Navigating the Complex World of Empire State Taxes
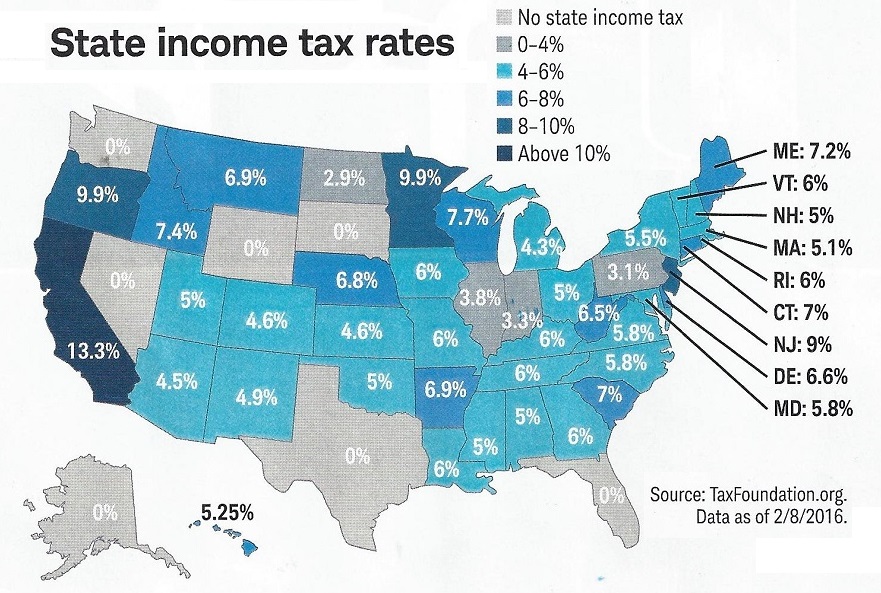
Understanding New York state income tax rates is crucial for individuals and businesses to minimize their tax liability. The state’s tax system is complex, with various tax brackets, deductions, and credits available to residents and non-residents. New York income tax rates range from 4% to 8.82%, depending on the tax bracket and filing status. By grasping the nuances of the tax system, taxpayers can optimize their financial planning and reduce their tax burden.
The New York State Department of Taxation and Finance provides resources to help taxpayers navigate the tax system. However, it is essential to stay informed about changes to tax laws and regulations, which can impact tax obligations. For instance, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act has introduced new tax brackets and deductions, affecting New York taxpayers. By staying up-to-date with these changes, taxpayers can ensure they are taking advantage of available tax savings.
New York’s tax system is designed to promote economic growth and fairness. The state offers various tax incentives, such as the Excelsior Jobs Program, to encourage businesses to invest and create jobs. Additionally, the state provides tax credits for individuals, including the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and the Child Tax Credit. By leveraging these incentives, taxpayers can reduce their tax liability and contribute to the state’s economic development.
Moreover, understanding New York income tax rates is vital for individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about their financial planning. By knowing their tax obligations, taxpayers can budget accordingly and avoid unexpected tax
Navigating the Complex World of Empire State Taxes
Understanding New York state income tax rates is crucial for individuals and businesses to minimize their tax liability. The state’s tax system is complex, with various tax brackets, deductions, and credits available to residents and non-residents. New York income tax rates range from 4% to 8.82%, depending on the tax bracket and filing status. By grasping the nuances of the tax system, taxpayers can optimize their financial planning and reduce their tax burden.
The New York State Department of Taxation and Finance provides resources to help taxpayers navigate the tax system. However, it is essential to stay informed about changes to tax laws and regulations, which can impact tax obligations. For instance, the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act has introduced new tax brackets and deductions, affecting New York taxpayers. By staying up-to-date with these changes, taxpayers can ensure they are taking advantage of available tax savings.
New York’s tax system is designed to promote economic growth and fairness. The state offers various tax incentives, such as the Excelsior Jobs Program, to encourage businesses to invest and create jobs. Additionally, the state provides tax credits for individuals, including the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and the Child Tax Credit. By leveraging these incentives, taxpayers can reduce their tax liability and contribute to the state’s economic development.
