The Foundation of Operational Excellence
Operational planning is a critical component of business strategy, enabling organizations to achieve their objectives and gain a competitive edge in the market. By developing a comprehensive operational plan, businesses can increase efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness, ultimately driving growth and success. Effective operational planning involves aligning resources, processes, and systems to support the organization’s overall mission and vision.
A well-crafted operational plan provides a roadmap for achieving business objectives, outlining specific goals, objectives, and key performance indicators (KPIs). This plan serves as a guide for decision-making, ensuring that all stakeholders are working towards common objectives. By establishing clear goals and objectives, organizations can focus their efforts, allocate resources effectively, and measure progress towards achieving their desired outcomes.
Operational planning also enables businesses to identify potential risks and opportunities, develop strategies to mitigate or capitalize on them, and establish contingency plans to address unexpected events. This proactive approach helps organizations stay agile and responsive to changing market conditions, customer needs, and other external factors.
In addition, operational planning facilitates collaboration and communication among teams, departments, and stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is working together towards common objectives. By fostering a culture of transparency, accountability, and continuous improvement, organizations can drive operational excellence and achieve sustainable success.
As businesses navigate increasingly complex and dynamic environments, the importance of operational planning cannot be overstated. By investing time and effort into developing a comprehensive operational plan, organizations can position themselves for long-term success, drive growth, and stay ahead of the competition.
Effective operational plan development requires a thorough understanding of the organization’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. By conducting a thorough analysis of these factors, businesses can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to address them.
Furthermore, operational planning enables businesses to allocate resources effectively, ensuring that the right people, equipment, and budget are in place to support the organization’s objectives. By establishing clear priorities and allocating resources accordingly, organizations can maximize their return on investment and achieve their desired outcomes.
In conclusion, operational planning is a critical component of business strategy, enabling organizations to achieve their objectives and gain a competitive edge in the market. By developing a comprehensive operational plan, businesses can increase efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness, ultimately driving growth and success.
How to Develop a Comprehensive Operational Plan
Developing a comprehensive operational plan is a critical step in achieving business objectives and driving growth. A well-crafted operational plan provides a roadmap for success, outlining specific goals, objectives, and key performance indicators (KPIs) that guide decision-making and resource allocation.
The process of operational plan development involves several key steps. First, define the organization’s mission, vision, and objectives, and ensure that they are aligned with the overall business strategy. Next, conduct a situation analysis to identify internal strengths and weaknesses, external opportunities and threats, and key stakeholders.
Once the situation analysis is complete, establish specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals that align with the organization’s objectives. These goals should be challenging yet attainable, and should provide a clear direction for the organization.
Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) that will be used to measure progress towards achieving the organization’s objectives. KPIs should be relevant, measurable, and aligned with the organization’s goals, and should provide a clear picture of the organization’s performance.
Establish a timeline for implementation, including specific milestones and deadlines. This timeline should be realistic and achievable, and should provide a clear roadmap for success.
Assign responsibilities and allocate resources, including personnel, equipment, and budget, to support operational plan implementation. Ensure that the right people, equipment, and budget are in place to support the organization’s objectives.
Finally, establish a process for monitoring and reviewing progress, including regular check-ins and progress reports. This process should provide a clear picture of the organization’s performance, and should identify areas for improvement.
By following these steps, organizations can develop a comprehensive operational plan that drives growth, increases efficiency, and improves competitiveness. A well-crafted operational plan provides a roadmap for success, and is essential for achieving business objectives.
Operational plan development is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and refinement. As the organization grows and changes, the operational plan should be updated to reflect new goals, objectives, and priorities.
By investing time and effort into operational plan development, organizations can position themselves for long-term success, drive growth, and stay ahead of the competition.
Conducting a Situation Analysis for Informed Decision-Making
A situation analysis is a critical component of operational plan development, providing a comprehensive understanding of the organization’s internal and external environment. This analysis enables businesses to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and to develop strategies to address them.
Internal analysis involves assessing the organization’s strengths and weaknesses, including its resources, capabilities, and competencies. This includes evaluating the organization’s financial performance, human resources, technology, and infrastructure. By understanding its internal strengths and weaknesses, the organization can identify areas for improvement and develop strategies to leverage its strengths.
External analysis involves assessing the organization’s external environment, including its opportunities and threats. This includes evaluating the market, competition, customers, suppliers, and regulatory environment. By understanding its external environment, the organization can identify opportunities to capitalize on and threats to mitigate.
