Defining Low Income: What You Need to Know
Low income is a term used to describe individuals or families who earn a limited amount of money, making it challenging to meet their basic needs. The concept of low income is significant in determining eligibility for government assistance programs, tax credits, and other benefits. However, the definition of low income varies across different countries and regions, making it essential to understand the specific guidelines and thresholds that apply to your area.
In the United States, for example, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) publishes a poverty guideline each year, which is used to determine eligibility for various government programs. The guideline is based on the number of people in the household and the gross income. For instance, in 2022, the poverty guideline for a family of four was $26,500. However, this number can vary significantly depending on the state and region you live in.
Similarly, in other countries, the definition of low income may be based on a percentage of the median income or a specific income threshold. For instance, in the United Kingdom, the low-income threshold is typically defined as 60% of the median income. Understanding these differences is crucial in determining what qualifies as low income and accessing the relevant benefits and assistance programs.
It’s also important to note that low income can affect individuals and families from all walks of life, regardless of their background or circumstances. According to the United States Census Bureau, in 2020, approximately 33.6 million people lived in poverty, which is about 10.5% of the population. This highlights the need for a comprehensive understanding of low income and the available resources to support those in need.
In the next section, we will explore how to determine if you qualify as low income, including calculating your gross income, understanding income limits, and considering factors such as family size and composition.
How to Determine if You Qualify as Low Income
Determining whether you qualify as low income requires a step-by-step approach. The first step is to calculate your gross income, which includes all sources of income, such as wages, salaries, tips, and self-employment income. You can use the IRS’s income tax return forms to calculate your gross income.
Next, you need to understand the income limits that apply to your household size and composition. The income limits vary depending on the government program or benefit you are applying for. For example, the income limit for Medicaid is typically lower than the income limit for food stamps. You can check the income limits for specific programs on the government’s website or by contacting the program’s administrator.
Another important factor to consider is family size and composition. The income limits are typically adjusted based on the number of people in your household and their relationships to you. For example, a household with two adults and two children may have a higher income limit than a household with one adult and one child.
To determine if you qualify as low income, you can use the following steps:
- Calculate your gross income
- Determine your household size and composition
- Check the income limits for the specific program or benefit you are applying for
- Compare your gross income to the income limit
If your gross income is below the income limit, you may qualify as low income and be eligible for government assistance programs, tax credits, and other benefits. However, the specific eligibility requirements may vary depending on the program or benefit, so it’s essential to review the eligibility criteria carefully.
In the next section, we will explore the income limits and guidelines for various government programs, including Medicaid, food stamps, and housing assistance, highlighting the differences across states and regions.
Income Limits and Guidelines: A State-by-State Breakdown
Income limits and guidelines for government programs vary significantly across states and regions. Understanding these differences is crucial in determining what qualifies as low income and accessing the relevant benefits and assistance programs.
For example, Medicaid income limits vary by state, with some states having more generous limits than others. In California, for instance, a family of four with an income of up to $2,504 per month may be eligible for Medicaid, while in Texas, the limit is $1,563 per month.
Similarly, food stamp income limits also vary by state. In New York, a family of four with an income of up to $2,790 per month may be eligible for food stamps, while in Florida, the limit is $2,313 per month.
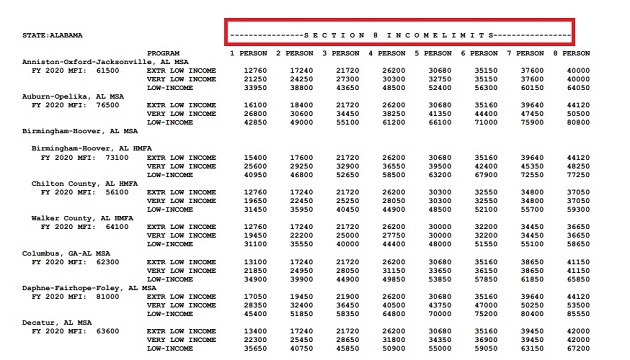
Housing assistance programs, such as Section 8, also have varying income limits across states. In Illinois, for example, a family of four with an income of up to $2,940 per month may be eligible for Section 8, while in Georgia, the limit is $2,433 per month.
It’s essential to note that these income limits are subject to change, and some states may have more restrictive or generous limits than others. Additionally, some programs may have additional eligibility requirements, such as asset tests or work requirements.
