Unlocking the Potential of Robotics in Manufacturing and Logistics
The integration of robotics in manufacturing and logistics has revolutionized the way companies operate, leading to significant improvements in efficiency, productivity, and accuracy. By leveraging robotics, businesses can stay competitive in a rapidly changing market, where adaptability and innovation are key to success. Robotics for manufacturing and logistics enables companies to automate repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more complex and creative work.
One of the primary benefits of robotics in manufacturing is the ability to increase production speed and accuracy. Robots can perform tasks with precision and consistency, reducing the likelihood of errors and defects. This, in turn, leads to improved product quality and reduced waste. Additionally, robotics can help companies to optimize their supply chain operations, streamlining the flow of goods and materials.
In logistics, robotics is transforming the way companies manage their warehouses and distribution centers. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) can navigate warehouses, track inventory, and optimize storage and retrieval processes. This enables companies to respond quickly to changing demand patterns and improve their overall responsiveness to customers.
Furthermore, the use of robotics in manufacturing and logistics can help companies to reduce their environmental footprint. By optimizing production processes and reducing waste, companies can minimize their energy consumption and lower their greenhouse gas emissions. This not only benefits the environment but also enhances the company’s reputation and contributes to a more sustainable future.
As the demand for robotics in manufacturing and logistics continues to grow, companies are recognizing the importance of investing in this technology. By embracing robotics, businesses can unlock new opportunities for growth, innovation, and competitiveness. Whether it’s improving production efficiency, optimizing logistics operations, or reducing environmental impact, robotics for manufacturing and logistics is a key driver of success in today’s fast-paced business landscape.
How to Choose the Right Robotics System for Your Business
When it comes to implementing robotics for manufacturing and logistics, selecting the right system is crucial for achieving desired outcomes. With numerous options available, businesses must carefully evaluate their specific needs and consider several key factors to ensure a successful integration. In this section, we will explore the essential considerations for choosing the most suitable robotics system for your business.
Payload capacity, reach, and precision are critical factors to consider when selecting a robotics system. The payload capacity refers to the maximum weight that the robot can lift, while the reach determines the robot’s range of motion. Precision, on the other hand, is essential for tasks that require high accuracy, such as assembly or inspection. By understanding the specific requirements of your manufacturing or logistics process, you can narrow down your options and choose a system that meets your needs.
Popular robotics systems like the FANUC CR-35iA and the KUKA LBR iiwa are widely used in various industries. The FANUC CR-35iA, for instance, is a collaborative robot designed for human-robot collaboration, offering a payload capacity of 35 kg and a reach of 1,831 mm. The KUKA LBR iiwa, on the other hand, is a lightweight robot with a payload capacity of 14 kg and a reach of 1,100 mm, ideal for tasks that require high precision and flexibility.
Another essential consideration is the level of customization required. Some robotics systems offer more flexibility in terms of programming and customization, while others may have more limited options. Businesses must assess their specific needs and choose a system that can be tailored to their unique requirements.
In addition to these technical considerations, businesses must also think about the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, training, and support. A comprehensive understanding of the costs associated with the robotics system will help you make an informed decision and ensure a successful implementation.
By carefully evaluating these factors and considering the specific needs of your business, you can choose the right robotics system for your manufacturing and logistics operations. This will enable you to unlock the full potential of robotics for manufacturing and logistics, driving efficiency, productivity, and accuracy in your business.
Streamlining Production with Robotic Process Automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry by optimizing workflows, improving quality control, and reducing labor costs. By automating repetitive tasks, RPA enables companies to increase productivity, efficiency, and accuracy, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction and competitiveness in the market.
RPA involves the use of software robots that mimic human actions, interacting with digital systems and applications to perform tasks such as data entry, document processing, and workflow management. In manufacturing, RPA can be applied to various processes, including production planning, inventory management, and quality control.
Successful implementations of RPA in industries like automotive and electronics have demonstrated significant benefits. For instance, a leading automotive manufacturer implemented RPA to automate its production planning process, resulting in a 30% reduction in planning time and a 25% increase in production capacity. Similarly, an electronics manufacturer used RPA to automate its quality control process, achieving a 90% reduction in defect rates and a 20% increase in overall productivity.
