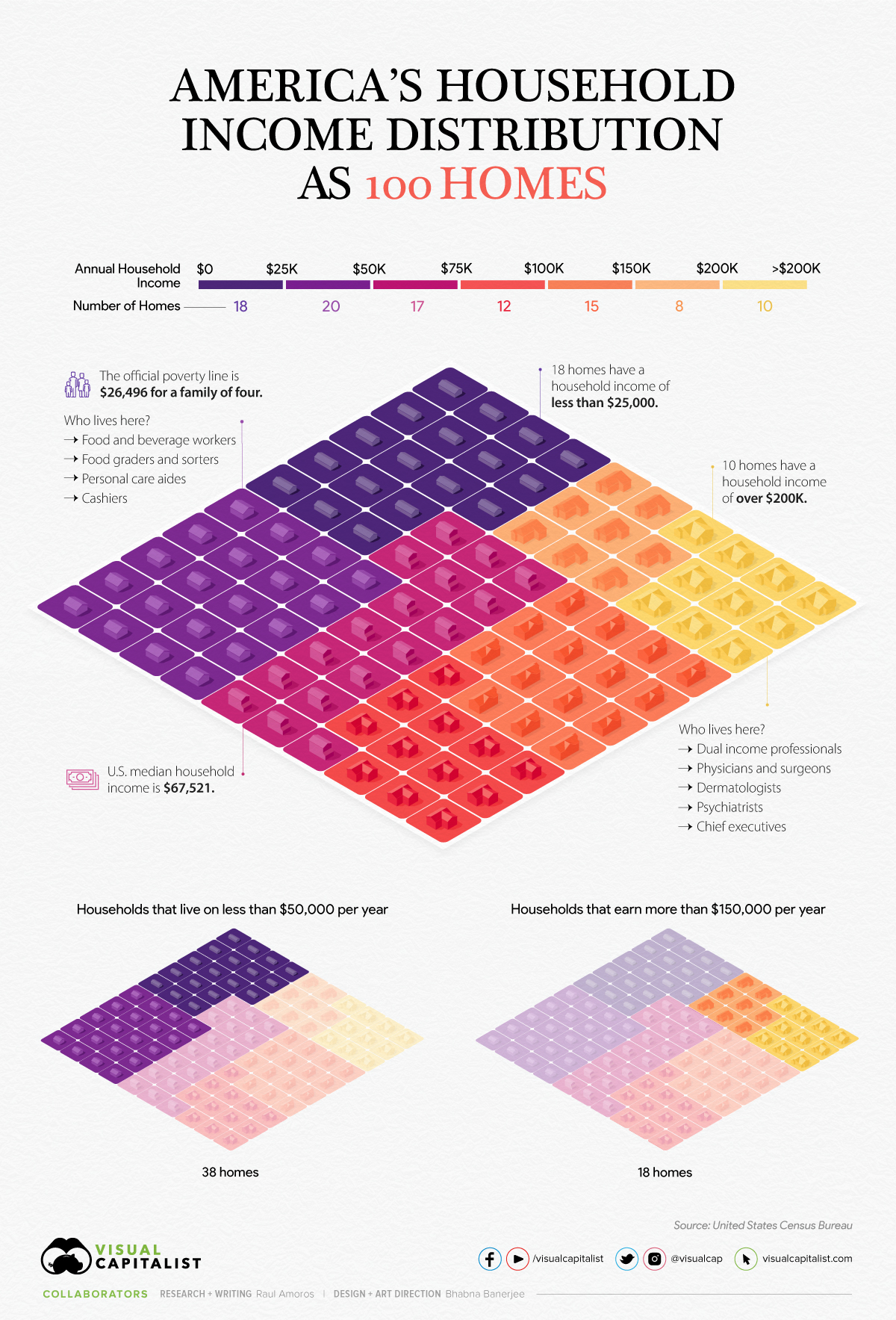
What Constitutes a Low-Income Household for One?
Defining low income for a single person can be a complex task, as it depends on various factors such as location, lifestyle, and personal choices. In the United States, for example, the federal government uses the Federal Poverty Guidelines (FPG) to determine eligibility for certain programs and benefits. According to the FPG, a single person with an annual income below $12,760 is considered to be living in poverty. However, this number does not necessarily reflect the reality of living on a low income, as the cost of living varies significantly across different regions and cities.