Moreover, understanding New York income tax rates is vital for individuals and businesses to make informed decisions about their financial planning. By knowing their tax obligations, taxpayers can budget accordingly and avoid unexpected tax bills. Furthermore, taxpayers can take advantage of tax-deferred savings options, such as 401(k) plans, to reduce their tax liability and build wealth over time.
In conclusion, navigating the complex world of Empire State taxes requires a deep understanding of New York income tax rates and the state’s tax system. By staying informed and leveraging available tax incentives, taxpayers can minimize their tax liability and contribute to the state’s economic growth. Whether you are a resident or non-resident, it is essential to grasp the nuances of New York’s tax system to optimize your financial planning and reduce your tax burden.
How to Determine Your New York Income Tax Rate
To calculate your New York income tax rate, you need to determine your filing status, report your income, and claim any eligible deductions and credits. The first step is to determine your filing status, which can be single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, head of household, or qualifying widow(er). Your filing status will determine which tax brackets and rates apply to you.
Next, you need to report your income from all sources, including wages, salaries, tips, and self-employment income. You will also need to report any income from investments, such as interest, dividends, and capital gains. New York state income tax rates range from 4% to 8.82%, depending on your income level and filing status.
Once you have reported your income, you can claim any eligible deductions and credits. New York offers a standard deduction, as well as itemized deductions for expenses such as mortgage interest, property taxes, and charitable donations. You may also be eligible for credits such as the earned income tax credit (EITC) or the child tax credit.
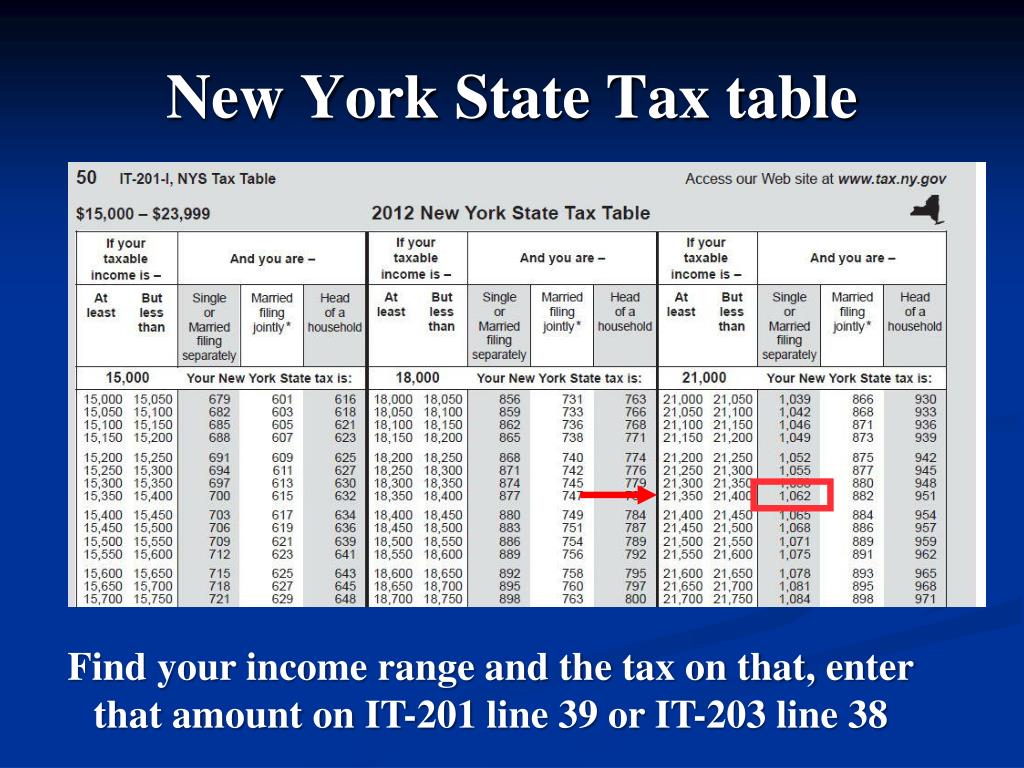
For example, let’s say you are a single person with a taxable income of $50,000. Using the New York state income tax tables, you would fall into the 6.09% tax bracket. However, if you are eligible for the standard deduction and itemize your deductions, you may be able to reduce your taxable income and lower your tax rate.