RPA can also be integrated with other technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to enhance its capabilities. For example, machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze data from RPA systems, identifying patterns and trends that can inform process improvements and optimize production workflows.
Moreover, RPA can help companies address common challenges in manufacturing, such as labor shortages and skills gaps. By automating repetitive tasks, RPA can free up human workers to focus on higher-value tasks that require creativity, problem-solving, and innovation.
However, implementing RPA requires careful planning and execution. Companies must assess their processes and identify areas where RPA can add value, develop a clear implementation strategy, and provide training and support to employees. Additionally, companies must ensure that RPA systems are integrated with existing systems and infrastructure, and that data security and integrity are maintained.
As the manufacturing industry continues to evolve, RPA is likely to play an increasingly important role in streamlining production and improving competitiveness. By leveraging RPA and other technologies, companies can unlock new levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation, ultimately driving growth and success in the market.
Robotics for manufacturing and logistics is a key area of focus for companies looking to stay ahead of the curve. By adopting RPA and other robotics technologies, companies can position themselves for success in a rapidly changing market, and reap the benefits of increased efficiency, productivity, and accuracy.
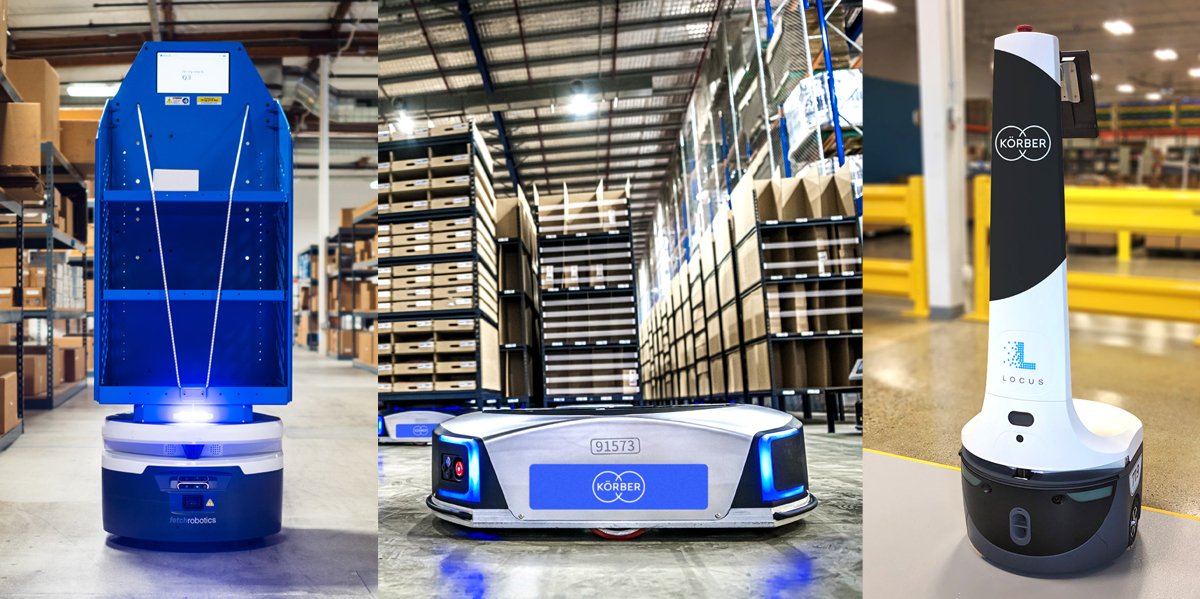
Maximizing Warehouse Efficiency with Autonomous Mobile Robots
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are transforming logistics operations by optimizing warehouse efficiency, reducing costs, and improving customer satisfaction. These robots are designed to navigate warehouses, track inventory, and optimize storage and retrieval processes, making them an essential component of robotics for manufacturing and logistics.
AMRs use advanced navigation systems, such as lidar and sensors, to move around warehouses and avoid obstacles. They can be programmed to perform a variety of tasks, including picking and placing items, transporting goods, and tracking inventory levels. This enables warehouses to operate more efficiently, reducing labor costs and improving productivity.