In general, a low-income household for one is characterized by limited financial resources, making it challenging to meet basic needs such as housing, food, healthcare, and transportation. For a single person, a low income can mean struggling to pay bills, accumulating debt, and having limited access to credit and other financial services. It can also impact mental and physical health, as the stress and anxiety of living on a low income can take a toll on overall well-being.
When determining what constitutes a low-income household for one, it’s essential to consider the 50/30/20 rule. This rule suggests that 50% of one’s income should go towards necessary expenses such as rent, utilities, and food, while 30% should be allocated towards discretionary spending, and 20% towards saving and debt repayment. For a single person living on a low income, it can be challenging to adhere to this rule, as necessary expenses often exceed 50% of their income.
Furthermore, the definition of low income can vary depending on the individual’s circumstances. For instance, a single person with a disability or chronic illness may require additional financial resources to cover medical expenses, which can impact their overall income level. Similarly, a single person with dependents, such as children or elderly parents, may require a higher income to support their loved ones.
In conclusion, defining low income for a single person is a complex task that requires considering various factors, including location, lifestyle, and personal choices. While the Federal Poverty Guidelines provide a general guideline, it’s essential to consider the individual’s circumstances and the 50/30/20 rule when determining what constitutes a low-income household for one.
How to Determine if You’re Living on a Low Income
Assessing one’s income level is crucial in determining whether you’re living on a low income. To do this, it’s essential to calculate your expenses, debt, and savings. Start by gathering all your financial documents, including pay stubs, bills, and bank statements. Next, categorize your expenses into needs (housing, food, utilities) and wants (entertainment, hobbies). This will help you identify areas where you can cut back and allocate funds more efficiently.
One way to determine if you’re living on a low income is to use the 50/30/20 rule. Allocate 50% of your income towards necessary expenses, 30% towards discretionary spending, and 20% towards saving and debt repayment. If you find it challenging to adhere to this rule, it may be an indication that you’re living on a low income.
Another way to assess your income level is to calculate your debt-to-income ratio. This is done by dividing your total monthly debt payments by your gross income. If your debt-to-income ratio is high, it may be a sign that you’re struggling to make ends meet.
Creating a budget is also an essential step in determining if you’re living on a low income. Start by tracking your income and expenses over a month to get a clear picture of your financial situation. Then, create a budget that allocates your income towards your expenses, savings, and debt repayment. Be sure to prioritize your needs over your wants and make adjustments as needed.
In addition to calculating your expenses and debt, it’s also essential to assess your savings. If you’re struggling to save money or have limited access to credit, it may be an indication that you’re living on a low income. Consider setting up an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses and working towards building a safety net.
For single individuals, determining if you’re living on a low income can be particularly challenging. With limited financial resources, it’s essential to be mindful of your spending habits and make adjustments as needed. By following these steps and being proactive about your finances, you can better understand your income level and make informed decisions about your financial future.
The Impact of Low Income on Mental and Physical Health
Living on a low income can have a profound impact on both mental and physical health. The stress and anxiety of struggling to make ends meet can lead to a range of mental health issues, including depression, anxiety disorders, and even suicidal thoughts. In fact, studies have shown that individuals living in poverty are more likely to experience mental health problems than those with higher incomes.
The physical health consequences of living on a low income are also significant. Poor nutrition, limited access to healthcare, and inadequate living conditions can all contribute to a range of health problems, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. Additionally, individuals living on a low income may be more likely to engage in unhealthy behaviors, such as smoking and excessive drinking, as a way of coping with stress and anxiety.
One of the most significant challenges facing individuals living on a low income is accessing healthcare. Without adequate health insurance, individuals may be forced to rely on emergency rooms and other safety-net providers, which can be costly and ineffective. This can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment of health problems, which can have serious consequences for overall health and well-being.
Furthermore, living on a low income can also impact an individual’s ability to engage in healthy behaviors. For example, individuals living in poverty may not have access to safe and affordable housing, which can make it difficult to maintain a healthy diet and engage in regular physical activity. Additionally, individuals living on a low income may be more likely to experience food insecurity, which can lead to a range of health problems, including malnutrition and obesity.
It’s essential to recognize that the impact of low income on mental and physical health is not limited to the individual. It can also have a profound impact on families and communities, perpetuating cycles of poverty and disadvantage. By addressing the root causes of poverty and providing support to individuals and families in need, we can work towards creating a healthier and more equitable society for all.