Key stakeholders, including customers, employees, suppliers
Setting SMART Goals for Operational Success
Setting Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) goals is a critical component of operational plan development. SMART goals provide a clear direction for the organization, ensuring that everyone is working towards common objectives. By setting SMART goals, businesses can increase efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness, ultimately driving growth and success.
A SMART goal is specific, clearly defining what needs to be achieved. It is measurable, allowing progress to be tracked and success to be evaluated. It is achievable, ensuring that the goal is realistic and attainable. It is relevant, aligning with the organization’s overall mission and vision. And it is time-bound, providing a clear deadline for completion.
Examples of well-crafted SMART goals include increasing sales revenue by 10% within the next 12 months, reducing production costs by 15% within the next 6 months, and improving customer satisfaction ratings by 20% within the next 9 months. These goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound, providing a clear direction for the organization.
SMART goals should be aligned with the organization’s overall mission and vision, ensuring that everyone is working towards common objectives. They should also be communicated clearly to all stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers, ensuring that everyone understands what needs to be achieved.
By setting SMART goals, businesses can increase focus, motivation, and accountability, ultimately driving operational success. SMART goals provide a clear direction for the organization, ensuring that everyone is working towards common objectives. They also provide a framework for evaluating progress and success, allowing businesses to make adjustments as needed.
Operational plan development is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and refinement. As the organization grows and changes, SMART goals should be updated to reflect new priorities and objectives. By incorporating SMART goals into the operational plan, businesses can ensure that they are well-positioned to achieve their goals and objectives.
SMART goals are a critical component of operational plan development, providing a clear direction for the organization and ensuring that everyone is working towards common objectives. By setting SMART goals, businesses can increase efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness, ultimately driving growth and success.
In addition to setting SMART goals, businesses should also establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress and success. KPIs provide a clear picture of the organization’s performance, allowing businesses to make adjustments as needed.
Identifying and Allocating Resources for Operational Execution
Identifying and allocating resources is a critical step in operational plan development, ensuring that the organization has the necessary personnel, equipment, and budget to support plan implementation. This process involves assessing the organization’s current resources and identifying any gaps or deficiencies that need to be addressed.
Personnel resources include the skills, knowledge, and experience of the organization’s employees. This includes identifying the necessary roles and responsibilities, as well as the skills and qualifications required for each position. Equipment resources include the physical assets and technology needed to support operational plan implementation, such as machinery, vehicles, and software.
Budget resources include the financial resources needed to support operational plan implementation, including funding for personnel, equipment, and other expenses. This includes identifying the necessary budget allocations and ensuring that the organization has the necessary financial resources to support plan implementation.
The process of identifying and allocating resources involves several key steps. First, the organization must assess its current resources and identify any gaps or deficiencies that need to be addressed. This includes conducting a thorough analysis of the organization’s personnel, equipment, and budget resources.
Next, the organization must identify the necessary resources needed to support operational plan implementation. This includes identifying the necessary personnel, equipment, and budget resources, as well as any additional resources that may be needed.
Once the necessary resources have been identified, the organization must allocate them accordingly. This includes assigning personnel to specific roles and responsibilities, allocating equipment and technology, and allocating budget resources to support plan implementation.
By identifying and allocating resources effectively, organizations can ensure that they have the necessary resources to support operational plan implementation, ultimately driving growth and success. This process is critical to operational plan development, as it ensures that the organization has the necessary resources to achieve its goals and objectives.
Operational plan development is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and refinement. As the organization grows and changes, the identification and allocation of resources must be updated to reflect new priorities and objectives.
By incorporating the identification and allocation of resources into the operational plan development process, organizations can ensure that they are well-positioned to achieve their goals and objectives. This process is critical to operational excellence, as it ensures that the organization has the necessary resources to drive growth and success.