Companies like Amazon and DHL are already leveraging AMRs to optimize their logistics operations. Amazon, for example, has deployed thousands of AMRs in its warehouses to improve order fulfillment and reduce costs. DHL, on the other hand, has implemented AMRs to optimize its warehouse operations, resulting in a 25% reduction in labor costs and a 30% increase in productivity.
AMRs can also be integrated with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to enhance their capabilities. For instance, AI-powered AMRs can learn from data and adapt to new situations, improving their navigation and decision-making abilities.
One of the key benefits of AMRs is their ability to improve warehouse safety. By automating tasks and reducing the need for human intervention, AMRs can minimize the risk of accidents and injuries. Additionally, AMRs can operate around the clock, reducing the need for overtime and improving overall warehouse efficiency.
Implementing AMRs requires careful planning and execution. Companies must assess their warehouse operations and identify areas where AMRs can add value. They must also develop a clear implementation strategy, including training and support for employees, to ensure a smooth transition.
As the logistics industry continues to evolve, AMRs are likely to play an increasingly important role in optimizing warehouse efficiency. By leveraging AMRs and other robotics technologies, companies can position themselves for success in a rapidly changing market, and reap the benefits of increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction.
Robotics for manufacturing and logistics is a key area of focus for companies looking to stay ahead of the curve. By adopting AMRs and other robotics technologies, companies can unlock new levels of efficiency, productivity, and innovation, ultimately driving growth and success in the market.
Overcoming Challenges in Robotics Implementation
Implementing robotics solutions can be a complex and challenging process, requiring careful planning and execution. Companies must address common challenges such as integration with existing systems, employee training, and maintenance requirements to ensure a smooth transition.
One of the primary challenges in robotics implementation is integrating the new system with existing infrastructure and software. This can be a time-consuming and costly process, requiring significant resources and expertise. To overcome this challenge, companies should work closely with their robotics provider to ensure seamless integration and minimal disruption to operations.
Employee training is another critical aspect of robotics implementation. As robotics systems become more advanced, employees must be trained to work effectively with these systems, ensuring that they can operate safely and efficiently. Companies should invest in comprehensive training programs that cover the operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of robotics systems.
Maintenance requirements are also a significant challenge in robotics implementation. Robotics systems require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and prevent downtime. Companies should develop a maintenance schedule and allocate resources to ensure that their robotics systems are properly maintained and serviced.
Change management is also essential when implementing robotics solutions. Companies must communicate the benefits and impact of robotics to employees, customers, and stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is aligned and prepared for the changes ahead.
Strategies for overcoming these challenges include developing a clear implementation plan, investing in employee training and development, and establishing a maintenance schedule. Companies should also work closely with their robotics provider to ensure seamless integration and minimal disruption to operations.
By addressing these common challenges, companies can ensure a smooth transition to a robotics-driven work environment, unlocking the full potential of robotics for manufacturing and logistics. This will enable them to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market, drive growth and innovation, and achieve long-term success.
Robotics for manufacturing and logistics is a key area of focus for companies looking to stay ahead of the curve. By adopting robotics technologies and addressing common implementation challenges, companies can position themselves for success in a rapidly changing market, and reap the benefits of increased efficiency, productivity, and accuracy.
Future-Proofing Your Business with Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing the field of robotics for manufacturing and logistics, enabling robots to learn from data, adapt to new situations, and improve overall performance. By integrating AI and ML into their robotics systems, companies can future-proof their businesses and stay ahead of the competition.
AI-powered robots can analyze data from various sources, including sensors, cameras, and other robots, to learn and improve their performance. This enables them to optimize their workflows, reduce errors, and improve overall efficiency. For example, AI-powered robots can learn to recognize and classify objects, allowing them to perform tasks such as quality control and inspection with greater accuracy.