For single individuals living on a low income, it’s crucial to prioritize mental and physical health. This can involve seeking out support from friends, family, and community resources, as well as accessing affordable healthcare and engaging in healthy behaviors. By taking proactive steps to protect their health and well-being, individuals can better navigate the challenges of living on a low income and work towards creating a brighter future.
Navigating the Challenges of Low Income: Strategies for Singles
Living on a low income can be a significant challenge, especially for single individuals. However, there are several strategies that can help navigate these challenges and improve financial stability. One of the most effective ways to manage finances on a low income is to create a budget and track expenses. This can help identify areas where costs can be reduced and allocate funds more efficiently.
Reducing expenses is a crucial step in managing finances on a low income. This can involve cutting back on non-essential spending, such as dining out or subscription services, and finding ways to save on essential expenses, such as groceries and transportation. Additionally, singles can explore ways to increase their income, such as taking on a side job or selling items they no longer need.
Accessing financial assistance programs can also be a vital strategy for singles living on a low income. These programs can provide support with essential expenses, such as food, housing, and healthcare. For example, the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) provides financial assistance for food purchases, while Medicaid provides access to affordable healthcare.
Another effective strategy for managing finances on a low income is to build an emergency fund. This can provide a safety net in case of unexpected expenses or financial setbacks. Singles can start by setting aside a small amount each month and gradually increasing the amount over time.
In addition to these strategies, singles living on a low income can also benefit from seeking out support from friends, family, and community resources. This can include accessing counseling services, joining a support group, or seeking out financial assistance from non-profit organizations.
For singles living on a low income, it’s essential to prioritize financial stability and take proactive steps to manage finances effectively. By creating a budget, reducing expenses, increasing income, and accessing financial assistance programs, singles can improve their financial stability and work towards a brighter financial future.
Furthermore, singles living on a low income can also benefit from exploring alternative forms of income, such as freelancing or selling products online. These opportunities can provide a supplemental source of income and help improve financial stability.
Government Assistance Programs for Low-Income Singles
For singles living on a low income, government assistance programs can provide a vital lifeline. These programs can help with essential expenses, such as food, housing, and healthcare, and can provide a safety net in times of financial crisis. In this section, we will explore some of the government assistance programs available to low-income singles.
One of the most well-known government assistance programs is the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), also known as food stamps. SNAP provides financial assistance for food purchases, helping low-income individuals and families to access nutritious food. To be eligible for SNAP, individuals must meet certain income and resource requirements, which vary by state.
Another important government assistance program is Medicaid. Medicaid provides health insurance coverage to low-income individuals and families, including singles. Medicaid covers a range of healthcare services, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and prescription medications. Eligibility for Medicaid varies by state, but generally, individuals with incomes below a certain threshold are eligible.
In addition to SNAP and Medicaid, there are several other government assistance programs available to low-income singles. These include the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) program, which provides financial assistance for low-income families, and the Section 8 Housing Choice Voucher Program, which helps low-income individuals and families to access affordable housing.
To access these government assistance programs, individuals must meet certain eligibility requirements and follow a specific application process. This typically involves submitting an application, providing documentation of income and resources, and undergoing an eligibility determination process.
It’s worth noting that government assistance programs can be complex and may have varying eligibility requirements and application processes. However, for singles living on a low income, these programs can provide a vital source of support and can help to alleviate financial stress.
For singles who are struggling to make ends meet, government assistance programs can provide a lifeline. By providing financial assistance for essential expenses, these programs can help to reduce financial stress and improve overall well-being. If you are a single individual living on a low income, it’s worth exploring the government assistance programs available to you.
Building a Support Network: Resources for Low-Income Singles
Living on a low income can be a challenging and isolating experience, but it doesn’t have to be. Building a support network of friends, family, and community resources can provide a vital lifeline for low-income singles. In this section, we will explore the importance of building a support network and introduce organizations that provide financial assistance, counseling, and other forms of support.
One of the most important resources for low-income singles is the United Way. The United Way is a non-profit organization that provides financial assistance, counseling, and other forms of support to low-income individuals and families. They offer a range of programs and services, including job training, education, and healthcare.
Another important resource for low-income singles is the Salvation Army. The Salvation Army is a non-profit organization that provides financial assistance, counseling, and other forms of support to low-income individuals and families. They offer a range of programs and services, including food and housing assistance, job training, and education.