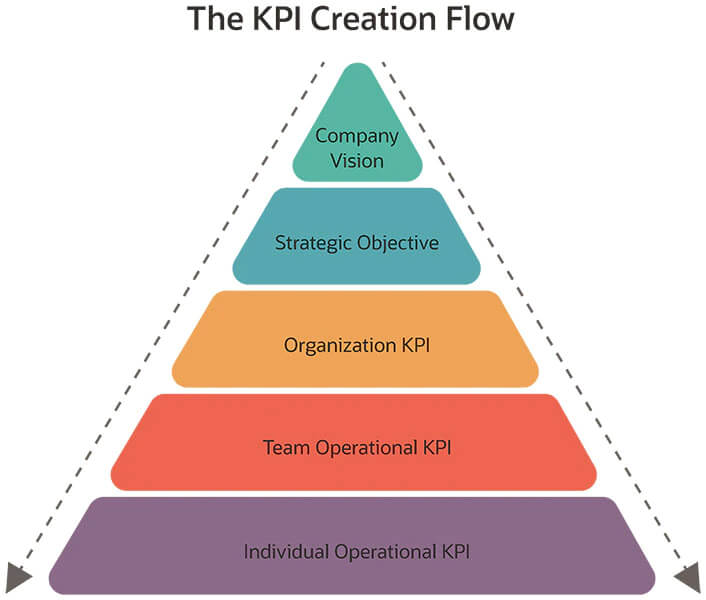
Establishing Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Operational Monitoring
Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) is a critical step in operational plan development, as it enables organizations to measure and monitor their progress towards achieving their goals and objectives. KPIs provide a clear picture of the organization’s performance, allowing for informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
KPIs should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), ensuring that they are aligned with the organization’s overall mission and vision. They should also be relevant to the organization’s goals and objectives, providing a clear picture of progress towards achieving them.
Examples of relevant KPIs include metrics such as customer satisfaction ratings, employee engagement scores, and financial performance indicators such as revenue growth and profit margins. These KPIs provide a clear picture of the organization’s performance, allowing for informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
The process of establishing KPIs involves several key steps. First, the organization must identify its goals and objectives, ensuring that they are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. Next, the organization must identify the necessary KPIs to measure progress towards achieving these goals and objectives.
Once the KPIs have been identified, the organization must establish a process for collecting and analyzing the data. This includes identifying the necessary data sources, establishing a data collection schedule, and developing a process for analyzing and interpreting the data.
By establishing KPIs, organizations can ensure that they are on track to achieving their goals and objectives. KPIs provide a clear picture of the organization’s performance, allowing for informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
Operational plan development is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and refinement. As the organization grows and changes, the KPIs must be updated to reflect new priorities and objectives.
By incorporating KPIs into the operational plan development process, organizations can ensure that they are well-positioned to achieve their goals and objectives. This process is critical to operational excellence, as it ensures that the organization has a clear picture of its performance and can make informed decisions to drive growth and success.
KPIs can be categorized into different types, including lagging indicators, leading indicators, and input indicators. Lagging indicators measure past performance, leading indicators measure future performance, and input indicators measure the resources used to achieve performance.
By using a combination of these types of KPIs, organizations can gain a comprehensive understanding of their performance and make informed decisions to drive growth and success.
Implementing and Reviewing the Operational Plan
Implementing and reviewing the operational plan is a critical step in operational plan development, as it ensures that the plan is executed effectively and that progress is monitored and evaluated regularly. This process involves assigning responsibilities, establishing a timeline, and reviewing progress regularly.
Assigning responsibilities involves identifying the individuals or teams responsible for implementing each component of the operational plan. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, as well as establishing clear lines of communication and decision-making authority.
Establishing a timeline involves creating a schedule for implementing each component of the operational plan. This includes setting deadlines, milestones, and checkpoints to ensure that progress is on track and that any issues or obstacles are addressed promptly.
Reviewing progress regularly involves monitoring and evaluating the implementation of the operational plan, including tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and making adjustments as needed. This includes conducting regular progress meetings, reviewing reports and data, and soliciting feedback from stakeholders.
By implementing and reviewing the operational plan regularly, organizations can ensure that they are on track to achieving their goals and objectives. This process is critical to operational excellence, as it ensures that the organization is executing its plan effectively and making adjustments as needed to stay on track.
Operational plan development is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and refinement. As the organization grows and changes, the operational plan must be updated to reflect new priorities and objectives.
By incorporating implementation and review into the operational plan development process, organizations can ensure that they are well-positioned to achieve their goals and objectives. This process is critical to operational excellence, as it ensures that the organization is executing its plan effectively and making adjustments as needed to stay on track.
Regular review and evaluation of the operational plan also helps to identify areas for improvement and opportunities for growth. By soliciting feedback from stakeholders and monitoring KPIs, organizations can make informed decisions to drive growth and success.
In addition, regular review and evaluation of the operational plan helps to ensure that the organization is aligned with its overall mission and vision. By monitoring progress and making adjustments as needed, organizations can ensure that they are on track to achieving their long-term goals and objectives.
