Unlocking the Secrets of Short Selling
Short selling, also known as “shorting the stock,” is a trading strategy that involves selling a security with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price to realize a profit. This concept may seem counterintuitive, as most investors focus on buying low and selling high. However, short selling can be a valuable tool for investors who want to profit from declining markets or individual stocks. In this article, we will delve into the world of short selling, exploring its benefits, risks, and strategies.
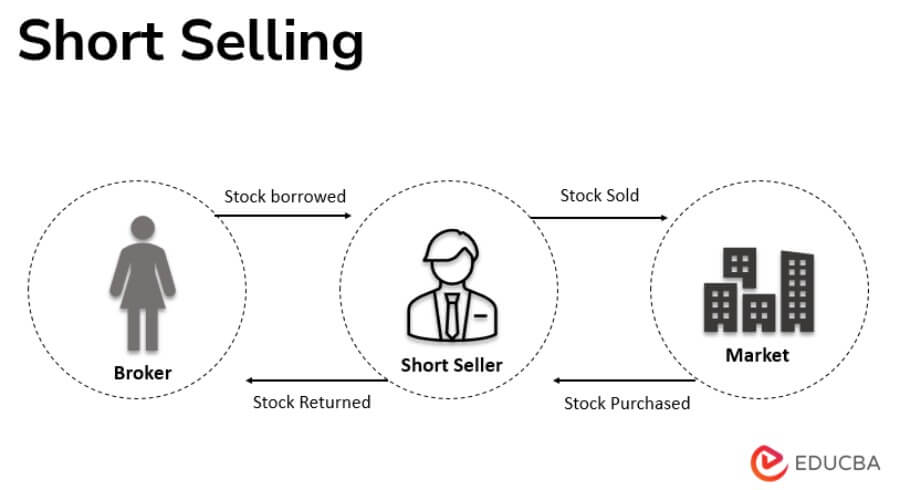
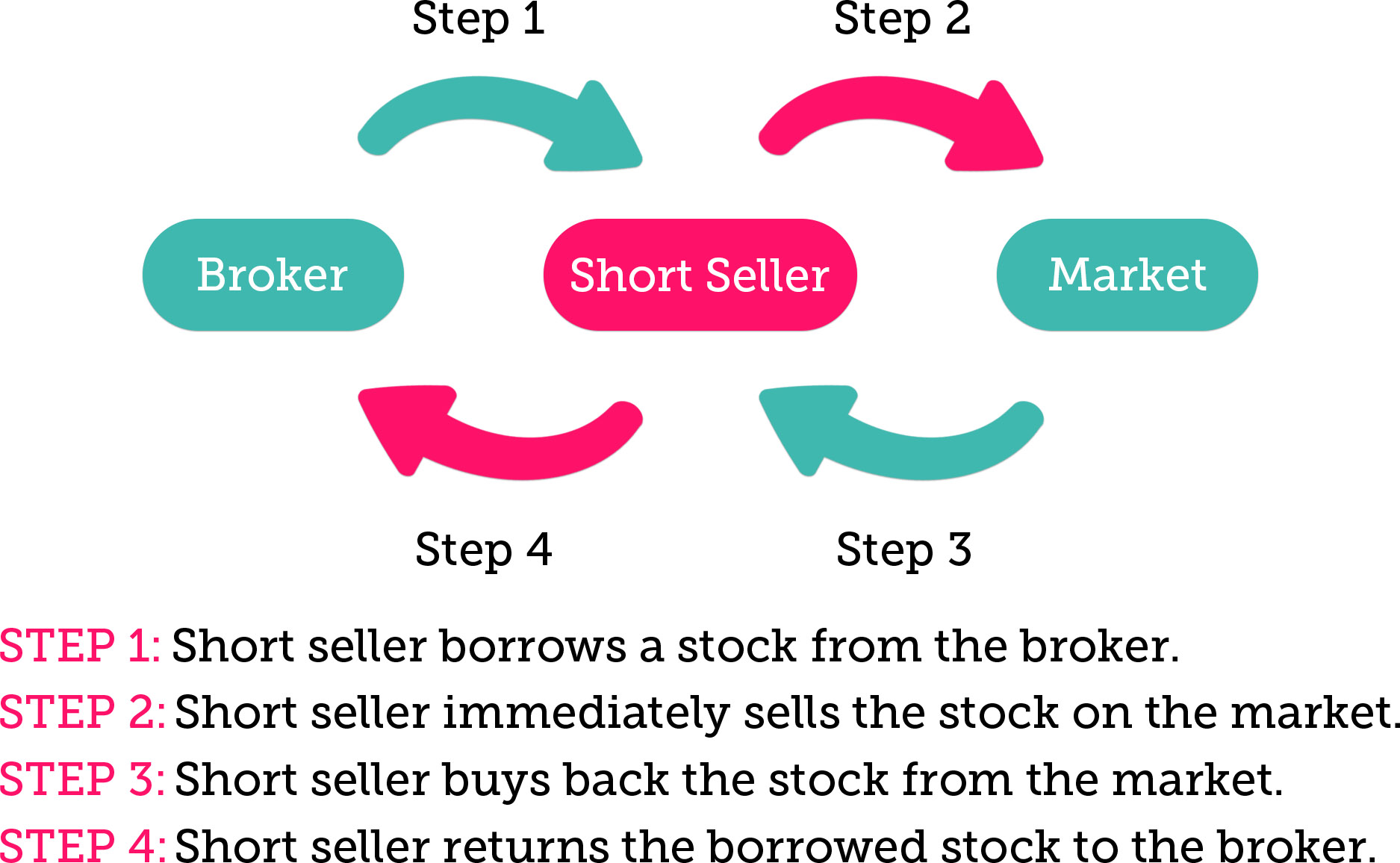
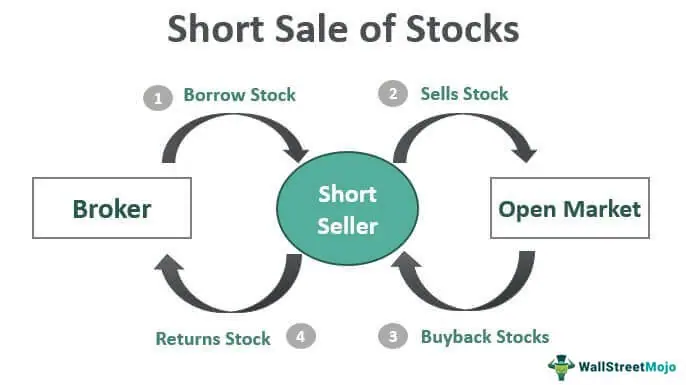
To understand short selling, it’s essential to grasp the concept of “what is short the stock.” In simple terms, shorting a stock means selling a security that you don’t own, with the expectation of buying it back later at a lower price. This is typically done by borrowing the security from a broker or another investor, selling it at the current market price, and then buying it back later to return to the lender. The difference between the selling price and the buying price is the profit, minus any fees or interest paid on the borrowed security.
Short selling can be an attractive strategy for investors who want to profit from declining markets or individual stocks. By selling short, investors can potentially profit from a stock’s decline in value, rather than just avoiding losses. However, short selling also involves significant risks, including the potential for unlimited losses if the stock price rises instead of falls. In the following sections, we will explore the risks and rewards of short selling, as well as strategies for identifying short selling opportunities and managing risks.
Understanding the Risks and Rewards of Shorting Stocks
Short selling, or “shorting the stock,” can be a lucrative strategy for investors who want to profit from declining markets or individual stocks. However, it’s essential to understand the risks and rewards associated with short selling before diving in. One of the most significant risks of short selling is the potential for unlimited losses. When an investor shorts a stock, they are essentially betting that the stock’s price will decline. If the stock’s price rises instead, the investor may be required to buy back the stock at the higher price, resulting in a loss.
Market volatility is another significant risk associated with short selling. When markets are highly volatile, stock prices can fluctuate rapidly, making it challenging to predict the direction of the market. This can result in significant losses for short sellers who are caught off guard by a sudden market reversal. Additionally, short selling involves borrowing money to buy the stock, which can result in interest charges and fees. These costs can eat into the investor’s profits, making it essential to carefully manage margin calls and maintain adequate capital.