To give you a better understanding of the income limits and guidelines for various government programs, we’ve compiled a state-by-state breakdown of the income limits for Medicaid, food stamps, and housing assistance programs.
| State | Medicaid Income Limit (Family of 4) | Food Stamp Income Limit (Family of 4) | Housing Assistance Income Limit (Family of 4) |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | $2,504 | $2,790 | $2,940 |
| Texas | $1,563 | $2,313 | $2,433 |
| New York | $2,790 | $2,940 | $3,140 |
| Florida | $2,313 | $2,433 | $2,563 |
This breakdown is not exhaustive, and income limits may vary depending on the specific program and location. However, it should give you a general idea of the income limits and guidelines for various government programs across different states.
The Impact of Low Income on Daily Life: Challenges and Opportunities
Living on a low income can have a significant impact on daily life, affecting not only financial stability but also access to basic necessities like healthcare, education, and job opportunities. Understanding the challenges and opportunities associated with low income is crucial in developing effective strategies to overcome these obstacles.
One of the most significant challenges faced by low-income individuals is limited access to healthcare. Without adequate health insurance, medical expenses can quickly become overwhelming, leading to delayed or foregone care. This can have serious consequences, particularly for individuals with chronic conditions or those who require ongoing medical attention.
Education is another area where low-income individuals often face significant barriers. Limited access to quality educational resources, including schools, tutors, and educational materials, can hinder academic achievement and future career prospects. Furthermore, the financial burden of pursuing higher education can be daunting, making it difficult for low-income individuals to break the cycle of poverty.
Job opportunities are also scarce for low-income individuals, who often face limited access to job training, education, and networking opportunities. This can lead to a cycle of low-wage, dead-end jobs, making it difficult to achieve financial stability.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for low-income individuals to access resources and support. For example, government programs like Medicaid and the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) can provide essential healthcare and nutrition assistance. Additionally, non-profit organizations and community groups often offer job training, education, and financial assistance programs specifically designed for low-income individuals.
To overcome the challenges associated with low income, it’s essential to develop a comprehensive strategy that addresses the root causes of poverty. This may include:
- Pursuing education and job training opportunities to enhance employability and earning potential
- Accessing government programs and non-profit resources to support basic needs like healthcare and nutrition
- Developing a budget and financial plan to manage limited resources effectively
- Building a support network of family, friends, and community members to provide emotional and practical support
By understanding the challenges and opportunities associated with low income, individuals can develop effective strategies to overcome these obstacles and achieve financial stability.
Low Income and Tax Credits: What You’re Eligible For
Low-income individuals and families may be eligible for various tax credits that can help reduce their tax liability and increase their refund. Understanding what tax credits are available and how to claim them can be a valuable resource for those struggling to make ends meet.
One of the most significant tax credits available to low-income individuals is the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). The EITC is a refundable tax credit that is designed to help low-income working individuals and families. To qualify for the EITC, you must have earned income from a job and meet certain income and family size requirements.
Another tax credit available to low-income families is the Child Tax Credit. This credit is designed to help families with children under the age of 17. The credit is worth up to $2,000 per child, and it can be claimed in addition to the EITC.
In addition to the EITC and Child Tax Credit, there are several other tax credits available to low-income individuals and families. These include the Savers Credit, which is designed to help low-income individuals save for retirement, and the Premium Tax Credit, which is designed to help low-income individuals and families afford health insurance.
To claim these tax credits, you will need to file a tax return and complete the necessary forms. You can file your tax return electronically or by mail, and you can use tax preparation software or work with a tax professional to help you navigate the process.
Here are some tips for claiming tax credits as a low-income individual:
- Make sure you meet the income and family size requirements for the tax credit you are claiming.
- Keep accurate records of your income and expenses, as you will need this information to complete your tax return.
- Use tax preparation software or work with a tax professional to help you navigate the tax filing process.
- File your tax return electronically, as this can help you get your refund faster.
By claiming the tax credits you are eligible for, you can reduce your tax liability and increase your refund. This can be a valuable resource for low-income individuals and families who are struggling to make ends meet.
Assistance Programs for Low-Income Families: A Comprehensive Guide
Low-income families often face significant challenges in accessing basic necessities like food, healthcare, and housing. Fortunately, there are various assistance programs available to help these families overcome these challenges. In this section, we will provide a comprehensive guide to assistance programs for low-income families, including Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF), the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP), and the Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP).
Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) is a federal program that provides financial assistance to low-income families with children. The program is designed to help families achieve self-sufficiency and independence. To be eligible for TANF, families must meet certain income and family size requirements, and they must also participate in work activities or job training programs.
The Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) is a federal program that provides food assistance to low-income individuals and families. The program is designed to help families purchase food and other groceries. To be eligible for SNAP, families must meet certain income and family size requirements, and they must also have limited resources.
The Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP) is a federal program that provides energy assistance to low-income families. The program is designed to help families pay for heating and cooling costs, as well as other energy-related expenses. To be eligible for LIHEAP, families must meet certain income and family size requirements, and they must also have limited resources.
In addition to these programs, there are many other assistance programs available to low-income families, including Medicaid, the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), and the Women, Infants, and Children (WIC) program. These programs provide healthcare, nutrition, and other benefits to low-income families.
To access these assistance programs, low-income families can contact their local social services department or visit the program’s website. They can also contact a non-profit organization or a community agency that specializes in providing assistance to low-income families.
Here are some tips for accessing assistance programs as a low-income family:
- Research the different assistance programs available to low-income families and determine which ones you may be eligible for.
- Contact your local social services department or visit the program’s website to learn more about the application process and eligibility requirements.
- Gather all necessary documents and information before applying for assistance programs.
- Follow up with the program administrator to ensure that your application is being processed and to ask any questions you may have.
By accessing these assistance programs, low-income families can overcome significant challenges and achieve greater stability and self-sufficiency.
Breaking the Cycle of Poverty: Strategies for Low-Income Individuals
Breaking the cycle of poverty requires a comprehensive approach that addresses the root causes of poverty and provides individuals with the tools and resources they need to achieve financial stability. In this section, we will provide practical advice and strategies for low-income individuals to break the cycle of poverty, including education and job training, budgeting and financial planning, and accessing community resources.
Education and job training are critical components of breaking the cycle of poverty. Low-income individuals can access education and job training programs that provide them with the skills and knowledge they need to secure better-paying jobs and improve their economic prospects. These programs can include vocational training, apprenticeships, and degree programs.
Budgeting and financial planning are also essential for low-income individuals who want to break the cycle of poverty. By creating a budget and prioritizing expenses, individuals can make the most of their limited financial resources and avoid debt. Additionally, financial planning can help individuals save for the future and achieve long-term financial goals.
Accessing community resources is another important strategy for low-income individuals who want to break the cycle of poverty. Community resources can include food banks, housing assistance programs, and healthcare services. These resources can provide individuals with the support they need to overcome the challenges of poverty and achieve financial stability.
Here are some additional strategies that low-income individuals can use to break the cycle of poverty:
- Build an emergency fund to cover unexpected expenses and avoid debt.
- Take advantage of tax credits and other government benefits that can help reduce expenses and increase income.
- Seek out affordable healthcare options, such as Medicaid or community health clinics.
- Use public transportation or walk/bike whenever possible to reduce transportation costs.
By using these strategies, low-income individuals can break the cycle of poverty and achieve financial stability. It’s important to remember that breaking the cycle of poverty takes time and effort, but with the right tools and resources, it is possible.
In the next section, we will provide tips and guidance for low-income individuals on how to navigate the complex system of government programs and services, including how to apply, what to expect, and how to appeal decisions.
Navigating the System: Tips for Low-Income Individuals
Navigating the complex system of government programs and services can be overwhelming for low-income individuals. However, with the right guidance and support, individuals can access the resources they need to improve their financial stability and overall well-being. In this section, we will provide tips and guidance for low-income individuals on how to navigate the system, including how to apply, what to expect, and how to appeal decisions.
Before applying for government programs or services, it’s essential to understand the eligibility requirements and application process. Individuals can start by visiting the website of the program or service they are interested in, or by contacting a local office or hotline. It’s also a good idea to gather all necessary documents and information before applying, such as proof of income, identification, and residency.
Once an individual has applied for a program or service, they can expect to receive a decision within a certain timeframe. If the application is approved, the individual will receive a notification with instructions on how to access the benefits. If the application is denied, the individual can appeal the decision by submitting a written request or by contacting a local office or hotline.
Here are some additional tips for navigating the system:
- Keep detailed records of all applications, correspondence, and interactions with government programs and services.
- Be prepared to provide documentation and information to support your application.
- Follow up with program administrators or caseworkers to ensure that your application is being processed and to ask any questions you may have.
- Seek assistance from a social worker, advocate, or other support person if needed.
By following these tips and guidelines, low-income individuals can navigate the complex system of government programs and services with confidence and success. Remember, accessing these resources is an important step towards achieving financial stability and improving overall well-being.