tax rates can have a significant impact on your take-home pay. It’s essential to understand how federal withholding tax rates affect your paycheck and to adjust your withholding rate accordingly to minimize your tax liability.
In addition to changes in tax rates, changes in withholding amounts can also impact your take-home pay. For example, if you claim additional dependents or deductions, your withholding amount may decrease, resulting in a higher take-home pay.
On the other hand, if you experience a change in income or filing status, your withholding amount may increase, resulting in a lower take-home pay.
It’s essential to regularly review your federal withholding tax rate and adjust it as needed to ensure that you’re not overpaying or underpaying your taxes throughout the year.
So, what is federal withholding tax rate? It’s the percentage of your income that’s deducted and paid to the government on your behalf. By understanding how federal withholding tax rates affect your paycheck, you can take control of your taxes and ensure you’re paying the correct amount throughout the year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Dealing with Federal Withholding Tax Rates
When dealing with federal withholding tax rates, there are several common mistakes that can occur, resulting in under-withholding or over-withholding of taxes. Here are some common errors to avoid:
Under-withholding: Under-withholding occurs when too little tax is withheld from your paycheck, resulting in a large tax bill at the end of the year. This can happen if you don’t account for changes in income, filing status, or number of dependents.
Over-withholding: Over-withholding occurs when too much tax is withheld from your paycheck, resulting in a large refund at the end of the year. While a large refund may seem like a good thing, it means that you’ve essentially given the government an interest-free loan throughout the year.
Incorrect Filing Status: Using the wrong filing status can result in incorrect withholding rates. For example, if you’re married but file as single, you may be subject to a higher withholding rate.
Incorrect Number of Dependents: Claiming too many or too few dependents can result in incorrect withholding rates. Make sure to review your dependents and adjust your withholding rate accordingly.
Not Accounting for Changes in Income: Failing to account for changes in income can result in incorrect withholding rates. If you experience a change in income, make sure to adjust your withholding rate accordingly.
Not Reviewing Withholding Rates Regularly: Failing to review your withholding rates regularly can result in under-withholding or over-withholding. Make sure to review your withholding rates at least once a year to ensure accuracy.
To avoid these common mistakes, it’s essential to regularly review and update your federal withholding tax rate. Use the IRS Form W-4 to make changes and review your withholding rates at least once a year.
So, what is federal withholding tax rate? It’s the percentage of your income that’s deducted and paid to the government on your behalf. By avoiding common mistakes and regularly reviewing your withholding rates, you can ensure accurate withholding rates throughout the year.
How to Review and Update Your Federal Withholding Tax Rate
Regularly reviewing and updating your federal withholding tax rate is essential to ensure accurate withholding rates throughout the year. Here’s how to review and update your federal withholding tax rate:
Use the IRS Form W-4: The IRS Form W-4 is used to determine your federal withholding tax rate. You can use the form to claim exemptions, deductions, and credits, and to adjust your withholding rate.
Review Your Withholding Rate Annually: It’s essential to review your withholding rate at least once a year to ensure accuracy. You can review your withholding rate by using the IRS withholding tables or online calculators.
Update Your Withholding Rate as Needed: If you experience a change in income, filing status, or number of dependents, you may need to update your withholding rate. Use the IRS Form W-4 to make changes to your withholding rate.
Consider Consulting a Tax Professional: If you’re unsure about how to review and update your federal withholding tax rate, consider consulting a tax professional. A tax professional can help you navigate the tax laws and regulations and ensure accurate withholding rates.
Why Review and Update Your Withholding Rate?: Reviewing and updating your withholding rate is essential to ensure accurate withholding rates throughout the year. By regularly reviewing and updating your withholding rate, you can avoid under-withholding or over-withholding, and ensure optimal tax savings.
So, what is federal withholding tax rate? It’s the percentage of your income that’s deducted and paid to the government on your behalf. By regularly reviewing and updating your federal withholding tax rate, you can ensure accurate withholding rates throughout the year and maximize your tax savings.
Maximizing Your Tax Savings with Accurate Federal Withholding Tax Rates
Understanding and managing federal withholding tax rates is crucial for optimal tax savings. By accurately determining your federal withholding tax rate, you can minimize your tax liability and ensure you’re not overpaying or underpaying your taxes throughout the year.
Here are some final tips to ensure accurate withholding rates throughout the year:
Regularly Review Your Withholding Rate: Regularly review your withholding rate to ensure accuracy. Use the IRS withholding tables or online calculators to determine your rate and make adjustments as needed.
Take Advantage of Tax Credits: Take advantage of tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or the Child Tax Credit, to reduce your tax liability.
Claim Exemptions: Claim exemptions, such as the standard deduction or personal exemptions, to reduce your taxable income.
Deduct Expenses: Deduct expenses, such as mortgage interest or charitable donations, to reduce your taxable income.
Consult a Tax Professional: If you’re unsure about how to manage your federal withholding tax rate, consider consulting a tax professional. A tax professional can help you navigate the tax laws and regulations and ensure accurate withholding rates.
By following these tips, you can maximize your tax savings and ensure accurate withholding rates throughout the year.
So, what is federal withholding tax rate? It’s the percentage of your income that’s deducted and paid to the government on your behalf. By understanding and managing federal withholding tax rates, you can minimize your tax liability and ensure optimal tax savings.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/with-holding-tax-4186749-4d023b8133e443588c8ce795732df79c.jpg)