Despite the risks, short selling can be a rewarding strategy for investors who are willing to take on the challenges. Successful short selling can result in significant profits, especially during times of market decline. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, many investors who shorted the stock market were able to profit from the decline in stock prices. To achieve success in short selling, it’s essential to have a solid understanding of the markets, as well as the ability to analyze market trends and stock performance.
In the next section, we will explore the process of shorting a stock, including finding a broker, selecting a stock, and executing the trade. We will also discuss the importance of analyzing market trends and stock performance when identifying short selling opportunities.
How to Short a Stock: A Step-by-Step Guide
Shorting a stock can seem like a complex process, but it can be broken down into a few simple steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to short a stock:
Step 1: Find a Broker
To short a stock, you’ll need to find a broker that offers short selling services. Not all brokers offer this service, so it’s essential to do your research and find a reputable broker that meets your needs. Some popular brokers that offer short selling services include Fidelity, Charles Schwab, and TD Ameritrade.
Step 2: Select a Stock
Once you’ve found a broker, you’ll need to select a stock that you want to short. This involves researching the stock’s fundamentals, technicals, and market trends to determine if it’s a good candidate for short selling. You can use various tools and resources, such as stock screeners and financial news websites, to help you make an informed decision.
Step 3: Execute the Trade
Once you’ve selected a stock, you’ll need to execute the trade. This involves placing a sell order for the stock, which will be executed at the current market price. You’ll also need to specify the number of shares you want to short and the duration of the trade.
Example: Let’s say you want to short 100 shares of XYZ stock, which is currently trading at $50 per share. You would place a sell order for 100 shares of XYZ stock at $50 per share, and the trade would be executed at the current market price.
Step 4: Monitor and Adjust
After you’ve executed the trade, you’ll need to monitor the stock’s performance and adjust your position as needed. This may involve setting stop-loss orders or adjusting your position size to minimize potential losses.
In the next section, we will discuss the importance of analyzing market trends and stock performance when identifying short selling opportunities. We will also explain how to use technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential short selling candidates.
Identifying Short Selling Opportunities: Analyzing Market Trends and Stock Performance
When it comes to short selling, identifying the right opportunities is crucial to success. To do this, traders and investors must analyze market trends and stock performance to determine which stocks are likely to decline in value. This involves using a combination of technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential short selling candidates.
Technical analysis involves studying charts and patterns to identify trends and predict future price movements. This can include analyzing indicators such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands to identify overbought or oversold conditions. By analyzing these indicators, traders can identify potential short selling opportunities and make informed decisions about when to enter a trade.
Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, involves analyzing a company’s financial statements, management team, industry trends, and competitive landscape to determine its overall health and potential for growth. This can include analyzing metrics such as earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, and debt-to-equity ratio to identify potential weaknesses or red flags.
When analyzing market trends, traders should consider the overall direction of the market, as well as the performance of specific sectors and industries. This can include analyzing trends such as economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events to determine their potential impact on the market.
By combining technical and fundamental analysis, traders can identify potential short selling opportunities and make informed decisions about when to enter a trade. For example, if a stock is showing signs of weakness on a chart, such as a declining trend line or a break below a key support level, and the company’s financial statements are showing signs of weakness, such as declining revenue or increasing debt, it may be a good candidate for a short sale.
It’s also important to consider the concept of “what is short the stock” and how it can be used to identify potential short selling opportunities. Shorting a stock involves selling a security that the seller does not own, with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price to realize a profit. By analyzing market trends and stock performance, traders can identify potential short selling opportunities and make informed decisions about when to enter a trade.
In addition to technical and fundamental analysis, traders should also consider other factors such as news and events, analyst estimates, and short interest when identifying potential short selling opportunities. By taking a comprehensive approach to analysis, traders can increase their chances of success and minimize their risk of losses.
The Role of Margin in Short Selling: Understanding the Requirements and Risks
When it comes to short selling, margin plays a critical role in the process. Margin is the amount of money required to be deposited in a brokerage account to cover the potential losses of a short sale. In this section, we will explore the concept of margin in short selling, including the requirements and risks associated with using borrowed money to short stocks.
