Understanding Life Insurance Policies: Whole Life and Term
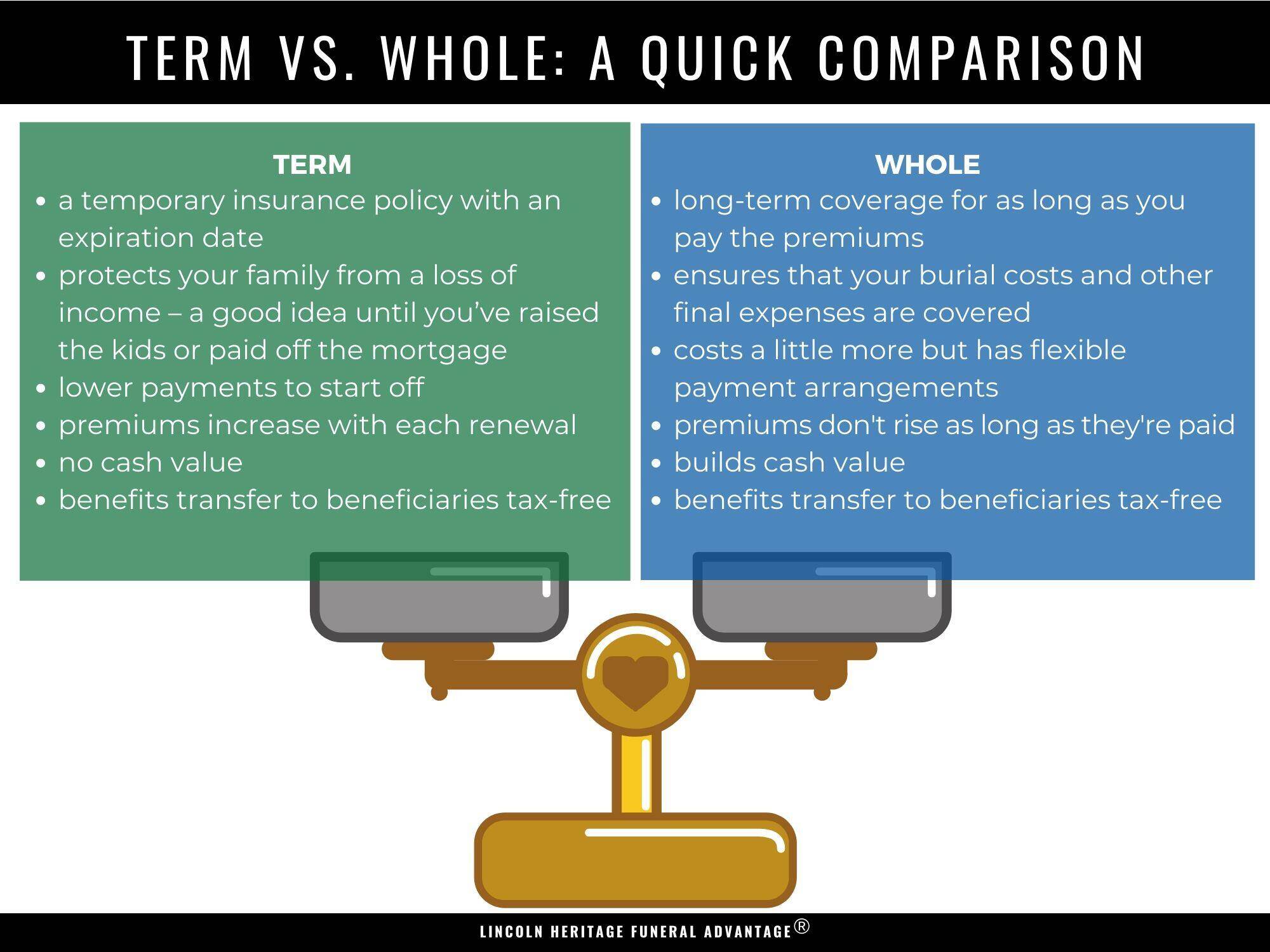
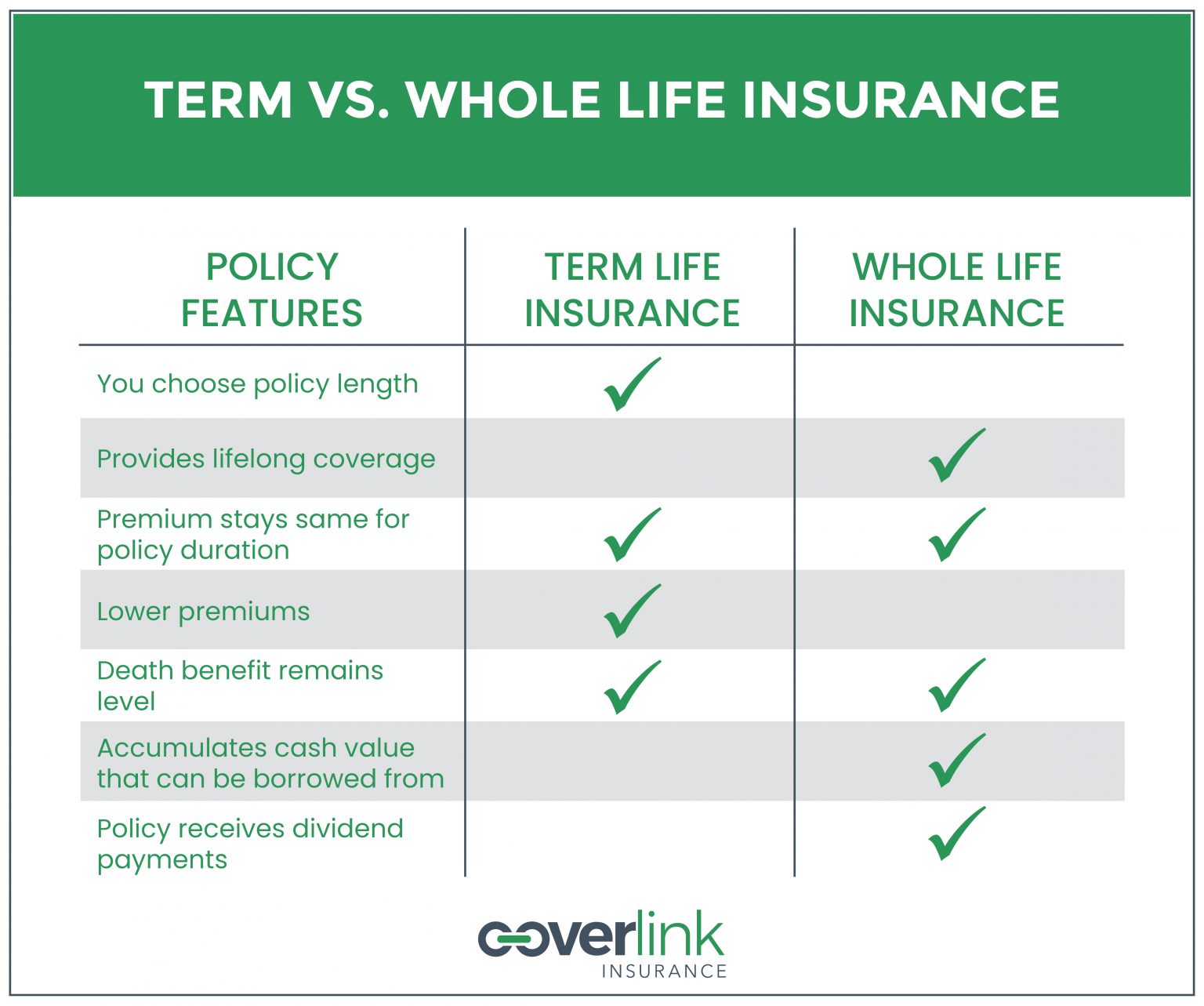
When it comes to life insurance, two primary types of policies are whole life insurance and term life insurance. These policies cater to different needs and financial goals, making it crucial to understand their unique features. Whole life insurance, often referred to as permanent life insurance, offers lifelong coverage and a cash value component that grows over time. In contrast, term life insurance provides coverage for a specified term, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years, and does not accumulate cash value.
Given the distinctions between whole life insurance versus term, choosing the right policy requires careful consideration. Your decision should align with your financial situation, long-term objectives, and family’s needs. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each policy type, you can make an informed decision and secure the financial future of your loved ones.
Whole Life Insurance: Pros and Cons
Whole life insurance, a type of permanent life insurance, offers several advantages. First, it provides lifelong coverage, ensuring that your beneficiaries receive a death benefit regardless of when you pass away. Second, whole life insurance accumulates a cash value component, which grows over time and can be borrowed against or used to pay premiums. Third, the premiums for whole life insurance remain consistent throughout the policy’s life, offering predictability and stability.