It’s also important to note that New York state income tax rates are subject to change, so it’s essential to stay up-to-date with any changes to the tax laws and regulations. By understanding how to determine your New York income tax rate, you can ensure you are in compliance with the tax laws and minimize your tax liability.
Residency and Non-Residency: How It Affects Your New York Tax Obligations
Understanding the differences between residency and non-residency in New York is crucial for determining your tax obligations. The state’s tax laws and regulations vary depending on whether you are a resident or non-resident, and it’s essential to know how these differences impact your New York income tax rates.
A resident is defined as an individual who maintains a permanent home in New York and spends more than 183 days in the state during the tax year. Residents are subject to New York state income tax on their worldwide income, regardless of where it’s earned. Non-residents, on the other hand, are only subject to tax on income earned from New York sources.
The rules for determining residency can be complex, and it’s not uncommon for individuals to be considered residents of multiple states. If you’re unsure about your residency status, it’s essential to consult with a tax professional to ensure you’re meeting your tax obligations.
Non-residents who work in New York are subject to tax on their New York-sourced income, which includes wages, salaries, and tips earned from working in the state. Non-residents may also be subject to tax on income from other New York sources, such as rental income or capital gains from the sale of New York property.
For example, if you’re a non-resident who works in New York City, you may be subject to the city’s income tax, which ranges from 2.907% to 3.648%. You may also be subject to New York state income tax on your earnings, which could range from 4% to 8.82%, depending on your income level and filing status.
Understanding the differences between residency and non-residency is essential for minimizing your New York tax liability. By knowing your residency status and how it impacts your tax obligations, you can plan your finances accordingly and take advantage of any available tax savings.
Common Deductions and Credits for New York Taxpayers
New York taxpayers can claim various deductions and credits to reduce their tax liability. Understanding these deductions and credits can help individuals and businesses minimize their New York income tax rates. In this section, we will discuss some common deductions and credits available to New York taxpayers.
The standard deduction is a common deduction available to New York taxpayers. For the 2022 tax year, the standard deduction is $8,000 for single filers and $16,000 for joint filers. Taxpayers can claim the standard deduction or itemize their deductions, whichever is greater.
Another common deduction is the mortgage interest deduction. New York taxpayers can deduct the interest paid on their primary residence and/or second home. This deduction can be claimed on Schedule A of the tax return.
The earned income tax credit (EITC) is a refundable credit available to low- and moderate-income working individuals and families. The EITC can be claimed on the tax return, and the amount of the credit varies based on income and family size.
Other common credits available to New York taxpayers include the child tax credit, the education credits, and the retirement savings credit. These credits can be claimed on the tax return, and the amount of the credit varies based on income and other factors.
To claim these deductions and credits, taxpayers must complete the necessary forms and schedules on their tax return. For example, to claim the mortgage interest deduction, taxpayers must complete Schedule A and attach Form 1098 to their tax return.
It’s essential to note that tax laws and regulations are subject to change, and taxpayers should consult with a tax professional to ensure they are taking advantage of all the deductions and credits available to them. By understanding these deductions and credits, New York taxpayers can minimize their tax liability and reduce their New York income tax rates.
Special Tax Considerations for New York City Residents
New York City residents have unique tax considerations that can impact their New York income tax rates. The city has its own income tax, which ranges from 2.907% to 3.648%. This tax is in addition to the state income tax, and it’s essential to understand how it affects your tax liability.