To short a stock, an investor must first open a margin account with a brokerage firm. A margin account allows the investor to borrow money from the brokerage firm to purchase or short securities. The amount of margin required varies depending on the brokerage firm and the type of security being shorted. Typically, the margin requirement for short selling is 50% of the value of the security being shorted.
For example, if an investor wants to short 100 shares of a stock trading at $50 per share, the margin requirement would be $2,500 (50% of $5,000). This means that the investor must have at least $2,500 in their margin account to cover the potential losses of the short sale.
Using margin to short stocks can be beneficial, as it allows investors to leverage their capital and potentially earn higher returns. However, it also increases the risk of losses, as the investor is responsible for repaying the borrowed money plus interest. If the stock price rises instead of falls, the investor may be required to deposit more money into their margin account to cover the losses, known as a margin call.
Margin calls can be a significant risk for short sellers, as they can result in substantial losses if not managed properly. To avoid margin calls, investors should carefully monitor their margin account and adjust their position sizes accordingly. It’s also essential to understand the margin requirements and risks associated with short selling before entering a trade.
When considering what is short the stock, it’s crucial to understand the role of margin in the process. Short selling involves selling a security that the seller does not own, with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price to realize a profit. Margin is used to cover the potential losses of the short sale, and investors should carefully manage their margin account to avoid margin calls and minimize potential losses.
In addition to understanding the margin requirements and risks, investors should also be aware of the different types of margin accounts available. Some brokerage firms offer different types of margin accounts, such as a standard margin account or a portfolio margin account. Each type of account has its own set of rules and requirements, and investors should carefully review the terms and conditions before opening an account.
In conclusion, margin plays a critical role in short selling, and investors should carefully understand the requirements and risks associated with using borrowed money to short stocks. By managing their margin account properly and adjusting their position sizes accordingly, investors can minimize potential losses and maximize their returns.
Short Selling Strategies: From Basic to Advanced Techniques
When it comes to short selling, having a solid strategy is crucial to success. In this section, we will explore various short selling strategies, ranging from basic to advanced techniques. We will discuss the pros and cons of each strategy and provide examples of successful implementation.
Basic Short Selling Strategy: This strategy involves shorting a stock that is showing signs of weakness, such as a declining trend line or a break below a key support level. This strategy is often used by beginners and is a good starting point for those new to short selling.
Advanced Short Selling Strategy: This strategy involves using technical indicators, such as moving averages and relative strength index (RSI), to identify potential short selling opportunities. This strategy requires a higher level of technical analysis and is often used by more experienced traders.
Pair Trading Strategy: This strategy involves shorting a stock that is highly correlated with another stock that is showing signs of weakness. This strategy is often used to profit from the relative weakness of one stock compared to another.
Event-Driven Strategy: This strategy involves shorting a stock that is affected by a specific event, such as a merger or acquisition. This strategy requires a high level of research and analysis to identify potential short selling opportunities.
Activist Short Selling Strategy: This strategy involves shorting a stock and then publicly disclosing the reasons for the short sale. This strategy is often used by activist investors who seek to influence the company’s management or operations.
When considering what is short the stock, it’s essential to understand the different short selling strategies available. Short selling involves selling a security that the seller does not own, with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price to realize a profit. By using the right strategy, investors can increase their chances of success and minimize potential losses.
In addition to understanding the different short selling strategies, investors should also be aware of the importance of risk management. Short selling involves a high level of risk, and investors should use techniques such as stop-loss orders and position sizing to minimize potential losses.
By combining a solid short selling strategy with effective risk management, investors can increase their chances of success and achieve their investment goals. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding the different short selling strategies and techniques is essential to success in the markets.
Some of the key takeaways from this section include the importance of having a solid short selling strategy, the use of technical indicators to identify potential short selling opportunities, and the importance of risk management. By incorporating these concepts into your investment approach, you can increase your chances of success and achieve your investment goals.
Managing Short Selling Risks: Stop-Loss Orders and Position Sizing
When it comes to short selling, managing risks is crucial to success. In this section, we will discuss the importance of using stop-loss orders and position sizing to minimize potential losses. We will also explain how to set stop-loss orders and adjust position sizes to maximize profits.