ML algorithms can also be used to improve the performance of robots in manufacturing and logistics. By analyzing data from various sources, ML algorithms can identify patterns and trends, enabling robots to predict and prevent errors, and optimize their workflows. For example, ML algorithms can be used to predict when a robot is likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
Companies such as Siemens and Bosch are already leveraging AI and ML to enhance their robotics capabilities. Siemens, for example, has developed an AI-powered robot that can learn to perform tasks such as assembly and inspection, while Bosch has developed an ML-powered robot that can predict and prevent errors in manufacturing processes.
The integration of AI and ML into robotics systems also enables companies to improve their supply chain management and logistics operations. For example, AI-powered robots can analyze data from various sources to optimize inventory management, predict demand, and improve delivery times.
However, the integration of AI and ML into robotics systems also raises several challenges, including the need for significant investment in data analytics and IT infrastructure, as well as the need for specialized skills and expertise. Companies must also address concerns around data security and privacy, as well as the potential for job displacement.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of integrating AI and ML into robotics systems are significant. By future-proofing their businesses with AI and ML, companies can improve their competitiveness, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. As the field of robotics for manufacturing and logistics continues to evolve, it is likely that AI and ML will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of industry.
Real-World Applications of Robotics in Manufacturing and Logistics
Robotics for manufacturing and logistics has been successfully implemented in various industries, resulting in increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction. Here are some real-world examples of companies that have leveraged robotics to transform their operations.
Amazon, the e-commerce giant, has been at the forefront of robotics adoption in logistics. The company has deployed thousands of robots in its warehouses to streamline order fulfillment, improve inventory management, and reduce labor costs. Amazon’s robotics system, which includes robots from Kiva Systems, has enabled the company to process orders faster and more accurately, resulting in improved customer satisfaction.
DHL, the logistics company, has also implemented robotics in its warehouses to improve efficiency and reduce costs. The company has deployed robots from Fetch Robotics to automate tasks such as inventory management and order fulfillment. DHL’s robotics system has enabled the company to reduce labor costs, improve accuracy, and increase productivity.
In the manufacturing sector, companies like Siemens and Bosch have successfully implemented robotics to improve production efficiency and reduce costs. Siemens has deployed robots from its own robotics division to automate tasks such as assembly and inspection, resulting in improved product quality and reduced labor costs. Bosch has also implemented robotics in its manufacturing operations, using robots from KUKA to automate tasks such as welding and assembly.
These examples demonstrate the potential of robotics for manufacturing and logistics to transform business operations and improve competitiveness. By leveraging robotics, companies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction, resulting in long-term success and growth.
Robotics for manufacturing and logistics is a rapidly evolving field, with new technologies and innovations emerging regularly. As the field continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more
Real-World Applications of Robotics in Manufacturing and Logistics
Robotics for manufacturing and logistics has been successfully implemented in various industries, resulting in increased productivity, reduced costs, and improved customer satisfaction. Here are some real-world examples of companies that have leveraged robotics to transform their operations.
Amazon, the e-commerce giant, has been at the forefront of robotics adoption in logistics. The company has deployed thousands of robots in its warehouses to streamline order fulfillment, improve inventory management, and reduce labor costs. Amazon’s robotics system, which includes robots from Kiva Systems, has enabled the company to process orders faster and more accurately, resulting in improved customer satisfaction.
DHL, the logistics company, has also implemented robotics in its warehouses to improve efficiency and reduce costs. The company has deployed robots from Fetch Robotics to automate tasks such as inventory management and order fulfillment. DHL’s robotics system has enabled the company to reduce labor costs, improve accuracy, and increase productivity.
In the manufacturing sector, companies like Siemens and Bosch have successfully implemented robotics to improve production efficiency and reduce costs. Siemens has deployed robots from its own robotics division to automate tasks such as assembly and inspection, resulting in improved product quality and reduced labor costs. Bosch has also implemented robotics in its manufacturing operations, using robots from KUKA to automate tasks such as welding and assembly.
These examples demonstrate the potential of robotics for manufacturing and logistics to transform business operations and improve competitiveness. By leveraging robotics, companies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction, resulting in long-term success and growth.
Robotics for manufacturing and logistics is a rapidly evolving field, with new technologies and innovations emerging regularly. As the field continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more