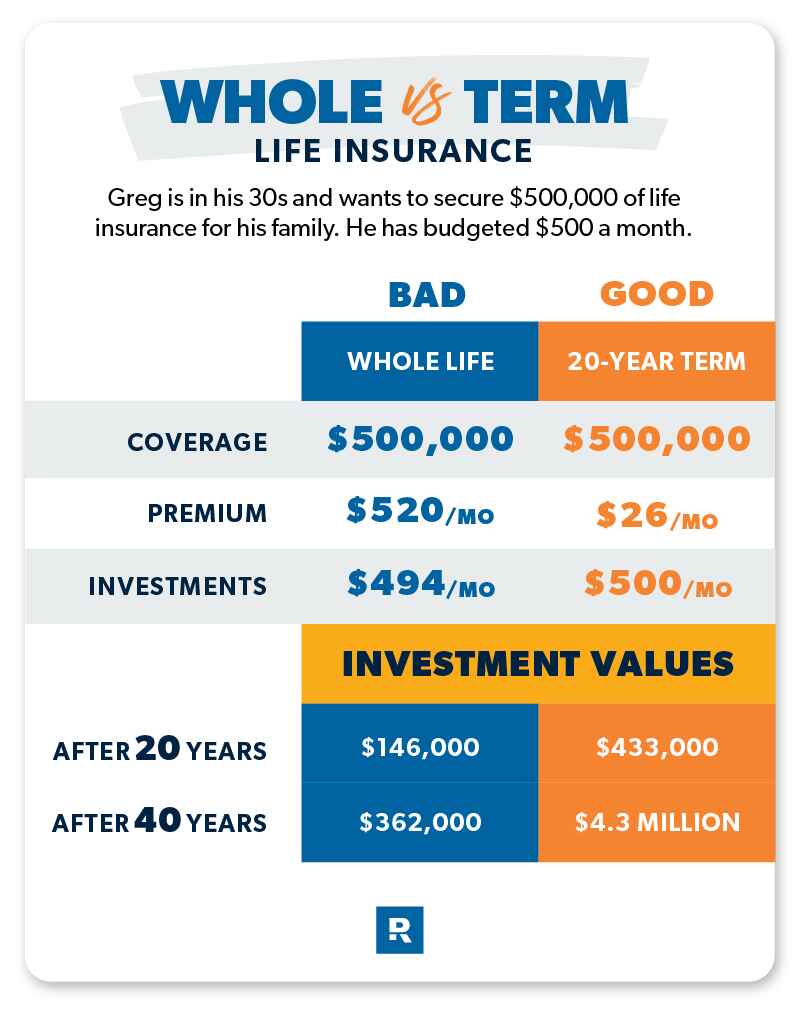
Despite these benefits, whole life insurance has its disadvantages. For starters, whole life insurance policies are generally more expensive than term life insurance policies due to the cash value component and lifelong coverage. Additionally, whole life insurance policies tend to be more complex, with various riders and features that can be challenging to understand. Furthermore, the investment component of whole life insurance may not offer the same returns as other investment options, making it less attractive for those looking to maximize their investment earnings.
Term Life Insurance: Pros and Cons
Term life insurance, the other primary type of life insurance, offers several benefits. First, term life insurance is typically more affordable than whole life insurance due to its simplicity and the absence of a cash value component. Second, term life insurance policies provide coverage for a specified term, allowing you to tailor your policy to your family’s needs and financial situation. Third, term life insurance policies are generally easier to understand, with fewer riders and features compared to whole life insurance.
However, term life insurance also has its drawbacks. For example, term life insurance policies expire after the specified term, leaving you without coverage unless you renew or convert your policy. Additionally, term life insurance policies do not accumulate a cash value component, which means they do not offer the same investment potential as whole life insurance. Lastly, if you outlive your term life insurance policy, you will not receive any benefits, unlike whole life insurance, which provides lifelong coverage.
How to Choose Between Whole Life and Term Life Insurance
Deciding between whole life and term life insurance involves careful consideration of several factors. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you make an informed decision:
Step 1: Evaluate Your Financial Situation
Assess your current financial situation, including your income, debts, and financial obligations. Consider your family’s needs and how they might change over time. For example, if you have young children, you may want to ensure that they are financially provided for in case of your untimely death.
Step 2: Determine Your Budget
Establish a budget for your life insurance premiums. Whole life insurance premiums are generally higher than term life insurance premiums, so it’s essential to determine how much you can afford to pay each month.
Step 3: Consider Your Long-Term Financial Goals
Think about your long-term financial goals, such as retirement savings or leaving a legacy for your heirs. Whole life insurance can serve as an investment tool, while term life insurance is primarily designed to provide death benefits.
Step 4: Compare Whole Life and Term Life Insurance Policies
Research and compare whole life and term life insurance policies from various providers. Look for policies that align with your budget, financial goals, and family needs. Pay attention to policy features, such as cash value accumulation, conversion options, and premium flexibility.
Step 5: Consult a Financial Advisor
Consider consulting a financial advisor to help you weigh the pros and cons of whole life and term life insurance. A financial advisor can provide personalized advice based on your unique circumstances and financial objectives.