In addition to these organizations, there are many other resources available to low-income singles. These include local food banks, housing assistance programs, and counseling services. By building a support network of friends, family, and community resources, low-income singles can access the help and support they need to improve their financial stability and overall well-being.
Building a support network is not just about accessing financial assistance and resources. It’s also about building relationships and connections with others who can provide emotional support and guidance. For low-income singles, building a support network can be a powerful way to break the cycle of poverty and improve their overall quality of life.
For low-income singles, building a support network can be a challenging task. It requires reaching out to others, building relationships, and accessing resources. However, with the right support and resources, low-income singles can build a support network that can help them achieve financial stability and improve their overall well-being.
By building a support network, low-income singles can access the help and support they need to improve their financial stability and overall well-being. Whether it’s through organizations like the United Way and the Salvation Army, or through local food banks and housing assistance programs, there are many resources available to low-income singles. By building a support network, low-income singles can break the cycle of poverty and improve their overall quality of life.
Breaking the Cycle of Low Income: Education and Career Advancement
Education and career advancement are key factors in breaking the cycle of low income. By acquiring new skills and knowledge, individuals can improve their employability and increase their earning potential. In this section, we will explore the role of education and career advancement in improving income levels and provide information on affordable education options, job training programs, and career development resources.
One of the most effective ways to break the cycle of low income is through education. By acquiring a degree or certification, individuals can significantly improve their earning potential and increase their chances of securing better-paying jobs. However, for many low-income individuals, accessing education can be a challenge due to financial constraints.
Fortunately, there are many affordable education options available to low-income individuals. These include online courses, vocational training programs, and community colleges. Additionally, many organizations offer scholarships and financial assistance to help low-income individuals access education.
In addition to education, career advancement is also crucial in breaking the cycle of low income. By acquiring new skills and knowledge, individuals can improve their employability and increase their earning potential. Job training programs, career development resources, and mentorship opportunities can all help individuals advance in their careers and improve their income levels.
For low-income singles, breaking the cycle of low income requires a strategic approach. By investing in education and career advancement, individuals can improve their employability and increase their earning potential. Additionally, by accessing affordable education options and job training programs, individuals can acquire the skills and knowledge needed to secure better-paying jobs.
Furthermore, many organizations offer resources and support to help low-income individuals access education and career advancement opportunities. These include career counseling services, job placement programs, and mentorship opportunities. By accessing these resources, individuals can gain the support and guidance needed to break the cycle of low income and improve their overall quality of life.
In conclusion, education and career advancement are key factors in breaking the cycle of low income. By acquiring new skills and knowledge, individuals can improve their employability and increase their earning potential. By accessing affordable education options, job training programs, and career development resources, individuals can break the cycle of low income and improve their overall quality of life.
Creating a Path to Financial Stability: Setting Goals and Priorities
Creating a path to financial stability requires setting clear goals and priorities. For low-income singles, this means creating a plan to increase income, reduce debt, and build savings. In this section, we will provide tips on how to set financial goals and priorities, and offer advice on how to stay motivated and track progress.
The first step in creating a path to financial stability is to set clear financial goals. This means identifying what you want to achieve, whether it’s paying off debt, building savings, or increasing income. Once you have set your goals, you can create a plan to achieve them.
One of the most effective ways to create a plan is to use the SMART goal framework. This means setting goals that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. For example, instead of setting a goal to “save more money,” you could set a goal to “save $1,000 in the next 6 months by setting aside $167 per month.”
In addition to setting goals, it’s also important to prioritize your spending. This means identifying what expenses are essential, such as rent/mortgage, utilities, and food, and what expenses are discretionary, such as entertainment and hobbies. By prioritizing your spending, you can make sure that you are allocating your resources effectively and making progress towards your financial goals.
Another key aspect of creating a path to financial stability is to track your progress. This means regularly reviewing your budget and financial statements to see how you are doing. By tracking your progress, you can identify areas where you need to make adjustments and stay motivated to continue working towards your goals.
For low-income singles, creating a path to financial stability can be challenging. However, by setting clear goals and priorities, and tracking progress, individuals can make progress towards financial stability and improve their overall quality of life.
Finally, it’s essential to stay motivated and focused on your financial goals. This means celebrating your successes, no matter how small, and seeking support from friends, family, or a financial advisor when needed. By staying motivated and focused, individuals can overcome the challenges of low income and achieve financial stability.