Stop-Loss Orders: A stop-loss order is an instruction to buy or sell a security when it reaches a certain price. In the context of short selling, a stop-loss order can be used to limit losses if the stock price rises instead of falls. For example, if an investor shorts a stock at $50 and sets a stop-loss order at $55, the order will be executed if the stock price reaches $55, limiting the investor’s losses.
Position Sizing: Position sizing refers to the amount of capital allocated to a particular trade. In short selling, position sizing is critical to managing risks. By allocating a smaller amount of capital to a trade, investors can limit their potential losses if the trade does not work out. For example, if an investor has a $10,000 trading account and allocates 10% of the account to a short selling trade, the maximum potential loss is $1,000.
When considering what is short the stock, it’s essential to understand the importance of managing risks. Short selling involves selling a security that the seller does not own, with the expectation of buying it back at a lower price to realize a profit. However, if the stock price rises instead of falls, the investor can face significant losses. By using stop-loss orders and position sizing, investors can minimize potential losses and maximize profits.
In addition to using stop-loss orders and position sizing, investors should also be aware of the importance of monitoring their trades. Short selling involves a high level of risk, and investors should be prepared to adjust their trades quickly if market conditions change. By monitoring their trades and adjusting their stop-loss orders and position sizes accordingly, investors can maximize their profits and minimize their losses.
Some of the key takeaways from this section include the importance of using stop-loss orders and position sizing to manage risks, the need to monitor trades and adjust stop-loss orders and position sizes accordingly, and the importance of allocating a smaller amount of capital to a trade to limit potential losses. By incorporating these concepts into your investment approach, you can increase your chances of success and achieve your investment goals.
By managing risks effectively, investors can maximize their profits and minimize their losses. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding the importance of stop-loss orders and position sizing is essential to success in the markets.
Real-Life Examples of Successful Short Selling: Lessons from the Pros
Successful short selling requires a combination of skill, experience, and a deep understanding of the markets. While it’s impossible to replicate the exact strategies used by professional traders and investors, analyzing their approaches can provide valuable insights for those looking to improve their own short selling skills. In this section, we’ll examine a few real-life examples of successful short selling and highlight the lessons that can be learned from these experiences.
One notable example of successful short selling is the story of George Soros, who famously shorted the British pound in 1992. At the time, the UK was struggling to maintain its membership in the European Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM), and Soros believed that the pound was overvalued. He took a massive short position against the pound, which ultimately paid off when the UK was forced to withdraw from the ERM and the pound plummeted in value. This trade earned Soros a reported $1 billion in profits and cemented his reputation as a master short seller.
Another example of successful short selling is the story of Andrew Left, a well-known short seller who has made a career out of identifying and shorting overvalued companies. In 2015, Left’s firm, Citron Research, published a scathing report on the nutritional supplement company, Valeant Pharmaceuticals. The report highlighted the company’s questionable business practices and overvalued stock price, and Left took a significant short position against the company. Over the next year, Valeant’s stock price plummeted by over 90%, earning Left and his investors a substantial profit.
These examples illustrate the importance of thorough research and analysis in successful short selling. Both Soros and Left conducted extensive research on their targets before taking a short position, and their efforts were rewarded with significant profits. They also demonstrate the importance of conviction and risk management in short selling. Both traders were willing to take significant risks to capitalize on their research, but they also had the discipline to manage their positions and limit their potential losses.
For those looking to improve their own short selling skills, these examples offer several key takeaways. First, the importance of thorough research and analysis cannot be overstated. Before taking a short position, it’s essential to conduct extensive research on the company and its stock price. This includes analyzing financial statements, industry trends, and market sentiment. Second, conviction and risk management are critical components of successful short selling. Traders must be willing to take calculated risks to capitalize on their research, but they must also have the discipline to manage their positions and limit their potential losses. Finally, successful short selling requires a deep understanding of the markets and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances. Traders must be able to adjust their strategies and positions in response to new information and changing market conditions.
By studying the strategies and techniques used by successful short sellers, traders and investors can gain valuable insights into the art of short selling. While there are no guarantees of success in the markets, a deep understanding of the principles and strategies outlined in this article can help traders and investors to improve their skills and increase their chances of success. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just starting out, the art of short selling offers a powerful tool for profiting from declining stock prices. By mastering the techniques outlined in this article, you can unlock the secrets of short selling and take your trading to the next level.