Real-World Examples: Popular Whole Life Insurance Policies
When shopping for whole life insurance, consider the following popular policies from reputable insurance providers:
Northwestern Mutual’s Whole Life Insurance
Northwestern Mutual’s whole life insurance policy offers lifelong coverage and a cash value component that grows over time. The policy also features flexible premiums and dividend payments, which can be used to increase the cash value or reduce premiums.
MassMutual’s Whole Life Insurance
MassMutual’s whole life insurance policy provides guaranteed death benefits and a cash value component that grows at a fixed rate. The policy also offers various riders, such as a waiver of premium rider and an accelerated death benefit rider, which can be added for an additional cost.
New York Life’s Whole Life Insurance
New York Life’s whole life insurance policy offers lifelong coverage and a cash value component that grows at a guaranteed rate. The policy also features flexible premiums and various riders, such as a child rider and a long-term care rider, which can be added for an additional cost.
State Farm’s Whole Life Insurance
State Farm’s whole life insurance policy provides lifelong coverage and a cash value component that grows over time. The policy also offers various riders, such as a waiver of premium rider and an accelerated death benefit rider, which can be added for an additional cost.
Real-World Examples: Popular Term Life Insurance Policies
When considering term life insurance, consider the following popular policies from trusted insurance providers:
Haven Life’s Term Life Insurance
Haven Life’s term life insurance policy offers level premiums and death benefits for the duration of the term. The policy is available in terms ranging from 10 to 30 years and can be purchased online without a medical exam for applicants who qualify.
Banner Life’s Term Life Insurance
Banner Life’s term life insurance policy provides level premiums and death benefits for the duration of the term. The policy is available in terms ranging from 10 to 30 years and offers accelerated underwriting for applicants who qualify.
Prudential’s Term Life Insurance
Prudential’s term life insurance policy offers level premiums and death benefits for the duration of the term. The policy is available in terms ranging from 10 to 30 years and offers various riders, such as a living needs benefit rider and a terminal illness rider, which can be added for an additional cost.
Transamerica’s Term Life Insurance
Transamerica’s term life insurance policy provides level premiums and death benefits for the duration of the term. The policy is available in terms ranging from 10 to 30 years and offers various riders, such as a children’s insurance rider and a waiver of premium rider, which can be added for an additional cost.
Maintaining and Adjusting Your Life Insurance Policy
As your life circumstances change, it’s essential to regularly review and adjust your life insurance policy to ensure it continues to meet your needs. Here’s how to make changes to your policy and when to consider updating your coverage:
When to Review Your Policy
Review your life insurance policy annually or when significant life events occur, such as marriage, divorce, the birth of a child, or a change in your financial situation. These events may require you to adjust your coverage or beneficiary designations.
How to Make Changes to Your Policy
To make changes to your life insurance policy, contact your insurance provider or agent. They can help you update your coverage, beneficiary designations, or policy features as needed.
When to Consider Updating Your Coverage
Consider increasing your coverage if you have a growing family, a higher income, or increased financial obligations. Decrease your coverage if your children are grown and financially independent, or if you’ve paid off significant debts.
Other Policy Adjustments
In addition to adjusting your coverage, consider changing your policy’s term length or converting your term life policy to a whole life policy. These adjustments can help ensure your policy continues to meet your needs as your life changes.
Additional Considerations: When Whole Life or Term Life May Not Be the Best Option
While whole life and term life insurance are the two primary types of life insurance policies, there may be situations where these options are not the best fit. In such cases, consider the following alternatives:
Universal Life Insurance
Universal life insurance is a type of permanent life insurance that offers more flexibility than whole life insurance. With universal life insurance, you can adjust your premiums and death benefit as your needs change. Additionally, universal life insurance policies accumulate cash value, which can be used to pay premiums or borrowed against.
Variable Life Insurance
Variable life insurance is another type of permanent life insurance that offers investment opportunities. With variable life insurance, you can invest your cash value in various investment options, such as mutual funds. The value of your cash value and death benefit will fluctuate based on the performance of your investments.
Indexed Universal Life Insurance
Indexed universal life insurance is a type of universal life insurance that offers investment opportunities tied to a stock market index. With indexed universal life insurance, your cash value will grow based on the performance of the index, up to a certain cap. However, if the index performs poorly, your cash value will not decrease.
Final Expense Insurance
Final expense insurance, also known as burial or funeral insurance, is a type of permanent life insurance with a small death benefit, typically ranging from $5,000 to $50,000. Final expense insurance is designed to cover end-of-life expenses, such as funeral costs and medical bills.
Group Life Insurance
Group life insurance is a type of life insurance offered through an employer or association. Group life insurance is often less expensive than individual life insurance policies, but it may not provide enough coverage for your needs. Additionally, group life insurance may not be portable, meaning you cannot take it with you if you leave your employer or association.