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) has also had a significant impact on New York City residents. The TCJA limited the state and local tax (SALT) deduction to $10,000, which can increase the tax burden for many city residents. However, New York State has implemented a workaround, allowing taxpayers to deduct charitable contributions to certain funds, which can help reduce their tax liability.
New York City residents may also be eligible for the NYC Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), which is a refundable credit that can help reduce their tax liability. The EITC is available to low- and moderate-income working individuals and families, and it can be claimed on the tax return.
Additionally, New York City residents may be subject to the city’s unincorporated business tax (UBT), which is a tax on the income of unincorporated businesses. The UBT rate is 4%, and it’s essential to understand how it affects your business’s tax liability.
To navigate these complexities, it’s essential to consult with a tax professional who is familiar with New York City’s tax laws and regulations. They can help you understand how these taxes impact your New York income tax rates and provide guidance on how to minimize your tax liability.
By understanding these special tax considerations, New York City residents can ensure they are in compliance with the tax laws and regulations and minimize their tax liability. It’s essential to stay informed about changes to the tax laws and regulations, as they can impact your tax obligations.
Planning Strategies to Minimize Your New York Tax Liability
Minimizing your New York tax liability requires careful planning and consideration of various strategies. By implementing these strategies, you can reduce your New York income tax rates and keep more of your hard-earned money.
One effective strategy is income deferral. By deferring income to a later tax year, you can reduce your tax liability in the current year. This can be achieved through various means, such as delaying the receipt of bonuses or income from self-employment.
Charitable giving is another strategy that can help minimize your New York tax liability. Donations to qualified charitable organizations can be deducted from your taxable income, reducing your tax liability. Additionally, charitable giving can also provide a sense of fulfillment and social responsibility.
Tax-loss harvesting is another strategy that can help minimize your New York tax liability. By selling securities that have declined in value, you can realize losses that can be used to offset gains from other investments. This can help reduce your tax liability and minimize the impact of investment losses.
Other planning strategies that can help minimize your New York tax liability include maximizing retirement contributions, utilizing tax-advantaged savings vehicles, and taking advantage of tax credits and deductions. By implementing these strategies, you can reduce your New York income tax rates and achieve your financial goals.
It’s essential to consult with a tax professional to determine the best planning strategies for your specific situation. They can help you navigate the complexities of New York tax laws and regulations and provide guidance on how to minimize your tax liability.
By implementing these planning strategies, you can reduce your New York tax liability and keep more of your hard-earned money. Remember to always stay informed about changes to New York tax laws and regulations, as they can impact your tax obligations.
Staying Up-to-Date with New York Tax Law Changes
Staying informed about changes to New York tax laws and regulations is crucial for taxpayers to minimize their tax liability and ensure compliance with the tax laws. The New York State Department of Taxation and Finance provides various resources to help taxpayers stay up-to-date with changes in the tax landscape.
The New York State Tax Law requires taxpayers to report changes in their income, deductions, and credits on their tax return. Taxpayers must also report any changes in their filing status, such as marriage, divorce, or the birth of a child. Failure to report these changes can result in penalties and interest.
Taxpayers can stay informed about changes to New York tax laws and regulations by visiting the New York State Department of Taxation and Finance website. The website provides information on tax law changes, including updates on tax rates, deductions, and credits. Taxpayers can also sign up for email alerts to receive notifications about changes in the tax laws.
Additionally, taxpayers can consult with a tax professional to ensure they are in compliance with the tax laws and regulations. Tax professionals can provide guidance on how to navigate the complexities of New York tax laws and regulations and help taxpayers minimize their tax liability.
By staying informed about changes to New York tax laws and regulations, taxpayers can ensure they are in compliance with the tax laws and minimize their tax liability. It’s essential to stay up-to-date with changes in the tax landscape to avoid penalties and interest.
New York income tax rates can be complex and subject to change, so it’s essential to stay informed about any changes that may affect your tax obligations. By staying informed and seeking the advice of a tax professional, you can ensure you are in compliance with the tax laws and regulations and minimize your tax liability.