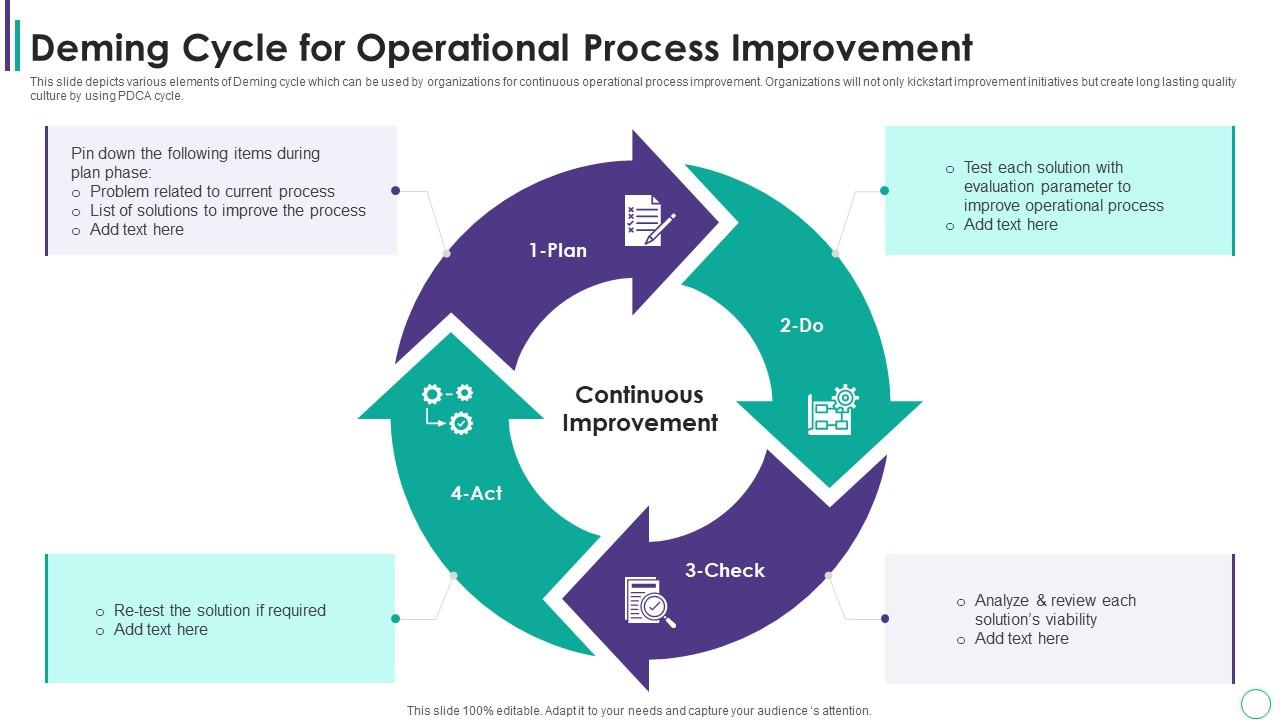
Continuous Improvement and Operational Plan Refinement
Continuous improvement and refinement of the operational plan is a critical step in operational plan development, as it ensures that the plan remains relevant and effective in achieving business objectives. This process involves soliciting feedback, identifying areas for improvement, and making adjustments as needed.
Soliciting feedback involves gathering input from stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers, to identify areas for improvement and opportunities for growth. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, and one-on-one meetings.
Identifying areas for improvement involves analyzing the feedback and data collected, and identifying gaps or weaknesses in the operational plan. This can include identifying inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or areas where the plan is not aligned with business objectives.
Making adjustments as needed involves updating the operational plan to reflect the changes and improvements identified. This can include revising goals and objectives, updating KPIs, and adjusting resource allocation.
By continuously improving and refining the operational plan, organizations can ensure that they are well-positioned to achieve their business objectives and stay ahead of the competition. This process is critical to operational excellence, as it ensures that the organization is always looking for ways to improve and optimize its operations.
Operational plan development is an ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring and refinement. As the organization grows and changes, the operational plan must be updated to reflect new priorities and objectives.
By incorporating continuous improvement and refinement into the operational plan development process, organizations can ensure that they are always striving for excellence and optimizing their operations for maximum efficiency and effectiveness.
Continuous improvement and refinement of the operational plan also helps to ensure that the organization is aligned with its overall mission and vision. By regularly reviewing and updating the plan, organizations can ensure that they are on track to achieving their long-term goals and objectives.
In addition, continuous improvement and refinement of the operational plan helps to foster a culture of innovation and continuous learning within the organization. By encouraging employees to identify areas for improvement and suggest new ideas, organizations can create a culture of innovation and continuous improvement.